Tourism is more than just visiting new places; it’s a multifaceted activity that shapes economies, societies, and environments. Ready to explore the world? With SIXT.VN, unlock seamless travel experiences in Vietnam. We offer expert travel consulting, airport transfer services, hotel booking assistance, tours, and flight ticket bookings.
1. Understanding the Essence of Tourism
Tourism is the temporary movement of people away from their usual place of residence and work, involving various activities undertaken for leisure, business, or other purposes. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), tourism encompasses activities of individuals traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes.
Tourism broadly includes:
- Recreational Travel: Visiting places for leisure and enjoyment.
- Business Travel: Journeys undertaken for professional purposes.
- Cultural Exploration: Discovering and engaging with different cultures.
- Visiting Friends and Relatives (VFR): Traveling to see loved ones.
- Medical Tourism: Seeking healthcare services in a different location.
2. What Defines Tourism Geography?
Tourism geography examines the spatial dimensions of tourism, including the location of destinations, tourist flows, and the impacts of tourism on places and people. Tourism geography is a branch of human geography that studies the spatial patterns and processes of tourism. It’s about where tourists go, how they get there, and what happens when they arrive.
Key aspects of tourism geography include:
- Spatial Analysis: Studying the distribution and arrangement of tourist activities.
- Economic Impacts: Assessing the economic effects of tourism on regions and nations.
- Social and Cultural Effects: Investigating how tourism influences societies and cultures.
- Environmental Aspects: Examining the environmental consequences of tourism.
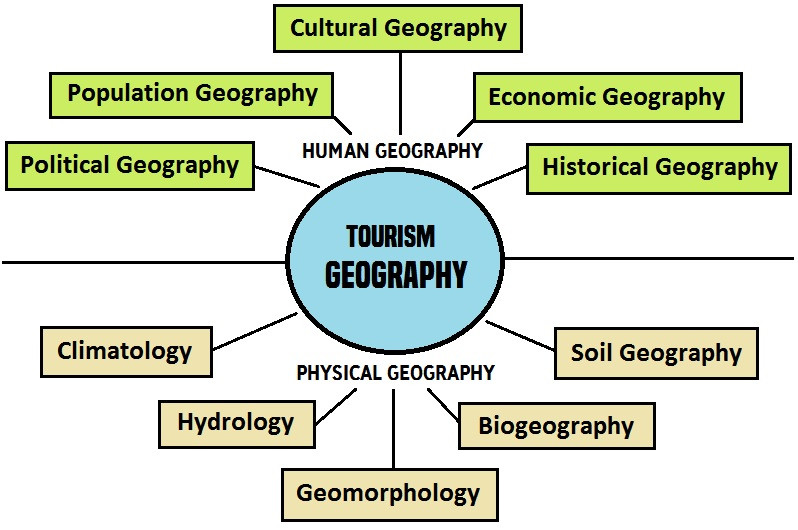 Tourism Geography Interdisciplinary Nature visualizing the convergence of geography, economics, sociology, anthropology, and environmental studies
Tourism Geography Interdisciplinary Nature visualizing the convergence of geography, economics, sociology, anthropology, and environmental studies
3. What Are The Main Characteristics of Tourism Geography?
Tourism geography is characterized by its spatial focus, social science perspective, and interdisciplinary nature.
- Spatial Science: Tourism geography focuses on the spatial patterns and processes of tourism.
- Social Science: It also addresses the social and cultural dimensions of tourism.
- Interdisciplinary Field: It draws from various disciplines, including geography, economics, sociology, and environmental studies.
4. What Is the Scope of Tourism Geography?
The scope of tourism geography is extensive, covering a wide range of topics from the location of tourist destinations to the impacts of tourism on the environment.
- Location of Tourist Destinations: Analyzing why certain places become popular tourist spots, considering factors such as natural beauty, cultural attractions, and historical significance.
- Tourist Flows: Studying how tourists move between different locations and the elements that influence their travel decisions.
