Are you considering transplant tourism and grappling with the ethical dilemmas it presents? SIXT.VN understands the complexities of seeking medical treatment abroad, particularly when it involves organ transplantation. This guide will delve into the Transplant Tourism Ethics, offering clarity and guidance to help you make informed decisions about your healthcare journey while exploring the beauty and culture of Vietnam. Discover insights on ethical considerations, the role of transplant tourism, and how SIXT.VN can assist you in navigating this intricate landscape with support for airport transfers, hotel bookings, and tours in Hanoi.
1. What is Transplant Tourism and Why is Ethics Important?
Transplant tourism is when patients travel across international borders seeking organ transplantation services. Ethics is crucial here because it involves complex issues such as organ sourcing, fair access to healthcare, and potential exploitation of vulnerable populations. Transplant tourism can be linked to serious issues like organ trafficking and commercialisation, which are against international laws and medical ethics.
1.1 Why is Understanding Transplant Tourism Ethics Important for Patients?
Understanding these ethics helps patients make informed choices, ensuring they are not inadvertently supporting unethical practices. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), unethical transplant practices can lead to severe health risks and exacerbate global health inequities. Knowing the ethical implications ensures you prioritize your health and well-being while respecting the rights and welfare of others.
1.2 What Role Does Transplant Tourism Play in Global Healthcare?
Transplant tourism has emerged due to disparities in organ availability and healthcare costs between countries. According to a study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), transplant tourism accounts for approximately 5-10% of kidney transplants performed worldwide each year. However, it raises ethical concerns if it deprives local populations of needed services or involves organ trafficking.
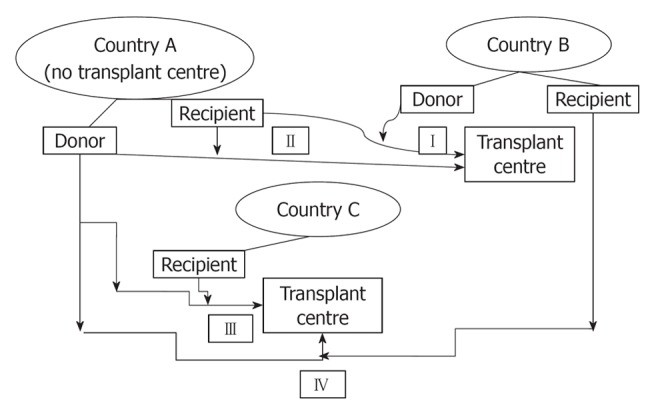 Transplant tourism raises significant ethical concerns due to the complexity of organ sourcing and potential for exploitation.
Transplant tourism raises significant ethical concerns due to the complexity of organ sourcing and potential for exploitation.
1.3 What Key Ethical Issues Arise in Transplant Tourism?
Several ethical issues arise, including:
- Organ Trafficking: Illegal procurement and sale of organs.
- Commercialisation: Treating organs as commodities.
- Exploitation of Vulnerable Donors: Coercing or taking advantage of individuals in impoverished situations.
- Equity of Access: Ensuring fair distribution of organs without disadvantaging local populations.
2. What are the Core Principles of Transplant Ethics?
Transplant ethics is guided by core principles that safeguard the well-being and rights of both donors and recipients. These principles include autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice, ensuring ethical and equitable practices in organ transplantation.
2.1 How Does Autonomy Apply to Transplant Decisions?
Autonomy refers to the right of individuals to make informed decisions about their medical treatment. According to the American Society of Transplantation (AST), patients must be fully informed about the risks, benefits, and alternatives to transplant tourism. Respecting autonomy means ensuring patients willingly consent without coercion or undue influence.
2.2 What is Beneficence and Non-Maleficence in Transplant Ethics?
Beneficence means acting in the best interest of the patient, while non-maleficence means avoiding harm. Transplant centers must ensure the transplant procedure benefits the patient while minimizing potential harm to both the recipient and the donor. The Transplantation Society emphasizes the importance of rigorous medical evaluations to uphold these principles.
2.3 How Does Justice Relate to Organ Allocation in Transplant Tourism?
Justice involves fair and equitable distribution of organs, regardless of a patient’s nationality or financial status. It is essential to prevent transplant tourism from exacerbating health inequities by ensuring local populations are not disadvantaged. The Declaration of Istanbul advocates for ethical practices that prioritize justice in organ allocation.
3. What are the Risks Associated with Unethical Transplant Tourism?
Unethical transplant tourism carries significant risks for both recipients and donors, ranging from health complications to legal and ethical violations. These risks underscore the importance of seeking transplantation services from reputable and ethical sources.
