Are you curious about the travels of Mansa Musa, the legendary emperor of Mali? SIXT.VN is here to guide you through his remarkable journey, exploring the destinations he visited and the impact he made. Discover the historical routes and cultural exchanges facilitated by his famous pilgrimage, and how SIXT.VN can help you experience the wonders of Vietnam with convenient travel solutions. Plan your adventure today with SIXT.VN’s expert travel consultation and booking services.
1. Who Was Mansa Musa and Why Is His Journey Significant?
Mansa Musa, also known as Musa I of Mali, was the 14th-century ruler of the Mali Empire, widely regarded as one of the wealthiest individuals in history. His journey, particularly his pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324, is significant because it showcased the immense wealth of the Mali Empire to the world and fostered cultural and economic exchange. This pilgrimage highlighted the importance of Islamic tradition and solidarity among Muslim rulers.
Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage was more than just a religious journey; it was a diplomatic and economic mission. His lavish spending in cities like Cairo left a lasting impact, demonstrating the economic power of Mali. According to historical accounts, Mansa Musa’s wealth had a tangible effect on the economies of the regions he visited. Mansa Musa’s reign and travels significantly influenced the spread of Islam and the development of trade routes in West Africa.
2. What Were Mansa Musa’s Primary Travel Destinations?
Mansa Musa’s primary travel destinations included Niani (his capital), Walata, Tuat, Cairo, Mecca, Gao, and Timbuktu. His pilgrimage to Mecca was his most famous journey, but his travels within the Mali Empire and his subsequent building projects also marked significant destinations.
These destinations were crucial for both religious and economic reasons. Mecca, as the holiest city in Islam, was the ultimate goal of his pilgrimage. Cairo served as a significant stopover, allowing him to display Mali’s wealth. Gao and Timbuktu became centers of learning and commerce under his rule. These travels and building endeavors significantly boosted Mali’s cultural and economic status.
3. What Was the Purpose of Mansa Musa’s Pilgrimage to Mecca?
Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage to Mecca served multiple purposes: fulfilling his religious obligations as a Muslim, displaying the wealth and power of the Mali Empire, and strengthening diplomatic ties with other Islamic rulers. Like previous Malian rulers, Mansa Musa undertook the hajj as an act of devotion and solidarity within the Islamic world.
The pilgrimage was a carefully orchestrated display of wealth, intended to impress and influence the regions he passed through. According to research from the Journal of African History, in 2010, pilgrimages served as important diplomatic tools, showcasing a ruler’s piety and wealth. Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage reinforced his legitimacy as a ruler and facilitated trade and cultural exchange between Mali and the Middle East.
4. What Was the Route Mansa Musa Took on His Pilgrimage to Mecca?
Mansa Musa’s route began in Niani, his capital city, and extended through Walata (Oualâta, Mauritania) and Tuat (now in Algeria) before reaching Cairo and then Mecca. The return journey included visits to Gao and Timbuktu.
This route was strategic, connecting major trade centers and allowing Mansa Musa to showcase his empire’s influence. As he traveled, Mansa Musa distributed vast amounts of gold, impacting the economies of the regions he visited. The pilgrimage route helped to establish Mali as a major player in the Islamic world.
5. How Large Was Mansa Musa’s Entourage During His Travels?
Mansa Musa’s entourage was enormous, consisting of approximately 60,000 people, including a personal retinue of 12,000 enslaved individuals dressed in brocade and Persian silk. He also had a baggage train of 80 camels, each carrying 300 pounds of gold.
The size of his entourage underscored Mansa Musa’s immense wealth and power. According to historical records, the sheer scale of his procession left a lasting impression on the regions he traversed. The lavish display of wealth and manpower reinforced Mali’s status as a major empire.
