Are you planning an unforgettable trip to Africa and wondering What Vaccinations Do You Need To Travel To Africa? With SIXT.VN, navigating the health requirements for your adventure is simple. Ensuring you’re up-to-date on your travel vaccinations for Africa is the first step for a safe and incredible journey. Let SIXT.VN guide you through the essential vaccinations and health precautions, so you can focus on the excitement of exploring Africa. With SIXT.VN, your Africa travel preparation is in expert hands, helping you discover stunning landscapes and amazing wildlife with health and safety assured.
1. Pre-Departure Health Preparations for Your African Adventure
Before embarking on your exciting journey to Africa, it’s crucial to prioritize your health and well-being. Getting informed about necessary vaccinations and health precautions is a key part of preparing for your trip. This section provides a detailed guide to help you navigate the health requirements for traveling to Africa.
1.1. Consult Your Doctor or Travel Clinic
The most important step in preparing for your trip is to consult your doctor or a travel clinic specialist well in advance—ideally, 6-8 weeks before your departure. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), early consultation allows enough time for vaccinations to take effect and for you to discuss any specific health concerns related to your destination. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized advice based on your medical history, the specific regions you plan to visit, and the duration of your stay.
1.2. Routine Vaccinations: Ensuring You’re Up-to-Date
Ensure your routine vaccinations are current. These are crucial for protecting you from diseases that, while rare in many developed countries, are more prevalent in other parts of the world.
- Flu: Annual flu shots are recommended, especially if traveling during flu season.
- MMR (Measles, Mumps, and Rubella): Essential for travelers, especially if you were not vaccinated as a child.
- Polio: A booster may be necessary depending on your vaccination history and the specific regions you plan to visit.
- Hepatitis A & B: Hepatitis A is transmitted through contaminated food and water, while Hepatitis B is spread through bodily fluids. Both are recommended for travelers to Africa.
- DPT (Diphtheria, Pertussis, and Tetanus): Ensure your tetanus booster is up-to-date, as it’s recommended every ten years.
1.3. Yellow Fever Vaccination: A Must for Many African Countries
Yellow fever is a viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes and is prevalent in many parts of Africa. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), vaccination against yellow fever is highly recommended and, in some cases, mandatory for entry into certain African countries.
1.3.1. Key Facts About Yellow Fever Vaccination
- Vaccination Requirement: Many African countries require proof of yellow fever vaccination for entry, especially if you are arriving from or have recently traveled through a yellow fever risk area.
- Timing: The yellow fever vaccine should be administered at least 10 days before your travel date to allow your body to develop immunity.
- International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (IVCP): After receiving the vaccine, you will be issued an IVCP, which serves as proof of vaccination. Ensure you carry this certificate with your travel documents.
- Where to Get Vaccinated: Only authorized travel clinics and healthcare providers can administer the yellow fever vaccine and issue the IVCP.
