The tourism multiplier effect is a powerful concept showing how tourist spending ripples through a local economy, and SIXT.VN understands its importance in Vietnam. This effect goes beyond initial transactions, creating jobs, boosting various sectors, and fostering community growth. Ready to explore Vietnam and contribute to its vibrant economy? SIXT.VN offers seamless travel experiences, from airport transfers to curated tours. Discover Vietnam’s hidden gems and be part of the positive economic cycle with reliable transport, comfortable accommodations, and unforgettable sightseeing adventures.
1. Understanding the Tourism Multiplier Effect
The tourism multiplier effect signifies how many times money spent by a tourist circulates within a country’s economy, amplifying its initial value. In essence, it illustrates the broader economic repercussions of tourism beyond the direct expenses incurred by visitors. This effect is crucial for grasping the complete influence of tourism on a region or nation.
When tourists spend money, a ripple effect is triggered, stimulating economic activity across diverse sectors. This multiplier effect can be quantified by assessing the direct and indirect consequences of tourism on the economy. According to research from the World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC), in 2022, the global tourism sector contributed $7.6 trillion to the global economy, highlighting the significant impact of tourist spending.
The multiplier effect arises because tourist expenditures not only benefit businesses directly catering to them but also permeate the broader local economy. This phenomenon is evident across a spectrum of industries, encompassing transportation, lodging, food and beverage, and retail. For example, when tourists dine at local restaurants, they not only support the restaurant owners and staff but also contribute to the income of local farmers and suppliers who provide the ingredients.
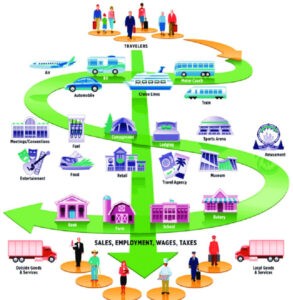 Tourism Multiplier Effect
Tourism Multiplier Effect
The tourism multiplier effect holds particular significance for countries heavily reliant on tourism as a revenue source. For instance, tourism constitutes a substantial portion of the GDP of destinations such as the Maldives and the Bahamas. Michigan State University reported in 2023 that tourism accounts for over 28% of the GDP of Maldives. Similarly, the International Trade Administration (ITA) noted in 2022 that tourism and related services contribute approximately 70 percent to the GDP of Bahamas and employ over half of the workforce. Consequently, policymakers and stakeholders in the tourism industry must comprehend the tourism multiplier effect.
2. What Are the Types of Tourism Multipliers?
There are primarily two types of tourism multipliers: direct and indirect. Direct multipliers encompass the initial spending by tourists, including expenses on accommodation, food, transportation, and activities. Indirect multipliers, on the other hand, refer to the subsequent spending by businesses that supply goods and services to the tourism sector.
- Direct Multipliers: These represent the immediate economic impact of tourist spending. For example, the money spent on a hotel room directly benefits the hotel, its employees, and its suppliers.
- Indirect Multipliers: These capture the knock-on effects of tourist spending. For instance, a hotel that purchases food from a local supplier generates indirect economic activity for that supplier.
For instance, a hotel purchasing food from a local supplier generates indirect economic activity for the supplier. This can lead to increased sales, hiring of additional staff, and enhanced tax revenue for the local government during peak tourism seasons.
The tourism multiplier effect also engenders induced multipliers, reflecting spending by employees and business owners benefiting from the direct and indirect impacts of tourism. For instance, a hotel employee earning a salary spends money on goods and services, fostering additional economic activities. This induced spending further amplifies the economic benefits of tourism.
3. How Does Tourism Impact Local Businesses Economically?
The tourism industry exerts a substantial influence on local businesses. Tourist spending on goods and services generates income for these businesses, which can then be reinvested into the local economy, fostering a multiplier effect that spurs economic growth. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that the tourism industry can also pose challenges to local businesses.
- Positive Impacts: Increased revenue, job creation, and infrastructure development.
- Negative Impacts: Potential displacement of small businesses by larger chains and increased competition.
The tourism industry can significantly impact local businesses both positively and negatively. According to a study by the United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) in 2019, tourism can increase local businesses’ revenue by 20-40% during peak seasons. However, the same study also noted that increased competition from international chains could negatively impact smaller, local businesses.
For example, the influx of tourists can strain resources and infrastructure, potentially leading to negative consequences for local communities. Therefore, policymakers must carefully consider the benefits and costs of tourism to ensure minimal adverse effects on local businesses and the environment.
4. How Does the Tourism Industry Create Jobs?
The tourism industry stands as a significant employment source for numerous countries, sometimes serving as the primary source. The jobs created span from low-skilled to high-skilled positions, encompassing roles such as tour guides, hotel managers, and chefs. These positions provide opportunities for individuals with varying levels of education and skills.
- Variety of Roles: Opportunities range from entry-level positions to management roles.
- Skill Development: The industry fosters skills in customer service, hospitality, and language proficiency.
The number of jobs generated by tourism hinges on the level and type of tourism activities. For instance, a large-scale resort may create thousands of jobs, while a small bed and breakfast may only generate a few. According to IBISWorld data from 2023, the total number of tourism employees in the USA is approximately 6 million. Similarly, tourism supports around 3.8 million jobs in the UK.
