Navigating the Great Lakes region during winter can be challenging, as lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous. SIXT.VN understands these challenges and offers reliable travel solutions for those seeking to explore the beauty of Vietnam. Consider SIXT.VN your trusted partner for navigating the roads with confidence, providing expert guidance and dependable services for a safe and memorable journey.
1. What is Lake-Effect Snow and Why is it Treacherous?
Lake-effect snow is a localized weather phenomenon that occurs when cold, dry air passes over the warmer waters of the Great Lakes. This process results in significant snowfall downwind of the lakes. Lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous because of the sudden and intense snowfall, reduced visibility, and icy road conditions, leading to hazardous driving conditions and travel disruptions. According to the National Weather Service, lake-effect snow can produce snowfall rates of 2-3 inches per hour, creating whiteout conditions that severely limit visibility and make navigation difficult. The rapid accumulation of snow can overwhelm road maintenance crews, further exacerbating travel difficulties. In addition, the localized nature of lake-effect snow means that conditions can vary dramatically over short distances, with clear roads quickly transitioning to heavily snow-covered ones, catching drivers off guard.
1.1. What Causes Lake-Effect Snow?
Lake-effect snow is caused by the interaction of cold air masses with the relatively warmer waters of large lakes. The process unfolds as follows:
- Cold Air Passage: Cold, dry air from Canada sweeps southward across the Great Lakes during the winter months.
- Moisture Absorption: As the cold air passes over the warmer lake waters, it picks up moisture through evaporation. The Great Lakes retain heat longer than the surrounding land, creating a temperature contrast.
- Atmospheric Instability: The warm, moist air rises and becomes unstable due to the temperature difference.
- Cloud Formation: As the air rises, it cools and condenses, forming clouds.
- Snowfall: If the air is cold enough, the moisture turns into snow, which is then deposited downwind of the lake.
1.2. Why is Lake-Effect Snow so Dangerous?
Lake-effect snow is dangerous for several reasons:
- High Snowfall Rates: Lake-effect snow can produce extremely high snowfall rates, sometimes exceeding 2-3 inches per hour. This rapid accumulation can quickly overwhelm roads and make travel nearly impossible.
- Reduced Visibility: Heavy snowfall significantly reduces visibility, creating “whiteout” conditions where drivers cannot see more than a few feet ahead.
- Localized Impact: Lake-effect snow is highly localized, meaning that conditions can vary dramatically over short distances. Drivers may encounter clear roads in one area and suddenly find themselves in heavy snow just a few miles away.
