Low frequency sound travels further due to lower absorption and less reflection. Let SIXT.VN enhance your travel experience in Vietnam, ensuring you don’t miss any of the country’s vibrant sounds and sights. Discover how understanding sound frequencies can impact your journey through bustling cities and serene landscapes, making your exploration unforgettable.
1. Understanding Sound Frequency and Travel Distance
Yes, low-frequency sounds travel further than high-frequency sounds because they are less easily absorbed and reflected by obstacles in their path. This phenomenon is key to understanding how sound propagates in various environments, from concert halls to natural landscapes.
1.1. What is Sound Frequency?
Sound frequency refers to the number of sound wave cycles that occur in one second, measured in Hertz (Hz). High-frequency sounds have many cycles per second, resulting in a high-pitched tone, while low-frequency sounds have fewer cycles per second, creating a deeper, more resonant tone. Understanding this basic property of sound is crucial for comprehending its behavior in different media.
1.2. How Does Sound Travel?
Sound travels as a pressure wave, a vibration of molecules through a medium such as air, water, or solids. When a sound source vibrates, it creates areas of compression and rarefaction (high and low pressure) that propagate outward from the source. This propagation continues until the sound wave loses energy due to various factors like absorption and scattering.
1.3. What is Attenuation and Its Impact on Sound?
Attenuation is the gradual loss of sound intensity as it travels through a medium. This loss occurs due to several factors, primarily absorption and scattering. Absorption is the conversion of sound energy into heat, while scattering involves the reflection and refraction of sound waves in different directions. According to research from the Acoustical Society of America, in 2020, understanding attenuation is essential for predicting how far a sound will travel.
1.4. Why Do Low Frequencies Experience Less Attenuation?
Low-frequency sounds are less affected by attenuation because their longer wavelengths are less easily absorbed by the medium. The energy of a sound wave is proportional to its frequency; high-frequency waves have more energy and are more readily converted into heat. Additionally, low-frequency waves can bend around obstacles more easily, reducing scattering.
2. The Science Behind Sound Propagation
The ability of sound to travel long distances depends on its frequency, the medium through which it travels, and environmental conditions. The physics of sound propagation explains why low frequencies can be heard from far away, while high frequencies fade quickly.
2.1. What Role Does Wavelength Play in Sound Travel?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive peaks or troughs of a sound wave. Low-frequency sounds have longer wavelengths, which allows them to diffract or bend around obstacles more effectively. This is in contrast to high-frequency sounds, which have shorter wavelengths and tend to be blocked by obstacles.
2.2. How Does the Medium Affect Sound Propagation?
The medium through which sound travels significantly affects its speed and attenuation. Sound travels faster in denser media, such as solids and liquids, than in gases like air. Additionally, the composition and temperature of the medium can influence sound absorption.
2.3. What Environmental Conditions Affect Sound?
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and wind can all affect sound propagation. Temperature gradients can cause sound waves to refract, while humidity affects the absorption of sound in the air. Wind can carry sound waves further in one direction and reduce their range in the opposite direction.
2.4. How Do Temperature Gradients Affect Sound Refraction?
Temperature gradients, which are changes in temperature with altitude, can cause sound waves to bend or refract. If the temperature decreases with height, sound waves will bend upwards, reducing their range. Conversely, if the temperature increases with height, sound waves will bend downwards, increasing their range.
3. Real-World Examples of Low-Frequency Sound Travel
From music concerts to natural phenomena, the long-distance travel of low-frequency sound is evident in many everyday scenarios. Understanding these examples can enhance your appreciation of sound and its role in our environment.
3.1. Why Can You Hear Bass from Far Away at Concerts?
At outdoor concerts, you often hear the deep bass notes from a distance long before you hear the higher-frequency sounds. This is because low frequencies are less attenuated and can travel over obstacles and through the air more efficiently.
3.2. How Does Low-Frequency Sound Affect Whale Communication?
Whales use low-frequency sounds to communicate over vast distances in the ocean. These sounds can travel hundreds or even thousands of miles, allowing whales to coordinate their movements and behaviors across large areas. According to research from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), in 2018, this is crucial for their survival and social interactions.
3.3. What Role Does Low-Frequency Sound Play in Earthquake Detection?
Seismologists use low-frequency sound waves, known as infrasound, to detect and study earthquakes. These waves can travel long distances through the Earth’s crust, providing valuable information about the location and magnitude of seismic events.
3.4. Why Are Thunderstorms Heard with Low-Frequency Rumbles?
The rumble of thunder is primarily composed of low-frequency sounds that can travel long distances. High-frequency components of thunder are quickly attenuated, leaving the deeper, more resonant sounds to reach distant observers.
