Are you curious about What Medium Is The Wave Traveling Through? Understanding wave propagation is key to grasping many phenomena, from sound to light. SIXT.VN is here to guide you through the fascinating world of wave mechanics, ensuring your journey of discovery is smooth and insightful, just like our hassle-free travel services in Vietnam. We’ll explore various types of waves and the media they need to travel, focusing on how this knowledge connects to everyday experiences and even travel planning. Ready to dive in?
1. What Exactly is a Wave and How Does It Travel?
A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy through a medium or space. How it travels depends on the type of wave. Let’s break down the basics.
Waves are disturbances that propagate energy from one point to another. There are two primary types of waves: mechanical and electromagnetic. Mechanical waves, like sound waves or water waves, require a medium to travel, while electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves, can travel through a vacuum. Understanding wave propagation is fundamental in various fields, including physics, engineering, and even travel technology, helping us optimize services and understand environmental factors. Whether you are interested in acoustic comfort, or the effects of EM radiation, it is important to understand waves.
- Mechanical Waves: These require a medium (solid, liquid, gas, or plasma) to travel. Examples include sound waves traveling through air or water waves moving across a lake.
- Electromagnetic Waves: These don’t need a medium and can travel through a vacuum like space. Examples include light, radio waves, and X-rays.
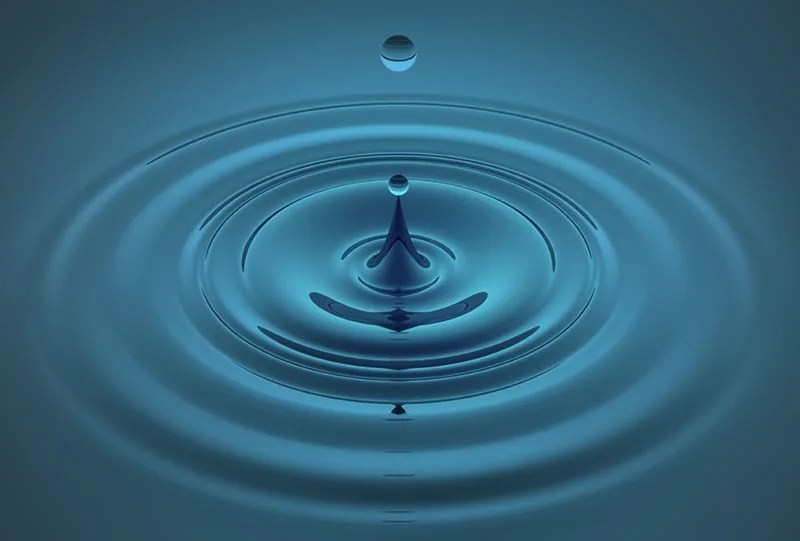 Ripples in a pool demonstrating wave propagation through water.
Ripples in a pool demonstrating wave propagation through water.
2. What Mediums Do Mechanical Waves Need to Travel?
Mechanical waves need a material medium to travel; this medium could be a solid, liquid, gas, or plasma. The medium provides the particles that vibrate and transmit the wave’s energy.
Mechanical waves, unlike their electromagnetic counterparts, rely on a medium for propagation. This requirement ties directly to their nature as disturbances that transfer energy through the vibration of particles within the medium. Without these particles, there’s nothing to carry the wave’s energy from one point to another. This fundamental dependency on a medium dictates where and how mechanical waves can travel. The velocity of mechanical waves are also related to the properties of the media it traverses.
- Solids: Sound travels faster in solids due to the close proximity of molecules. For example, sound travels faster through steel than through air.
- Liquids: Water waves are a common example, demonstrating how energy moves through a liquid medium.
- Gases: Sound waves commonly travel through air, where air molecules vibrate to carry the sound.
- Plasma: Plasma, an ionized gas, can also support mechanical waves.
3. Can Sound Waves Travel in Space? Why or Why Not?
No, sound waves cannot travel in the vacuum of space. Sound waves are mechanical waves, meaning they require a medium—such as air, water, or solids—to propagate. In the vacuum of space, there are virtually no particles to vibrate, so sound waves have no way to travel.
Space is essentially a vacuum, devoid of the matter needed for mechanical waves like sound to propagate. This absence means that the disturbances necessary for transmitting sound energy—vibrations of particles—cannot occur. Therefore, in the silent expanse of space, sound waves are unable to travel, reinforcing the vital role of a medium for their transmission.
4. What Mediums Can Electromagnetic Waves Travel Through?
Electromagnetic waves have the unique ability to travel through both mediums and the vacuum of space. This is because they do not rely on the vibration of particles.
Unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves are self-propagating and do not need a medium. They consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that generate each other, allowing them to travel through vacuums, gases, liquids, and solids. Each of these mediums interacts differently with electromagnetic waves, influencing their speed and direction. Understanding these interactions is crucial for various technologies, from telecommunications to medical imaging.
- Vacuum: Light from the sun travels through the vacuum of space to reach Earth.