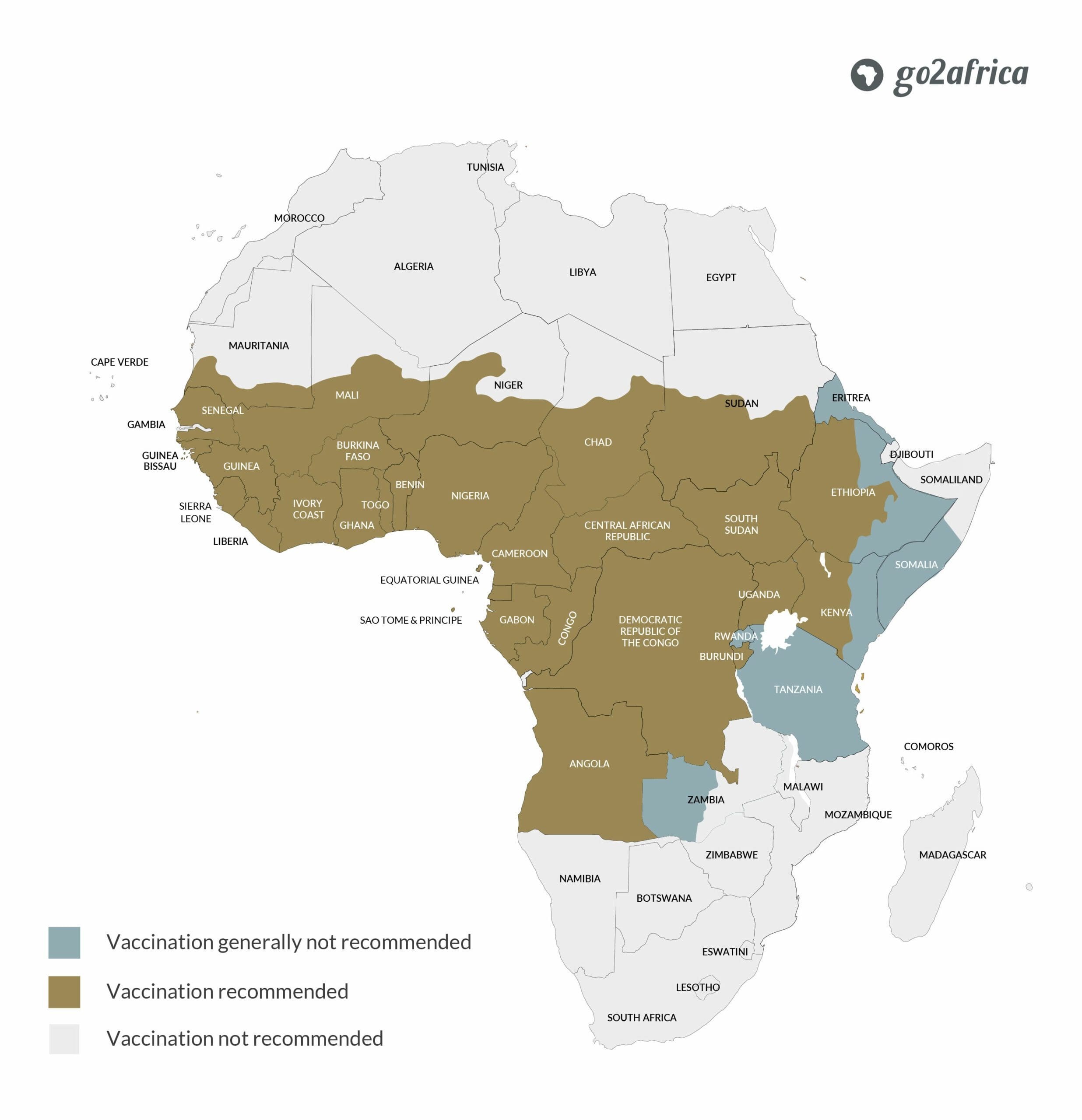
1.3.2. Yellow Fever Vaccination Requirements by Country
The table below provides a summary of yellow fever vaccination requirements in various African countries. Please note that this information can change, so it’s crucial to verify the latest requirements with your doctor or travel clinic before your trip.
| Vaccination is an entry requirement | Vaccination required if you’ve been to a country in the yellow fever belt |
|---|---|
| Republic of the Congo | Botswana |
| Uganda | Madagascar |
| Kenya | Rwanda |
| Tanzania | |
| Namibia | |
| Seychelles | |
| South Africa | |
| Mozambique | |
| Zimbabwe | |
| Zambia |
1.4. Malaria Prevention: Protecting Yourself from Mosquito Bites
Malaria is a significant health risk in many African countries, transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes. Prevention is key, and there are several strategies to protect yourself:
1.4.1. Antimalarial Medication
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss the best antimalarial medication for your trip with your doctor. The choice of medication depends on your destination, health history, and any other medications you are taking.
