Space tourism, a concept once relegated to science fiction, is rapidly becoming a reality. But What Do You Think About Space Tourism? At SIXT.VN, we’re here to explore this exciting frontier, weighing its potential benefits against its challenges and considering the perspectives of experts and the public alike to help you make informed travel decisions. Space exploration and space travel could be closer than you think.
1. What is Space Tourism and Why Is It Gaining Popularity?
Space tourism involves recreational travel beyond Earth’s atmosphere. Its increasing popularity stems from technological advancements, reduced launch costs, and the allure of experiencing space firsthand.
Space tourism is rapidly evolving from a far-fetched concept to a tangible reality, capturing the imagination of people worldwide. This surge in popularity can be attributed to several key factors:
- Technological Advancements: Significant strides in aerospace engineering have made space travel safer and more accessible. Reusable rockets and advanced spacecraft are reducing the risks associated with spaceflight.
- Decreasing Launch Costs: While still expensive, the cost of launching payloads into space has decreased substantially due to innovations in rocket technology and the entry of private companies.
- The Allure of Space: The sheer wonder and awe of experiencing space firsthand is a powerful draw for many. The opportunity to witness the Earth from orbit, float in zero gravity, and potentially visit celestial bodies is a unique and compelling prospect.
According to research from the Space Foundation, in 2023, the space economy is valued at over $400 billion and is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2040.
2. What Are the Different Types of Space Tourism Experiences?
Space tourism offers various experiences:
- Suborbital Flights: Brief trips to the edge of space, providing a few minutes of weightlessness.
- Orbital Flights: Longer journeys orbiting Earth, allowing for extended stays in space.
- Lunar Missions: Ambitious trips to the Moon, potentially involving lunar surface exploration.
- Space Hotel Stays: Future plans include hotels in orbit offering unique accommodation experiences.
Each type caters to different levels of adventure and budgets.
The burgeoning space tourism industry offers a diverse range of experiences, each designed to cater to different levels of adventure, budgets, and interests. Here’s a breakdown of the primary types of space tourism experiences currently available or under development:
-
Suborbital Flights:
- Definition: These flights offer a brief journey to the edge of space, typically reaching an altitude of around 100 kilometers (62 miles), known as the Kármán line, which is often considered the boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space.
- Experience: Passengers experience a few minutes of weightlessness and breathtaking views of Earth’s curvature against the blackness of space.
- Providers: Companies like Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin are pioneers in this category.
- Target Audience: This option is popular among those seeking a taste of space without the extensive training and commitment required for orbital flights.
-
Orbital Flights:
- Definition: These flights involve traveling into orbit around Earth, providing a longer and more immersive space experience.
- Experience: Passengers can spend days or even weeks in space, conducting experiments, observing Earth, and enjoying the unique environment of zero gravity.
- Providers: Space Adventures has facilitated orbital flights to the International Space Station (ISS) for private citizens.
- Target Audience: This is suited for individuals with a higher budget and a strong interest in space exploration, offering a more profound and extended experience.
-
Lunar Missions:
- Definition: The most ambitious and challenging form of space tourism, lunar missions involve traveling to the Moon, either orbiting it or landing on its surface.
- Experience: Passengers could potentially explore the lunar surface, conduct scientific research, and witness the Earth from a completely different perspective.
- Providers: Companies like SpaceX are planning lunar missions for private citizens.
- Target Audience: This is aimed at highly adventurous and wealthy individuals who aspire to be among the first private citizens to visit the Moon.
-
Space Hotel Stays:
- Definition: An emerging concept that envisions the construction of hotels in orbit, offering unique accommodation and recreational facilities.
- Experience: Guests could enjoy stunning views of Earth, experience zero gravity, participate in space-themed activities, and potentially conduct research.
- Providers: Companies like Orion Span and Axiom Space are developing plans for space hotels.
- Target Audience: This targets affluent travelers seeking an unparalleled and luxurious space experience, combining tourism with elements of scientific research and adventure.
Each type of space tourism experience promises unique and unforgettable adventures, pushing the boundaries of human exploration and making space accessible to a broader audience. As technology evolves and costs decrease, these opportunities are likely to expand, paving the way for a future where space travel becomes more commonplace.
3. What Are the Potential Benefits of Space Tourism?
Space tourism could:
- Drive Technological Innovation: Fuel advancements in aerospace technology.
- Stimulate Economic Growth: Create jobs and new industries.
- Inspire Future Generations: Encourage interest in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields.