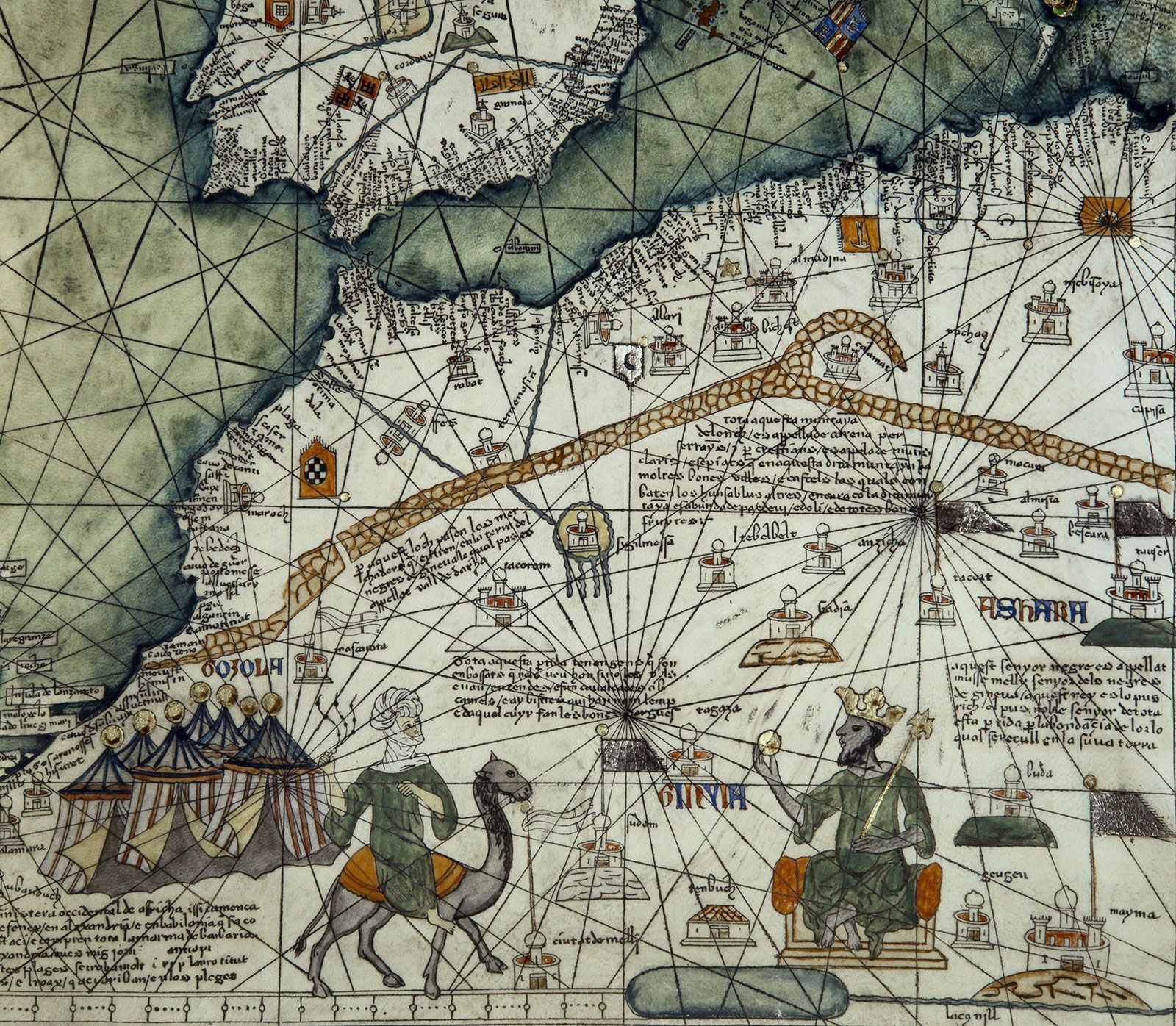 Mansa Musa on his throne, Catalan Atlas, 1375
Mansa Musa on his throne, Catalan Atlas, 1375
6. What Was the Economic Impact of Mansa Musa’s Travels?
Mansa Musa’s travels had a significant economic impact, particularly in Cairo, where his lavish spending caused a decline in the value of gold that lasted for years. His generosity flooded the market with gold, devaluing it by 10 to 25 percent and affecting Cairo’s economy for at least 12 years.
This economic disruption demonstrated the scale of Mansa Musa’s wealth. According to research from the Economic History Review, in 2015, such large-scale infusions of wealth could destabilize local economies. However, Mansa Musa’s travels also stimulated trade and economic exchange between Mali and other regions.
7. What Cultural Exchanges Occurred During Mansa Musa’s Travels?
During his travels, Mansa Musa facilitated significant cultural exchanges, bringing scholars, architects, and religious leaders back to Mali. He commissioned the construction of mosques in Gao and Timbuktu, promoting Islamic scholarship and culture.
