A marketing plan for a tourism company is a comprehensive strategy that outlines your company’s current market position, your objectives for the future, and the specific steps you’ll take to achieve those objectives. SIXT.VN understands that in the vibrant and competitive tourism landscape of Vietnam, a well-crafted marketing plan is essential for success. Let’s dive into how to create a compelling marketing plan and see how it can boost your tourism business, attracting more visitors to explore the wonders of Vietnam.
1. Conduct a Thorough SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is a critical first step, identifying your tourism company’s Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This foundational analysis will help you understand your current position and guide your strategic decisions.
-
What is SWOT Analysis? SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the internal and external factors that can affect a project or business venture. It provides a structured approach to assessing these elements, helping organizations make informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
- Strengths: Internal attributes that give your organization an advantage.
- Weaknesses: Internal attributes that put your organization at a disadvantage.
- Opportunities: External factors that your organization could exploit to its advantage.
- Threats: External factors that could cause trouble for your organization.
 SWOT analysis grid
SWOT analysis grid -
How to Conduct a SWOT Analysis?
-
Gather a Diverse Team: Include representatives from different departments to gain varied perspectives.
-
Brainstorm: Answer specific questions related to each element:
- Strengths: What does your tourism company excel at? What do visitors appreciate most about your offerings?
- Weaknesses: Which areas need improvement? What do competitors do better?
- Opportunities: Are there underserved markets you can target? Are there emerging travel trends you can capitalize on?
- Threats: Are there new regulations that could impact your business? How are competitors evolving?
-
Summarize in a SWOT Grid: Organize your findings into a 2×2 grid for a clear visual overview.
-
1.1 Strengths: Leveraging What You Do Best
-
What are Strengths? Strengths are internal positive attributes that give your tourism company a competitive edge. These can include tangible resources, unique capabilities, or positive characteristics that differentiate you from competitors.
-
Examples of Strengths in Tourism:
- Prime Location: A hotel located in a popular tourist destination has a significant advantage.
- Unique Experiences: Offering exclusive tours or activities that competitors don’t provide.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Consistent positive reviews and high customer satisfaction ratings.
- Strong Brand Reputation: A well-established and trusted brand name.
- Skilled Staff: Experienced and knowledgeable staff who can provide excellent service.
For example, if your tour company specializes in eco-tourism in the Mekong Delta, highlight your knowledgeable guides, sustainable practices, and unique access to remote areas.
-
How to Maximize Strengths?
- Identify and Document: Conduct a thorough assessment to identify all your company’s strengths.
- Leverage in Marketing: Emphasize your strengths in your marketing messages to attract customers.
- Invest and Enhance: Continuously invest in and improve your strengths to maintain your competitive advantage.
- Integrate into Strategy: Incorporate your strengths into your overall business strategy to drive success.
1.2 Weaknesses: Addressing Areas for Improvement
-
What are Weaknesses? Weaknesses are internal negative attributes that put your tourism company at a disadvantage. These are areas where you need to improve to remain competitive.
-
Examples of Weaknesses in Tourism:
- Poor Online Presence: An outdated website or ineffective social media strategy.
- Lack of Differentiation: Offering similar experiences to many other companies.
- High Prices: Pricing that is significantly higher than competitors without a clear justification.
- Negative Reviews: Consistent complaints about specific aspects of your service.
- Limited Resources: Insufficient funding or staff to effectively market your business.
For example, if your hotel suffers from outdated facilities, acknowledge this and plan renovations or focus on marketing other strengths like exceptional service or a prime location.
-
How to Mitigate Weaknesses?
- Acknowledge and Prioritize: Identify and prioritize your weaknesses based on their impact on your business.
- Develop Improvement Plans: Create specific plans to address each weakness, with clear goals and timelines.
- Seek External Support: Consider hiring consultants or trainers to help improve areas where you lack expertise.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly track your progress and adjust your plans as needed.
1.3 Opportunities: Capitalizing on External Trends
-
What are Opportunities? Opportunities are external factors that your tourism company can exploit to its advantage. These are trends, events, or changes in the market that can lead to new business prospects.
-
Examples of Opportunities in Tourism:
- Emerging Markets: Growing interest in travel to specific regions or countries.
- Technological Advancements: New technologies that can improve customer experience or operational efficiency.
- Changing Demographics: Shifts in the age, income, or lifestyle of target customers.