- Offer New Perspectives: Provide unique insights into Earth and its place in the universe.
The potential benefits of space tourism extend far beyond the thrill of individual travelers. This burgeoning industry holds the promise of driving significant advancements in technology, stimulating economic growth, inspiring future generations, and offering profound new perspectives on our planet and our place in the cosmos.
-
Driving Technological Innovation:
- Aerospace Advancements: The demand for safer, more efficient, and cost-effective space travel is a powerful catalyst for innovation in aerospace technology. This includes the development of reusable rockets, advanced propulsion systems, improved spacecraft design, and enhanced life support systems.
- Materials Science: The extreme conditions of space require the creation of new materials that are lightweight, durable, and resistant to radiation. These advancements can have applications in various industries, including transportation, construction, and medicine.
- Communication Technologies: Reliable and high-speed communication is essential for space travel. This drives the development of advanced communication technologies that can also benefit terrestrial applications, such as improved satellite communication and wireless networks.
-
Stimulating Economic Growth:
- Job Creation: The space tourism industry creates a wide range of jobs, from engineers and scientists to pilots, trainers, and hospitality staff.
- New Industries: The growth of space tourism fosters the development of new industries, including spaceport construction, spacecraft manufacturing, space-themed entertainment, and specialized training programs.
- Investment Opportunities: Space tourism attracts significant investment from both private and public sectors, driving economic growth and innovation.
-
Inspiring Future Generations:
- STEM Education: The excitement and wonder of space travel can inspire young people to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields.
- Educational Opportunities: Space tourism can provide unique educational opportunities, allowing students and researchers to conduct experiments in space and learn firsthand about the challenges and possibilities of space exploration.
- Public Engagement: Space missions and discoveries capture the public’s imagination, fostering a greater appreciation for science and technology.
-
Offering New Perspectives:
- The Overview Effect: Astronauts often report experiencing the “overview effect,” a profound sense of awe and interconnectedness when viewing Earth from space. This can lead to a deeper appreciation for our planet and a stronger commitment to environmental stewardship.
- Scientific Research: Space tourism can facilitate scientific research by providing access to the unique environment of space, allowing for experiments in fields such as biology, physics, and astronomy.
- Cultural Exchange: Space travel can foster cultural exchange and understanding by bringing people from different backgrounds together in a shared experience.
According to research from Deloitte, the commercial space industry is expected to generate trillions of dollars in revenue over the next few decades, creating countless opportunities for innovation and economic growth.
4. What Are the Potential Risks and Challenges of Space Tourism?
Despite the potential benefits, space tourism also presents risks:
- Safety Concerns: Space travel is inherently risky, with potential for accidents during launch, flight, or landing.
- Environmental Impact: Rocket launches can contribute to air pollution and ozone depletion.
- High Costs: Space tourism remains expensive, limiting access to a select few.
- Ethical Considerations: Questions arise about the fairness of allocating resources to space tourism when pressing issues exist on Earth.
Space tourism, while promising incredible opportunities, also presents several significant risks and challenges that need careful consideration. These concerns span safety, environmental impact, cost, and ethical considerations:
-
Safety Concerns:
- Inherent Risks of Space Travel: Space travel is inherently risky, with potential for accidents during launch, flight, and landing. The extreme conditions of space, including radiation exposure, microgravity, and the vacuum of space, pose significant challenges.
- Emergency Preparedness: Developing effective emergency procedures and rescue systems for space tourists is crucial but complex. The remoteness of space and the limited resources available in orbit make emergency response particularly challenging.
- Training and Medical Screening: Ensuring that space tourists are adequately trained and medically fit for space travel is essential to minimize risks. Thorough medical screening and comprehensive training programs are necessary to prepare individuals for the physical and psychological demands of spaceflight.
-
Environmental Impact:
- Air Pollution: Rocket launches release significant amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide, black carbon, and other harmful substances. These emissions can contribute to air pollution and climate change.
- Ozone Depletion: Some rocket propellants, such as solid rocket boosters, can deplete the ozone layer, which protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
- Space Debris: The increasing number of satellites and space missions contributes to the growing problem of space debris, which poses a threat to operational spacecraft and can create a cascade effect of collisions.
-
High Costs:
- Accessibility: Space tourism remains extremely expensive, limiting access to a select few wealthy individuals. This raises concerns about equity and fairness.