- Impacts of Tourism: Investigating the various effects of tourism, both positive (economic growth, job creation, cultural exchange) and negative (environmental damage, social issues).
- Tourism Planning and Development: Devising strategies for sustainable tourism development, ensuring that tourism benefits both the local community and the environment.
- Tourism Marketing: Promoting tourism destinations effectively to attract more visitors.
- Tourism Management: Managing tourism destinations to minimize negative impacts and maximize benefits, including implementing regulations and resolving conflicts.
5. What is The Nature of Tourism Geography?
Tourism geography is diverse and dynamic, involving recreational, cultural, historical, and environmental aspects.
- Recreational: Tourism is inherently recreational, providing opportunities for leisure and enjoyment.
- Specialty: It focuses on specific aspects of travel and tourism activities.
- Diversity: Tourism includes a wide range of activities and destinations.
- Dynamic: Tourism patterns and preferences change over time.
- Interdisciplinary: It combines insights from various academic fields.
- Seasonal: Many tourism destinations experience peaks and troughs depending on the time of year.
- Cultural and Religious: Tourism often involves exploring different cultures and religious sites.
- Geographical Nature: It emphasizes the spatial distribution of tourist activities and destinations.
- Historical Nature: Tourism includes visits to historical sites and learning about the past.
6. Examples of The Scope of Tourism Geography
Specific examples of the scope of tourism geography include studying the physical and cultural attributes of destinations, analyzing tourist movement patterns, and assessing tourism’s impacts.
- Physical Geography: Analyzing the climate, terrain, and natural resources of a tourist destination.
- Cultural Geography: Studying the history, art, and architecture of a destination.
- Tourist Movement: Tracking where tourists come from, where they go, and how they travel.
- Influencing Factors: Examining elements that influence tourist travel decisions, such as price and weather.
- Positive Impacts: Evaluating economic development, job creation, and cultural exchange resulting from tourism.
- Negative Impacts: Identifying environmental degradation, social problems, and cultural erosion caused by tourism.
- Sustainable Planning: Collaborating with governments and businesses to plan and develop sustainable tourism destinations.
- Infrastructure Improvement: Enhancing transportation infrastructure and managing tourism’s impacts.
- Marketing Strategies: Developing marketing campaigns and creating websites to promote tourism.
- Effective Management: Managing tourism destinations to minimize negative impacts and maximize benefits through regulations and information dissemination.
7. What Are The Key Elements of Tourism Geography?
Key elements of tourism geography include attractions, accessibility, accommodation, amenities, activities, and infrastructure.
- Attractions: The primary draws for tourists, such as historical sites, museums, theme parks, beaches, and mountains.
- Accessibility: Ease with which tourists can reach a destination, including transportation options and visa requirements.
- Accommodation: Places for tourists to stay, ranging from budget hostels to luxury resorts.
- Amenities: Supporting services that enhance the tourist experience, such as restaurants, bars, and shops.
- Activities: Things for tourists to do, including sightseeing, hiking, shopping, and dining.
- Price: Cost of visiting a destination, influencing its attractiveness to different travelers.
- Infrastructure: Essential facilities like roads, airports, and telecommunications.
- Human Resources: Skilled workforce providing services in hotels, restaurants, and transportation.
- Tourism Marketing: Promotion of a destination through advertising and social media.
- Tourism Policy: Regulations governing the tourism industry, including visa requirements and environmental regulations.
8. How Do Attractions Influence Tourism Geography?
Attractions are central to tourism geography because they draw tourists to specific locations, shaping the spatial patterns of tourism.
- Natural Attractions: Natural features such as mountains, beaches, and forests attract tourists seeking outdoor experiences.
- Cultural Attractions: Historical sites, museums, and cultural events draw visitors interested in history and culture.
- Economic Impact: Attractions drive economic activity by attracting tourists who spend money on accommodation, food, and souvenirs.
- Spatial Distribution: The location of attractions influences the spatial distribution of tourism, with areas around major attractions becoming tourism hubs.