3.1 What Health Risks are Associated with Transplant Tourism?
Patients undergoing transplants in unregulated environments face increased risks of:
- Infections: Exposure to drug-resistant bacteria or diseases. A study in Transplantation journal found higher rates of infection in transplant tourists compared to those receiving transplants in their home countries.
- Poor Surgical Outcomes: Substandard medical care and facilities.
- Lack of Follow-Up Care: Inadequate post-transplant monitoring and support.
3.2 How Can Transplant Tourism Lead to Organ Trafficking and Exploitation?
Unethical transplant tourism often involves organ trafficking, where vulnerable individuals are coerced into selling their organs. According to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), this practice exploits poverty and desperation, violating fundamental human rights.
3.3 What Legal and Ethical Violations are Involved in Transplant Tourism?
Engaging in transplant tourism can lead to legal and ethical violations, including:
- Violation of National Laws: Many countries prohibit commercial organ transplantation.
- Breach of Medical Ethics: Violating principles of informed consent and patient welfare.
- Complicity in Criminal Activities: Supporting organ trafficking networks.
4. How Can You Ensure Ethical Transplant Tourism?
Ensuring ethical transplant tourism involves careful planning, due diligence, and adherence to international guidelines and regulations. It requires thorough research, selecting reputable transplant centers, and respecting the legal and ethical standards of both your home country and the destination country.
4.1 What Questions Should You Ask Potential Transplant Centers?
Before committing to a transplant center, ask:
- Accreditation: Is the center accredited by international medical organizations?
- Organ Sourcing: How are organs sourced, and what measures are in place to prevent organ trafficking?
- Donor Consent: How is informed consent obtained from donors?
- Patient Outcomes: What are the center’s success rates and patient survival rates?
- Ethical Oversight: Does the center have an ethics committee or board to ensure ethical practices?
4.2 How Can You Verify the Legitimacy of a Transplant Program?
Verify the legitimacy of a transplant program by:
- Checking Accreditation: Look for accreditation from reputable organizations like Joint Commission International (JCI).
- Consulting Medical Professionals: Seek advice from your doctor or transplant specialist.
- Reviewing Patient Testimonials: Look for unbiased reviews and testimonials from past patients.
- Contacting Regulatory Bodies: Verify the program’s compliance with national and international regulations.
4.3 What Role Do International Guidelines Play in Ethical Transplant Tourism?
International guidelines, such as the Declaration of Istanbul, provide a framework for ethical practices in organ transplantation. These guidelines promote transparency, prevent organ trafficking, and ensure equitable access to transplantation services. Adhering to these guidelines helps ensure ethical and safe transplant tourism.
5. What is the Declaration of Istanbul and its Significance?
The Declaration of Istanbul is a global ethical framework aimed at combating organ trafficking and transplant commercialism. It sets forth principles and guidelines for ethical practices in organ donation and transplantation, promoting transparency, preventing exploitation, and ensuring equitable access to transplantation services worldwide.
5.1 What are the Key Principles of the Declaration of Istanbul?
The key principles include:
- Prohibition of Commercialisation: Organs should not be treated as commodities.
- Prevention of Organ Trafficking: Measures to combat illegal organ trade.
- Protection of Vulnerable Donors: Ensuring donors are not coerced or exploited.
- Transparency and Traceability: Clear documentation and tracking of organ donation and transplantation processes.
- Equitable Access: Fair distribution of organs to all patients in need.
5.2 How Does the Declaration Address Transplant Tourism?
The Declaration addresses transplant tourism by:
- Defining Unethical Practices: Clearly defining what constitutes unethical transplant tourism, such as commercialisation and exploitation.
- Promoting National Self-Sufficiency: Encouraging countries to develop their own organ donation and transplantation programs to reduce the need for patients to travel abroad.
- Encouraging International Cooperation: Fostering collaboration between countries to combat organ trafficking and promote ethical practices.
5.3 How Can Patients Ensure Their Transplant Complies with the Declaration?
Patients can ensure compliance by:
- Choosing Accredited Centers: Selecting transplant centers that adhere to international guidelines and ethical standards.
- Seeking Transparent Information: Asking detailed questions about organ sourcing, donor consent, and the center’s ethical policies.
- Consulting Medical Professionals: Seeking advice from doctors and transplant specialists who are familiar with the Declaration of Istanbul.