- Infrastructure Development: The development of spaceports, spacecraft, and other necessary infrastructure requires massive investments, which could be directed towards other pressing societal needs.
- Insurance: The high risks associated with space travel make insurance premiums exorbitant, adding to the overall cost of space tourism.
-
Ethical Considerations:
- Resource Allocation: Questions arise about the ethical implications of allocating vast resources to space tourism when pressing issues such as poverty, disease, and climate change exist on Earth.
- Environmental Responsibility: Concerns exist about the environmental impact of space tourism and the need to balance the pursuit of space exploration with the protection of our planet.
- Commodification of Space: Some critics argue that space tourism commodifies space, turning it into a playground for the wealthy rather than a realm for scientific exploration and discovery.
According to research from the World Economic Forum, the environmental impact of space activities is a growing concern, with potential long-term consequences for Earth’s atmosphere and the space environment.
5. How Safe Is Space Tourism?
Safety is paramount. Space tourism companies are developing stringent safety protocols, including:
- Rigorous Vehicle Testing: Ensuring spacecraft undergo extensive testing before carrying passengers.
- Crew Training: Providing comprehensive training for pilots and crew members.
- Passenger Preparation: Educating passengers about the risks and procedures involved in spaceflight.
- Emergency Systems: Implementing robust emergency systems and procedures.
However, the inherent risks of space travel cannot be eliminated entirely.
Safety is of paramount importance in the burgeoning space tourism industry. Companies are investing heavily in developing stringent safety protocols and technologies to mitigate the risks associated with space travel. Here are some key aspects of safety measures:
-
Rigorous Vehicle Testing:
- Comprehensive Testing Programs: Spacecraft undergo extensive testing before carrying passengers, including structural integrity tests, engine performance evaluations, and simulations of various flight scenarios.
- Redundancy and Fail-Safe Systems: Spacecraft are designed with redundant systems to ensure that critical functions can continue even if one component fails. Fail-safe mechanisms are implemented to prevent catastrophic events in case of emergencies.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspections: Spacecraft are subject to regular maintenance and inspections to identify and address potential issues before they become safety hazards.
-
Crew Training:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Pilots and crew members undergo comprehensive training programs that cover all aspects of spaceflight, including flight procedures, emergency response, and spacecraft systems.
- Simulations and Drills: Crew members participate in realistic simulations and drills to prepare them for various scenarios, including emergency situations such as engine failures, cabin depressurization, and landing malfunctions.
- Medical Training: Crew members receive medical training to provide basic medical care to passengers in case of illness or injury during flight.
-
Passenger Preparation:
- Pre-Flight Education: Passengers are educated about the risks and procedures involved in spaceflight, including the effects of microgravity, radiation exposure, and emergency protocols.
- Medical Screening: Passengers undergo thorough medical screening to ensure they are fit for space travel and to identify any pre-existing conditions that could pose a risk during flight.
- Safety Briefings: Passengers receive detailed safety briefings before each flight, covering emergency procedures, use of safety equipment, and other important information.
-
Emergency Systems:
- Abort Systems: Spacecraft are equipped with abort systems that can be activated in case of an emergency during launch or ascent, allowing the crew and passengers to safely return to Earth.
- Life Support Systems: Advanced life support systems provide breathable air, regulate temperature, and remove waste products to ensure the safety and comfort of passengers during flight.
- Emergency Landing Procedures: Detailed emergency landing procedures are in place to guide the crew and passengers in the event of an unexpected landing, including procedures for landing on water or in remote areas.
Despite these efforts, it is important to acknowledge that the inherent risks of space travel cannot be eliminated entirely. Spaceflight is a complex and challenging endeavor, and unforeseen events can occur. However, the space tourism industry is committed to minimizing these risks and ensuring the safety of its passengers to the greatest extent possible.
6. What is the Environmental Impact of Space Tourism?
Minimizing environmental impact is crucial:
- Developing Cleaner Propellants: Researching and using less polluting rocket fuels.
- Reducing Launch Frequency: Optimizing mission planning to minimize the number of launches.
- Managing Space Debris: Implementing measures to prevent and remove space debris.
- Offsetting Carbon Emissions: Investing in carbon offset programs to mitigate the impact of launches.
The environmental impact of space tourism is a significant concern that requires careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies. The industry is actively exploring various approaches to minimize its footprint and ensure the long-term sustainability of space activities. Here are some key areas of focus:
-
Developing Cleaner Propellants:
- Research and Development: The industry is investing in research and development to identify and utilize less polluting rocket fuels. This includes exploring alternative propellants such as liquid oxygen and methane, which produce fewer emissions than traditional fuels like kerosene.
