Are you curious about the science behind heat transfer and how it impacts your daily life, even your travel experiences in Vietnam? Heat always moves from hotter objects to colder ones. SIXT.VN is here to explain this phenomenon and how understanding it can enhance your travels with our convenient services. Discover how thermal energy flows and affects everything around you.
1. Understanding the Basics of Heat Transfer
What Exactly is Heat?
Heat is the transfer of thermal energy from one object or system to another due to a temperature difference. Thermal energy is the energy a substance or system has due to the movement of its atoms or molecules. It’s a form of kinetic energy, and the more these particles move, the higher the thermal energy and temperature. Heat is measured in Joules (J) or calories (cal).
What is the difference between Heat and Temperature?
Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. It indicates how hot or cold something is relative to a standard. Heat, on the other hand, is the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another due to a temperature difference. Temperature is measured in degrees Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), or Kelvin (K), while heat is measured in Joules or calories.
 Pot of water on a stove illustrating the difference between heat and temperature
Pot of water on a stove illustrating the difference between heat and temperature
Alt Text: Illustration comparing temperature as a measure of hotness and heat as the energy transferred to a pot on a stove, highlighting thermal dynamics.
What are the 3 Methods of Heat Transfer?
Heat transfer occurs through three primary mechanisms: conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Conduction: The transfer of heat through direct contact.
- Convection: The transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids and gases).
- Radiation: The transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves.
2. Diving Deeper into Why Heat Flows from Hot to Cold
Why is Heat Always Transferred from Hot to Cold?
Heat transfer follows the Second Law of Thermodynamics, which states that the total entropy (disorder) of an isolated system can only increase over time. When heat flows from a hot object to a cold object, the system moves towards a state of thermal equilibrium, where the temperature is uniform throughout. This process increases the system’s entropy.
What is Thermal Equilibrium?
Thermal equilibrium is a state where two or more objects in thermal contact have reached the same temperature, and there is no net flow of heat between them. At this point, the system is in its most stable state, and the entropy is maximized.
How Does Conduction Cause Heat Transfer?
Conduction occurs when two objects at different temperatures are in direct contact. The molecules in the hotter object vibrate more vigorously and collide with the molecules in the colder object, transferring some of their kinetic energy. This process continues until both objects reach thermal equilibrium.
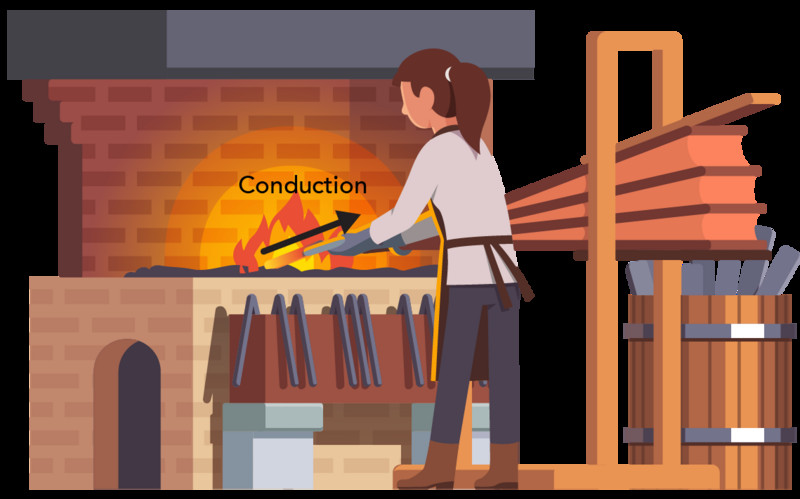 Blacksmith heating metal illustrating heat transfer by conduction
Blacksmith heating metal illustrating heat transfer by conduction
Alt Text: Blacksmith using conduction to heat metal bar, showcasing thermal energy transfer and heat conductivity in metalworking.
How Does Convection Cause Heat Transfer?