According to the U.S. Travel Association, tourism directly and indirectly supports 15.8 million jobs in the United States, accounting for nearly 10% of total U.S. employment. These statistics underscore the vital role of tourism in driving employment and economic prosperity.
5. Can Tourism Lead to Community Development?
Tourism can indeed foster community development by generating income and creating jobs, which can then be utilized to enhance infrastructure, support local businesses, and invest in community projects. For instance, a city attracting a substantial number of tourists may allocate tax revenue generated from tourism to improve public transportation or construct new community facilities.
- Infrastructure Improvement: Tourism revenue can fund better roads, public transportation, and utilities.
- Support for Local Businesses: Increased tourism can help local businesses thrive.
- Community Projects: Tourism revenue can be invested in schools, parks, and other community amenities.
Tourism can also exert a cultural influence on local communities by promoting cultural exchange and understanding as tourists learn about local customs and traditions. This can aid in preserving and promoting local culture, yielding positive impacts on the community. A study by the World Bank in 2018 found that communities actively involved in tourism development experience increased social cohesion and improved quality of life.
However, it’s crucial to manage tourism sustainably to avoid negative impacts such as cultural commodification or environmental degradation. Responsible tourism practices can ensure that communities benefit from tourism while preserving their cultural heritage and natural resources.
6. How Does Tourism Affect the Environment?
Tourism can have both positive and negative environmental impacts. On the positive side, it can promote conservation and protection of natural resources. For example, a national park attracting tourists may receive funding for conservation efforts, aiding in preserving the park’s ecosystem.
- Positive Impacts: Funding for conservation, increased awareness of environmental issues.
- Negative Impacts: Pollution, habitat destruction, resource depletion.
However, tourism can also negatively impact the environment. The construction of new hotels and resorts can lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution. Additionally, tourists can contribute to environmental degradation by generating waste and consuming natural resources.
Therefore, the tourism industry must embrace sustainable practices to minimize its environmental impact. This includes reducing waste, conserving energy, and protecting natural habitats. According to a report by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) in 2020, sustainable tourism practices can reduce the negative environmental impact of tourism by up to 50%.
7. How Can the Tourism Multiplier Effect Be Measured?
Measuring the tourism multiplier effect can be challenging due to the involvement of multiple factors. However, several methods can be employed, including input-output analysis, employment multipliers, and value-added multipliers.
- Input-Output Analysis: This method examines the flow of money through the local economy to determine the direct and indirect impacts of tourism spending on local businesses.
- Employment Multipliers: These measure the number of jobs created by a given level of tourism spending, allowing for the estimation of tourism’s employment impact in a specific area.
- Value-Added Multipliers: These measure the additional income generated by a given level of tourism spending, providing an estimate of tourism’s overall economic impact in a particular area.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), input-output analysis is the most comprehensive method for measuring the tourism multiplier effect, as it captures both direct and indirect impacts across various sectors of the economy.
These methods offer valuable insights into the economic impact of tourism, enabling policymakers and stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding tourism development and management.
8. Examples of the Tourism Multiplier Effect in Action
Numerous countries and regions have successfully leveraged the tourism multiplier effect to stimulate economic growth and promote community development.
- London: Tourism and the night-time economy contribute £36 billion a year to London’s economy overall and employ 700,000 people, according to the Greater London Authority (2023).
- United States: The tourism industry has been a significant contributor to the economic growth of the USA, creating jobs and stimulating economic activities in various sectors, such as agriculture, transportation, and retail. It has contributed nearly $1.3 trillion to the GDP (Statista, 2022).
- Canada: The tourism industry contributes around 19.96 billion Canadian dollars to Canada’s GDP.
- Australia: Australia’s direct tourism gross domestic product reached around 35.14 billion Australian dollars in 2022.
- Costa Rica: Costa Rica has developed a sustainable tourism industry that promotes conservation and community development. Its tourism industry generates significant income and employment opportunities while protecting its natural resources.
- Iceland: Iceland has developed a tourism industry that promotes its unique natural features, such as geysers, glaciers, and hot springs. Its tourism industry has created jobs and generated income while promoting sustainable tourism practices.
These examples demonstrate the potential of tourism to drive economic growth and improve the quality of life for local communities. By implementing sustainable tourism practices and investing in tourism infrastructure, countries and regions can maximize the benefits of tourism while minimizing its negative impacts.
9. What Are the Limitations of the Tourism Multiplier?
One of the primary challenges associated with tourism is economic leakage. This occurs when international companies provide hotel accommodations, flights, car rentals, food, and excursions at a destination, and a significant portion of the revenue generated from these activities exits the destination to the country where their headquarters are located.
- Economic Leakage: Revenue generated by tourism often leaves the local economy.
- Dependence on External Factors: Tourism can be vulnerable to economic downturns, natural disasters, and political instability.
- Seasonality: Many tourism destinations experience seasonal fluctuations in tourist arrivals, leading to economic instability.