- Special Events: Major events like festivals, conferences, or sporting competitions that attract visitors.
- Government Initiatives: New policies or funding programs that support tourism development.
For example, with the increasing popularity of sustainable tourism, create eco-friendly tours and promote your company’s commitment to environmental conservation. According to research from the United Nations Environment Programme, in 2023, sustainable tourism grew by 30%, providing environmentally conscious services.
-
How to Capitalize on Opportunities?
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with industry news, trends, and market research.
- Be Proactive: Identify and evaluate potential opportunities before they become mainstream.
- Develop Strategies: Create specific strategies to take advantage of each opportunity.
- Allocate Resources: Invest resources in areas that align with promising opportunities.
1.4 Threats: Preparing for Potential Challenges
-
What are Threats? Threats are external factors that could cause trouble for your tourism company. These are challenges or obstacles that could negatively impact your business.
-
Examples of Threats in Tourism:
- Economic Downturns: Recessions or economic slowdowns that reduce travel spending.
- Increased Competition: New competitors entering the market or existing competitors becoming more aggressive.
- Changing Regulations: New laws or policies that increase costs or restrict business activities.
- Natural Disasters: Events like hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods that disrupt travel.
- Geopolitical Instability: Political unrest or terrorism that deters tourists from visiting certain areas.
For example, monitor the impact of new travel regulations and adjust your marketing strategies to address potential concerns or offer alternative destinations.
-
How to Prepare for Threats?
- Identify Potential Threats: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential threats.
- Develop Contingency Plans: Create backup plans to mitigate the impact of each threat.
- Diversify Markets: Reduce your reliance on a single market by targeting multiple customer segments.
- Build Resilience: Strengthen your company’s financial and operational resilience to withstand challenges.
2. Define Your Unique Value Proposition
Your value proposition is a clear statement that explains why customers should choose your tourism company over the competition. It highlights the unique benefits and value you offer.
-
What is a Value Proposition? A value proposition is a clear and concise statement that communicates the unique benefits and value a customer receives from using a company’s products or services. It explains how you solve customers’ problems or improve their situation better than the alternatives.
-
Key Elements of a Strong Value Proposition:
- Relevance: Explains how your product or service solves a customer’s problem or need.
- Quantified Value: Delivers specific benefits (e.g., saves time, reduces costs, improves performance).
- Differentiation: Highlights what makes your offering unique and better than competitors.
-
Examples of Value Propositions in Tourism:
- Luxury Hotels: “Experience unparalleled luxury and personalized service in the heart of Hanoi.”
- Adventure Tours: “Embark on thrilling adventures and discover Vietnam’s hidden gems with our expert guides.”
- Budget Hostels: “Enjoy affordable, comfortable accommodation and meet fellow travelers in a vibrant social atmosphere.”
- SIXT.VN: “Effortless travel solutions for exploring Vietnam, with reliable airport transfers, comfortable accommodations, and unforgettable tours.”
For instance, if your tour company specializes in cultural immersion experiences, your value proposition might be: “Experience the authentic culture of Vietnam through immersive tours led by local experts.”
-
How to Develop a Compelling Value Proposition?
- Identify Your Target Audience: Understand their needs, pain points, and desires.
- List Your Features and Benefits: Create a comprehensive list of what you offer and the resulting benefits.
- Connect Features to Benefits: Explain how each feature solves a specific customer problem or need.
- Highlight Differentiation: Identify what makes your offering unique and better than competitors.
- Craft a Concise Statement: Write a clear and compelling statement that summarizes the value you provide.
 Value proposition chart
Value proposition chart
3. Create Detailed Guest Personas
Guest personas are fictional representations of your ideal customers. They help you understand your target audience’s motivations, behaviors, and preferences, allowing you to tailor your marketing efforts effectively.
-
What is a Guest Persona? A guest persona is a detailed profile of a fictional character that represents your ideal customer. It includes demographic information, psychographic traits, behaviors, and motivations.
-
Why Create Guest Personas?
- Personalized Marketing: Tailor your marketing messages to resonate with specific customer segments.
- Targeted Advertising: Identify the best channels and platforms to reach your ideal customers.
- Product Development: Develop products and services that meet the specific needs of your target audience.
-
Key Elements of a Guest Persona:
- Demographics: Age, gender, location, income, education, occupation.