- Air: Radio waves travel through the air, allowing us to receive broadcasts.
- Water: Light can penetrate water, though the depth and clarity depend on the wavelength.
- Solids: X-rays can pass through many solids, which is how medical imaging works.
5. What is the Relationship Between Electricity and Magnetism in Electromagnetic Waves?
Electricity and magnetism are intrinsically linked in electromagnetic waves. A changing magnetic field induces a changing electric field, and vice versa. This interplay allows electromagnetic waves to propagate without a medium.
In electromagnetic waves, electricity and magnetism are not just related—they are dynamically intertwined. The oscillation of an electric field creates a magnetic field, which in turn creates another electric field, and this cycle continues, propelling the wave forward. This relationship, described by Maxwell’s equations, is fundamental to how these waves propagate through space, highlighting their ability to travel without a physical medium. The continuous interplay between these fields is what enables electromagnetic waves to carry energy and information across vast distances.
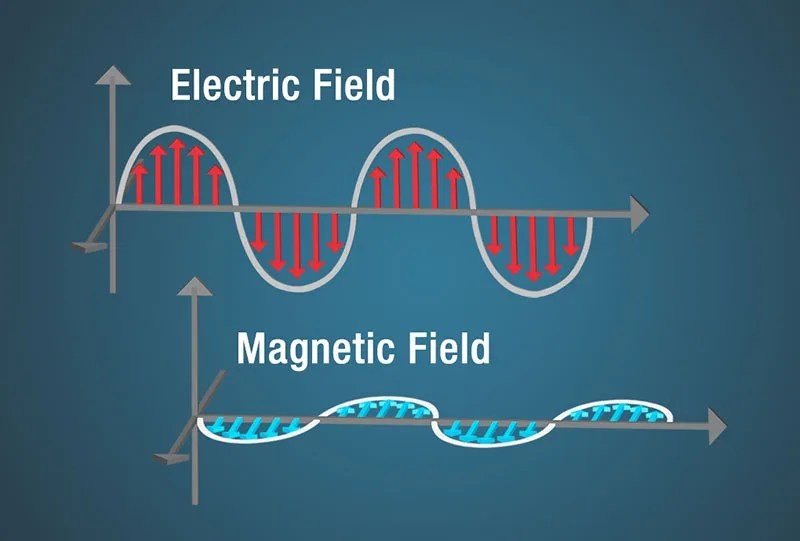 Diagram of electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave.
Diagram of electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave.
6. What are Maxwell’s Equations and Why are They Important?
Maxwell’s equations are a set of four fundamental equations that describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields and their interaction. They are crucial because they unified electricity, magnetism, and light into a single theory of electromagnetism.
Maxwell’s equations are the cornerstone of classical electromagnetism, providing a comprehensive description of how electric and magnetic fields are generated, interact, and change. These equations not only unified previously disparate phenomena but also predicted the existence of electromagnetic waves, laying the groundwork for technologies like radio, television, and the internet. Their importance extends beyond theoretical physics, influencing engineering, telecommunications, and countless other fields that rely on electromagnetic principles.
7. Who was Heinrich Hertz and What Did He Contribute to Our Understanding of Waves?
Heinrich Hertz was a German physicist who proved James Clerk Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism by producing and detecting radio waves. He demonstrated that radio waves are a form of electromagnetic radiation and can travel through air, confirming that these waves could propagate without a medium.
Heinrich Hertz experimentally validated Maxwell’s theoretical predictions of electromagnetic waves by creating and detecting radio waves. His work demonstrated that these waves could travel through the air and that they exhibited properties similar to light, confirming their electromagnetic nature. Hertz’s discoveries revolutionized communication technology and paved the way for the development of radio, television, and wireless communication systems. The unit of frequency, the hertz (Hz), is named in his honor, recognizing his foundational contributions to our understanding of electromagnetic phenomena.
8. Are Light Waves Particles or Waves?
Light exhibits properties of both waves and particles, a concept known as wave-particle duality. Light is composed of photons, which are discrete packets of energy that behave as both waves and particles.
Light’s behavior as both a wave and a particle, known as wave-particle duality, is a foundational concept in quantum mechanics. In some experiments, light acts as a wave, exhibiting phenomena like interference and diffraction. In other experiments, it behaves as a stream of particles (photons), each carrying a specific amount of energy. This dual nature is not a contradiction but a deeper understanding of how light interacts with matter. The wave-particle duality is essential in technologies like quantum computing and advanced imaging techniques.
9. What is Polarization of Light and How Does It Work?
Polarization of light refers to the alignment of the electromagnetic field’s oscillations in a specific direction. Polarized light waves oscillate in a single plane, while unpolarized light waves oscillate in all directions.
Polarization of light is the phenomenon where the electric field of an electromagnetic wave oscillates in a specific direction. This alignment can be achieved through various means, such as filters that block waves oscillating in other directions. Polarized light is crucial in many applications, including reducing glare in sunglasses, enhancing contrast in LCD screens, and enabling 3D movie technology. By controlling the direction of light oscillation, we can manipulate and utilize light in diverse and innovative ways.
