Intangible Cultural Heritage, encompassing songs, dances, and rituals, faces significant challenges in preservation, but with SIXT.VN, exploring and supporting Vietnamese culture becomes easier than ever. SIXT.VN provides seamless access to the heart of Vietnamese traditions, ensuring their longevity. By understanding these hurdles and actively engaging with preservation efforts, we can ensure these invaluable expressions thrive for generations to come. Let’s explore the main obstacles and discover how you can contribute to safeguarding cultural heritage.
1. What are the Main Challenges in Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
The main challenges in preserving intangible cultural heritage include homogenization, tourism impacts, environmental factors, documentation difficulties, and transmission issues. These challenges threaten the survival of unique cultural expressions like songs, dances, and rituals. Addressing these issues requires comprehensive strategies focused on education, community involvement, and sustainable practices.
- Homogenization: The standardization of cultural practices can lead to the abandonment of traditional forms, reducing diversity.
- Tourism Impacts: While tourism can boost revenue, it often distorts performances, reducing them to simplified versions for tourists.
- Environmental Factors: Deforestation and other environmental issues can deprive communities of essential resources for creating traditional instruments.
- Documentation Difficulties: Accurately documenting intangible heritage can be challenging due to its fluid and dynamic nature.
- Transmission Issues: Ensuring the transmission of knowledge and techniques from master to apprentice is crucial but often faces obstacles.
2. How Does Globalization Affect the Preservation of Traditional Songs?
Globalization poses both opportunities and threats to the preservation of traditional songs. While it can spread awareness and appreciation, it also introduces the risk of homogenization and commercialization, diluting the authenticity of these cultural expressions. According to research from UNESCO in 2021, globalization can lead to the standardization of musical forms, threatening the survival of unique local traditions.
- Increased Exposure: Globalization increases exposure to diverse musical traditions, fostering cross-cultural exchange and appreciation.
- Risk of Homogenization: The drive for commercial success can lead to the simplification and standardization of traditional songs, diminishing their unique characteristics.
- Cultural Exchange: Globalization facilitates cultural exchange, allowing traditional songs to reach wider audiences and inspire new interpretations.
- Commercialization: The commercialization of traditional songs can result in their adaptation for mass consumption, often at the expense of cultural integrity.
- Preservation Efforts: Globalization can also support preservation efforts by providing access to funding, technology, and expertise.
3. What Role Does Tourism Play in the Preservation (or Destruction) of Traditional Dances?
Tourism can be a double-edged sword for traditional dances. While it can provide economic incentives for preservation, it also risks altering these dances to meet tourist expectations, leading to a loss of authenticity. A study by the World Tourism Organization in 2019 found that tourism can both revitalize and distort cultural heritage, depending on how it is managed.
- Economic Incentives: Tourism can generate revenue that supports the preservation and promotion of traditional dances.
- Distortion of Authenticity: Dances may be modified or simplified to appeal to tourist audiences, compromising their cultural significance.
- Cultural Exchange: Tourism can facilitate cultural exchange, allowing visitors to learn about and appreciate traditional dances.
- Commodification: Traditional dances can become commodified, losing their original meaning and purpose.
- Community Empowerment: When managed sustainably, tourism can empower local communities and support the preservation of their cultural heritage.
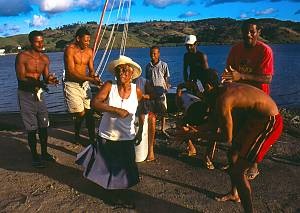 Samba de Roda of the Recôncavo of Bahia, showcasing the vibrant cultural dance
Samba de Roda of the Recôncavo of Bahia, showcasing the vibrant cultural dance
4. How Do Environmental Changes Threaten Rituals and Ceremonies?
Environmental changes, such as deforestation and climate change, can disrupt rituals and ceremonies by limiting access to natural resources essential for their performance. These resources include specific plants, animals, and landscapes that hold cultural and spiritual significance. According to the United Nations Environment Programme in 2020, environmental degradation poses a significant threat to intangible cultural heritage linked to nature.
- Resource Depletion: Deforestation and pollution can deplete essential natural resources needed for rituals.
- Disruption of Sacred Sites: Climate change and natural disasters can damage or destroy sacred sites where ceremonies are performed.
- Loss of Biodiversity: The loss of plant and animal species can affect rituals that rely on these elements.
- Community Displacement: Environmental changes can displace communities, disrupting their ability to maintain traditional practices.
- Cultural Adaptation: Communities may need to adapt their rituals to reflect the changing environment, potentially altering their original form.