- Psychographics: Interests, hobbies, values, lifestyle, attitudes.
- Behaviors: Online behavior, travel habits, booking preferences.
- Motivations: Reasons for traveling, goals for their trip, pain points.
-
Examples of Guest Personas in Tourism:
- Solo Traveler Sarah: A young professional who enjoys solo adventures and cultural experiences.
- Family Fun Frank: A parent who seeks family-friendly activities and comfortable accommodations.
- Budget Backpacker Ben: A student who looks for affordable travel options and social experiences.
- Corporate Catrina: A business traveler who needs convenient accommodations and efficient services.
For example, create a persona for “Luxury Seeker Linh,” a high-income traveler who values exclusive experiences, personalized service, and high-end accommodations.
-
How to Create Effective Guest Personas?
- Collect Data: Gather data from booking records, customer surveys, social media insights, and website analytics.
- Identify Common Traits: Look for common patterns and characteristics among your customers.
- Develop Persona Profiles: Create detailed profiles for each persona, including a name, photo, and background story.
- Share and Utilize Personas: Share your personas with your marketing team and use them to guide your marketing strategies.
4. Develop a Comprehensive Competitor Profile
Understanding your competitors is essential for identifying opportunities and threats in the market. A competitor profile provides detailed insights into your rivals’ strengths, weaknesses, and strategies.
-
What is a Competitor Profile? A competitor profile is a detailed analysis of your key competitors, including their strengths, weaknesses, marketing strategies, and customer base.
-
Why Create Competitor Profiles?
- Identify Opportunities: Spot gaps in the market that your company can fill.
- Assess Threats: Understand potential challenges and prepare for competitive actions.
- Improve Strategies: Learn from your competitors’ successes and mistakes.
-
Key Elements of a Competitor Profile:
- Company Overview: Basic information about the company, including its history, mission, and values.
- Products and Services: Detailed description of their offerings, including pricing and features.
- Target Market: Analysis of their customer base and target segments.
- Marketing Strategies: Evaluation of their marketing channels, messaging, and promotional activities.
- Strengths and Weaknesses: Assessment of their key advantages and disadvantages.
- Customer Reviews: Analysis of customer feedback and ratings on review sites and social media.
-
How to Create Detailed Competitor Profiles?
- Identify Key Competitors: List your main competitors in the market.
- Gather Information: Collect data from their websites, social media, marketing materials, and customer reviews.
- Analyze Data: Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, and strategies.
- Create Profiles: Develop detailed profiles for each competitor, summarizing your findings.
- Monitor Regularly: Continuously track their activities and update your profiles as needed.
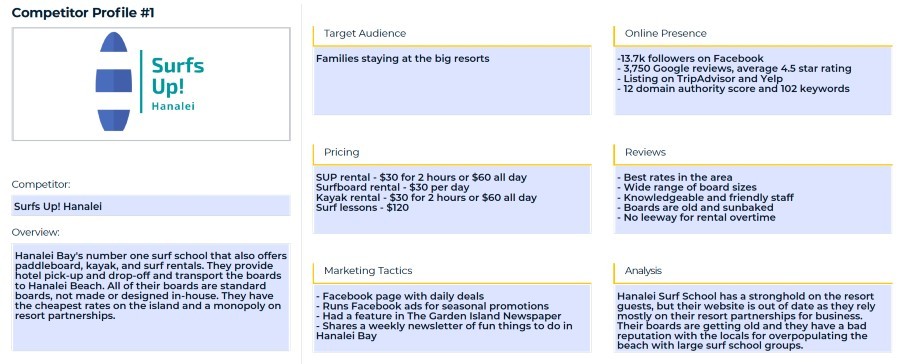 Competitor profile of a tourism company
Competitor profile of a tourism company
5. Craft a Strategic Tourism Marketing Mix (8Ps)
A tourism marketing mix is a combination of factors you can control to influence a guest’s decision to book with you. Think of it as a broad guideline for how to market travel and tours so that everything works together seamlessly.
Historically, there are 7ps of tourism marketing, but since tourism operators are unique in the products and services they provide, we’ve stretched it to include eight.
What is a Tourism Marketing Mix?
5.1 Product: Define Your Experiences
The experiences you offer and what’s included. Take note of everything that would go into the product description, such as duration, itinerary, special features, and other important details.