10. How are Frequency, Wavelength, and Energy Related in Electromagnetic Waves?
Frequency, wavelength, and energy are interconnected in electromagnetic waves. Frequency is the number of wave cycles per second, wavelength is the distance between wave crests, and energy is related to both frequency and wavelength. The relationship can be summarized as:
- Energy is directly proportional to frequency. Higher frequency means higher energy.
- Wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency. Longer wavelength means lower frequency, and vice versa.
The relationship between frequency, wavelength, and energy in electromagnetic waves is fundamental. Frequency measures how many wave cycles pass a point per second, while wavelength measures the distance between consecutive wave crests. Energy is directly proportional to frequency and inversely proportional to wavelength, as described by the equation E = hf, where E is energy, h is Planck’s constant, and f is frequency. This relationship is essential for understanding the electromagnetic spectrum, from low-energy radio waves to high-energy gamma rays.
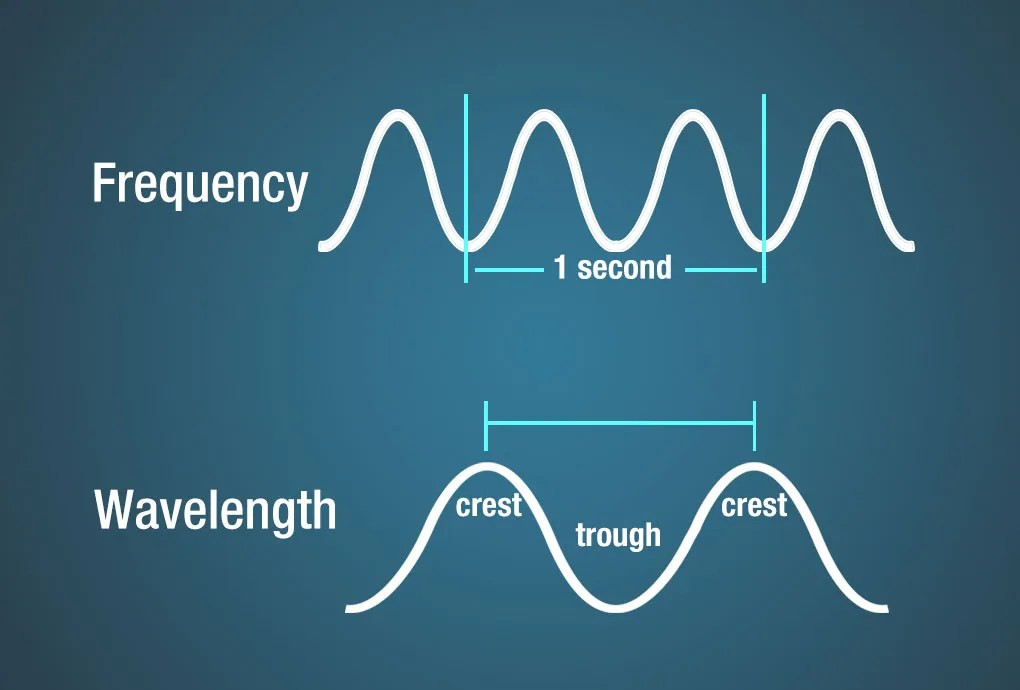 Diagram illustrating the relationship between frequency and wavelength.
Diagram illustrating the relationship between frequency and wavelength.
11. What is Frequency and How is it Measured?
Frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a fixed point in one second. It is measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz is one cycle per second.
Frequency is a measure of how often a wave repeats itself within a given time frame, specifically the number of complete cycles that pass a point per second. It’s measured in hertz (Hz), with 1 Hz equaling one cycle per second. Understanding frequency is crucial in fields like telecommunications, where different frequencies are used to transmit radio waves, and in music, where frequency determines the pitch of a sound. Accurately measuring frequency is essential for tuning instruments and ensuring clear signal transmission.
12. What is Wavelength and How is it Measured?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests (or troughs) of a wave. It is typically measured in meters (m) or nanometers (nm), depending on the type of wave.
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points in a wave that are in phase, such as the distance between two crests or two troughs. It is typically measured in meters (m) for longer waves like radio waves and in nanometers (nm) for shorter waves like visible light and X-rays. Wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency; the longer the wavelength, the lower the frequency, and vice versa. Understanding wavelength is essential in fields such as optics, where it determines the color of light, and in telecommunications, where it affects the range and penetration of radio waves.
13. How is Energy Related to Wavelength and Frequency in Electromagnetic Waves?
Energy is directly proportional to the frequency and inversely proportional to the wavelength of an electromagnetic wave. Higher frequency (shorter wavelength) waves have more energy, while lower frequency (longer wavelength) waves have less energy.