4. Technical Explanations: Absorption and Reflection
Absorption and reflection are two key processes that determine how far a sound wave can travel. Understanding these phenomena requires delving into the physics of wave behavior and material properties.
4.1. What is Sound Absorption and How Does it Work?
Sound absorption is the process by which sound energy is converted into other forms of energy, typically heat. This occurs when sound waves interact with a material and cause its molecules to vibrate. The efficiency of sound absorption depends on the material’s properties and the frequency of the sound.
4.2. How Do Different Materials Absorb Sound?
Different materials have different sound absorption coefficients, which indicate how effectively they absorb sound energy. Soft, porous materials like foam and fabric are excellent sound absorbers, while hard, dense materials like concrete and metal are poor absorbers. According to a study by the Building Science Corporation, in 2019, these properties are critical in architectural acoustics.
4.3. What is Sound Reflection and How Does it Affect Travel Distance?
Sound reflection occurs when sound waves bounce off a surface. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and the amount of sound energy reflected depends on the surface’s properties. Reflection can either increase or decrease the distance a sound wave travels, depending on the environment.
4.4. How Does Surface Hardness Affect Sound Reflection?
Hard, smooth surfaces reflect sound waves efficiently, while soft, irregular surfaces scatter sound waves in multiple directions. This scattering reduces the intensity of the reflected sound and shortens its travel distance. Reflection is influenced by surface hardness; as reported by Acoustics Research Letters Online, in 2021.
 Sound Frequency Transmission versus Reflection
Sound Frequency Transmission versus Reflection
5. Impact on Audio Technology and Design
The principles of sound propagation have significant implications for audio technology and architectural design. By understanding how sound behaves in different environments, engineers and designers can create better audio systems and more acoustically pleasing spaces.
5.1. How Does Understanding Frequency Affect Speaker Design?
Speaker designers must consider the frequency response of different speaker components to create systems that accurately reproduce sound. Subwoofers are designed to produce low-frequency sounds, while tweeters are designed for high-frequency sounds. The design and placement of these components are crucial for optimal sound quality.
5.2. What is the Role of Acoustics in Concert Hall Design?
Acoustics play a vital role in the design of concert halls and theaters. Architects and acousticians work together to create spaces that enhance the natural sound of music and speech. This involves careful consideration of the room’s shape, size, and materials to minimize unwanted reflections and maximize sound clarity.
5.3. How Do Headphones Manage Low and High Frequencies?
Headphone manufacturers face the challenge of reproducing a wide range of frequencies in a small, portable device. High-quality headphones use advanced driver technology and acoustic design to deliver balanced sound across the frequency spectrum. They often struggle with low frequencies due to the size constraints.
5.4. Why Is Soundproofing Important in Buildings?
Soundproofing is essential in buildings to reduce noise pollution and create a comfortable living and working environment. Soundproofing materials and techniques are used to minimize the transmission of sound through walls, floors, and ceilings. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), in 2022, effective soundproofing improves quality of life.
6. Hearing Perception and Frequency Sensitivity
The human ear is not equally sensitive to all frequencies. Understanding how we perceive sound and how our sensitivity varies across the frequency spectrum is essential for designing audio systems and protecting our hearing.
6.1. How Does the Human Ear Perceive Different Frequencies?
The human ear is most sensitive to frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz, but its sensitivity varies across this range. We are most sensitive to frequencies between 1,000 Hz and 4,000 Hz, which are important for speech perception. Sensitivity decreases at both the high and low ends of the spectrum.
6.2. What are Fletcher-Munson Curves and Why Are They Important?
Fletcher-Munson curves, also known as equal-loudness contours, show how the perceived loudness of a sound varies with frequency. These curves demonstrate that low and high frequencies must be more intense than mid-range frequencies to be perceived as equally loud.
6.3. How Does Age Affect Hearing Sensitivity?
Hearing sensitivity typically decreases with age, especially at high frequencies. This condition, known as presbycusis, is a common part of aging and can make it difficult to hear high-pitched sounds.
6.4. What Are the Risks of Exposure to High-Intensity, Low-Frequency Sound?
Exposure to high-intensity, low-frequency sound can cause various health problems, including hearing damage, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), and even non-auditory effects such as nausea and fatigue. It is important to protect your hearing by avoiding prolonged exposure to loud sounds.