-
What is “Product” in the Marketing Mix? In the marketing mix, “Product” refers to what you are offering to your target market. In the context of tourism, this includes the experiences, services, and amenities that you provide to your customers.
-
Key Aspects of the “Product” Element:
- Experiences: The tours, activities, and events that you offer.
- Services: The level of customer support, convenience, and customization you provide.
- Amenities: The facilities, resources, and extras that enhance the customer experience.
- Quality: The standard of excellence and reliability of your offerings.
-
Examples of “Product” in Tourism:
- Accommodation: Hotels, resorts, hostels, and guesthouses.
- Tours: Guided excursions, adventure activities, and cultural experiences.
- Transportation: Airport transfers, rental cars, and shuttle services.
- Dining: Restaurants, cafes, and food tours.
- Events: Festivals, concerts, and sporting competitions.
For instance, a tour company might offer a unique “Ha Long Bay Cruise with Kayaking and Cave Exploration” as its product.
-
How to Optimize the “Product” Element?
- Understand Customer Needs: Identify what your target audience wants and expects from their travel experiences.
- Design Differentiated Offerings: Create unique and compelling products that stand out from the competition.
- Ensure Quality and Consistency: Maintain high standards and deliver consistent experiences to build trust and loyalty.
- Innovate and Update: Continuously improve and update your products to stay relevant and exciting.
- Gather Customer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement.
5.2 Place: Where to Book Your Services
Where people can book your experiences. Traditionally, that would be your ticket office or travel agents, but there are now countless ways people can book — OTAs, email, chatbots, Facebook, your website. Figure out the number one place you want to direct prospects.
-
What is “Place” in the Marketing Mix? In the marketing mix, “Place” refers to the distribution channels and locations where your products or services are available to customers. It’s about making your offerings accessible and convenient to your target market.
-
Key Aspects of the “Place” Element:
- Distribution Channels: The methods through which customers can book or purchase your services (e.g., online, travel agencies, direct sales).
- Location: The physical or virtual locations where your products are offered.
- Accessibility: How easy it is for customers to find and access your products.
- Coverage: The extent to which your products are available in different markets and regions.
-
Examples of “Place” in Tourism:
- Online Booking Platforms: Your website, online travel agencies (OTAs) like Booking.com and Expedia.
- Physical Locations: Travel agencies, tour operator offices, hotel front desks.
- Mobile Apps: Dedicated apps for booking and managing travel services.
- Partnerships: Collaborations with other businesses to expand distribution reach.
For instance, SIXT.VN focuses on providing convenient online booking and airport transfer services to ensure easy access for international visitors.
-
How to Optimize the “Place” Element?
- Identify Key Distribution Channels: Determine the channels where your target audience is most likely to book their travel services.
- Optimize Online Presence: Ensure your website is user-friendly, mobile-responsive, and search engine optimized.
- Establish Partnerships: Collaborate with travel agencies, tour operators, and other businesses to expand your reach.
- Offer Multiple Booking Options: Provide various ways for customers to book, including online, phone, and in-person options.
- Ensure Seamless Integration: Integrate your booking system with other systems to streamline operations and improve customer experience.
5.3 Price: Finding the Right Balance
The price guests will pay based on the perceived value. Factor in what your competitors charge, how much it costs you to provide the experience, your revenue target, and where the market is heading.
-
What is “Price” in the Marketing Mix? In the marketing mix, “Price” refers to the amount of money customers are willing to pay for your products or services. It is a critical factor that affects your profitability, competitiveness, and customer perception.
-
Key Aspects of the “Price” Element:
- Pricing Strategy: The approach you use to set prices (e.g., cost-plus, competitive, value-based).
- Pricing Tactics: The specific techniques you use to adjust prices (e.g., discounts, promotions, dynamic pricing).
- Perceived Value: The customer’s perception of the benefits and quality of your offering relative to the price.
- Profitability: The extent to which your prices cover your costs and generate a profit.
-
Examples of “Price” in Tourism:
- Hotel Room Rates: Varying prices based on room type, season, and demand.
- Tour Packages: Bundled prices for tours, accommodation, and transportation.
- Entrance Fees: Charges for access to attractions, museums, and parks.
- Airline Tickets: Prices that fluctuate based on availability, time of booking, and destination.
For instance, a hotel might use dynamic pricing to adjust room rates based on real-time demand and competitor prices.
-
How to Optimize the “Price” Element?