6. What are the Laws and Regulations Governing Transplant Tourism?
Laws and regulations governing transplant tourism vary by country, but many nations have laws prohibiting commercial organ transplantation and organ trafficking. These laws aim to protect vulnerable populations, prevent exploitation, and ensure ethical practices in organ donation and transplantation.
6.1 How Do Different Countries Regulate Transplant Tourism?
- United States: The National Organ Transplant Act prohibits the sale of human organs.
- European Union: The EU Directive on Organ Transplantation sets standards for quality and safety and prohibits commercialisation.
- Canada: The Human Organ Donation and Transplantation Act prohibits the purchase and sale of organs.
- Australia: Similar laws prohibit commercial organ transplantation.
- Vietnam: The Law on Donation, Removal and Transplantation of Human Tissues and Organs prohibits commercial activities related to organ transplantation.
6.2 What are the Legal Consequences of Engaging in Illegal Transplant Activities?
Legal consequences can include:
- Criminal Charges: Involvement in organ trafficking can lead to imprisonment and hefty fines.
- Civil Liability: Lawsuits for damages related to unethical practices.
- Professional Sanctions: Medical professionals involved in illegal activities may face license revocation.
- Travel Restrictions: Restrictions on international travel for individuals involved in organ trafficking.
6.3 How Can You Ensure Your Transplant Tourism is Legal?
Ensure legality by:
- Consulting Legal Experts: Seek advice from lawyers specializing in international healthcare law.
- Choosing Compliant Centers: Select transplant centers that adhere to all relevant national and international laws.
- Documenting Everything: Keep detailed records of all medical and financial transactions related to your transplant.
7. What is the Role of Transplant Centers in Promoting Ethical Practices?
Transplant centers play a crucial role in promoting ethical practices by adhering to international guidelines, ensuring transparency, and protecting the rights and welfare of both donors and recipients. Their commitment to ethical standards helps prevent exploitation and fosters trust in the transplant process.
7.1 How Can Transplant Centers Ensure Ethical Organ Sourcing?
Transplant centers can ensure ethical organ sourcing by:
- Establishing Robust Protocols: Implementing strict protocols to verify donor consent and prevent coercion.
- Working with Reputable Organizations: Collaborating with organizations that promote ethical organ donation.
- Transparency: Providing clear and transparent information about organ sourcing practices.
- Regular Audits: Conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with ethical and legal standards.
7.2 What Measures Should Centers Take to Protect Vulnerable Donors?
Measures to protect vulnerable donors include:
- Thorough Screening: Conducting comprehensive medical and psychological evaluations to assess donor suitability.
- Independent Advocacy: Providing donors with independent advocates to ensure their rights are protected.
- Financial Safeguards: Ensuring donors are not exploited for financial gain.
- Post-Donation Support: Offering long-term medical and psychological support to donors.
7.3 How Can Centers Ensure Transparency in the Transplant Process?
Transparency can be ensured by:
- Providing Detailed Information: Giving patients comprehensive information about the transplant process, risks, and outcomes.
- Open Communication: Maintaining open communication with patients and their families.
- Data Reporting: Publicly reporting data on transplant outcomes and ethical practices.
- Ethical Oversight: Establishing ethics committees to oversee transplant practices and address ethical concerns.
8. How Can Patients Advocate for Ethical Transplant Tourism?
Patients can advocate for ethical transplant tourism by educating themselves, supporting reputable organizations, and demanding transparency from transplant centers. By making informed choices and promoting ethical practices, patients can help combat organ trafficking and ensure fair access to transplantation for all.
8.1 What Questions Should Patients Ask Their Doctors About Transplant Options?
Patients should ask their doctors:
- Risks and Benefits: What are the potential risks and benefits of transplant tourism?
- Ethical Considerations: What ethical considerations should I be aware of?
- Accredited Centers: Can you recommend accredited transplant centers?
- Legal Implications: What are the legal implications of seeking a transplant abroad?
- Follow-Up Care: How will follow-up care be managed after the transplant?
8.2 How Can Patients Support Ethical Transplant Organizations?
Support ethical organizations by:
- Donating: Contributing financially to organizations that combat organ trafficking.
- Volunteering: Offering your time and skills to support their mission.
- Raising Awareness: Educating others about ethical transplant practices.
- Advocating: Supporting policies that promote ethical organ donation and transplantation.
8.3 What Steps Can Patients Take to Report Suspected Unethical Practices?
Steps to report suspected unethical practices include:
- Contacting Regulatory Bodies: Reporting concerns to national and international regulatory agencies.