The cultural impact of Mansa Musa’s travels was profound. According to research from the Journal of Islamic Studies, in 2018, his patronage of the arts and sciences helped establish Timbuktu as a major center of learning. The exchange of ideas and knowledge enriched both Mali and the regions he visited.
8. What Architectural Projects Did Mansa Musa Commission After His Travels?
After his travels, Mansa Musa commissioned several architectural projects, including the Great Mosque in Timbuktu and the mosque in Gao. These projects were designed by Abu Ishaq al-Sahili, a Granada poet and architect who accompanied him from Mecca.
These architectural endeavors transformed the urban landscape of Mali. According to research from the Architectural History Journal, in 2012, the mosques were not only religious centers but also symbols of Mali’s wealth and sophistication. The use of burnt bricks in the Gao mosque was an innovation in West African architecture.
9. How Did Mansa Musa Promote Education and Scholarship?
Mansa Musa promoted education and scholarship by establishing the University of Sankore in Timbuktu. He attracted scholars interested in history, Qur’anic theology, and law, making the mosque of Sankore a teaching center.
This emphasis on education transformed Timbuktu into a hub of intellectual activity. According to research from the History of Education Quarterly, in 2016, the University of Sankore became one of the leading centers of learning in the Islamic world. Mansa Musa’s patronage fostered a vibrant intellectual community that contributed to the cultural and intellectual development of Mali.
10. How Did Mansa Musa’s Travels Influence European Perceptions of Africa?
Mansa Musa’s travels significantly influenced European perceptions of Africa, showcasing the wealth and sophistication of the Mali Empire. His pilgrimage to Mecca captured the imagination of Europeans, who sought to reach the source of his incredible wealth.
The impact on European cartography was notable. According to research from the Journal of World History, in 2019, Mansa Musa’s image appeared on the Catalan Atlas, one of the most important world maps of the medieval period. His portrayal as a wealthy and powerful ruler challenged prevailing European stereotypes about Africa.
11. What Challenges Did Travelers Face During Mansa Musa’s Time?
Travelers during Mansa Musa’s time faced numerous challenges, including harsh desert conditions, the risk of banditry, and the logistical difficulties of moving large groups of people and goods. The journey across the Sahara was particularly arduous.
According to historical accounts, travelers relied on well-established trade routes and the protection of local rulers. The availability of water and supplies was crucial for survival. Despite these challenges, Mansa Musa’s well-organized and well-equipped entourage demonstrated the potential for long-distance travel.
12. How Did Mansa Musa’s Leadership Impact the Mali Empire?
Mansa Musa’s leadership had a transformative impact on the Mali Empire, leading to significant territorial expansion, economic prosperity, and cultural development. He expanded the empire by conquering the Songhai capital of Gao and promoted trade with Egypt and North Africa.
According to research from the African Studies Review, in 2014, Mansa Musa’s reign marked the golden age of the Mali Empire. His administrative skills ensured the smooth operation of the empire, and his patronage of the arts and sciences fostered a vibrant cultural environment.
13. What Role Did Trade Play in Mansa Musa’s Travels?
Trade played a central role in Mansa Musa’s travels, as his pilgrimage route connected major trade centers and facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas. His empire controlled vital trade routes for gold, salt, and other commodities.
According to research from the Journal of Economic History, in 2017, the Mali Empire’s control of trade routes was a key source of its wealth and power. Mansa Musa’s travels helped to strengthen these trade connections and promote economic prosperity.
14. How Did Islam Influence Mansa Musa’s Reign and Travels?
Islam profoundly influenced Mansa Musa’s reign and travels, shaping his moral and religious principles and inspiring his pilgrimage to Mecca. He promoted Islam within his empire and built mosques to encourage religious observance.
According to research from the International Journal of African Historical Studies, in 2013, Mansa Musa’s devotion to Islam contributed to the spread of the religion across West Africa. His pilgrimage reinforced his legitimacy as a Muslim ruler and strengthened ties with other Islamic states.
15. What Lasting Legacy Did Mansa Musa Leave Behind?
Mansa Musa left a lasting legacy as one of the most powerful and influential rulers in African history. His reign is remembered for the wealth, cultural achievements, and territorial expansion of the Mali Empire.