- Types of Antimalarials: Common antimalarials include Atovaquone/Proguanil (Malarone), Doxycycline, and Mefloquine. Each has its own set of side effects, so it’s important to discuss these with your doctor.
- Timing: Start taking the medication as prescribed before, during, and after your trip to ensure continuous protection.
1.4.2. Preventative Measures
- Insect Repellent: Use insect repellent containing DEET (20-30%) on exposed skin. Apply it regularly, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks, especially at night. Light-colored clothing is preferable as it attracts fewer mosquitoes.
- Mosquito Nets: Sleep under a mosquito net treated with insecticide, particularly in areas where malaria is prevalent.
- Stay Indoors: If possible, stay in air-conditioned or screened accommodations to minimize exposure to mosquitoes.
1.5. Other Recommended Vaccinations and Health Precautions
Depending on your specific travel plans and activities, your doctor may recommend additional vaccinations and health precautions:
- Typhoid: Recommended if you plan to eat at local restaurants or street food stalls, as typhoid is transmitted through contaminated food and water.
- Cholera: Vaccination may be advised if you are traveling to areas with poor sanitation.
- Meningitis: Recommended for travel to the meningitis belt in sub-Saharan Africa, especially during the dry season.
- Rabies: Consider vaccination if you plan to engage in activities that may bring you into contact with animals, such as hiking or camping.
- Traveler’s Diarrhea: Pack over-the-counter medications to treat traveler’s diarrhea, and be mindful of food and water safety. Drink bottled or boiled water, and avoid raw or undercooked foods.
1.6. General Health Tips for Traveling to Africa
In addition to vaccinations and preventative medications, consider these general health tips:
- Travel Health Insurance: Ensure you have comprehensive travel health insurance that covers medical emergencies, evacuation, and repatriation.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration, especially in hot climates.
- Food and Water Safety: Be cautious about what you eat and drink. Avoid tap water, ice cubes, and raw or undercooked foods.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen with a high SPF, wear a hat, and sunglasses to protect yourself from the sun.
- Personal Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, or use hand sanitizer.
- Avoid Contact with Wild Animals: Do not approach or feed wild animals, as they may carry diseases.
- Altitude Sickness: If traveling to high-altitude areas, allow time to acclimatize and be aware of the symptoms of altitude sickness.
By taking these health precautions and consulting with your doctor, you can ensure a safe and healthy trip to Africa, allowing you to fully enjoy the incredible experiences the continent has to offer. Let SIXT.VN assist you in planning your journey, ensuring you have all the necessary information and support for a memorable adventure.
2. Understanding the Key Diseases and Vaccinations for Africa
Traveling to Africa requires careful planning, especially when it comes to your health. This section provides a detailed overview of the key diseases you should be aware of and the vaccinations that can help protect you. By understanding these health risks and taking the necessary precautions, you can enjoy a safe and memorable trip to Africa.
2.1. Yellow Fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. It is prevalent in many parts of Africa and South America. The disease can cause fever, headache, jaundice, muscle pain, nausea, fatigue, and in severe cases, death.
2.1.1. Vaccination
- Importance: Yellow fever vaccination is highly effective in preventing the disease.
- Requirements: Many African countries require proof of yellow fever vaccination for entry, especially if you are arriving from or have recently traveled through a yellow fever risk area.
- Certificate: After receiving the vaccine, you will be issued an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (IVCP), which serves as proof of vaccination. This certificate is valid for life, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Timing: The vaccine should be administered at least 10 days before your travel date to allow your body to develop immunity.
- Side Effects: Some people may experience mild side effects such as fever, headache, or muscle pain. Serious side effects are rare.
2.1.2. Prevention
In addition to vaccination, take these preventative measures to reduce your risk of yellow fever:
- Use insect repellent containing DEET (20-30%) on exposed skin.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks, especially at night.
- Sleep under a mosquito net treated with insecticide.
- Stay in air-conditioned or screened accommodations to minimize exposure to mosquitoes.