Convection involves the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids and gases). When a fluid is heated, it expands and becomes less dense, causing it to rise. Cooler, denser fluid then flows in to replace the warmer fluid, creating a convection current. This process continues until the temperature is evenly distributed throughout the fluid.
How Does Radiation Cause Heat Transfer?
Radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves. All objects emit thermal radiation, with the amount and wavelength of the radiation depending on the object’s temperature. When these waves strike another object, some of the energy is absorbed, causing the object to heat up. This process does not require any medium and can occur even in a vacuum.
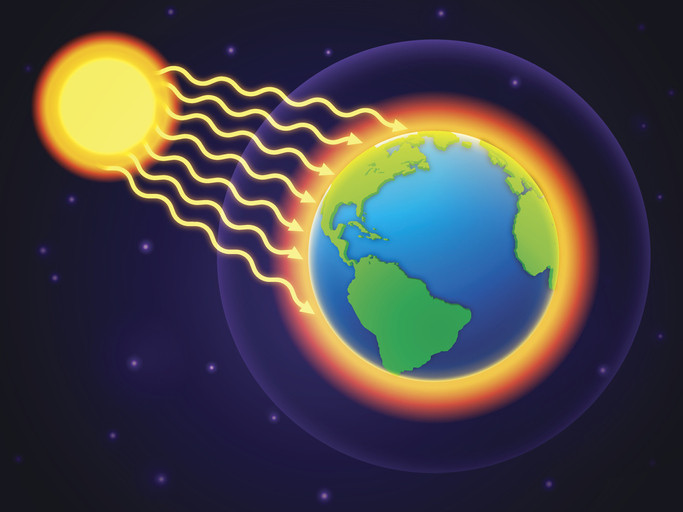 Solar radiation shown as waves travelling towards Earth
Solar radiation shown as waves travelling towards Earth
Alt Text: Radiation from sun heating Earth, showing electromagnetic waves and thermal energy transfer in the solar system.
3. Real-World Examples of Heat Transfer
How Does Heat Transfer Work in a House?
Heat transfer plays a significant role in maintaining the temperature inside a house.
- Conduction: Heat can be conducted through the walls, roof, and windows. Insulation helps to reduce heat transfer by conduction.
- Convection: Convection currents circulate air within a room, distributing heat evenly.
- Radiation: Sunlight can heat the house through windows, and the house itself radiates heat to the surrounding environment.
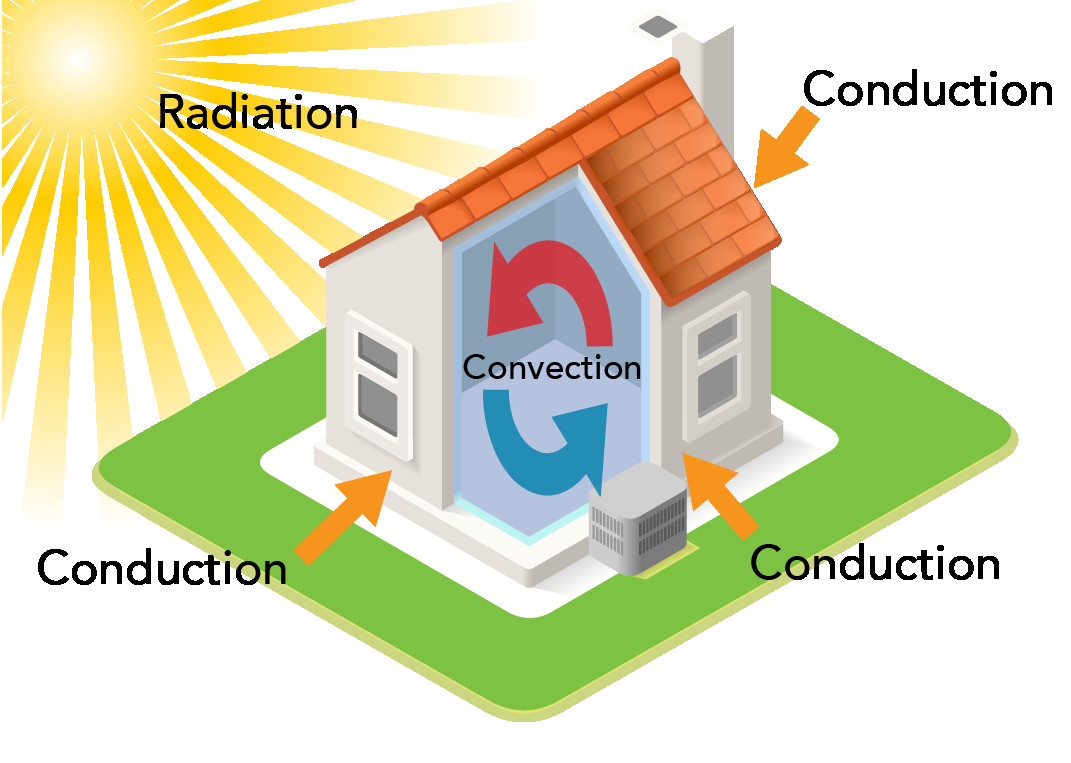 Heat transfer in a house showing radiation from the Sun, convection inside, and conduction through walls
Heat transfer in a house showing radiation from the Sun, convection inside, and conduction through walls
Alt Text: Heat transfer diagram in a house showcasing radiation, convection, and conduction processes for thermal management and energy efficiency.