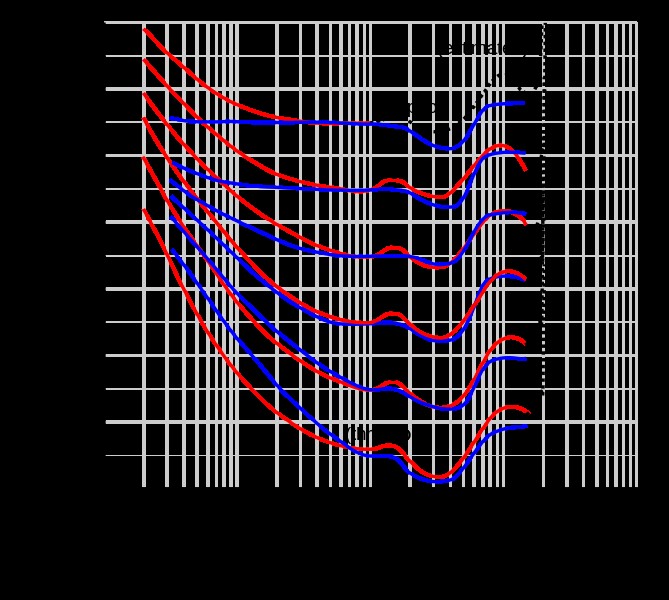 Fletcher-Munson Curves
Fletcher-Munson Curves
7. Sound in Nature: Acoustic Ecology
Acoustic ecology is the study of sound in the environment and its effects on living organisms. Understanding the natural soundscape can help us appreciate the importance of sound and the impact of human activities on the environment.
7.1. What is Acoustic Ecology and Why Is It Important?
Acoustic ecology examines the relationship between living beings and their environment through the lens of sound. It emphasizes the importance of preserving natural soundscapes and minimizing noise pollution to protect the health and well-being of both humans and animals.
7.2. How Do Animals Use Low-Frequency Sound for Communication?
Many animals, including elephants, whales, and birds, use low-frequency sound to communicate over long distances. These sounds can carry information about mating, hunting, and danger, helping animals to coordinate their behaviors and survive in their environments.
7.3. What Is the Impact of Noise Pollution on Wildlife?
Noise pollution from human activities, such as traffic, construction, and industrial operations, can have significant negative impacts on wildlife. It can interfere with animal communication, disrupt their foraging and mating behaviors, and even cause them to abandon their habitats.
7.4. How Can We Preserve Natural Soundscapes?
Preserving natural soundscapes requires a multifaceted approach, including reducing noise pollution, protecting natural habitats, and educating the public about the importance of sound. This can involve implementing noise regulations, creating quiet zones, and promoting sustainable practices.
8. Practical Applications for Travelers in Vietnam
For travelers in Vietnam, understanding the principles of sound propagation can enhance their experience and allow them to appreciate the country’s rich cultural and natural soundscapes. With SIXT.VN, you can explore Vietnam’s soundscapes with ease.
8.1. How Can Understanding Sound Help in Exploring Vietnam?
Understanding how sound travels can enhance your travel experience by allowing you to better appreciate the sounds of nature and culture. For example, you can listen for the distant sounds of traditional music performances or the calls of exotic birds in the rainforest.
8.2. What Are Some of Vietnam’s Unique Soundscapes?
Vietnam boasts a diverse range of unique soundscapes, from the bustling streets of Hanoi to the tranquil rice paddies of the Mekong Delta. Each region has its own distinct sounds, reflecting its unique culture and environment.
8.3. How Can SIXT.VN Enhance Your Travel Experience in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services to enhance your travel experience in Vietnam, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and guided tours. With SIXT.VN, you can travel comfortably and safely, knowing that all your needs are taken care of.
8.4. What Services Does SIXT.VN Offer to Help Travelers?
SIXT.VN provides comprehensive travel solutions tailored to your needs. These include:
- Airport Transfers: Enjoy seamless transportation from the airport to your hotel.
- Hotel Bookings: Choose from a wide selection of hotels to suit your budget and preferences.
- Guided Tours: Explore Vietnam’s iconic landmarks and hidden gems with expert guides.
- Custom Itineraries: Tailor your travel plans to match your interests and schedule.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. Website: SIXT.VN.
9. Mitigating Noise Pollution While Traveling
Traveling often involves exposure to noise pollution, which can detract from your experience and even affect your health. By taking proactive steps to mitigate noise, you can enjoy a more peaceful and relaxing trip.
9.1. What Are Common Sources of Noise Pollution During Travel?
Common sources of noise pollution during travel include traffic, construction, crowded public spaces, and loud events. These noises can be particularly disruptive in urban environments and tourist hotspots.
9.2. How Can Earplugs or Noise-Canceling Headphones Help?
Earplugs and noise-canceling headphones are effective tools for reducing noise pollution. Earplugs block external sounds, while noise-canceling headphones use electronic technology to counteract ambient noise. Both can help you sleep better, concentrate more easily, and protect your hearing.