5. What are the Challenges in Documenting Intangible Cultural Heritage Like Oral Traditions?
Documenting intangible cultural heritage, such as oral traditions, presents unique challenges due to its dynamic and ephemeral nature. Traditional methods of documentation may not capture the nuances and context of these expressions. UNESCO’s guidelines on documenting intangible heritage emphasize the need for participatory approaches that involve local communities.
- Dynamic Nature: Oral traditions are constantly evolving, making it difficult to create a definitive record.
- Contextual Understanding: Documentation needs to capture the cultural context in which oral traditions are performed.
- Language Barriers: Linguistic diversity can complicate documentation efforts, requiring translation and interpretation.
- Ethical Considerations: Documenting oral traditions requires respecting the rights and sensitivities of the communities involved.
- Technological Limitations: Traditional documentation methods may not fully capture the richness and complexity of oral traditions.
6. Why is Transmission of Knowledge Important, and What Hinders It?
Transmission of knowledge is crucial for preserving intangible cultural heritage, ensuring that traditions are passed down from one generation to the next. However, factors like modernization, migration, and lack of resources can hinder this process. A report by the International Council on Monuments and Sites in 2018 highlights the importance of supporting intergenerational learning to safeguard cultural heritage.
- Continuity of Traditions: Transmission ensures the continuity of cultural traditions, preventing them from being lost over time.
- Cultural Identity: Passing down knowledge helps maintain cultural identity and strengthens community bonds.
- Skills and Techniques: Transmission preserves the skills and techniques needed to perform and create traditional art forms.
- Modernization: Modern lifestyles and education systems can distract young people from learning traditional practices.
- Migration: Migration can lead to the dispersal of communities, making it difficult to maintain traditional knowledge.
- Lack of Resources: Insufficient funding and support for cultural education can hinder transmission efforts.
7. How Do Economic Pressures Affect the Sustainability of Cultural Practices?
Economic pressures can threaten the sustainability of cultural practices by forcing individuals to prioritize income-generating activities over traditional arts and rituals. This can lead to a decline in participation and a loss of cultural skills. The World Bank’s research on culture and development shows that economic incentives can play a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage.
- Prioritization of Income: Economic pressures can force individuals to prioritize income-generating activities over cultural practices.
- Loss of Cultural Skills: As fewer people engage in traditional arts, cultural skills can be lost over time.
- Commercialization: Economic incentives can lead to the commercialization of cultural practices, potentially altering their authenticity.
- Migration: Economic opportunities in urban areas can lead to migration, disrupting the transmission of cultural knowledge.
- Support for Cultural Enterprises: Providing economic support for cultural enterprises can help sustain traditional practices.
8. What is the Impact of Armed Conflicts on Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Armed conflicts pose a severe threat to intangible cultural heritage, leading to the destruction of cultural sites, displacement of communities, and suppression of cultural expressions. UNESCO’s reports on culture in conflict zones document the devastating impact of war on cultural heritage.
- Destruction of Cultural Sites: Armed conflicts can result in the destruction of sacred sites and cultural spaces.
- Displacement of Communities: Displacement disrupts cultural practices and makes it difficult to maintain traditions.
- Suppression of Cultural Expressions: Authoritarian regimes may suppress cultural expressions that are seen as a threat to their power.
- Loss of Cultural Memory: Armed conflicts can lead to the loss of cultural memory and collective identity.
- Post-Conflict Recovery: Recovering and revitalizing cultural heritage is essential for post-conflict reconciliation and healing.
9. How Can Technology be Used to Preserve Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Technology offers powerful tools for preserving intangible cultural heritage, including digital archives, virtual museums, and interactive platforms for cultural exchange. These tools can help document, share, and revitalize cultural traditions. According to a study by the Getty Conservation Institute in 2022, technology can enhance preservation efforts by providing new ways to engage with cultural heritage.
- Digital Archives: Creating digital archives can help preserve and share intangible cultural heritage with a wider audience.
- Virtual Museums: Virtual museums can offer immersive experiences of cultural traditions, promoting education and appreciation.
- Interactive Platforms: Interactive platforms can facilitate cultural exchange and collaboration among communities.
- Documentation Tools: Technology can provide tools for documenting and analyzing cultural expressions, such as music and dance.
- Educational Resources: Technology can be used to create educational resources that promote understanding and appreciation of cultural heritage.