- Development: Planning and development of new attractions can reshape tourism geography, creating new destinations and economic opportunities.
9. How Does Accessibility Impact Tourism Geography?
Accessibility plays a crucial role in tourism geography by determining how easily tourists can reach and move around a destination.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Airports, roads, and railways facilitate tourist movement, influencing destination choice.
- Visa Policies: Visa requirements can either encourage or discourage tourist visits, affecting tourism patterns.
- Distance: Proximity to major population centers affects a destination’s popularity.
- Technology: Online booking platforms and digital maps enhance accessibility by providing information and facilitating travel arrangements.
- Spatial Connectivity: Improved accessibility can transform remote areas into tourist destinations, redistributing tourism activity.
10. What Are The Primary Types of Tourism?
There are numerous types of tourism, each catering to different interests and motivations.
- Leisure Tourism: Traveling for relaxation and enjoyment, often involving visits to beaches and theme parks.
- Adventure Tourism: Engaging in activities that require physical exertion, such as hiking and skiing.
- Cultural Tourism: Exploring different cultures through visits to museums and historical sites.
- Eco-Tourism: Traveling to natural areas with a focus on environmental conservation.
- Medical Tourism: Seeking medical treatment in another country.
- Religious Tourism: Visiting places of religious significance.
- Heritage Tourism: Learning about a place’s history and culture through historical sites.
- Agro Tourism: Visiting farms and agricultural operations.
- Sport Tourism: Traveling to participate in or watch sporting events.
 Conceptualization of Tourism showing stages like anticipation, travel to site, on-site experience, return travel, and recollection
Conceptualization of Tourism showing stages like anticipation, travel to site, on-site experience, return travel, and recollection
11. How Does Leisure Tourism Shape Destinations?
Leisure tourism significantly shapes destinations by driving economic activity, influencing infrastructure development, and impacting local cultures.
- Economic Contributions: Generates revenue through accommodation, dining, and entertainment.
- Infrastructure Development: Stimulates investment in roads, hotels, and recreational facilities.
- Cultural Impacts: Can lead to cultural commodification, where local traditions are adapted for tourist consumption.
- Environmental Concerns: May result in environmental degradation, such as pollution and habitat loss.
- Spatial Patterns: Creates concentrated tourism zones around beaches, resorts, and theme parks.
12. What Role Does Adventure Tourism Play in Geography?
Adventure tourism plays a unique role in geography by promoting exploration of remote areas, supporting conservation efforts, and creating niche economic opportunities.
- Remote Exploration: Encourages travel to less accessible areas, driving infrastructure improvements.
- Conservation Support: Provides funding for conservation projects through tourism revenue.
- Niche Economies: Creates specialized markets for adventure gear, guides, and eco-lodges.
- Environmental Awareness: Raises awareness of environmental issues among tourists.
- Spatial Distribution: Concentrates tourism in areas with unique natural features, such as mountains and rivers.
13. How Does Cultural Tourism Impact Local Communities?
Cultural tourism significantly impacts local communities by promoting cultural preservation, generating income, and creating opportunities for cross-cultural exchange.
- Preservation Efforts: Supports the preservation of historical sites, traditions, and cultural heritage.
- Economic Benefits: Generates income for local artisans, guides, and businesses.
- Cross-Cultural Exchange: Fosters understanding and appreciation between tourists and local residents.
- Social Impacts: Can lead to cultural adaptation, where local traditions are modified to meet tourist expectations.
- Community Development: Tourism revenue can fund community development projects, such as schools and healthcare facilities.
14. How Does Eco-Tourism Promote Sustainable Practices?
Eco-tourism promotes sustainable practices by minimizing environmental impact, supporting local communities, and educating travelers about conservation.
- Minimal Impact: Encourages responsible travel that reduces pollution and waste.
- Community Support: Provides economic benefits to local communities, incentivizing conservation efforts.
- Educational Opportunities: Educates tourists about environmental issues and conservation practices.