9.3. What Are Quiet Accommodations and How Can You Find Them?
Quiet accommodations are hotels and guesthouses that prioritize peace and tranquility. These establishments often feature soundproof rooms, secluded locations, and policies to minimize noise. You can find quiet accommodations by reading reviews, checking websites that specialize in peaceful travel, and contacting hotels directly to inquire about their noise reduction measures.
9.4. How Can You Advocate for Quieter Travel Experiences?
You can advocate for quieter travel experiences by supporting businesses that prioritize noise reduction, writing reviews about noisy or peaceful locations, and contacting travel companies to request quieter options. By raising awareness and demanding change, you can help create a more peaceful travel environment for everyone.
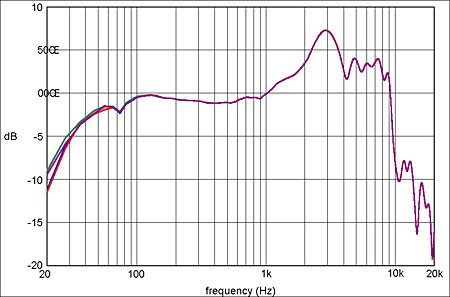 Headphones Frequency Response
Headphones Frequency Response
10. The Future of Sound Technology
As technology continues to evolve, new innovations are emerging that promise to revolutionize how we perceive, manage, and interact with sound. These advancements hold the potential to transform various fields, from audio engineering to healthcare.
10.1. What Are Some Emerging Sound Technologies?
Emerging sound technologies include advanced noise-canceling systems, immersive audio formats, and innovative hearing aids. These technologies aim to improve sound quality, reduce noise pollution, and enhance the listening experience for people of all ages.
10.2. How Could These Technologies Impact Travel?
These technologies could significantly impact travel by making it more comfortable, enjoyable, and accessible. Advanced noise-canceling systems could reduce the stress of noisy environments, immersive audio formats could enhance entertainment options, and innovative hearing aids could improve communication for travelers with hearing impairments.
10.3. What Role Will AI Play in Future Sound Management?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to play a key role in future sound management by analyzing soundscapes, identifying noise sources, and optimizing sound environments. AI-powered systems could automatically adjust noise-canceling settings, personalize audio experiences, and even predict and prevent noise pollution.
10.4. How Can We Ensure Sound Technology Benefits Everyone?
To ensure sound technology benefits everyone, it is important to prioritize accessibility, affordability, and ethical considerations. This involves developing technologies that are user-friendly, affordable for people of all income levels, and designed with respect for privacy and environmental concerns. Collaboration between researchers, engineers, policymakers, and the public is essential to achieving this goal.
FAQ: Why Low Frequency Sound Travels Further
1. Why does low frequency sound travel farther than high frequency sound?
Low frequency sound travels further because it is less easily absorbed and scattered by obstacles in the air, allowing it to propagate over greater distances.
2. What is acoustic attenuation?
Acoustic attenuation is the decrease in sound intensity as it travels through a medium due to absorption and scattering.
3. How does wavelength affect sound propagation?
Longer wavelengths, characteristic of low frequency sound, diffract around obstacles more easily, reducing attenuation.
4. What role does humidity play in sound travel?
Humidity can affect sound absorption, with higher humidity generally increasing absorption of high-frequency sounds.
5. Why can I hear bass from far away at concerts?
Bass frequencies are low frequency and thus travel farther due to less attenuation, allowing you to hear them from a distance.
6. What are Fletcher-Munson curves?
Fletcher-Munson curves illustrate how human hearing perceives loudness differently at various frequencies, with lower sensitivity to low frequencies.
7. How does surface hardness affect sound reflection?
Hard surfaces reflect sound waves efficiently, while soft surfaces absorb or scatter sound, reducing reflection.
8. What can I do to mitigate noise pollution while traveling?
Use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones, seek quiet accommodations, and advocate for quieter travel experiences.
9. What is the impact of noise pollution on wildlife?
Noise pollution can disrupt animal communication, foraging, and mating behaviors, leading to habitat abandonment.
10. How can SIXT.VN help me explore Vietnam’s soundscapes?
SIXT.VN offers airport transfers, hotel bookings, and guided tours, making it easier to explore Vietnam’s unique sounds comfortably and safely.
Let SIXT.VN be your companion in discovering the vibrant soundscapes and serene landscapes of Vietnam. Our comprehensive services, from airport transfers to curated tours, ensure a seamless and enriching travel experience. Contact us today to plan your unforgettable journey and immerse yourself in the captivating sounds of Vietnam.