- Icy Roads: The combination of snow and cold temperatures can lead to icy road conditions, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Unpredictability: Lake-effect snow is notoriously difficult to forecast accurately, making it challenging for travelers to plan accordingly.
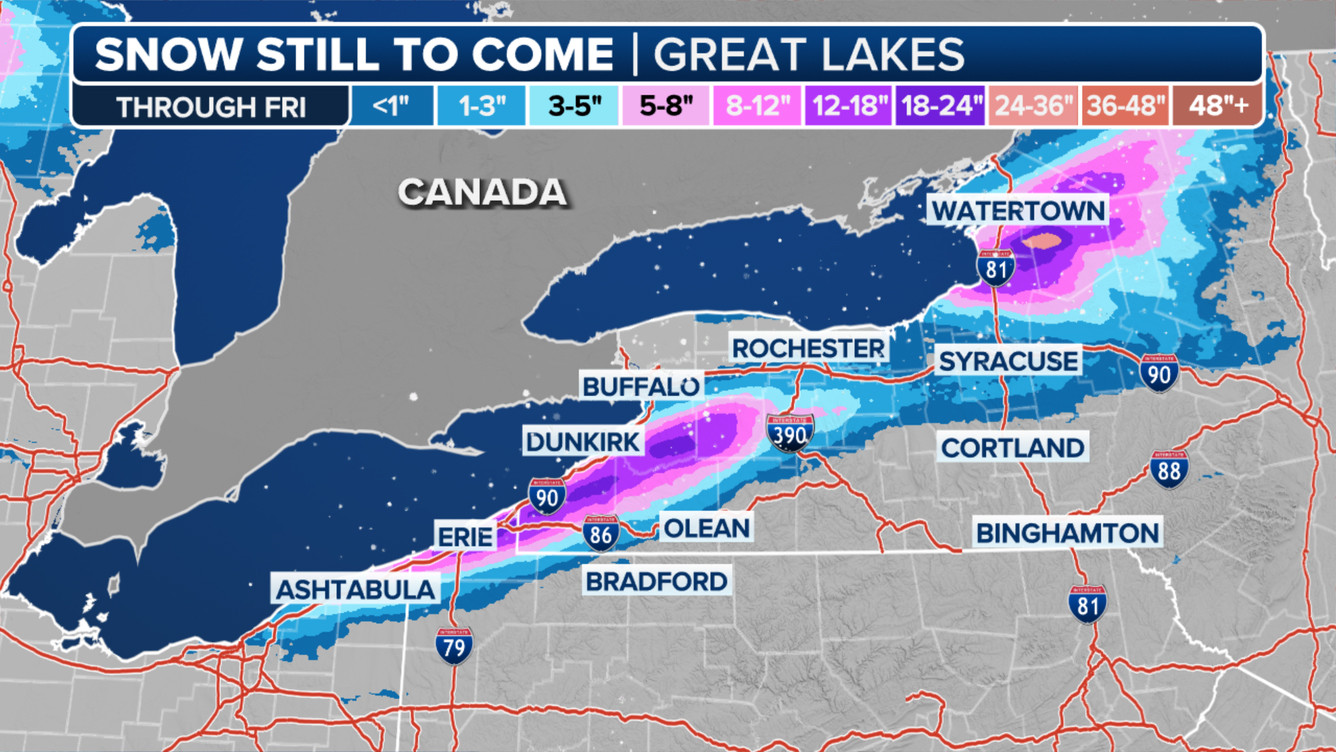
1.3. What Regions are Most Affected by Lake-Effect Snow?
The regions most affected by lake-effect snow are those downwind of the Great Lakes, including:
- Western New York: Areas east of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario, such as Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse, often experience significant lake-effect snow.
- Northwestern Pennsylvania: Communities near Lake Erie, including Erie, PA, are frequently impacted.
- Northeastern Ohio: The snowbelt region of Ohio, particularly areas near Cleveland, is prone to lake-effect snow.
- Michigan: The western and northern parts of Michigan, including areas near Lake Michigan and Lake Superior, can see heavy lake-effect snow.
- Southern Ontario, Canada: The Niagara Peninsula and areas east of Lake Ontario also experience lake-effect snow.
1.4. What Makes Lake-Effect Snowfall Difficult to Predict?
Lake-effect snowfall is difficult to predict due to its localized nature and dependence on specific atmospheric conditions. The following factors contribute to the unpredictability of lake-effect snow:
- Wind Direction: The direction of the wind plays a crucial role in determining where the heaviest snow will fall. Slight changes in wind direction can shift the location of the snow bands, making it challenging to pinpoint the exact areas that will be affected.
- Temperature Difference: The temperature difference between the lake water and the air above it must be significant enough to create atmospheric instability. This temperature contrast can vary, affecting the intensity of the snowfall.
- Fetch: The distance that the wind travels over the lake (known as the fetch) influences the amount of moisture that the air can absorb. A longer fetch generally results in more intense snowfall.
- Lake Ice Cover: The extent of ice cover on the lakes can reduce evaporation and suppress lake-effect snow. The formation and melting of ice cover can vary from year to year, adding to the uncertainty.
- Atmospheric Stability: The overall stability of the atmosphere affects the ability of air to rise and form clouds. Stable conditions can inhibit lake-effect snow, while unstable conditions can enhance it.
- Mesoscale Features: Small-scale weather features, such as lake breezes and convergence zones, can influence the development and movement of lake-effect snow bands, making them difficult to forecast.