- Conservation Funding: Generates revenue for conservation projects through tourism fees and donations.
- Spatial Distribution: Concentrates tourism in protected areas and eco-lodges, minimizing disruption to natural habitats.
15. What Are The Key Challenges in Tourism Geography?
Key challenges in tourism geography include over tourism, environmental degradation, cultural erosion, and social tensions.
- Over Tourism: Occurs when too many tourists visit a destination, overwhelming its capacity and infrastructure.
- Environmental Degradation: Results from pollution, deforestation, and resource depletion due to tourism activities.
- Cultural Erosion: Involves the loss of traditional practices and commodification of culture.
- Social Tensions: Arises from conflicts between tourists and local residents.
- Tourism Bubbles: Sudden increases in tourism can lead to price inflation and lack of affordable housing for locals.
- Tourism Poverty Traps: Situations where tourism contributes to poverty due to mismanagement.
16. What Is Over Tourism and Its Effects?
Over tourism occurs when a destination becomes too popular, exceeding its capacity to handle visitors, leading to negative impacts on the environment, culture, and local quality of life.
- Environmental Damage: Increased pollution, waste, and degradation of natural resources.
- Cultural Strain: Loss of authenticity, commodification of traditions, and resentment from locals.
- Infrastructure Overload: Congestion, strain on public services, and increased cost of living.
- Visitor Dissatisfaction: Crowds, long waits, and diminished experiences for tourists.
- Economic Imbalance: Benefits may not reach all residents, leading to inequality.
17. What Is the Impact of Tourism on the Environment?
Tourism significantly impacts the environment through pollution, resource depletion, and habitat destruction.
- Pollution: Air and water pollution from transportation, waste disposal, and energy consumption.
- Resource Depletion: Overuse of water, energy, and land resources.
- Habitat Destruction: Deforestation, coastal erosion, and damage to ecosystems from construction and tourist activities.
- Carbon Footprint: Greenhouse gas emissions from travel and tourism-related activities.
- Waste Generation: Increased waste production, leading to landfill issues and pollution.
18. How Does Tourism Affect Local Cultures?
Tourism can have both positive and negative effects on local cultures, leading to cultural exchange but also potential commodification and loss of authenticity.
- Cultural Exchange: Exposure to different cultures can broaden perspectives and promote understanding.
- Economic Support: Tourism revenue can help preserve cultural heritage and traditions.
- Commodification: Traditional practices may be altered to cater to tourist expectations, leading to loss of authenticity.
- Cultural Erosion: Overemphasis on tourism can lead to neglect of traditional values and customs.
- Social Disruption: Increased tourism can cause social friction between tourists and local communities.
19. What Are Tourism Poverty Traps?
Tourism poverty traps occur when tourism fails to benefit local communities, instead exacerbating poverty due to unequal distribution of income and resources.
- Unequal Distribution: Most revenue goes to foreign-owned businesses, leaving little for local residents.
- Low-Paying Jobs: Tourism jobs are often seasonal and low-paying, providing little opportunity for advancement.
- Land Grabbing: Local communities are displaced to make way for tourist developments.
- Resource Exploitation: Local resources are exploited for tourism without fair compensation.
- Dependency: Over-reliance on tourism makes communities vulnerable to economic shocks.
20. How Can Sustainable Tourism Address These Issues?
Sustainable tourism aims to mitigate the negative impacts of tourism by promoting responsible practices, supporting local communities, and preserving cultural and natural resources.
- Responsible Practices: Encouraging eco-friendly behaviors among tourists and businesses.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in tourism planning and decision-making.
- Cultural Preservation: Supporting efforts to preserve and promote local culture and heritage.
- Environmental Protection: Implementing measures to protect natural resources and reduce pollution.
- Economic Benefits: Ensuring that tourism revenue benefits local communities through fair wages and business opportunities.
21. What is The Future of Tourism Geography?
The future of tourism geography involves a greater focus on sustainability, technology, and personalized travel experiences.