How is Heat Transferred in Cooking?
Cooking relies on all three methods of heat transfer.
- Conduction: Heat is conducted from the stove to the pot and then to the food.
- Convection: Hot air or liquid circulates around the food, cooking it evenly.
- Radiation: Broiling or grilling involves direct radiation from a heat source to the food.
How Do Insulated Containers Work?
Insulated containers, such as thermoses and coolers, minimize heat transfer to keep their contents at a desired temperature. They use several strategies:
- Vacuum: A vacuum between the inner and outer walls prevents heat transfer by conduction and convection.
- Reflective surfaces: Reflective surfaces minimize heat transfer by radiation.
- Insulating materials: Materials with low thermal conductivity reduce heat transfer by conduction.
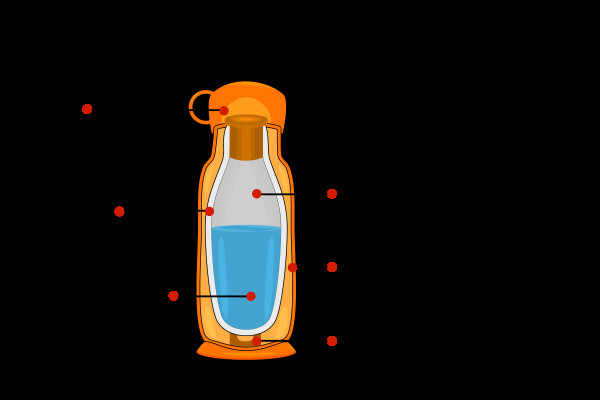 Cross-section of an insulated flask illustrating the design for minimizing heat transfer
Cross-section of an insulated flask illustrating the design for minimizing heat transfer
Alt Text: Diagram showing insulation layers in a flask to minimize heat transfer through vacuum, reflective surfaces, and insulating materials.
4. The Impact of Heat Transfer on Travel in Vietnam
How Does Vietnam’s Climate Affect Travel?
Vietnam’s tropical climate significantly influences travel experiences. High temperatures and humidity levels can affect comfort and require careful planning. Understanding heat transfer principles can help travelers stay cool and comfortable.
How to Stay Cool in Vietnam’s Heat
- Wear light-colored, breathable clothing: Light colors reflect more sunlight, reducing heat absorption.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps your body regulate its temperature through evaporation.
- Seek shade: Avoid direct sunlight during peak hours.
- Use fans and air conditioning: These methods facilitate convective heat transfer, cooling your body more efficiently.