Energy in electromagnetic waves is intrinsically linked to their frequency and wavelength. High-frequency waves, like gamma rays and X-rays, have short wavelengths and carry a significant amount of energy. Conversely, low-frequency waves, like radio waves and microwaves, have long wavelengths and carry less energy. This relationship is described by the equation E = hc/λ, where E is energy, h is Planck’s constant, c is the speed of light, and λ is wavelength. This principle is crucial in applications such as medical imaging, where high-energy X-rays are used to penetrate tissues, and in telecommunications, where low-energy radio waves are used for broadcasting.
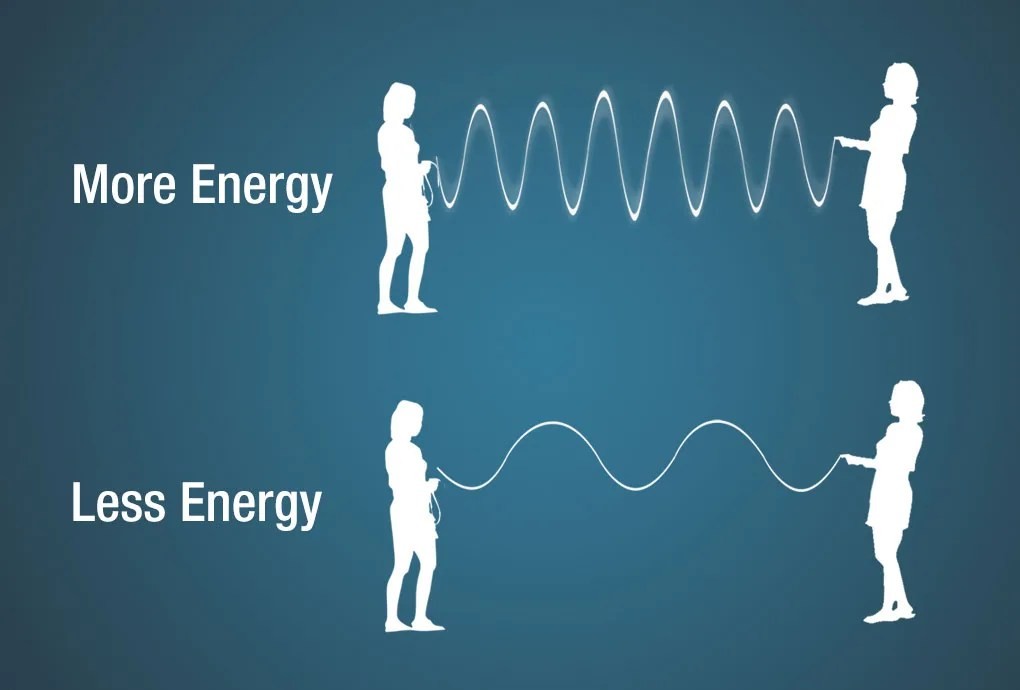 Diagram illustrating the relationship between energy and wavelength.
Diagram illustrating the relationship between energy and wavelength.
14. What are Some Examples of Electromagnetic Waves in Our Daily Lives?
Electromagnetic waves are all around us, playing vital roles in various aspects of our daily lives:
- Radio Waves: Used for broadcasting radio and television signals.
- Microwaves: Used in microwave ovens for heating food and in communication technologies.
- Infrared: Used in remote controls and thermal imaging.
- Visible Light: The light we see, enabling vision and photography.
- Ultraviolet: From the sun, can cause sunburns but is also used for sterilization.
- X-rays: Used in medical imaging to see inside the body.
- Gamma Rays: Used in cancer treatment and sterilization.
Electromagnetic waves pervade our daily lives, enabling a vast array of technologies and natural processes. Radio waves carry signals for radio and television, while microwaves heat our food and facilitate wireless communication. Infrared radiation is used in remote controls and thermal imaging, and visible light allows us to see the world around us. Ultraviolet rays from the sun can cause sunburn, but are also used for sterilization. X-rays enable medical imaging, and gamma rays are used in cancer treatment. Each type of electromagnetic wave plays a unique role in shaping our modern world.
15. How Do Radio Waves Travel Through the Atmosphere?
Radio waves travel through the atmosphere via several mechanisms, including ground waves, sky waves, and direct waves. The specific method depends on the frequency of the radio wave and atmospheric conditions.
Radio waves travel through the atmosphere using a variety of methods, each influenced by the wave’s frequency and atmospheric conditions. Ground waves follow the Earth’s surface, making them ideal for local broadcasting. Sky waves are reflected by the ionosphere, allowing for long-distance communication. Direct waves travel in a straight line, requiring a clear path between the transmitter and receiver. Understanding these propagation mechanisms is crucial for optimizing communication systems and ensuring reliable signal transmission across different distances.
16. What is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation. Radiation is energy that travels and spreads out as it goes – the visible light that comes from a lamp in your house and the radio waves that come from a radio station are two types of electromagnetic radiation. The other types of electromagnetic radiation that make up the electromagnetic spectrum are microwaves, infrared light, ultraviolet light, X-rays and gamma-rays.