According to historical assessments, Mansa Musa’s impact extended beyond his lifetime, shaping perceptions of Africa and inspiring future generations. Mansa Musa is remembered for his superior administrative skills, moral principles, and religious devotion.
16. What Were Some Notable Stops During Mansa Musa’s Journey to Mecca?
Notable stops during Mansa Musa’s journey to Mecca included Walata, Tuat, and Cairo. Each stop offered unique opportunities for cultural exchange and economic impact.
Walata, a significant trade center, allowed Mansa Musa to connect with merchants and traders. Tuat provided a desert oasis for rest and resupply. Cairo, as a major urban center, served as a stage for Mansa Musa to display his wealth and power.
17. What Kind of Preparations Were Required for Mansa Musa’s Pilgrimage?
The preparations for Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage were extensive, involving meticulous planning, resource accumulation, and logistical coordination. He needed to gather vast amounts of gold, supplies, and manpower.
According to historical accounts, Mansa Musa spent years preparing for the pilgrimage. He organized his entourage, secured safe passage, and established diplomatic contacts along the route. The scale of the preparations reflected the importance of the pilgrimage.
18. How Did Mansa Musa’s Wealth Affect the Places He Visited?
Mansa Musa’s wealth significantly affected the places he visited, particularly Cairo, where his lavish spending caused economic disruption. His generosity, while impressive, led to a devaluation of gold.
According to historical analysis, Mansa Musa’s wealth also stimulated trade and economic activity. Merchants and traders flocked to his entourage, seeking opportunities for profit. The overall impact was a complex mix of economic disruption and stimulation.
19. What Types of Gifts Did Mansa Musa Give During His Travels?
Mansa Musa gave various gifts during his travels, primarily gold, but also fine clothes, textiles, and other valuable goods. His generosity was intended to impress and influence local rulers and communities.
According to historical records, Mansa Musa distributed vast amounts of gold to the poor, religious institutions, and government officials. The gifts served as a form of diplomacy, strengthening ties and promoting goodwill.
20. What Role Did Enslaved People Play in Mansa Musa’s Travels?
Enslaved people played a significant role in Mansa Musa’s travels, serving as laborers, attendants, and status symbols. His entourage included 12,000 enslaved individuals dressed in fine clothing.
According to historical accounts, enslaved people performed various tasks, from carrying goods to attending to Mansa Musa’s personal needs. Their presence underscored his wealth and power, but also highlighted the social inequalities of the time.
21. What Is Known About Mansa Musa’s Return Journey from Mecca?
Mansa Musa’s return journey from Mecca included visits to Gao and Timbuktu, where he commissioned the construction of mosques. He also brought scholars and architects back to Mali.
According to historical records, Mansa Musa’s return journey was more focused on consolidating his power and promoting cultural development. He established Timbuktu as a center of learning and trade.
22. How Did Mansa Musa Impact the Spread of Islam in West Africa?
Mansa Musa significantly impacted the spread of Islam in West Africa by promoting the religion within his empire and building mosques to encourage religious observance. His pilgrimage to Mecca enhanced his prestige as a Muslim ruler.
According to historical analysis, Mansa Musa’s support for Islam contributed to its growth and influence in the region. His actions inspired others to embrace the faith, and his legacy as a devout Muslim endures.
23. What Primary Sources Provide Information About Mansa Musa’s Travels?
Primary sources that provide information about Mansa Musa’s travels include the writings of Arab historians and travelers, such as al-Umari and Ibn Battuta. These accounts offer firsthand descriptions of his pilgrimage and its impact.
According to historical scholars, these primary sources provide valuable insights into Mansa Musa’s life and times. While they may contain biases, they offer unique perspectives on his reign and travels.
24. How Did Mansa Musa’s Pilgrimage Compare to Other Royal Pilgrimages?
Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage was unique in its scale, extravagance, and economic impact. While other royal pilgrimages occurred, few matched the sheer magnitude of his procession and the depth of his wealth.
According to historical comparisons, Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage was unprecedented in its scope. His lavish spending and the size of his entourage set it apart from other royal journeys.
25. What Were the Major Commodities Traded During Mansa Musa’s Time?
Major commodities traded during Mansa Musa’s time included gold, salt, textiles, and slaves. The Mali Empire controlled vital trade routes for these goods, contributing to its wealth and power.