 Khazan Rajabiy, Master of maqoms, during a masterclass, demonstrating traditional musical knowledge
Khazan Rajabiy, Master of maqoms, during a masterclass, demonstrating traditional musical knowledge
10. What Strategies Can Communities Implement to Protect Their Cultural Heritage?
Communities can implement various strategies to protect their cultural heritage, including cultural education programs, community-based tourism initiatives, and advocacy for cultural rights. These strategies empower communities to take ownership of their heritage and ensure its sustainability. The International Council of Museums recommends that communities be at the center of all cultural heritage preservation efforts.
- Cultural Education Programs: Implementing cultural education programs can help transmit knowledge and skills to younger generations.
- Community-Based Tourism: Developing community-based tourism initiatives can generate income and support cultural preservation.
- Advocacy for Cultural Rights: Advocating for cultural rights can help protect cultural heritage from external threats.
- Documentation and Archiving: Documenting and archiving cultural expressions can ensure their preservation for future generations.
- Collaboration with Stakeholders: Collaborating with governments, NGOs, and other stakeholders can strengthen preservation efforts.
11. What Role Do Governments and NGOs Play in Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Governments and NGOs play a crucial role in preserving intangible cultural heritage by providing funding, expertise, and policy support. They can also help raise awareness and promote international cooperation. UNESCO’s work in safeguarding intangible cultural heritage highlights the importance of collaboration between governments and NGOs.
- Funding and Resources: Governments and NGOs can provide funding and resources for preservation projects.
- Policy Support: Governments can enact policies that protect cultural heritage and promote its transmission.
- Expertise and Training: NGOs can offer expertise and training in documentation, conservation, and cultural management.
- Awareness Campaigns: Governments and NGOs can conduct awareness campaigns to promote understanding and appreciation of cultural heritage.
- International Cooperation: Governments and NGOs can foster international cooperation in safeguarding intangible cultural heritage.
12. How Can Cultural Policies Support the Preservation of Songs, Dances, and Rituals?
Cultural policies can play a vital role in preserving songs, dances, and rituals by providing legal protection, financial support, and institutional frameworks for cultural preservation. These policies should be inclusive, participatory, and aligned with international standards. The Council of Europe’s cultural policy guidelines emphasize the importance of integrating cultural heritage into broader development strategies.
- Legal Protection: Cultural policies can provide legal protection for songs, dances, and rituals, preventing their misuse or exploitation.
- Financial Support: Policies can allocate funding for cultural education, documentation, and preservation projects.
- Institutional Frameworks: Policies can establish institutions responsible for cultural heritage management and promotion.
- Community Participation: Policies should promote community participation in cultural preservation efforts.
- International Standards: Policies should align with international standards and conventions on cultural heritage.
13. What are the Ethical Considerations in Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Preserving intangible cultural heritage involves several ethical considerations, including respecting cultural rights, ensuring community consent, and avoiding cultural appropriation. Preservation efforts should be guided by principles of equity, transparency, and accountability. The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) addresses the ethical and legal aspects of protecting traditional knowledge and cultural expressions.
- Cultural Rights: Preservation efforts should respect the cultural rights of communities to maintain and transmit their heritage.
- Community Consent: Obtaining free, prior, and informed consent from communities is essential for ethical preservation.
- Avoiding Cultural Appropriation: Preservation efforts should avoid appropriating or commodifying cultural heritage without permission.
- Equity and Fairness: Preservation initiatives should be equitable and benefit all members of the community.
- Transparency and Accountability: Preservation projects should be transparent and accountable to the communities they serve.
14. How Does Climate Change Impact Intangible Cultural Heritage in Coastal Communities?
Climate change poses unique threats to intangible cultural heritage in coastal communities, including the loss of traditional fishing practices, disruption of maritime rituals, and displacement of communities due to rising sea levels. These impacts can lead to the erosion of cultural identity and the loss of traditional knowledge. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reports highlight the vulnerability of coastal communities and their cultural heritage to climate change.
- Loss of Traditional Practices: Climate change can disrupt traditional fishing and agricultural practices, leading to the loss of associated knowledge and skills.
- Disruption of Maritime Rituals: Rising sea levels and extreme weather events can disrupt maritime rituals and ceremonies.
- Community Displacement: Coastal erosion and flooding can displace communities, disrupting their ability to maintain cultural traditions.
- Damage to Cultural Sites: Climate change can damage or destroy cultural sites located in coastal areas.
- Adaptation Strategies: Coastal communities need to develop adaptation strategies to protect their cultural heritage from the impacts of climate change.