The electromagnetic spectrum is the continuum of all electromagnetic radiation, arranged by frequency and wavelength. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. Each region of the spectrum has unique properties and applications, from low-frequency radio waves used in broadcasting to high-frequency gamma rays used in medical treatments. Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum is fundamental to numerous fields, including astronomy, telecommunications, and medicine, enabling advancements in technology and scientific discovery.
17. How Do Microwaves Heat Food?
Microwaves heat food by causing water molecules within the food to vibrate rapidly. This vibration generates heat, cooking the food from the inside out.
Microwaves heat food efficiently by targeting water molecules. When microwaves penetrate food, they cause the water molecules to vibrate rapidly. This molecular friction generates heat, cooking the food from the inside out. This method is particularly effective because most foods contain water. The process is efficient and quick, making microwave ovens a staple in modern kitchens.
18. What are Infrared Waves Used For?
Infrared waves are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Remote Controls: To transmit signals to devices like TVs and air conditioners.
- Thermal Imaging: To detect heat signatures, used in security and medical diagnostics.
- Night Vision: To see in the dark by detecting infrared radiation emitted by objects.
Infrared waves are invaluable in numerous applications due to their ability to transmit heat and signals. Remote controls use infrared radiation to communicate with devices like TVs, while thermal imaging detects heat signatures for security and medical purposes. Night vision technology relies on infrared waves to allow visibility in the dark by capturing the infrared radiation emitted by objects.
19. Why is Ultraviolet Light Harmful?
Ultraviolet (UV) light is harmful because it has enough energy to damage DNA in skin cells. This damage can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Ultraviolet (UV) light poses a significant threat due to its high energy levels, which can damage DNA in skin cells. Prolonged exposure to UV radiation can result in sunburn, premature aging, and a heightened risk of developing skin cancer. It is crucial to protect oneself from excessive UV exposure by using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure during peak hours.
20. How are X-Rays Used in Medicine?
X-rays are used in medicine to create images of the inside of the body. Because X-rays can pass through soft tissues but are absorbed by dense tissues like bones, they can reveal fractures, tumors, and other medical conditions.
X-rays are indispensable in medical diagnostics, allowing doctors to visualize the internal structures of the body. These high-energy electromagnetic waves can penetrate soft tissues but are absorbed by denser materials like bones, creating detailed images of fractures, tumors, and other abnormalities. X-ray imaging is a non-invasive and rapid technique that helps in the diagnosis and treatment planning for a wide range of medical conditions.
21. How Does SIXT.VN Utilize the Knowledge of Wave Propagation to Improve Services?
SIXT.VN leverages the knowledge of wave propagation in several ways to enhance our services:
- Optimizing Communication Systems: Understanding radio wave propagation helps us ensure reliable communication for our transportation and support services.
- Enhancing Navigation Systems: Using GPS, which relies on radio waves, to provide accurate and efficient navigation for our drivers and customers.
- Improving Comfort in Vehicles: Applying principles of sound wave management to reduce noise and enhance acoustic comfort in our vehicles.
- Developing Smart Travel Solutions: Integrating weather forecasting data, which relies on understanding electromagnetic waves, to anticipate and mitigate travel disruptions.
SIXT.VN strategically applies its understanding of wave propagation to optimize various aspects of its services. By leveraging radio wave propagation, SIXT.VN ensures reliable communication for transportation and support. GPS technology, reliant on radio waves, provides accurate navigation for drivers and customers. Principles of sound wave management are applied to reduce noise and enhance acoustic comfort in vehicles. Furthermore, integrating weather forecasting data, which depends on understanding electromagnetic waves, helps SIXT.VN anticipate and mitigate potential travel disruptions.
22. What Are the Implications of Wave Propagation for Travel in Vietnam?
Understanding wave propagation is essential for travel in Vietnam, particularly for:
- Communication: Ensuring reliable mobile and internet connectivity for travelers.
- Navigation: Providing accurate GPS navigation, especially in remote areas.
- Weather Forecasting: Predicting weather patterns to plan safe and efficient travel routes.
- Disaster Management: Monitoring and responding to natural disasters using satellite and radio communications.
Understanding wave propagation significantly enhances travel experiences in Vietnam. Reliable mobile and internet connectivity ensures seamless communication, while accurate GPS navigation guides travelers, especially in remote regions. Weather forecasting, informed by wave propagation principles, enables safer and more efficient travel planning, and satellite and radio communications play a crucial role in disaster management and response.
23. How Can Travelers Benefit from Understanding Wave Phenomena?
Travelers can benefit in numerous ways by understanding wave phenomena:
- Better Communication: Understanding how radio waves work can help travelers choose the best mobile networks for reliable communication.
- Improved Navigation: Knowing how GPS works allows travelers to use navigation apps more effectively.
- Safer Travel: Understanding weather patterns and potential hazards through weather forecasts.
- Appreciating Technology: Gaining a deeper appreciation for the technology that makes modern travel possible.