2.2. Malaria
Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by parasites that are transmitted to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes. It is a major health risk in many African countries, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa. Symptoms of malaria include fever, chills, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
2.2.1. Prevention
Preventing malaria involves a combination of antimalarial medication and preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
- Antimalarial Medication: Consult your doctor about the best antimalarial medication for your trip. Common options include Atovaquone/Proguanil (Malarone), Doxycycline, and Mefloquine. Start taking the medication as prescribed before, during, and after your trip.
- Insect Repellent: Use insect repellent containing DEET (20-30%) on exposed skin.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks, especially at night.
- Mosquito Nets: Sleep under a mosquito net treated with insecticide.
- Stay Indoors: Stay in air-conditioned or screened accommodations to minimize exposure to mosquitoes.
2.2.2. Symptoms and Treatment
Seek immediate medical attention if you develop a fever or flu-like symptoms within a few weeks of returning from a malaria-risk area. Malaria can be treated with prescription medications, but early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications.
2.3. Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is a viral liver disease transmitted through contaminated food and water or through close contact with an infected person. Symptoms include fever, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, jaundice, dark urine, and clay-colored stools.
2.3.1. Vaccination
- Importance: Hepatitis A vaccination is highly effective in preventing the disease.
- Recommendation: It is recommended for travelers to Africa, especially those who plan to eat at local restaurants or street food stalls.
- Dosage: The vaccine is given in two doses, with the second dose administered 6-12 months after the first.
2.3.2. Prevention
In addition to vaccination, take these preventative measures to reduce your risk of hepatitis A:
- Drink bottled or boiled water.
- Avoid ice cubes made from tap water.
- Eat food that has been thoroughly cooked and is served hot.
- Avoid raw or undercooked seafood.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating.
2.4. Typhoid Fever
Typhoid fever is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella Typhi, transmitted through contaminated food and water. Symptoms include fever, headache, abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea, and a rash.
2.4.1. Vaccination
- Importance: Typhoid vaccination can help protect against the disease.
- Recommendation: It is recommended for travelers to Africa, especially those who plan to eat at local restaurants or street food stalls.
- Types: There are two types of typhoid vaccines available: an injectable vaccine and an oral vaccine. Consult your doctor to determine which vaccine is best for you.
2.4.2. Prevention
In addition to vaccination, take these preventative measures to reduce your risk of typhoid fever:
- Drink bottled or boiled water.
- Avoid ice cubes made from tap water.
- Eat food that has been thoroughly cooked and is served hot.
- Avoid raw or undercooked seafood.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating.
2.5. Meningitis
Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, typically caused by a bacterial or viral infection. Symptoms include fever, headache, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light, and confusion.
2.5.1. Vaccination
- Importance: Meningitis vaccination can help protect against certain types of bacterial meningitis.
- Recommendation: It is recommended for travel to the meningitis belt in sub-Saharan Africa, especially during the dry season.
- Types: The type of meningitis vaccine recommended depends on your age and the specific regions you plan to visit.
2.6. Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that affects the central nervous system, transmitted through the saliva of infected animals, typically through a bite or scratch. Symptoms include fever, headache, anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, and paralysis. Rabies is almost always fatal if left untreated.
2.6.1. Vaccination
- Importance: Rabies vaccination is recommended for travelers who plan to engage in activities that may bring them into contact with animals, such as hiking, camping, or working with animals.
- Pre-Exposure Vaccination: The rabies vaccine is given in a series of three doses over a period of 3-4 weeks.
- Post-Exposure Treatment: If you are bitten or scratched by an animal in a rabies-risk area, wash the wound thoroughly with soap and water and seek immediate medical attention. You may need to receive additional doses of the rabies vaccine and rabies immunoglobulin.
2.6.2. Prevention
- Avoid contact with wild and domestic animals.
- Do not approach or feed animals.
- Report any animal bites or scratches to local authorities.