- Sustainability: Increased emphasis on eco-friendly practices and responsible travel.
- Technology: Use of virtual reality, augmented reality, and AI to enhance travel experiences.
- Personalization: Tailored travel itineraries based on individual preferences and interests.
- Data Analysis: Use of big data to understand tourist behavior and improve destination management.
- Resilience: Developing strategies to cope with crises such as pandemics and climate change.
22. How Does Technology Shape Tourism Geography?
Technology transforms tourism geography by enhancing accessibility, providing real-time information, and enabling personalized travel experiences.
- Online Booking: Platforms for booking flights, accommodations, and tours simplify travel planning.
- Digital Mapping: GPS and digital maps facilitate navigation and exploration.
- Social Media: Platforms for sharing travel experiences and influencing destination choices.
- Virtual Reality: Virtual tours and experiences allow potential tourists to explore destinations remotely.
- Data Analytics: Provides insights into tourist behavior, enabling better destination management.
23. What Role Does Tourism Play in Economic Development?
Tourism plays a significant role in economic development by generating revenue, creating jobs, and stimulating local economies.
- Revenue Generation: Tourism revenue supports local businesses, infrastructure development, and government services.
- Job Creation: Tourism creates jobs in accommodation, food service, transportation, and entertainment.
- Stimulating Local Economies: Tourists spend money on local goods and services, boosting local businesses.
- Infrastructure Investment: Tourism drives investment in infrastructure, improving living standards.
- Diversification: Tourism diversifies economies, reducing reliance on traditional industries.
24. What Strategies Can Mitigate Over Tourism?
Mitigating over tourism involves strategies such as managing visitor flows, diversifying attractions, and involving local communities in tourism planning.
- Visitor Management: Implementing measures to control the number of tourists visiting a destination.
- Diversification: Developing new attractions and activities to spread tourists across different areas.
- Community Engagement: Involving local communities in tourism planning and decision-making.
- Pricing Strategies: Using pricing to manage demand and discourage overcrowding.
- Education: Educating tourists about responsible travel practices.
25. What Are Some Emerging Trends in Tourism Geography?
Emerging trends in tourism geography include sustainable tourism, experiential travel, and the use of technology to enhance travel experiences.
- Sustainable Tourism: Focus on minimizing environmental impact and supporting local communities.
- Experiential Travel: Emphasis on immersive and authentic travel experiences.
- Technology Integration: Use of technology to enhance travel planning, navigation, and cultural understanding.
- Wellness Tourism: Growing interest in travel focused on health and well-being.
- Regenerative Tourism: Aiming to leave a positive impact on the environment and local communities.
 Tourism visualized showing various aspects like destination, hospitality, transportation, attractions, and more
Tourism visualized showing various aspects like destination, hospitality, transportation, attractions, and more
26. How Can Geographers Contribute to Sustainable Tourism?
Geographers contribute to sustainable tourism by studying spatial patterns, assessing environmental impacts, and developing strategies for responsible tourism management.
- Spatial Analysis: Mapping and analyzing tourism activities to identify areas of concern.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluating the environmental, social, and economic impacts of tourism.
- Planning and Management: Developing strategies for sustainable tourism planning and management.
- Community Engagement: Facilitating community involvement in tourism decision-making.
- Education: Educating tourists, businesses, and policymakers about sustainable tourism practices.
27. What Is The Role of Local Communities in Tourism Planning?
Local communities play a critical role in tourism planning by providing insights into local culture, ensuring equitable distribution of benefits, and promoting sustainable practices.
- Cultural Knowledge: Providing insights into local culture, traditions, and values.
- Equitable Benefits: Ensuring that tourism revenue benefits local communities through job creation and business opportunities.
- Sustainable Practices: Promoting responsible tourism practices that minimize environmental impact.
- Community Ownership: Fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility for tourism development.
- Conflict Resolution: Resolving conflicts between tourists and local communities.