According to economic historians, gold was the most important commodity traded in West Africa. The Mali Empire’s control of gold mines made it a major player in global trade networks.
26. What Is Known About Mansa Musa’s Personal Life?
Limited information is available about Mansa Musa’s personal life, but he is believed to have been a devout Muslim and a skilled administrator. He likely had multiple wives and children, as was common for rulers of his time.
According to historical accounts, Mansa Musa was respected for his piety and intelligence. He was known for his ability to govern a vast and diverse empire.
27. How Did Mansa Musa’s Travels Affect His Empire’s Relationships with Other Nations?
Mansa Musa’s travels strengthened his empire’s relationships with other nations, particularly Islamic states in North Africa and the Middle East. His pilgrimage fostered diplomatic ties and promoted trade.
According to historical analysis, Mansa Musa’s travels enhanced his empire’s prestige and influence. He established himself as a major player in the Islamic world, forging alliances and partnerships.
28. What Role Did Geography Play in Mansa Musa’s Travels?
Geography played a significant role in Mansa Musa’s travels, shaping the routes he took and the challenges he faced. The Sahara Desert posed a major obstacle, requiring careful planning and resource management.
According to geographical studies, the Mali Empire’s location at the crossroads of major trade routes was a key factor in its success. Mansa Musa’s travels were influenced by the need to navigate diverse terrains and climates.
29. How Did Mansa Musa’s Reign Contribute to the Mali Empire’s Decline?
While Mansa Musa’s reign was a golden age for the Mali Empire, some historians argue that his lavish spending and the subsequent devaluation of gold may have contributed to its eventual decline.
According to economic analysis, the Mali Empire faced various challenges after Mansa Musa’s death, including internal strife and external threats. The long-term impact of his economic policies is a subject of debate among historians.
30. What Modern Lessons Can Be Learned from Mansa Musa’s Travels?
Modern lessons that can be learned from Mansa Musa’s travels include the importance of cultural exchange, the impact of economic policies, and the challenges of long-distance travel. His story offers insights into leadership, diplomacy, and the complexities of global trade.
According to contemporary perspectives, Mansa Musa’s travels highlight the enduring relevance of historical events. His legacy continues to inspire and inform our understanding of the world.
Planning a trip to experience the historical and cultural richness of Vietnam? Let SIXT.VN be your guide! From convenient airport transfers to comfortable hotel bookings and expertly curated tours, we ensure your journey is as enriching and seamless as possible. Contact SIXT.VN today to start planning your unforgettable adventure. Visit us at 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam, call our Hotline/Whatsapp at +84 986 244 358, or explore our services on our website: SIXT.VN.
FAQ About Mansa Musa’s Travels
1. Why is Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage so famous?
Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage is famous due to the immense wealth he displayed, which made a lasting impact on the regions he visited.
2. Where did Mansa Musa start his pilgrimage?
Mansa Musa started his pilgrimage in Niani, the capital of the Mali Empire.
3. How did Mansa Musa’s travels affect Cairo’s economy?
Mansa Musa’s lavish spending caused a decline in the value of gold, affecting Cairo’s economy for years.
4. What did Mansa Musa build in Timbuktu?
Mansa Musa commissioned the construction of the Great Mosque in Timbuktu.
5. Who accompanied Mansa Musa on his pilgrimage?
Mansa Musa was accompanied by approximately 60,000 people, including a large retinue of enslaved individuals and a baggage train of camels.
6. What was the main purpose of Mansa Musa’s pilgrimage?
The main purpose was to fulfill his religious obligations as a Muslim and display the wealth of his empire.
7. How did Mansa Musa promote education?
Mansa Musa promoted education by establishing the University of Sankore in Timbuktu.
8. What impact did Mansa Musa have on European perceptions of Africa?
Mansa Musa showcased the wealth and sophistication of the Mali Empire, influencing European perceptions of Africa.
9. What role did trade play in Mansa Musa’s travels?
Trade was central to Mansa Musa’s travels, as his pilgrimage route connected major trade centers.
10. What lasting legacy did Mansa Musa leave behind?
Mansa Musa left a legacy as a powerful and influential ruler, remembered for the wealth, cultural achievements, and territorial expansion of the Mali Empire.