How SIXT.VN Helps You Beat the Heat
SIXT.VN understands the challenges of traveling in Vietnam’s climate and offers services designed to enhance your comfort.
- Airport Transfer: Our reliable and air-conditioned airport transfer services ensure a comfortable start to your journey, shielding you from the heat and humidity upon arrival. Imagine stepping off the plane into the cool comfort of a SIXT.VN vehicle, ready to whisk you away to your hotel.
- Hotel Booking: We provide a curated selection of hotels with excellent air conditioning and other amenities to help you stay cool and relaxed during your stay.
- Tour Packages: Our expertly planned tour packages include transportation in air-conditioned vehicles, ensuring you can explore Vietnam’s attractions without suffering from the heat.
- Car Rental: Rent a car with SIXT.VN and enjoy the flexibility to travel at your own pace, with the added comfort of air conditioning. This allows you to escape the heat and humidity while exploring the country’s diverse landscapes.
5. Practical Applications of Heat Transfer in Daily Life
Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating and cooling systems rely on heat transfer principles to maintain comfortable temperatures in buildings. Furnaces, air conditioners, and heat pumps all use various methods of heat transfer to either add or remove heat from the indoor environment.
Electronic Devices
Heat transfer is crucial in electronic devices to prevent overheating. Heat sinks and fans are used to dissipate heat away from components, ensuring they operate efficiently and reliably.
Clothing and Insulation
Clothing and insulation materials are designed to minimize heat transfer between the body and the environment. Insulating materials trap air, reducing heat transfer by conduction and convection, while breathable fabrics allow moisture to evaporate, cooling the body through evaporative cooling.
6. Advanced Concepts in Heat Transfer
Fourier’s Law of Conduction
Fourier’s Law states that the rate of heat transfer by conduction is proportional to the temperature gradient and the area through which heat is transferred. It is expressed as:
Q = -kA(dT/dx)
Where:
Qis the rate of heat transferkis the thermal conductivity of the materialAis the area through which heat is transferreddT/dxis the temperature gradient
Newton’s Law of Cooling
Newton’s Law of Cooling states that the rate of heat loss of a body is proportional to the difference in temperatures between the body and its surroundings. It is expressed as:
Q = hA(Ts - Tf)
Where:
Qis the rate of heat transferhis the convective heat transfer coefficientAis the surface area of the objectTsis the surface temperature of the objectTfis the temperature of the surrounding fluid
Stefan-Boltzmann Law of Radiation
The Stefan-Boltzmann Law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a black body is proportional to the fourth power of its absolute temperature. It is expressed as:
Q = εσAT^4
Where:
Qis the rate of heat transferεis the emissivity of the objectσis the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 x 10^-8 W/m^2K^4)Ais the surface area of the objectTis the absolute temperature of the object in Kelvin
7. Recent Advances in Heat Transfer Technology
Nanomaterials for Enhanced Heat Transfer
Researchers are exploring the use of nanomaterials, such as carbon nanotubes and graphene, to enhance heat transfer in various applications. These materials have exceptionally high thermal conductivity, making them ideal for use in heat sinks, thermal interface materials, and heat exchangers.
Phase Change Materials (PCMs) for Thermal Storage
PCMs are materials that absorb and release heat during phase transitions (e.g., melting and freezing). They are used in thermal storage systems to store energy and release it later when needed. PCMs are being explored for use in building insulation, electronic cooling, and solar energy storage.
Additive Manufacturing for Heat Exchangers
Additive manufacturing (3D printing) is being used to create complex heat exchanger designs with enhanced heat transfer performance. This technology allows for the creation of intricate geometries and internal structures that are difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods.
8. How to Book Your Comfortable Trip to Vietnam with SIXT.VN
Step-by-Step Guide to Booking Services on SIXT.VN
- Visit the SIXT.VN Website: Go to SIXT.VN on your computer or mobile device.
- Select Your Service: Choose from airport transfer, hotel booking, tour packages, or car rental.