28. How Can Tourism Destinations Balance Economic Growth with Environmental Protection?
Tourism destinations can balance economic growth with environmental protection by implementing sustainable practices, investing in green infrastructure, and promoting responsible tourism.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging eco-friendly behaviors among tourists and businesses.
- Green Infrastructure: Investing in green infrastructure, such as renewable energy and waste management systems.
- Responsible Tourism: Promoting responsible tourism through education and certification programs.
- Conservation Efforts: Supporting conservation efforts to protect natural resources and biodiversity.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: Monitoring environmental impacts and enforcing regulations to protect the environment.
29. What Are The Ethical Considerations in Tourism Geography?
Ethical considerations in tourism geography include respecting local cultures, ensuring fair labor practices, and minimizing environmental impact.
- Cultural Respect: Respecting local cultures, traditions, and values.
- Fair Labor: Ensuring fair wages and working conditions for tourism employees.
- Environmental Responsibility: Minimizing environmental impact through responsible tourism practices.
- Community Benefits: Ensuring that tourism revenue benefits local communities.
- Transparency: Being transparent about the impacts of tourism and involving local communities in decision-making.
30. How Can Travelers Contribute to Sustainable Tourism?
Travelers can contribute to sustainable tourism by choosing eco-friendly accommodations, supporting local businesses, and respecting local cultures.
- Eco-Friendly Choices: Choosing eco-friendly accommodations and transportation options.
- Local Support: Supporting local businesses, restaurants, and artisans.
- Cultural Respect: Respecting local cultures, traditions, and customs.
- Waste Reduction: Reducing waste by bringing reusable water bottles and shopping bags.
- Responsible Behavior: Behaving responsibly and respecting the environment.
31. What Policies Support Sustainable Tourism Development?
Policies supporting sustainable tourism development include environmental regulations, zoning laws, and incentives for eco-friendly businesses.
- Environmental Regulations: Implementing regulations to protect natural resources and minimize pollution.
- Zoning Laws: Establishing zoning laws to control development and protect environmentally sensitive areas.
- Incentives: Providing incentives for eco-friendly businesses, such as tax breaks and grants.
- Certification Programs: Supporting certification programs that recognize sustainable tourism practices.
- Community Involvement: Encouraging community involvement in tourism planning and decision-making.
32. What Are the Benefits of Experiential Travel?
Experiential travel offers benefits such as deeper cultural understanding, personal growth, and the creation of meaningful memories.
- Cultural Immersion: Immersing oneself in local culture and traditions.
- Personal Growth: Developing new skills, perspectives, and self-awareness.
- Meaningful Memories: Creating lasting memories through unique and authentic experiences.
- Community Engagement: Supporting local communities and contributing to their well-being.
- Authentic Experiences: Engaging in activities that reflect the true character of a destination.
33. How Is AI Transforming Tourism Geography?
AI is transforming tourism geography by providing personalized recommendations, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing the travel experience.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI algorithms analyze data to provide personalized recommendations for destinations, activities, and accommodations.
- Operational Efficiency: AI improves operational efficiency in areas such as transportation, hospitality, and customer service.
- Enhanced Experience: AI enhances the travel experience through virtual assistants, chatbots, and augmented reality.
- Data Analysis: AI analyzes big data to understand tourist behavior and improve destination management.
- Predictive Analytics: AI predicts travel trends and helps businesses prepare for future demand.
34. How Does Climate Change Impact Tourism Geography?
Climate change significantly impacts tourism geography by altering destinations, increasing risks, and requiring adaptations in tourism planning.
- Destination Changes: Melting glaciers, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events alter popular tourist destinations.
- Increased Risks: Climate change increases the risk of natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, and wildfires.
- Adaptation Needs: Tourism businesses and destinations must adapt to climate change by implementing mitigation and adaptation strategies.
- Seasonal Shifts: Climate change causes shifts in seasonal weather patterns, affecting tourism seasons.
- Sustainability Concerns: Climate change raises concerns about the sustainability of tourism practices.