- Green Propellants: Some companies are developing “green” propellants that are non-toxic and produce minimal emissions. These propellants are based on substances such as hydrogen peroxide and ammonium dinitramide.
- Electric Propulsion: Electric propulsion systems, which use electricity to accelerate propellant, offer the potential for significantly reduced emissions compared to chemical rockets. These systems are particularly well-suited for in-space propulsion and satellite maneuvering.
-
Reducing Launch Frequency:
- Optimizing Mission Planning: Space agencies and companies are optimizing mission planning to minimize the number of launches required to achieve specific objectives. This includes using more efficient spacecraft designs, consolidating payloads, and extending the lifespan of satellites.
- Reusable Rockets: The development and use of reusable rockets, such as those pioneered by SpaceX, significantly reduces the environmental impact of space launches. Reusable rockets can be flown multiple times, reducing the need for new rocket construction and minimizing waste.
- In-Space Manufacturing: In the future, in-space manufacturing could reduce the need for launching materials and equipment from Earth. This would involve using resources available in space, such as lunar regolith or asteroids, to construct spacecraft and other structures.
-
Managing Space Debris:
- Debris Mitigation Strategies: Space agencies and companies are implementing debris mitigation strategies to prevent the creation of new space debris. This includes designing spacecraft to minimize the release of debris, avoiding intentional destruction of satellites, and maneuvering satellites to avoid collisions.
- Active Debris Removal: Active debris removal technologies are being developed to remove existing space debris from orbit. These technologies include robotic spacecraft that can capture and deorbit debris, as well as laser systems that can vaporize small debris particles.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is essential for addressing the problem of space debris. Space agencies and governments are working together to establish guidelines and regulations for responsible space operations.
-
Offsetting Carbon Emissions:
- Carbon Offset Programs: Some space tourism companies are investing in carbon offset programs to mitigate the impact of their launches. These programs involve funding projects that reduce carbon emissions, such as reforestation, renewable energy development, and energy efficiency improvements.
- Sustainable Practices: Companies are adopting sustainable practices throughout their operations, including reducing energy consumption, using recycled materials, and minimizing waste.
- Public Awareness: Raising public awareness about the environmental impact of space activities and encouraging responsible behavior is crucial for promoting sustainability in the space sector.
According to research from the European Space Agency, the long-term sustainability of space activities depends on the development and implementation of effective environmental mitigation strategies.
 Earth from space
Earth from space
7. How Much Does Space Tourism Cost?
Space tourism is currently a luxury experience:
- Suborbital Flights: Prices range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars per seat.
- Orbital Flights: Can cost millions of dollars per person.
- Lunar Missions: Projected to cost hundreds of millions of dollars per seat.
Costs are expected to decrease over time as technology advances and competition increases.
Space tourism is currently positioned as a luxury experience, with prices reflecting the cutting-edge technology, extensive research and development, and inherent risks associated with space travel. The cost of space tourism varies significantly depending on the type of experience, duration of the flight, and the provider. Here’s a breakdown of the current cost landscape:
-
Suborbital Flights:
- Price Range: Prices for suborbital flights typically range from tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars per seat.
- Providers: Virgin Galactic, for example, has offered tickets for suborbital flights at prices ranging from $250,000 to $450,000 per seat. Blue Origin has not publicly disclosed its pricing, but industry experts estimate that its suborbital flights are in a similar range.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The cost of suborbital flights is influenced by factors such as the spacecraft’s design, the level of training provided, and the overall experience offered.
-
Orbital Flights:
- Price Range: Orbital flights, which involve traveling into orbit around Earth, can cost millions of dollars per person.
- Providers: Space Adventures has facilitated orbital flights to the International Space Station (ISS) for private citizens, with prices ranging from $20 million to $40 million per seat.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The high cost of orbital flights is due to the complexity of the mission, the extensive training required, and the limited availability of seats.
-
Lunar Missions:
- Projected Cost: Lunar missions, which involve traveling to the Moon, are projected to cost hundreds of millions of dollars per seat.
- Providers: SpaceX is planning lunar missions for private citizens, but has not yet announced pricing. However, industry experts estimate that the cost of a lunar mission could be in the range of $100 million to $500 million per seat.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The extreme cost of lunar missions is due to the technological challenges involved, the long duration of the flight, and the need for specialized equipment and training.