A basic understanding of wave phenomena can significantly enhance a traveler’s experience. Knowing how radio waves function aids in selecting the best mobile networks for reliable communication, while understanding GPS principles allows for more effective use of navigation apps. Awareness of weather patterns and potential hazards through weather forecasts contributes to safer travels. Additionally, such knowledge fosters a deeper appreciation for the technologies that underpin modern travel.
24. What Measures Can Travelers Take to Mitigate the Effects of Wave Interference?
Travelers can mitigate the effects of wave interference by:
- Using Noise-Canceling Headphones: To block out unwanted sound waves during travel.
- Choosing Appropriate Communication Channels: Selecting the best mobile network or frequency for clear communication.
- Adjusting Navigation Settings: Optimizing GPS settings for accuracy in different environments.
- Staying Informed: Monitoring weather forecasts and advisories to avoid potential disruptions.
Travelers can take proactive steps to mitigate the effects of wave interference. Utilizing noise-canceling headphones helps block out unwanted sound waves during travel, while selecting the appropriate mobile network or frequency ensures clear communication. Adjusting navigation settings optimizes GPS accuracy in various environments, and staying informed through weather forecasts and advisories aids in avoiding potential disruptions caused by wave phenomena.
25. How Does SIXT.VN Ensure Reliable Communication for Travelers in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN ensures reliable communication for travelers in Vietnam by:
- Partnering with Top Mobile Networks: Offering SIM cards and mobile Wi-Fi devices with strong coverage.
- Providing GPS-Enabled Vehicles: Equipping our vehicles with reliable GPS navigation systems.
- Offering 24/7 Support: Ensuring assistance is always available via phone, email, or chat.
- Utilizing Real-Time Monitoring: Tracking vehicle locations and providing timely updates to travelers.
SIXT.VN ensures reliable communication for travelers in Vietnam through several key strategies. The company partners with top mobile networks to offer SIM cards and mobile Wi-Fi devices with robust coverage. Vehicles are equipped with reliable GPS navigation systems, and 24/7 support is provided via phone, email, or chat. Real-time monitoring of vehicle locations allows SIXT.VN to offer timely updates to travelers.
26. How Does Weather Forecasting Help Travelers Plan Their Trips More Effectively?
Weather forecasting is crucial for travelers to plan their trips effectively by:
- Predicting Weather Conditions: Providing accurate forecasts of temperature, rainfall, and other weather elements.
- Identifying Potential Hazards: Alerting travelers to severe weather events like storms, floods, and typhoons.
- Optimizing Travel Routes: Helping travelers choose the safest and most efficient routes.
- Adjusting Travel Plans: Allowing travelers to modify their itineraries to avoid adverse weather conditions.
Weather forecasting significantly enhances travel planning by offering accurate predictions of temperature, rainfall, and other weather elements. It identifies potential hazards such as storms, floods, and typhoons, enabling travelers to optimize routes for safety and efficiency. By allowing travelers to adjust itineraries to avoid adverse weather conditions, weather forecasting ensures a smoother and more enjoyable trip.
27. How Does SIXT.VN Use GPS Technology to Enhance Navigation for Travelers?
SIXT.VN uses GPS technology to enhance navigation for travelers by:
- Providing Real-Time Navigation: Offering turn-by-turn directions and real-time traffic updates.
- Offering Route Optimization: Helping travelers find the fastest and most efficient routes.
- Providing Location-Based Services: Recommending nearby attractions, restaurants, and services.
- Ensuring Safety and Security: Tracking vehicle locations and providing emergency assistance when needed.
SIXT.VN enhances navigation for travelers by using GPS technology to provide real-time, turn-by-turn directions and traffic updates. Route optimization helps travelers discover the fastest and most efficient routes, while location-based services recommend nearby attractions, restaurants, and other useful services. Additionally, GPS tracking ensures safety and security by monitoring vehicle locations and providing emergency assistance when required.
28. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Wave Propagation?
Some common misconceptions about wave propagation include:
- Waves Carry Matter: Waves transfer energy, not matter.
- All Waves Need a Medium: Only mechanical waves need a medium; electromagnetic waves do not.
- Waves Travel at a Constant Speed: Wave speed varies depending on the medium and conditions.
- Higher Frequency Means Higher Speed: Frequency and speed are related but not directly proportional; speed depends on the medium.
Common misconceptions about wave propagation include the belief that waves carry matter, when in fact they transfer energy, and that all waves require a medium, which is only true for mechanical waves. Additionally, waves do not always travel at a constant speed; their speed varies depending on the medium and environmental conditions. It is also a misconception that higher frequency directly implies higher speed, as wave speed is primarily determined by the properties of the medium.
29. What Innovations are on the Horizon in Wave Technology?
Innovations on the horizon in wave technology include:
- Advanced Communication Systems: Developing faster and more reliable wireless communication technologies.
- Improved Weather Forecasting: Enhancing weather models and prediction accuracy.
- New Medical Imaging Techniques: Creating more detailed and safer medical imaging technologies.
- Quantum Computing: Harnessing wave properties of particles for advanced computing.