2.7. Cholera
Cholera is an acute diarrheal infection caused by ingestion of food or water contaminated with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Symptoms include profuse watery diarrhea, vomiting, and dehydration. Cholera can be fatal if left untreated.
2.7.1. Vaccination
- Importance: Cholera vaccination can provide protection against the disease.
- Recommendation: It may be advised if you are traveling to areas with poor sanitation or experiencing a cholera outbreak.
- Types: There are several types of cholera vaccines available, including oral and injectable vaccines.
2.7.2. Prevention
- Drink bottled or boiled water.
- Avoid ice cubes made from tap water.
- Eat food that has been thoroughly cooked and is served hot.
- Avoid raw or undercooked seafood.
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the toilet.
- Use hand sanitizer if soap and water are not available.
By understanding these key diseases and taking the recommended vaccinations and preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of illness and enjoy a healthy and memorable trip to Africa. Always consult with your doctor or a travel clinic specialist to get personalized advice based on your specific travel plans and health history. Let SIXT.VN assist you in planning your journey, ensuring you have all the necessary information and support for a safe and enjoyable adventure.
 African safari adventure vaccinations
African safari adventure vaccinations
3. Country-Specific Vaccination Requirements in Africa
Understanding the specific vaccination requirements for each country you plan to visit in Africa is essential for ensuring a safe and healthy trip. This section provides an overview of the vaccination requirements and recommendations for some popular African destinations. It is important to note that these requirements can change, so it is always best to consult with your doctor or a travel clinic specialist before your trip.
3.1. South Africa
South Africa is a popular destination for tourists, offering a wide range of attractions including wildlife safaris, beautiful beaches, and vibrant cities.
3.1.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for travelers arriving from or having transited through a yellow fever risk country.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to South Africa, especially those who plan to eat at local restaurants or engage in outdoor activities.
3.1.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk in some parts of South Africa, particularly in the northern and eastern regions, including Kruger National Park. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.2. Kenya
Kenya is renowned for its wildlife safaris, stunning landscapes, and diverse cultures.
3.2.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for all travelers entering Kenya.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Kenya.
3.2.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk throughout Kenya, especially in the coastal and western regions. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.3. Tanzania
Tanzania is home to some of Africa’s most iconic landmarks, including Mount Kilimanjaro and the Serengeti National Park.
3.3.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for all travelers entering Tanzania.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Tanzania.
3.3.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk throughout Tanzania, including Zanzibar. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.4. Uganda
Uganda is known as the “Pearl of Africa,” offering stunning landscapes, diverse wildlife, and the opportunity to trek with gorillas.
3.4.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for all travelers entering Uganda.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Uganda.
3.4.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk throughout Uganda. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.5. Botswana
Botswana is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, known for its wildlife, particularly in the Okavango Delta and Chobe National Park.
3.5.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for travelers arriving from or having transited through a yellow fever risk country.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Botswana.
3.5.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Botswana, particularly in the northern regions. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.6. Namibia
Namibia is a country in southwest Africa, characterized by the Namib Desert along its Atlantic coast. It offers unique landscapes, wildlife, and cultural experiences.
3.6.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for travelers arriving from or having transited through a yellow fever risk country.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Namibia.
3.6.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Namibia, particularly in the northern regions. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.7. Zambia
Zambia is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, known for its rugged terrain, diverse wildlife, and Victoria Falls.
3.7.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for travelers arriving from or having transited through a yellow fever risk country.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Zambia.
3.7.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk throughout Zambia. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
3.8. Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, known for its dramatic landscapes, wildlife, and ancient ruins such as Great Zimbabwe.
3.8.1. Vaccination Requirements
- Yellow Fever: A yellow fever vaccination certificate is required for travelers arriving from or having transited through a yellow fever risk country.
- Other Vaccinations: Hepatitis A and B, Typhoid, and Rabies are recommended for travelers to Zimbabwe.