It is important to note that these prices are subject to change as the space tourism industry evolves and new providers enter the market. However, as technology advances and competition increases, costs are expected to decrease over time, making space tourism more accessible to a broader range of individuals.
According to research from Morgan Stanley, space tourism is expected to become a multi-billion dollar industry in the coming decades, with prices decreasing as technology matures and competition intensifies.
8. Who Are the Key Players in the Space Tourism Industry?
Several companies are leading the way:
- Virgin Galactic: Offering suborbital flights with its SpaceShipTwo vehicle.
- Blue Origin: Providing suborbital flights with its New Shepard rocket.
- SpaceX: Planning orbital and lunar missions with its Falcon and Starship rockets.
- Axiom Space: Developing private space stations and offering stays in orbit.
These companies are investing heavily in technology and infrastructure.
The space tourism industry is rapidly evolving, with several key players leading the way in developing and offering commercial spaceflight opportunities. These companies are investing heavily in technology, infrastructure, and training to make space travel accessible to a broader audience. Here are some of the major players in the space tourism industry:
-
Virgin Galactic:
- Focus: Virgin Galactic is focused on providing suborbital flights to paying customers.
- Technology: The company’s SpaceShipTwo vehicle is designed to carry passengers to an altitude of around 80 kilometers (50 miles), providing a few minutes of weightlessness and stunning views of Earth.
- Achievements: Virgin Galactic has conducted several successful test flights with its SpaceShipTwo vehicle, including flights with paying customers.
- Future Plans: The company plans to offer regular suborbital flights to tourists from its spaceport in New Mexico.
-
Blue Origin:
- Focus: Blue Origin is also focused on providing suborbital flights, but with a different approach than Virgin Galactic.
- Technology: The company’s New Shepard rocket is designed to carry passengers in a capsule to an altitude of around 100 kilometers (62 miles), providing a few minutes of weightlessness and panoramic views of Earth.
- Achievements: Blue Origin has conducted several successful test flights with its New Shepard rocket, including flights with the company’s founder, Jeff Bezos.
- Future Plans: The company plans to offer regular suborbital flights to tourists from its launch site in West Texas.
-
SpaceX:
- Focus: SpaceX has more ambitious plans than Virgin Galactic and Blue Origin, including orbital and lunar missions for private citizens.
- Technology: The company’s Falcon and Starship rockets are designed to carry passengers and cargo to orbit and beyond.
- Achievements: SpaceX has already achieved significant milestones in space travel, including launching and landing reusable rockets, delivering cargo to the International Space Station (ISS), and launching astronauts into orbit.
- Future Plans: The company is planning to offer orbital flights around Earth and lunar missions for private citizens, including a mission to send Japanese billionaire Yusaku Maezawa and a group of artists around the Moon.
-
Axiom Space:
- Focus: Axiom Space is focused on developing private space stations and offering stays in orbit for tourists and researchers.
- Technology: The company is planning to build a private module that will be attached to the ISS, providing additional living and working space. Eventually, Axiom Space plans to detach its module from the ISS and operate it as a standalone space station.
- Achievements: Axiom Space has already sent private citizens to the ISS, paving the way for commercial space stations and orbital tourism.
- Future Plans: The company plans to offer regular stays in orbit for tourists and researchers, as well as conduct scientific experiments and develop new technologies in space.
These companies are investing heavily in technology and infrastructure to make space tourism a reality. As the industry evolves and new players emerge, space travel is likely to become more accessible and affordable in the coming years.
9. What Are the Ethical Considerations of Space Tourism?
Ethical considerations are paramount:
- Environmental Responsibility: Ensuring space tourism is conducted in an environmentally sustainable manner.
- Social Equity: Addressing concerns about access and affordability.
- Resource Allocation: Balancing investment in space tourism with other societal needs.
- Preservation of Space: Protecting the space environment for future generations.
The ethical considerations surrounding space tourism are multifaceted and require careful examination. As this industry expands, it’s crucial to address these concerns to ensure that space tourism is conducted in a responsible, sustainable, and equitable manner. Here are some key ethical considerations:
-
Environmental Responsibility:
- Sustainable Practices: Space tourism must be conducted in an environmentally sustainable manner to minimize its impact on Earth’s atmosphere and the space environment. This includes developing cleaner propellants, reducing launch frequency, and managing space debris.
- Preservation of Ecosystems: Protecting sensitive ecosystems on Earth and in space is essential. Spaceports and launch sites should be located and operated in a way that minimizes their impact on local environments.