Faith (2023) reports that 80% of the revenue generated from tourism activities goes away from the local communities to foreign countries. This highlights how local communities, intended to benefit from tourism multiplier effects, do not optimally benefit.
To mitigate economic leakage and maximize the benefits of tourism for local communities, it is essential to promote local businesses, encourage tourists to purchase locally made products and services, and invest in tourism infrastructure that supports local employment and economic development.
10. SIXT.VN: Your Gateway to Experiencing Vietnam’s Tourism Multiplier Effect
Planning your dream trip to Vietnam? SIXT.VN is your reliable partner for seamless and enriching travel experiences. By choosing SIXT.VN, you’re not just booking a service; you’re actively contributing to the local economy and supporting the tourism multiplier effect.
- Convenient Airport Transfers: Start your journey stress-free with SIXT.VN’s reliable airport transfer services, ensuring a smooth transition from the airport to your accommodation.
- Comfortable Hotel Bookings: Choose from a wide range of hotels that suit your budget and preferences, all while supporting local businesses and communities.
- Exciting Tour Packages: Explore the wonders of Hanoi and beyond with SIXT.VN’s curated tour packages, designed to immerse you in the rich culture and history of Vietnam.
Why Choose SIXT.VN?
- Convenience: Easy online booking and 24/7 customer support.
- Reliability: Trusted services with a proven track record.
- Local Support: By using SIXT.VN, you directly support local businesses and contribute to the sustainable growth of Vietnam’s tourism industry.
Ready to experience the magic of Vietnam and be part of the positive economic cycle? Visit SIXT.VN today and start planning your unforgettable adventure. With SIXT.VN, your journey will not only be memorable but also contribute to the prosperity of local communities, embodying the true essence of the tourism multiplier effect.
Contact Information:
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About the Tourism Multiplier Effect
1. What exactly is the tourism multiplier effect?
The tourism multiplier effect refers to the ripple effect of tourist spending within a local economy. It’s how many times money spent by a tourist circulates in the country’s economy, creating jobs, stimulating economic growth, and promoting community development.
2. How does tourist spending contribute to the economy?
Tourist spending supports businesses directly and indirectly. Direct spending includes accommodation, food, and transportation, while indirect spending involves businesses that supply goods and services to the tourism industry.
3. What are the different types of tourism multipliers?
The two main types are direct and indirect multipliers. Direct multipliers refer to the initial spending by tourists, while indirect multipliers refer to the subsequent spending by businesses that supply goods and services to the tourism industry.
4. How can tourism benefit local businesses?
Tourism can increase revenue for local businesses, leading to reinvestment in the local economy, job creation, and infrastructure development.
5. What are the potential negative impacts of tourism on local businesses?
Negative impacts include increased competition from larger chains, potential displacement of small businesses, and strain on local resources.
6. How does the tourism industry create jobs?
The tourism industry offers a wide range of jobs, from low-skilled to high-skilled positions, providing opportunities for individuals with varying levels of education and skills.
7. Can tourism lead to community development?
Yes, tourism can foster community development by generating income and creating jobs, which can then be used to enhance infrastructure, support local businesses, and invest in community projects.
8. What are the environmental impacts of tourism?
Tourism can have both positive and negative environmental impacts. It can promote conservation efforts but also lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution if not managed sustainably.
9. How can the tourism multiplier effect be measured?
The tourism multiplier effect can be measured using methods such as input-output analysis, employment multipliers, and value-added multipliers, which help assess the economic impact of tourism.
10. What is economic leakage in the context of tourism?
Economic leakage occurs when revenue generated from tourism activities goes away from the local communities to foreign countries, often through international companies providing services like hotels and tours.
References:
- Byju’s. (2023). What is the tourism multiplier effect? Available at: https://byjus.com/ias-questions/what-is-the-tourism-multiplier-effect/ (accessed 02 April 2023)
- Faith, S. (2023). Tourism’s dirty secret. Available at: https://www.euronews.com/travel/2023/02/26/tourisms-dirty-secret-what-is-tourism-leakage-and-how-can-you-avoid-contributing-to-it (accessed 01 April 2023)
- Greater London Authority. (2023). Supporting the tourism sector. Available at: https://www.london.gov.uk/programmes-strategies/business-and-economy/supporting-londons-sectors/supporting-tourism-sector (accessed 02 April 2023)
- IBISWorld. (2023). Tourism in the USA. https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/employment/tourism-united-states/ (accessed 02 April 2023)
- ITA. (2022). Bahamas- the country economic guide. Available at: https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/bahamas-market-overview# (accessed 03 April 2023)
- Michigan State University. (2023). Maldives economy. Available at: https://globaledge.msu.edu/countries/maldives/economy (accessed 03 April 2023)
- Statista. (2022). Total contribution of travel and tourism to the gross domestic product in the United States. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/292518/contribution-of-travel-and-tourism-to-gdp-in-us-time-series/ (accessed 03 April 2023)
- United Nations World Tourism Organization (UNWTO)
- U.S. Travel Association
- U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA)
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- World Bank
- World Travel & Tourism Council (WTTC)