3.8.2. Malaria
Malaria is a risk in some parts of Zimbabwe, particularly in the northern and eastern regions. Consult your doctor about antimalarial medication and take preventative measures to avoid mosquito bites.
By understanding the country-specific vaccination requirements and health risks, you can better prepare for your trip to Africa and ensure a safe and healthy travel experience. Always consult with your doctor or a travel clinic specialist to get personalized advice based on your specific travel plans and health history. Let SIXT.VN assist you in planning your journey, ensuring you have all the necessary information and support for an unforgettable adventure.
4. Essential Travel Health Kit for Africa
Packing a well-stocked travel health kit is essential for addressing minor health issues and preventing more serious problems while traveling in Africa. This section provides a comprehensive list of items to include in your travel health kit, ensuring you are prepared for a range of potential health concerns.
4.1. Medications
- Prescription Medications: Bring an adequate supply of any prescription medications you take regularly. Be sure to pack them in their original containers and bring a copy of your prescription.
- Antimalarial Medication: If traveling to a malaria-risk area, bring the antimalarial medication prescribed by your doctor.
- Pain Relievers: Include over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil) for headaches, muscle aches, and fever.
- Antihistamines: Pack antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) or loratadine (Claritin) for allergies and insect bites.
- Decongestants: Bring decongestants such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) for nasal congestion due to colds or allergies.
- Anti-Diarrheal Medication: Include loperamide (Imodium) or bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) for treating traveler’s diarrhea.
- Motion Sickness Medication: If you are prone to motion sickness, bring dimenhydrinate (Dramamine) or meclizine (Bonine).
- Antacids: Pack antacids such as Tums or Rolaids for heartburn and indigestion.
- Laxatives: Bring a mild laxative such as senna or docusate sodium for constipation.
4.2. First Aid Supplies
- Bandages: Include a variety of bandages in different sizes for cuts and scrapes.
- Antiseptic Wipes: Pack antiseptic wipes for cleaning wounds.
- Antibiotic Ointment: Bring antibiotic ointment such as Neosporin for preventing infection in minor cuts and scrapes.
- Gauze Pads: Include gauze pads for covering and protecting wounds.
- Medical Tape: Pack medical tape for securing bandages.
- Scissors: Bring a small pair of scissors for cutting bandages and tape.
- Tweezers: Include tweezers for removing splinters and ticks.
- Thermometer: Pack a thermometer for monitoring fever.
- Hand Sanitizer: Bring hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol for cleaning your hands when soap and water are not available.
- Insect Repellent: Pack insect repellent containing DEET (20-30%) for preventing mosquito bites.
- Sunscreen: Bring sunscreen with a high SPF (30 or higher) for protecting your skin from the sun.
- Lip Balm: Include lip balm with SPF for protecting your lips from the sun.
4.3. Other Essential Items
- Water Purification Tablets: Pack water purification tablets or a portable water filter for purifying drinking water.
- Oral Rehydration Salts: Bring oral rehydration salts for treating dehydration due to diarrhea or vomiting.
- Eye Drops: Include lubricating eye drops for dry eyes.
- Ear Drops: Pack ear drops for treating ear infections or swimmer’s ear.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Bring a supply of face masks and disposable gloves for protection against infectious diseases.
- Travel Health Insurance Information: Carry a copy of your travel health insurance policy and contact information for your insurance provider.
- Medical Information: Bring a list of your medical conditions, allergies, and medications.
4.4. Tips for Packing Your Travel Health Kit
- Check Expiration Dates: Ensure that all medications and supplies in your travel health kit are not expired.
- Store Medications Properly: Store medications in a cool, dry place and protect them from direct sunlight.
- Pack Medications in Your Carry-On Luggage: Pack essential medications in your carry-on luggage in case your checked luggage is lost or delayed.
- Know How to Use Your Medications: Make sure you know how to use all the medications and supplies in your travel health kit.