- International Cooperation: International cooperation is needed to establish environmental standards and regulations for space activities. This includes developing guidelines for responsible space operations and promoting the sharing of best practices.
-
Social Equity:
- Accessibility: Addressing concerns about access and affordability is crucial. Space tourism should not be limited to the wealthy elite, but should be made accessible to a broader range of individuals.
- Educational Opportunities: Providing educational opportunities and scholarships for students from underrepresented groups can help to promote diversity and inclusion in the space sector.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with local communities near spaceports and launch sites is essential. Space tourism companies should work with local communities to address their concerns and ensure that they benefit from the industry’s growth.
-
Resource Allocation:
- Balancing Investments: Balancing investment in space tourism with other societal needs is a complex ethical challenge. Resources should be allocated in a way that addresses both the potential benefits of space exploration and the pressing needs of people on Earth.
- Prioritizing Social Programs: Ensuring that basic needs such as food, shelter, and healthcare are met before investing heavily in space tourism is essential.
- Transparency and Accountability: Promoting transparency and accountability in the allocation of resources can help to ensure that investments in space tourism are justified and aligned with societal priorities.
-
Preservation of Space:
- Protecting the Space Environment: Protecting the space environment for future generations is a fundamental ethical responsibility. This includes managing space debris, preventing the militarization of space, and preserving the scientific value of space.
- International Agreements: International agreements are needed to establish rules of the road for space activities. This includes developing guidelines for responsible behavior in space and promoting the peaceful exploration and use of space for all nations.
- Ethical Frameworks: Developing ethical frameworks for space exploration and development can help to guide decision-making and ensure that space activities are conducted in a responsible and sustainable manner.
According to research from the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs, international cooperation is essential for addressing the ethical challenges of space tourism and ensuring that space activities benefit all of humanity.
10. What Do Experts Say About Space Tourism?
Experts have varying opinions:
- Proponents: Highlight the potential for technological innovation and economic growth.
- Critics: Express concerns about safety, environmental impact, and social equity.
A balanced approach is needed to address these concerns.
Experts in the fields of space exploration, technology, ethics, and environmental science hold diverse opinions regarding the potential benefits and drawbacks of space tourism. Their insights provide a balanced perspective on this emerging industry, highlighting both its promise and its challenges. Here’s a summary of the views held by proponents and critics:
-
Proponents:
- Technological Innovation: Advocates emphasize that space tourism has the potential to drive significant technological innovation in areas such as aerospace engineering, materials science, and communication technologies. The demand for safer, more efficient, and cost-effective space travel can spur advancements that have applications in various industries.
- Economic Growth: Supporters highlight the potential for space tourism to stimulate economic growth by creating jobs, fostering new industries, and attracting investment. The development of spaceports, spacecraft manufacturing, and space-themed entertainment can generate significant economic activity.
- Inspiration and Education: Proponents argue that space tourism can inspire future generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. The excitement and wonder of space travel can capture the public’s imagination and foster a greater appreciation for science and technology.
- New Perspectives: Advocates believe that space tourism can offer unique perspectives on our planet and our place in the universe. The “overview effect,” experienced by astronauts who view Earth from space, can lead to a deeper appreciation for our planet and a stronger commitment to environmental stewardship.
-
Critics:
- Safety Concerns: Critics express concerns about the safety of space tourism, particularly for untrained civilians. The risks associated with space travel, such as launch accidents, radiation exposure, and equipment malfunctions, are significant and require careful mitigation.
- Environmental Impact: Detractors raise concerns about the environmental impact of space tourism, including air pollution from rocket launches, ozone depletion, and the accumulation of space debris. The industry needs to adopt sustainable practices to minimize its footprint on Earth and in space.
- Social Equity: Opponents highlight the social equity issues associated with space tourism, arguing that it is a luxury activity that is only accessible to the wealthy elite. The industry should address concerns about access and affordability to ensure that space tourism benefits a broader range of individuals.
- Resource Allocation: Critics question the ethical implications of allocating vast resources to space tourism when pressing issues such as poverty, disease, and climate change exist on Earth. Resources should be allocated in a way that addresses both the potential benefits of space exploration and the urgent needs of people on Earth.