- Informing Medical Professionals: Sharing information with your doctor or transplant specialist.
- Documenting Evidence: Gathering and preserving any evidence of unethical practices.
- Seeking Legal Advice: Consulting with a lawyer specializing in healthcare law.
9. What Resources are Available to Learn More About Transplant Ethics?
Numerous resources are available to learn more about transplant ethics, including academic research, international guidelines, and organizations dedicated to promoting ethical practices. These resources can help patients, healthcare professionals, and policymakers make informed decisions and advocate for ethical transplantation.
9.1 What are Some Key Publications on Transplant Ethics?
Key publications include:
- The Declaration of Istanbul on Organ Trafficking and Transplant Tourism
- World Health Organization (WHO) Guiding Principles on Human Cell, Tissue and Organ Transplantation
- Articles in peer-reviewed medical journals such as Transplantation and American Journal of Transplantation.
9.2 What Organizations Promote Ethical Transplant Practices?
Organizations include:
- The Transplantation Society (TTS)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- American Society of Transplantation (AST)
- Declaration of Istanbul Custodian Group (DICG)
9.3 What Websites Offer Information on Transplant Ethics and Regulations?
Websites include:
- WHO (World Health Organization): www.who.int
- TTS (The Transplantation Society): www.tts.org
- AST (American Society of Transplantation): www.myast.org
- DICG (Declaration of Istanbul Custodian Group): www.declarationofistanbul.org
10. How Can SIXT.VN Assist You in Ethical Medical Travel?
SIXT.VN is committed to supporting ethical medical travel by providing reliable and transparent services for patients seeking medical treatment in Vietnam. We ensure our services align with ethical standards, offering you a safe and trustworthy experience.
10.1 What Travel Services Does SIXT.VN Offer for Medical Tourists?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services, including:
- Airport Transfers: Safe and reliable transportation from the airport to your hotel or medical facility.
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358.
- Hotel Booking: Assistance in finding accommodations that meet your specific needs and preferences.
- Tour Services: Opportunities to explore Hanoi and its surroundings while adhering to your medical schedule.
10.2 How Does SIXT.VN Ensure Ethical Practices in its Services?
We ensure ethical practices by:
- Partnering with Reputable Providers: Collaborating with hotels and transportation services that adhere to ethical standards.
- Transparency: Providing clear and accurate information about our services and fees.
- Support: Offering dedicated support to address your concerns and ensure a safe and ethical experience.
10.3 What Steps Can You Take to Plan Your Medical Trip with SIXT.VN?
To plan your medical trip with SIXT.VN:
- Contact Us: Reach out through our website or hotline to discuss your needs.
- Website: SIXT.VN.
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358.
- Consultation: Receive personalized assistance in planning your travel arrangements.
- Booking: Secure your airport transfers, hotel accommodations, and tours with our transparent and reliable services.
By choosing SIXT.VN, you can ensure your medical travel is not only convenient and comfortable but also aligned with the highest ethical standards.
Navigating the world of transplant tourism requires a deep understanding of transplant tourism ethics, adherence to international guidelines, and support from reputable organizations and service providers. SIXT.VN is here to assist you every step of the way, ensuring your journey is safe, ethical, and aligned with your values.
FAQ: Transplant Tourism Ethics
1. Is transplant tourism always unethical?
Not always. It becomes unethical when it involves organ trafficking, commercialisation, or exploitation of vulnerable populations.
2. What is the Declaration of Istanbul?
A global ethical framework aimed at combating organ trafficking and transplant commercialism.
3. How can I verify the legitimacy of a transplant program?
Check for accreditation from reputable organizations and consult medical professionals.
4. What are the health risks associated with transplant tourism?
Increased risks of infections, poor surgical outcomes, and lack of follow-up care.
5. What questions should I ask a potential transplant center?
Inquire about accreditation, organ sourcing, donor consent, and patient outcomes.
6. What laws govern transplant tourism?
Vary by country, but many prohibit commercial organ transplantation and organ trafficking.
7. How can transplant centers ensure ethical organ sourcing?
By establishing robust protocols, working with reputable organizations, and ensuring transparency.
8. How can patients advocate for ethical transplant tourism?
By educating themselves, supporting ethical organizations, and demanding transparency.
9. What resources are available to learn more about transplant ethics?
Key publications, organizations, and websites dedicated to promoting ethical practices.
10. How can SIXT.VN assist with ethical medical travel?
By providing reliable and transparent travel services, partnering with reputable providers, and ensuring ethical practices in our services.