35. What Is Regenerative Tourism?
Regenerative tourism goes beyond sustainability by aiming to leave a positive impact on the environment and local communities, restoring and enhancing destinations.
- Positive Impact: Focusing on actions that improve the environment and communities.
- Restoration: Restoring degraded ecosystems and cultural sites.
- Community Empowerment: Empowering local communities to manage and benefit from tourism.
- Education: Educating tourists about the importance of regenerative practices.
- Long-Term Vision: Taking a long-term perspective and planning for the future.
36. What Are Some Best Practices for Sustainable Tourism?
Best practices for sustainable tourism include reducing waste, conserving resources, supporting local communities, and respecting cultural heritage.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste through recycling, composting, and reducing single-use plastics.
- Resource Conservation: Conserving water and energy through efficient practices and technologies.
- Community Support: Supporting local businesses and organizations.
- Cultural Respect: Respecting local cultures and traditions.
- Environmental Protection: Protecting natural resources and biodiversity.
37. How Can Tourism Boost Local Economies in Vietnam?
Tourism can significantly boost local economies in Vietnam by generating revenue, creating jobs, and supporting small businesses. SIXT.VN helps connect travelers with these opportunities.
- Revenue Generation: Attracting tourists who spend money on accommodation, food, transportation, and souvenirs.
- Job Creation: Creating jobs in hotels, restaurants, tour companies, and other tourism-related businesses.
- Small Business Support: Supporting small businesses such as family-run guesthouses, local restaurants, and artisan shops.
- Infrastructure Development: Funding infrastructure projects such as roads, airports, and public transportation.
- Cultural Preservation: Providing resources to preserve and promote Vietnamese culture and heritage.
38. How Can SIXT.VN Enhance Your Travel Experience in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN enhances your travel experience in Vietnam by providing expert travel consulting, convenient airport transfer services, hotel booking assistance, tour bookings, and flight ticket bookings.
- Expert Consulting: Providing personalized travel advice and itinerary planning.
- Airport Transfers: Offering reliable and comfortable airport transfer services.
- Hotel Booking: Assisting with hotel bookings to find the perfect accommodation.
- Tour Bookings: Arranging tours to explore the best of Vietnam.
- Flight Tickets: Helping you book affordable flight tickets.
With SIXT.VN, experience hassle-free and unforgettable trips to Vietnam. Let us take care of the details so you can focus on enjoying your adventure.
FAQ About The Nature and Scope of Tourism
-
What is the definition of tourism according to UNWTO?
Tourism involves activities of people traveling and staying in places outside their usual environment for no more than one consecutive year for leisure, business, and other purposes.
-
What are the main components of tourism geography?
The main components include spatial analysis, economic impacts, social and cultural effects, and environmental aspects of tourism.
-
How does tourism impact local communities?
Tourism can promote cultural preservation and generate income, but it can also lead to cultural commodification and social friction.
-
What are the ethical considerations in tourism?
Ethical considerations include respecting local cultures, ensuring fair labor practices, and minimizing environmental impact.
-
What are the challenges in tourism geography?
Key challenges include over tourism, environmental degradation, cultural erosion, and social tensions.
-
How can sustainable tourism mitigate negative impacts?
Sustainable tourism promotes responsible practices, supports local communities, and preserves cultural and natural resources.
-
What is the role of technology in tourism?
Technology enhances accessibility, provides real-time information, and enables personalized travel experiences.
-
How does climate change impact tourism?
Climate change alters destinations, increases risks, and requires adaptations in tourism planning.
-
What is regenerative tourism?
Regenerative tourism aims to leave a positive impact on the environment and local communities, restoring and enhancing destinations.
-
How can travelers contribute to sustainable tourism?
Travelers can choose eco-friendly accommodations, support local businesses, and respect local cultures.
Ready to explore Vietnam? Contact SIXT.VN today at Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358 or visit our Website: SIXT.VN to start planning your adventure. Let us help you create unforgettable travel experiences!