By packing a well-stocked travel health kit, you can be prepared for a range of potential health concerns while traveling in Africa. Always consult with your doctor or a travel clinic specialist to get personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific travel plans and health history. Let SIXT.VN assist you in planning your journey, ensuring you have all the necessary information and support for a safe and enjoyable adventure.
 Health and safety tips Africa travel
Health and safety tips Africa travel
5. Staying Healthy During Your Trip to Africa
Maintaining good health while traveling in Africa involves more than just vaccinations and a well-stocked travel health kit. This section provides practical tips and advice for staying healthy throughout your trip, ensuring you can fully enjoy your adventure.
5.1. Food and Water Safety
One of the most common health risks for travelers is food and waterborne illnesses. Follow these guidelines to minimize your risk:
- Drink Safe Water: Drink bottled or boiled water whenever possible. Avoid tap water, ice cubes made from tap water, and unpasteurized beverages.
- Eat Safe Food: Eat food that has been thoroughly cooked and is served hot. Avoid raw or undercooked seafood, meat, and poultry. Be cautious when eating at local restaurants or street food stalls.
- Wash Fruits and Vegetables: Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly with safe water before eating them. Peel fruits and vegetables whenever possible.
- Avoid Unpasteurized Dairy Products: Avoid unpasteurized milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Be Careful with Buffets: Be cautious when eating at buffets, as food may not be stored at the proper temperature.
5.2. Sun Protection
The African sun can be intense, so it’s important to protect your skin from sunburn and long-term damage.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply sunscreen with a high SPF (30 or higher) to all exposed skin. Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and a wide-brimmed hat to protect your skin from the sun.
- Wear Sunglasses: Wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from the sun’s harmful rays.
- Avoid Peak Sun Hours: Avoid being outdoors during the peak sun hours of 10:00 AM to 4:00 PM.
5.3. Insect Bite Prevention
Insects, particularly mosquitoes, can transmit diseases such as malaria, yellow fever, and dengue fever. Take these steps to prevent insect bites:
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply insect repellent containing DEET (20-30%) to exposed skin. Reapply insect repellent every few hours, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks, especially at night.
- Sleep Under a Mosquito Net: Sleep under a mosquito net treated with insecticide, particularly in areas where malaria is prevalent.
- Stay Indoors: Stay in air-conditioned or screened accommodations to minimize exposure to mosquitoes.
5.4. Personal Hygiene
Practicing good personal hygiene is essential for preventing the spread of germs and staying healthy.
- Wash Your Hands: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially before eating and after using the toilet.
- Use Hand Sanitizer: Use hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol when soap and water are not available.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Avoid touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, to prevent the spread of germs.
- Cover Your Mouth and Nose: Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when you cough or sneeze.
- Dispose of Tissues Properly: Dispose of used tissues in a trash can.
5.5. Altitude Sickness
If traveling to high-altitude areas, such as Mount Kilimanjaro, be aware of the symptoms of altitude sickness and take steps to prevent it.
- Acclimatize Gradually: Ascend to higher altitudes gradually to allow your body to acclimatize.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: Avoid alcohol and caffeine, as they can worsen the symptoms of altitude sickness.
- Eat Light Meals: Eat light, easily digestible meals.
- Avoid Strenuous Activity: Avoid strenuous activity during the first few days at high altitude.
- Descend if Necessary: If you develop symptoms of altitude sickness, descend to a lower altitude immediately.
5.6. General Health Tips
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated, especially in hot climates.
- Get Enough Rest: Get enough sleep to keep your immune system strong.
- Avoid Overexertion: Avoid overexertion, especially during the first few days of your trip.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body and seek medical attention if you feel unwell.
By following these tips, you can stay healthy during your trip to Africa and fully enjoy your adventure. Always consult with your doctor or a travel clinic specialist to get personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific travel plans and health history. Let SIXT.VN assist you in planning your journey, ensuring you have all the necessary information and support for an unforgettable adventure.