In light of these diverse opinions, it is clear that a balanced approach is needed to address the concerns raised by critics while also harnessing the potential benefits of space tourism. This requires careful consideration of ethical, environmental, and safety issues, as well as a commitment to promoting social equity and responsible resource allocation. By taking a balanced and thoughtful approach, the space tourism industry can contribute to the advancement of human knowledge, the stimulation of economic growth, and the inspiration of future generations.
11. What Does the Public Think About Space Tourism?
Public opinion is mixed:
- Excitement: Many are excited about the prospect of space travel and its potential benefits.
- Skepticism: Some are skeptical about the safety, cost, and environmental impact of space tourism.
- Priorities: Others believe resources should be focused on addressing problems on Earth.
Understanding public sentiment is crucial for shaping the future of space tourism.
Public opinion regarding space tourism is complex and multifaceted, reflecting a mix of excitement, skepticism, and concern. Understanding public sentiment is crucial for shaping the future of space tourism and ensuring that it aligns with societal values and priorities. Here’s a breakdown of the key attitudes and opinions held by the public:
-
Excitement:
- A Sense of Wonder: Many people are excited about the prospect of space travel and the opportunity to experience the wonder and awe of space firsthand. The idea of seeing Earth from orbit, floating in zero gravity, and potentially visiting other celestial bodies is a compelling draw for many.
- Technological Progress: Space tourism is seen by some as a symbol of technological progress and human ingenuity. The ability to travel to space is a testament to the advancements in aerospace engineering and the boundless potential of human innovation.
- Inspiration: Space tourism can inspire people to dream big and pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. The excitement surrounding space travel can spark a passion for learning and discovery.
-
Skepticism:
- Safety Concerns: Some people are skeptical about the safety of space tourism, particularly for untrained civilians. The risks associated with space travel are significant, and the potential for accidents and emergencies is a major concern for many.
- High Costs: The high cost of space tourism is a barrier for many people, who see it as an exclusive activity for the wealthy elite. There is concern that space tourism will exacerbate social inequalities and create a divide between those who can afford to travel to space and those who cannot.
- Environmental Impact: Concerns about the environmental impact of space tourism are also prevalent. Rocket launches can contribute to air pollution and ozone depletion, and the accumulation of space debris is a growing problem.
-
Priorities:
- Focus on Earth: Some people believe that resources should be focused on addressing problems on Earth, such as poverty, disease, and climate change, rather than investing in space tourism. They argue that the money spent on space travel could be better used to improve the lives of people on Earth.
- Ethical Considerations: Ethical concerns about the commodification of space and the potential for exploitation are also raised. Some people believe that space should be reserved for scientific exploration and discovery, rather than being turned into a playground for the wealthy.
- Sustainability: There is a growing awareness of the need for sustainable practices in space tourism. People are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of space activities and want to see the industry adopt responsible and sustainable practices.