The horizon of wave technology is filled with promising innovations, including the development of faster and more reliable wireless communication systems. Advances in weather modeling are leading to improved forecasting accuracy, while new medical imaging techniques are creating more detailed and safer diagnostic tools. Additionally, harnessing the wave properties of particles is paving the way for significant breakthroughs in quantum computing.
30. How Can SIXT.VN Help You Plan Your Next Trip to Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers a comprehensive range of services to help you plan your next trip to Vietnam:
- Airport Transfers: Providing convenient and reliable airport pickup and drop-off services.
- Hotel Booking: Offering a wide selection of hotels to suit every budget and preference.
- Tour Packages: Organizing guided tours to popular attractions and hidden gems.
- Flight Booking: Helping you find the best flight deals and itineraries.
- Car Rentals: Providing a variety of vehicles to explore Vietnam at your own pace.
SIXT.VN offers comprehensive support for planning your trip to Vietnam. Convenient and reliable airport transfers ensure a smooth start and end to your journey, while a wide selection of hotels caters to every budget and preference. Guided tour packages are available for popular attractions and hidden gems, and assistance with flight booking helps you find the best deals and itineraries. Additionally, a variety of rental vehicles allows you to explore Vietnam at your own pace.
Navigating Vietnam becomes a breeze with SIXT.VN. From convenient airport transfers to comfortable hotel bookings and expertly curated tour packages, we ensure your journey is seamless. Contact us via Hotline/WhatsApp at +84 986 244 358 or visit SIXT.VN to discover the best travel solutions tailored to your needs.
31. What are the Key Factors That Influence Radio Wave Propagation in Vietnam?
Key factors influencing radio wave propagation in Vietnam include:
- Terrain: Mountainous regions and dense forests can block or reflect radio waves.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Humidity, temperature, and rainfall can affect signal strength and range.
- Urban Development: Buildings and infrastructure can cause signal interference and shadowing.
- Frequency: Different frequencies behave differently; lower frequencies travel further but have lower bandwidth.
- Time of Day: The ionosphere’s condition changes throughout the day, affecting skywave propagation.
Various factors influence radio wave propagation in Vietnam. Terrain, such as mountainous regions and dense forests, can block or reflect radio waves, while atmospheric conditions like humidity, temperature, and rainfall affect signal strength and range. Urban development can cause signal interference and shadowing. Different frequencies behave differently, with lower frequencies traveling further but offering lower bandwidth. The time of day also impacts skywave propagation due to changes in the ionosphere.
32. How Can Travelers Stay Connected in Remote Areas of Vietnam?
Travelers can stay connected in remote areas of Vietnam by:
- Using Satellite Phones: Providing reliable communication where mobile networks are unavailable.
- Renting Mobile Wi-Fi Devices: Offering internet access through local mobile networks.
- Purchasing Local SIM Cards: Taking advantage of local mobile networks with better coverage.
- Downloading Offline Maps and Apps: Ensuring access to essential information without internet connectivity.
Staying connected in remote areas of Vietnam can be achieved through several strategies. Satellite phones offer reliable communication where mobile networks are unavailable. Renting mobile Wi-Fi devices provides internet access via local mobile networks, and purchasing local SIM cards allows travelers to leverage networks with better coverage. Downloading offline maps and apps ensures access to essential information without internet connectivity.
33. What Are the Benefits of Understanding Atmospheric Conditions for Travelers?
Understanding atmospheric conditions is beneficial for travelers because it:
- Helps Predict Weather Changes: Allowing travelers to prepare for rain, storms, or extreme temperatures.
- Aids in Planning Outdoor Activities: Informing decisions about hiking, biking, and water sports.
- Improves Safety: Alerting travelers to potential hazards like fog, strong winds, or UV radiation.
- Optimizes Travel Routes: Helping travelers choose the safest and most efficient routes based on weather conditions.
Understanding atmospheric conditions is highly beneficial for travelers as it aids in predicting weather changes, enabling preparation for rain, storms, or extreme temperatures. It also informs decisions about outdoor activities like hiking, biking, and water sports, improves safety by alerting travelers to potential hazards such as fog, strong winds, or UV radiation, and optimizes travel routes by helping travelers choose the safest and most efficient paths based on weather conditions.
34. How Can Travelers Use GPS Technology to Explore Vietnam More Effectively?
Travelers can use GPS technology to explore Vietnam more effectively by:
- Navigating to Tourist Attractions: Finding directions to popular landmarks and points of interest.
- Discovering Hidden Gems: Exploring off-the-beaten-path destinations with accurate location data.
- Planning Efficient Routes: Optimizing travel itineraries to save time and reduce travel costs.
- Locating Essential Services: Finding nearby restaurants, hotels, hospitals, and ATMs.
Travelers can leverage GPS technology to enhance their exploration of Vietnam by navigating to tourist attractions and discovering hidden gems with accurate location data. GPS facilitates the planning of efficient routes, saving time and reducing travel costs, and helps locate essential services such as restaurants, hotels, hospitals, and ATMs.