6. What to Do If You Get Sick in Africa
Despite your best efforts, you may still get sick while traveling in Africa. Knowing what to do in such a situation can help you get the care you need and minimize the impact on your trip.
6.1. Assess Your Symptoms
The first step is to assess your symptoms and determine the severity of your illness. Mild symptoms such as a minor headache or slight diarrhea may be manageable with over-the-counter medications and rest. However, more severe symptoms such as high fever, severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, or persistent vomiting require immediate medical attention.
6.2. Seek Medical Attention
If you have severe symptoms or if your condition does not improve after a few days of self-care, seek medical attention as soon as possible. Contact your travel insurance provider to find a reputable doctor or medical facility in your area.
6.3. Contact Your Travel Insurance Provider
Contact your travel insurance provider as soon as possible to inform them of your illness and to get guidance on seeking medical care. Your insurance provider can help you find a doctor or medical facility, arrange for transportation, and provide assistance with medical bills.
6.4. Inform Your Tour Operator or Accommodation
If you are traveling with a tour group or staying at a hotel, inform your tour operator or hotel staff of your illness. They may be able to provide assistance, such as arranging for transportation to a medical facility or providing meals that are easy to digest.
6.5. Follow Medical Advice
Follow the advice of your doctor or medical provider carefully. Take all medications as prescribed and attend any follow-up appointments.
6.6. Rest and Hydrate
Get plenty of rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body recover. Avoid strenuous activities and eat light, easily digestible meals.
6.7. Monitor Your Symptoms
Monitor your symptoms closely and seek medical attention if your condition worsens or if you develop new symptoms.
6.8. Keep Records
Keep detailed records of your symptoms, medical care, and expenses. This information will be helpful when filing a claim with your travel insurance provider.
6.9. Prevent the Spread of Illness
Take steps to prevent the spread of illness to others. Wash your hands frequently, cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze, and avoid close contact with others.
6.10. Consider Evacuation
In some cases, it may be necessary to evacuate to a better-equipped medical facility in another city or country. Your travel insurance provider can help you arrange for medical evacuation if necessary.
By knowing what to do if you get sick in Africa, you can be prepared to get the care you need and minimize the impact on your trip. Always consult with your doctor or a travel clinic specialist to get personalized advice and recommendations based on your specific travel plans and health history. Let SIXT.VN assist you in planning your journey, ensuring you have all the necessary information and support for a safe and enjoyable adventure.
7. Booking Travel Services with SIXT.VN for a Safe and Healthy Trip
Planning a trip to Africa involves many details, and ensuring your health and safety is a top priority. SIXT.VN offers a range of travel services designed to make your journey as smooth and worry-free as possible.
7.1. Personalized Travel Consultations
SIXT.VN provides personalized travel consultations to help you plan your trip according to your specific needs and preferences. Our experienced travel experts can offer advice on the best destinations, activities, and accommodations for a safe and healthy trip.
7.2. Airport Transfer Services
Arriving in a new country can be stressful, especially after a long flight. SIXT.VN offers reliable and comfortable airport transfer services to ensure you get to your hotel safely and conveniently. Our professional drivers are knowledgeable about the local area and can provide useful information and tips for staying healthy during your trip.
7.3. Hotel Booking Services
SIXT.VN offers a wide range of hotel options to suit every budget and preference. We can help you find accommodations that meet your specific needs, such as hotels with air conditioning, mosquito nets, and access to clean water and safe food.
7.4. Tour and Excursion Planning
SIXT.VN can help you plan tours and excursions that minimize your risk of exposure to health hazards. We can arrange for private tours with knowledgeable guides who can provide information about local health risks and how to avoid them.
7.5. Travel Insurance Assistance
SIXT.VN can provide assistance with purchasing travel insurance that covers medical expenses, evacuation, and other travel-related emergencies. We can help you find a policy that meets your specific needs and budget.
7.6. 24/7 Customer Support
SIXT.VN offers 24/7 customer support to assist you with any questions or