- Enter Your Details: Provide the necessary information, such as your travel dates, destination, and preferences.
- Choose Your Options: Select the specific services you need, such as the type of car, hotel room, or tour package.
- Review Your Booking: Double-check all the details to ensure they are correct.
- Make Payment: Complete your booking by making a secure online payment.
- Receive Confirmation: You will receive a confirmation email with all the details of your booking.
Benefits of Using SIXT.VN for Your Travel Needs
- Convenience: Book all your travel services in one place.
- Reliability: Trustworthy and dependable services.
- Comfort: Enjoy air-conditioned transportation and comfortable accommodations.
- Expertise: Benefit from our knowledge of Vietnam’s travel landscape.
Contact Information for SIXT.VN
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/WhatsApp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN
9. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Heat Transfer
Objects Don’t “Contain” Heat
Objects do not contain heat; they contain thermal energy. Heat is the transfer of this energy from one object to another due to a temperature difference.
Cold is Not the Opposite of Heat
Cold is simply the absence of heat. Heat flows from hotter objects to colder objects, not the other way around.
Heat Transfer Only Occurs in Solids
Heat transfer can occur in solids, liquids, and gases through conduction, convection, and radiation.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Heat Transfer
FAQ 1: Why does heat always flow from hot to cold?
Heat flows from hot to cold due to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, which states that systems tend to move towards a state of thermal equilibrium and maximum entropy.
FAQ 2: What is the difference between heat and thermal energy?
Thermal energy is the total kinetic and potential energy of the particles within an object, while heat is the transfer of thermal energy between objects due to a temperature difference.
FAQ 3: How does insulation prevent heat transfer?
Insulation materials have low thermal conductivity, which reduces heat transfer by conduction. They also trap air, which minimizes heat transfer by convection and radiation.
FAQ 4: Can heat transfer occur in a vacuum?
Yes, heat transfer can occur in a vacuum through radiation. Electromagnetic waves can travel through space without needing a medium.
FAQ 5: What is the role of convection in weather patterns?
Convection plays a significant role in weather patterns by creating wind and ocean currents. Warm air and water rise, while cooler air and water sink, creating large-scale circulation patterns.
FAQ 6: How do heat sinks work in electronic devices?
Heat sinks are designed to increase the surface area available for heat transfer, allowing heat to dissipate more quickly from electronic components and preventing overheating.
FAQ 7: What are some common examples of conduction in everyday life?
Common examples of conduction include touching a hot stove, holding a cup of hot coffee, and walking barefoot on a cold tile floor.
FAQ 8: How does the color of an object affect heat transfer?
Dark-colored objects absorb more radiation than light-colored objects, causing them to heat up more quickly in sunlight. Light-colored objects reflect more radiation, keeping them cooler.
FAQ 9: What are some advanced technologies that use heat transfer principles?
Advanced technologies that use heat transfer principles include heat pumps, geothermal energy systems, and concentrated solar power plants.
FAQ 10: How can understanding heat transfer help me travel more comfortably in hot climates like Vietnam?
Understanding heat transfer can help you make informed decisions about clothing, hydration, and seeking shade to stay cool and comfortable. Additionally, using services like SIXT.VN that provide air-conditioned transportation and accommodations can significantly enhance your travel experience.
Conclusion: Embrace the Science of Comfort with SIXT.VN
Understanding why heat travels from hot to cold is more than just a scientific curiosity; it’s a key to enhancing your travel experiences, especially in a vibrant and warm country like Vietnam. From choosing the right clothing to utilizing air-conditioned transport, every decision can impact your comfort.
Let SIXT.VN be your partner in ensuring a pleasant and comfortable journey. Our services, from airport transfers to curated hotel bookings and expertly planned tours, are designed to keep you cool and relaxed, allowing you to fully enjoy the beauty and culture of Vietnam.
Ready to experience Vietnam in ultimate comfort? Visit SIXT.VN today and book your next adventure!