35. What Safety Measures Should Travelers Take During Severe Weather Events?
During severe weather events, travelers should take the following safety measures:
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and advisories from reliable sources.
- Seek Shelter: Find safe, secure buildings to protect against storms, floods, or typhoons.
- Avoid Travel: Refrain from traveling during severe weather to minimize risks.
- Follow Local Guidelines: Adhere to instructions and recommendations from local authorities.
- Prepare Emergency Supplies: Keep essential items like water, food, and a first-aid kit readily available.
Travelers should prioritize safety during severe weather events by staying informed through reliable weather forecasts and advisories. Seeking shelter in secure buildings protects against storms, floods, or typhoons, and avoiding travel minimizes risks. Adhering to local guidelines and recommendations from authorities is crucial, and preparing emergency supplies like water, food, and a first-aid kit ensures readiness for potential disruptions.
36. What Role Do Satellites Play in Providing Communication and Navigation Services in Vietnam?
Satellites play a crucial role in providing communication and navigation services in Vietnam by:
- Enabling GPS Navigation: Providing positioning and timing data for accurate navigation.
- Facilitating Mobile Communication: Supporting mobile networks in remote areas.
- Supporting Weather Forecasting: Collecting weather data and transmitting forecasts.
- Providing Disaster Relief Support: Aiding in emergency communication and coordination during natural disasters.
- Broadcasting Television and Radio Signals: Delivering media content to remote communities.
Satellites are essential for communication and navigation in Vietnam. They enable GPS navigation by providing positioning and timing data, support mobile networks in remote areas, and aid weather forecasting by collecting and transmitting data. Satellites also provide disaster relief support through emergency communication and coordination and broadcast television and radio signals to remote communities.
37. How Can SIXT.VN Help Travelers Navigate Language Barriers in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN helps travelers navigate language barriers in Vietnam by:
- Providing Multilingual Staff: Offering assistance in multiple languages at our service locations.
- Offering Translation Services: Providing on-demand translation services via phone or app.
- Providing Pre-Translated Phrases: Supplying travelers with useful phrases for common situations.
- Partnering with Local Guides: Connecting travelers with knowledgeable local guides who speak their language.
SIXT.VN assists travelers in overcoming language barriers in Vietnam through several means. Multilingual staff are available at service locations, and on-demand translation services are provided via phone or app. Useful pre-translated phrases are supplied for common situations, and partnerships with local guides connect travelers with knowledgeable locals who speak their language.
38. What Are Some Practical Tips for Using Mobile Data While Traveling in Vietnam?
Practical tips for using mobile data while traveling in Vietnam include:
- Purchase a Local SIM Card: Often more cost-effective than using international roaming.
- Use Wi-Fi When Available: Connect to Wi-Fi hotspots to save on mobile data.
- Disable Automatic Updates: Prevent apps from using data in the background.
- Download Offline Content: Save maps, translations, and other resources for offline use.
- Monitor Data Usage: Keep track of your data consumption to avoid overage charges.
Practical tips for using mobile data while traveling in Vietnam include purchasing a local SIM card, which is often more cost-effective than international roaming, and using Wi-Fi whenever available to save on mobile data. Disabling automatic updates prevents apps from using data in the background, while downloading offline content ensures access to resources without internet connectivity. Monitoring data usage helps avoid overage charges.
FAQ: What Medium is the Wave Traveling Through?
-
What are the two main types of waves?
Mechanical and electromagnetic waves are the two main types of waves. Mechanical waves require a medium, while electromagnetic waves do not. -
Can electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum?
Yes, electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum because they do not require a medium to propagate. -
Why can’t sound travel in space?
Sound waves are mechanical waves and require a medium to travel. Space is a vacuum, so there is no medium for the sound to propagate. -
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional. As frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa. -
How are electromagnetic waves used in communication?
Electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves and microwaves, are used to transmit signals for radio, television, and mobile communication. -
What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, arranged by frequency and wavelength, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. -
How does SIXT.VN use wave technology to improve services?
SIXT.VN uses knowledge of wave propagation to optimize communication systems, enhance navigation systems, improve vehicle comfort, and develop smart travel solutions. -
How does understanding wave phenomena benefit travelers?
Understanding wave phenomena helps travelers with better communication, improved navigation, safer travel planning, and a deeper appreciation for technology. -
What is polarized light?
Polarized light is light in which the electromagnetic field’s oscillations are aligned in a specific direction. -
What is the unit of measurement for frequency?
The unit of measurement for frequency is Hertz (Hz), which represents one cycle per second.
Understanding what medium is the wave traveling through is crucial for grasping various phenomena that impact our daily lives and travel experiences. SIXT.VN is dedicated to providing services that leverage this knowledge to enhance your travel experience in Vietnam. From reliable communication to safe navigation, we ensure that your journey is smooth and enjoyable. Let SIXT.VN be your trusted partner in exploring the beauty and culture of Vietnam. Contact us today and plan your unforgettable adventure.