15. What are the Challenges in Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage in Urban Environments?
Preserving intangible cultural heritage in urban environments presents unique challenges, including the rapid pace of development, cultural diversity, and competition for resources. Urbanization can lead to the displacement of communities and the loss of traditional cultural spaces. UN-Habitat’s reports on sustainable cities emphasize the importance of integrating cultural heritage into urban planning.
- Rapid Development: Urban development can lead to the demolition of cultural sites and the displacement of communities.
- Cultural Diversity: Urban environments are often culturally diverse, making it challenging to prioritize and preserve specific traditions.
- Competition for Resources: Cultural heritage projects may face competition for funding and resources from other urban priorities.
- Loss of Cultural Spaces: Urbanization can lead to the loss of traditional cultural spaces, such as markets and community centers.
- Integration into Urban Planning: Integrating cultural heritage into urban planning can help ensure its preservation in the face of development.
16. How Can Storytelling Contribute to the Preservation of Cultural Heritage?
Storytelling is a powerful tool for preserving and transmitting cultural heritage, helping to maintain collective memory, reinforce cultural values, and foster a sense of identity. Stories can convey historical events, cultural practices, and moral lessons in an engaging and memorable way. Research from the National Endowment for the Arts in 2023 shows that storytelling can enhance cultural understanding and promote intergenerational connections.
- Maintaining Collective Memory: Stories help maintain collective memory by recounting historical events and cultural traditions.
- Reinforcing Cultural Values: Stories reinforce cultural values and norms, guiding behavior and shaping identity.
- Fostering a Sense of Identity: Stories foster a sense of identity by connecting individuals to their cultural heritage.
- Engaging and Memorable: Storytelling is an engaging and memorable way to transmit cultural knowledge.
- Promoting Intergenerational Connections: Storytelling can promote intergenerational connections by bringing together younger and older generations.
17. What are the Key Indicators for Measuring the Success of Intangible Cultural Heritage Preservation Programs?
Measuring the success of intangible cultural heritage preservation programs requires a range of indicators, including increased community participation, improved transmission rates, enhanced cultural awareness, and sustainable resource management. These indicators should be context-specific and aligned with the goals of the preservation program. The UNESCO Culture Sector provides guidelines for monitoring and evaluating cultural heritage projects.
- Community Participation: Increased community participation in cultural activities and preservation efforts.
- Transmission Rates: Improved rates of transmission of cultural knowledge and skills from one generation to the next.
- Cultural Awareness: Enhanced cultural awareness and appreciation among the general public.
- Sustainable Resource Management: Sustainable management of natural and cultural resources associated with intangible heritage.
- Policy Support: Supportive policies and institutional frameworks for cultural preservation.
18. How Can Museums and Cultural Institutions Support the Preservation of Performing Arts?
Museums and cultural institutions can play a vital role in preserving performing arts by documenting performances, creating exhibitions, offering educational programs, and supporting artists. They can also collaborate with communities to ensure that preservation efforts are culturally appropriate and sustainable. The American Alliance of Museums provides resources and best practices for preserving and presenting cultural heritage.
- Documentation of Performances: Museums can document performances through recordings, photographs, and oral histories.
- Creating Exhibitions: Museums can create exhibitions that showcase the history and significance of performing arts.
- Offering Educational Programs: Museums can offer educational programs that teach about performing arts and their cultural context.
- Supporting Artists: Museums can support artists through grants, residencies, and performance opportunities.
- Community Collaboration: Museums can collaborate with communities to ensure that preservation efforts are culturally appropriate and sustainable.
19. What are the Benefits of Integrating Intangible Cultural Heritage into Education Systems?
Integrating intangible cultural heritage into education systems can provide numerous benefits, including promoting cultural identity, fostering critical thinking, and enhancing intercultural understanding. It can also help students develop a deeper appreciation for their own culture and the cultures of others. A report by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2024 emphasizes the importance of integrating cultural heritage into education.
- Promoting Cultural Identity: Integrating cultural heritage into education helps students develop a strong sense of cultural identity.
- Fostering Critical Thinking: Studying cultural heritage can foster critical thinking skills by encouraging students to analyze and interpret cultural expressions.
- Enhancing Intercultural Understanding: Learning about different cultures can enhance intercultural understanding and promote tolerance.
- Engaging Learning Experiences: Cultural heritage can provide engaging and relevant learning experiences for students.
- Preserving Cultural Knowledge: Integrating cultural heritage into education helps preserve and transmit cultural knowledge to future generations.