Understanding these diverse perspectives is crucial for shaping the future of space tourism. By addressing concerns about safety, cost, and environmental impact, and by ensuring that space tourism aligns with societal values and priorities, the industry can gain broader public support and contribute to the advancement of human knowledge and the betterment of society.
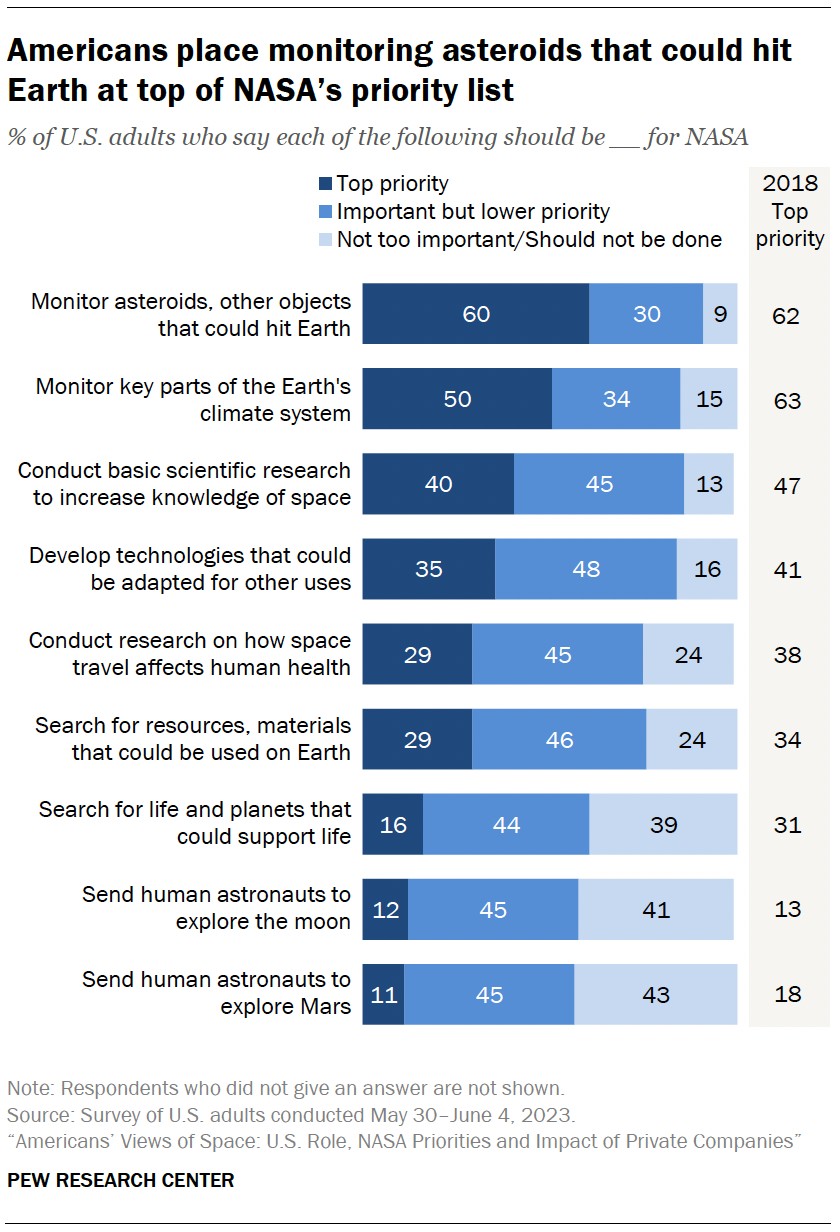
According to research from Pew Research Center, public opinion on space exploration is divided, with many expressing excitement about the potential benefits but also concerns about the costs and risks involved.
12. How Can I Prepare for Space Tourism?
If you’re considering space tourism:
- Research: Learn about the different types of experiences and providers.
- Training: Participate in training programs to prepare for the physical and mental demands of spaceflight.
- Medical Check-up: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation to ensure you’re fit for space travel.
- Financial Planning: Be prepared for the high costs involved.
Preparing for space tourism is a unique and challenging endeavor that requires careful planning, thorough training, and a significant financial investment. If you’re considering embarking on this extraordinary adventure, here are some key steps to take in preparation:
-
Research:
- Explore Options: Learn about the different types of space tourism experiences available, including suborbital flights, orbital flights, and lunar missions. Research the various providers and their offerings to determine which option best suits your interests, budget, and physical capabilities.
- Understand Risks: Familiarize yourself with the risks associated with space travel, including the potential for accidents, radiation exposure, and equipment malfunctions. Be sure to fully understand the safety protocols and emergency procedures in place.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on the latest developments in the space tourism industry by following reputable news sources, industry publications, and social media accounts.
-
Training:
- Enroll in Programs: Participate in training programs designed to prepare you for the physical and mental demands of spaceflight. These programs may include centrifuge training to simulate the effects of g-forces, parabolic flights to experience weightlessness, and survival training to prepare for emergency situations.
- Physical Fitness: Maintain a high level of physical fitness through regular exercise and a healthy diet. Space travel can be physically demanding, and it’s important to be in good shape to withstand the stresses of spaceflight.
- Mental Preparation: Prepare yourself mentally for the challenges of space travel. This may involve practicing relaxation techniques, developing coping strategies for dealing with stress, and visualizing the experience to build confidence.
-
Medical Check-Up:
- Consult a Doctor: Undergo a thorough medical evaluation by a qualified physician to ensure that you are fit for space travel. This evaluation may include a physical exam, blood tests, and other diagnostic procedures.
- Disclose Conditions: Disclose any pre-existing medical conditions to your physician and the space tourism provider. Certain medical conditions may preclude you from participating in space travel.
- Obtain Clearances: Obtain any necessary medical clearances or waivers from your physician and the space tourism provider.
-
Financial Planning:
- Assess Costs: Be prepared for the high costs involved in space tourism. Suborbital flights can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, while orbital flights and lunar missions can cost millions of dollars.
- Secure Funding: Develop a financial plan to secure the necessary funding for your space tourism adventure. This may involve saving money, taking out loans, or seeking sponsorship.