- Understand Your Costs: Know your fixed and variable costs to set prices that cover your expenses and generate a profit.
- Analyze Competitor Pricing: Research what your competitors are charging to stay competitive.
- Determine Customer Value: Assess the perceived value of your products or services to set prices that customers are willing to pay.
- Implement a Pricing Strategy: Choose a pricing strategy that aligns with your business goals and target market.
- Monitor and Adjust Prices: Continuously monitor market conditions and adjust your prices as needed to maximize revenue and profitability.
5.4 Promotion: Getting the Word Out
How you’re going to get the word out. Look at what has worked well in the past, where you already have some traction, new social media opportunities, and the best content format for your target audience.
-
What is “Promotion” in the Marketing Mix? In the marketing mix, “Promotion” refers to the communication strategies and tactics you use to inform, persuade, and remind customers about your products or services. It’s about creating awareness, generating interest, and driving sales.
-
Key Aspects of the “Promotion” Element:
- Marketing Channels: The media and platforms you use to reach your target audience (e.g., social media, email, advertising).
- Marketing Messages: The content and information you communicate to your customers.
- Promotional Activities: The specific actions you take to promote your products (e.g., advertising, discounts, events).
- Communication Strategy: The overall plan for how you will communicate with your customers.
-
Examples of “Promotion” in Tourism:
- Social Media Marketing: Using platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok to engage with potential customers.
- Content Marketing: Creating informative and engaging content like blog posts, videos, and infographics.
- Email Marketing: Sending newsletters and promotional emails to subscribers.
- Advertising: Running online ads on search engines, social media, and travel websites.
- Public Relations: Building relationships with media outlets to generate positive coverage.
For instance, SIXT.VN uses social media marketing and targeted advertising to reach international visitors planning trips to Vietnam.
-
How to Optimize the “Promotion” Element?
- Identify Your Target Audience: Understand who you are trying to reach and what motivates them.
- Choose the Right Channels: Select the marketing channels that are most effective for reaching your target audience.
- Develop Compelling Messages: Create messages that resonate with your target audience and highlight the benefits of your products.
- Implement a Promotional Plan: Develop a detailed plan for your promotional activities, including timelines, budgets, and metrics.
- Measure and Analyze Results: Track the performance of your promotional activities and make adjustments as needed to improve effectiveness.
5.5 People: The Human Touch
The people who facilitate the experience. What are the standout qualities your staff has that align with your brand? What skills do your guides have that make the experience memorable, entertaining, and informative?
-
What is “People” in the Marketing Mix? In the marketing mix, “People” refers to the individuals who are involved in delivering your products or services to customers. It emphasizes the importance of employee skills, attitudes, and customer service in creating a positive customer experience.
-
Key Aspects of the “People” Element:
- Customer Service: The quality of interactions between employees and customers.
- Employee Training: The level of training and development provided to employees.
- Employee Attitudes: The positive and professional attitudes of employees.
- Skills and Knowledge: The relevant skills and expertise of employees.
- Internal Culture: The values, beliefs, and practices that shape employee behavior.
-
Examples of “People” in Tourism:
- Hotel Staff: Front desk agents, housekeeping staff, and concierge services.
- Tour Guides: Knowledgeable and engaging guides who lead tours and provide information.
- Restaurant Servers: Friendly and efficient staff who provide excellent dining experiences.
- Transportation Providers: Courteous drivers who offer safe and reliable transportation.
For instance, SIXT.VN trains its drivers to provide exceptional customer service and ensure comfortable and reliable airport transfers.
-
How to Optimize the “People” Element?
- Hire the Right People: Recruit employees who have the skills, attitudes, and values that align with your brand.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Invest in training programs to develop employee skills and knowledge.
- Empower Employees: Give employees the autonomy and authority to make decisions that benefit customers.
- Recognize and Reward Performance: Acknowledge and reward employees who provide excellent customer service.
- Create a Positive Work Environment: Foster a culture of teamwork, respect, and continuous improvement.
5.6 Planning: Staying Ahead of the Game
The measures you take to keep guests in the loop. How do you ensure they show up prepared? How do you tell them about your flexible cancellation policy? Are there any tactics you use to prevent refunds? What if you have to make unwanted changes?
-
What is “Planning” in the Marketing Mix? “Planning” involves proactive measures to ensure guests are well-informed and prepared for their experiences, addressing potential issues before they arise.
-
Key Aspects of the “Planning” Element:
- Pre-Trip Communication: Providing essential information to guests before their arrival.
- Contingency Plans: Developing strategies for managing unexpected changes or disruptions.
- Clear Policies: Establishing transparent cancellation and refund policies.
- Guest Preparation: Ensuring guests know what to expect and how to prepare for their activities.
-
Examples of “Planning” in Tourism:
- Pre-Arrival Emails: Sending detailed itineraries, packing lists, and important reminders to guests.
- Flexible Cancellation Policies: Offering guests the option to cancel or reschedule bookings without penalty.
- Weather Contingency Plans: Providing alternative activities or refunds in case of inclement weather.
- Emergency Contact Information: Sharing contact details for local authorities and emergency services.
For instance, SIXT.VN provides detailed booking confirmations and pre-trip communication to ensure travelers are well-prepared for their arrival in Vietnam.
-
How to Optimize the “Planning” Element?
- Anticipate Guest Needs: Identify common questions and concerns guests may have.
- Develop Comprehensive Communication: Create clear and informative pre-trip communication materials.
- Establish Flexible Policies: Offer reasonable cancellation and refund options to build trust.
- Prepare for Unexpected Events: Develop contingency plans to address potential disruptions.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from guests to improve your planning and communication processes.
5.7 Processes: Ensuring Seamless Experiences
The processes you have in place to guarantee guests get the experience they expect. Everything should run smoothly from the get-go. Consider ways to shorten check-in, stay on schedule, and make them feel valued.
-
What is “Processes” in the Marketing Mix? “Processes” refers to the systems and procedures that ensure consistent and high-quality service delivery, from booking to departure.
-
Key Aspects of the “Processes” Element:
- Booking and Reservations: Streamlining the booking process for convenience.
- Check-In and Check-Out: Ensuring quick and efficient procedures.
- Service Delivery: Providing consistent and high-quality service at every touchpoint.
- Customer Support: Offering timely and helpful assistance to guests.
-
Examples of “Processes” in Tourism:
- Online Booking Systems: User-friendly platforms that allow guests to easily book services.
- Mobile Check-In: Allowing guests to check in via their smartphones.
- Automated Customer Service: Using chatbots to answer common questions.
- Feedback Collection: Implementing systems for gathering and responding to customer feedback.
For instance, SIXT.VN provides a seamless online booking system and reliable airport transfer processes to ensure a smooth start to travelers’ visits to Vietnam.
-
How to Optimize the “Processes” Element?
- Map Customer Journeys: Identify all the touchpoints where customers interact with your business.
- Streamline Operations: Simplify and automate processes to reduce wait times and improve efficiency.
- Implement Quality Control: Monitor and evaluate processes to ensure consistency and quality.
- Provide Training: Train employees to follow processes and deliver excellent service.
- Gather Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for process improvement.
5.8 Proof: Showcasing Positive Experiences
The physical evidence that proves your guests had the best time. This could be in the form of professional photos or merchandise. But it can also be online reviews you encourage them to write on popular platforms.
-
What is “Proof” in the Marketing Mix? “Proof” refers to the tangible evidence that demonstrates the quality and value of your services, building trust and credibility with potential customers.
-
Key Aspects of the “Proof” Element:
- Customer Reviews: Online reviews and testimonials that showcase positive experiences.
- Ratings and Awards: Recognition from reputable organizations and rating platforms.
- Photos and Videos: Visual content that highlights the quality and appeal of your offerings.
- Success Stories: Case studies that illustrate how your services have benefited customers.
-
Examples of “Proof” in Tourism:
- Online Reviews: Positive reviews on platforms like TripAdvisor, Google Reviews, and Booking.com.
- Awards and Certifications: Recognition from travel industry organizations and sustainability certifications.
- Professional Photos: High-quality images of accommodations, tours, and activities.
- Video Testimonials: Authentic testimonials from satisfied customers.
For instance, SIXT.VN showcases positive customer reviews and testimonials on its website to build trust and demonstrate the reliability of its services.
-
How to Optimize the “Proof” Element?
- Encourage Reviews: Actively solicit reviews from satisfied customers.
- Highlight Positive Feedback: Showcase positive reviews and testimonials on your website and marketing materials.
- Display Ratings and Awards: Prominently display any awards or certifications you have received.
- Use Visual Content: Incorporate high-quality photos and videos to showcase your offerings.
- Share Success Stories: Create case studies that illustrate how your services have benefited customers.
6. Budget and Resource Allocation
Realistic budget and resource allocation is key to marketing success. Consider available funds and skills when planning.
-
Why Budgeting is Important?
- Effective Resource Management: Ensures you use your resources efficiently and effectively.
- Measurable Results: Allows you to track your marketing expenses and measure the return on investment (ROI).
- Prioritization: Helps you focus on the most impactful marketing activities.
-
Key Steps in Budget and Resource Allocation:
- Assess Available Resources: Determine your financial budget and available staff.
- Prioritize Marketing Activities: Focus on activities that align with your goals and target audience.
- Allocate Budget: Assign funds to specific marketing activities, such as social media, content creation, and advertising.
- Monitor Expenses: Track your spending and make adjustments as needed.
-
Examples of Resource Allocation:
- Social Media Marketing: Allocating funds for social media advertising and content creation.
- Content Marketing: Budgeting for blog posts, videos, and infographics.
- SEO Optimization: Investing in tools and expertise to improve search engine rankings.
-
Tips for Effective Budgeting:
- Set Realistic Goals: Establish achievable marketing goals based on your available resources.
- Track Your ROI: Monitor the return on investment for each marketing activity.
- Be Flexible: Adjust your budget as needed based on performance and changing market conditions.
7. Establish Clear Goals, Metrics, and Activities
SMART goals are the foundation for measurable progress in your marketing efforts.
-
Why Set Goals?
- Focus: Gives your marketing efforts direction and purpose.
- Motivation: Keeps your team motivated and engaged.
- Accountability: Provides a clear standard for measuring success.
-
Key Components of SMART Goals:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Establish metrics to track progress.
- Achievable: Set realistic goals that are within reach.
- Relevant: Ensure your goals align with your overall business objectives.
- Time-Bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goals.
-
Examples of SMART Goals:
- Increase Website Traffic: Increase organic website traffic by 30% in the next six months.
- Generate Leads: Generate 100 qualified leads per month through content marketing.
- Improve Customer Satisfaction: Increase customer satisfaction scores by 15% in the next quarter.
7.1 Goals: Setting Your Sights High
When it comes to setting marketing goals, it’s important to be SMART. Don’t just put your finger to the wind and say, “I think we should go this way.” Your goals should be:
-
Specific: clearly explains what you want to achieve
-
Measurable: has a metric you can objectively measure
-
Attainable: something you have to stretch for, but still within your reach
-
Realistic: relevant to your business and where you want to go
-
Time-bound: when you want to accomplish the goal by
Here’s an example using the SMART method:
Increase organic website traffic 40% by the end of 2021 from getting 1000 visitors per month from Google.
7.2 Metrics: Measuring What Matters
How are you going to track your progress? As you can see in the above example, the number of website visitors is the primary metric. Now, many people will tell you to steer clear of vanity metrics — like traffic, followers, and shares — because they don’t directly impact your bottom line.
We couldn’t agree less. Marketing is about the long-game. While those metrics don’t always translate into transactions, they do strengthen brand equity, which in turn drives bookings over time because guests gravitate towards operators with extra oomph online.
The Content Marketing Institute puts it best: think of vanity metrics as optimization metrics. Instead of tying them to ROI, consider their overall value for better understanding your audience on specific channels.
For instance, if a particular social media post generates way more likes than average, it indicates something about that content resonates with your audience. You can pinpoint what that may be and replicate it in future posts or use it as a blueprint for creating effective Facebook ads.
- Examples of Metrics:
- Website Traffic: Track the number of visitors to your website using tools like Google Analytics.
- Conversion Rates: Measure the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as booking a tour or requesting a quote.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Calculate the cost of acquiring a new customer through marketing activities.
7.3 Activities: Defining Your Action Plan
For each goal you set, figure out one key activity that’ll help you hit it. Don’t be afraid to think big here. By that, I mean, come up with a significant marketing project that you and your team can chip away at — more on that in the next step.
-
Examples of Key Activities:
- Content Creation: Producing high-quality blog posts, videos, and infographics to attract and engage your target audience.
- Social Media Engagement: Building a strong presence on social media through regular posting, engaging with followers, and running targeted ads.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with other businesses