20. How Can Intangible Cultural Heritage Contribute to Sustainable Development?
Intangible cultural heritage can contribute to sustainable development by promoting cultural tourism, supporting traditional livelihoods, and fostering social cohesion. It can also help communities build resilience to environmental and economic challenges. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) recognize the importance of culture in achieving sustainable development.
- Promoting Cultural Tourism: Intangible cultural heritage can attract tourists and generate income for local communities.
- Supporting Traditional Livelihoods: Cultural heritage can support traditional livelihoods, such as crafts, agriculture, and fishing.
- Fostering Social Cohesion: Cultural heritage can foster social cohesion by strengthening community bonds and promoting shared values.
- Building Resilience: Cultural heritage can help communities build resilience to environmental and economic challenges.
- Environmental Sustainability: Traditional knowledge and practices associated with intangible heritage can contribute to environmental sustainability.
21. What are the Current Trends in Safeguarding Intangible Cultural Heritage Globally?
Current trends in safeguarding intangible cultural heritage globally include increased community involvement, the use of digital technologies, and the integration of cultural heritage into sustainable development strategies. There is also a growing emphasis on promoting cultural diversity and intercultural dialogue. UNESCO’s Intangible Heritage Section provides up-to-date information on global trends and initiatives.
- Increased Community Involvement: Greater emphasis on involving communities in all aspects of safeguarding intangible heritage.
- Use of Digital Technologies: Wider use of digital technologies for documenting, preserving, and sharing cultural heritage.
- Integration into Sustainable Development: Integrating cultural heritage into sustainable development strategies and policies.
- Promoting Cultural Diversity: Greater emphasis on promoting cultural diversity and intercultural dialogue.
- International Cooperation: Increased international cooperation in safeguarding intangible cultural heritage.
22. How Can SIXT.VN Assist in Exploring and Preserving Vietnamese Intangible Cultural Heritage?
SIXT.VN can assist in exploring and preserving Vietnamese intangible cultural heritage by providing convenient and reliable transportation services to cultural sites, offering curated tours that highlight traditional arts and practices, and supporting local communities through sustainable tourism initiatives. With SIXT.VN, you can experience the richness of Vietnamese culture while contributing to its preservation.
- Transportation Services: Providing convenient transportation to cultural sites, making it easier for tourists to explore Vietnamese heritage.
- Curated Tours: Offering tours that showcase traditional arts, music, dance, and culinary practices.
- Sustainable Tourism: Supporting local communities through sustainable tourism initiatives that promote cultural preservation.
- Cultural Education: Providing educational resources and information about Vietnamese intangible cultural heritage.
- Community Partnerships: Collaborating with local communities to develop and promote authentic cultural experiences.
FAQ Section
1. What is Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Intangible Cultural Heritage refers to the practices, representations, expressions, knowledge, skills – as well as the instruments, objects, artifacts, and cultural spaces associated therewith – that communities, groups and, in some cases, individuals recognize as part of their cultural heritage.
2. Why is Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage Important?
Preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage is important because it maintains cultural diversity, promotes social cohesion, and provides a sense of identity for communities.
3. What are some examples of Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Examples of Intangible Cultural Heritage include oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe, and traditional craftsmanship.
4. How can I contribute to preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
You can contribute by supporting local cultural events, participating in community-based tourism, advocating for cultural preservation policies, and documenting and sharing cultural traditions.
5. What role does UNESCO play in preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
UNESCO plays a key role by promoting international cooperation, providing funding and expertise, and recognizing and safeguarding Intangible Cultural Heritage through its conventions and programs.
6. What are the biggest threats to Intangible Cultural Heritage?
The biggest threats include globalization, modernization, environmental changes, armed conflicts, and lack of resources.
7. How can technology help preserve Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Technology can help by creating digital archives, virtual museums, interactive platforms, and documentation tools for cultural expressions.
8. What is the role of cultural policies in preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Cultural policies can provide legal protection, financial support, and institutional frameworks for cultural preservation, ensuring community participation and aligning with international standards.
9. How does tourism impact Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Tourism can have both positive and negative impacts. It can provide economic incentives for preservation but also risks altering cultural expressions to meet tourist expectations.
10. What are some ethical considerations in preserving Intangible Cultural Heritage?
Ethical considerations include respecting cultural rights, ensuring community consent, and avoiding cultural appropriation in preservation efforts.
Ready to embark on a journey to discover and support Vietnam’s rich cultural tapestry? Let SIXT.VN be your trusted companion. Explore our curated tours, reliable transportation services, and sustainable tourism initiatives designed to connect you with the heart of Vietnamese heritage. Visit SIXT.VN today and start your adventure!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN