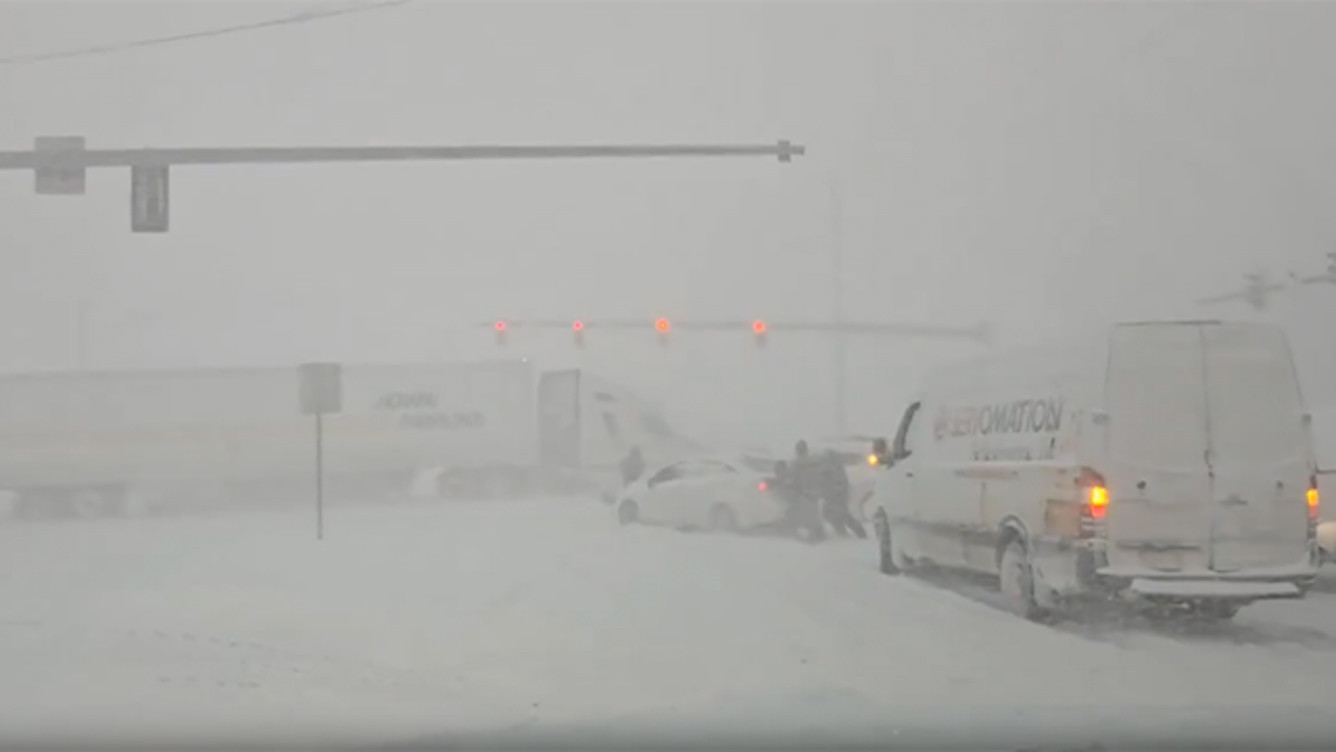 Lake-effect snow creates chaos on the roads of Hamburg, New York, making road identification difficult
Lake-effect snow creates chaos on the roads of Hamburg, New York, making road identification difficult
2. How Does Lake-Effect Snow Affect Travel in the Great Lakes Region?
Lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous because it leads to hazardous road conditions, airport closures, and transportation delays. The heavy snowfall and reduced visibility can make driving dangerous, leading to accidents and road closures. According to the U.S. Department of Transportation, weather-related crashes account for over 15% of all vehicle crashes in the United States, with snow and ice being major contributing factors. During severe lake-effect snow events, many roads and highways may be closed, and even when roads are open, travel can be slow and difficult. Airports in affected areas may also close due to poor visibility and snow accumulation on runways, disrupting air travel.
2.1. What Road Conditions Can Be Expected During Lake-Effect Snow?
During lake-effect snow events, drivers can expect the following road conditions:
- Snow-Covered Roads: Roads can quickly become covered with snow, making it difficult to maintain traction.
- Icy Patches: Melting and refreezing of snow can create icy patches, which are particularly hazardous.
- Reduced Visibility: Heavy snowfall can significantly reduce visibility, making it hard to see other vehicles and road signs.
- Drifting Snow: Strong winds can cause snow to drift across roads, creating additional hazards.
- Slow Traffic: Even when roads are open, traffic often moves slowly due to the challenging conditions.
- Road Closures: In severe cases, roads may be closed altogether, and travel bans may be implemented.
2.2. How Do Airports Handle Lake-Effect Snow?
Airports in the Great Lakes region have procedures in place to handle lake-effect snow:
- Snow Removal Equipment: Airports use specialized snow removal equipment, such as plows, blowers, and sweepers, to clear runways and taxiways.
- De-icing Operations: Aircraft are de-iced to remove snow and ice that can affect their performance.
- Reduced Operations: During heavy snowfall, airports may reduce the number of flights to allow for snow removal and de-icing.
- Temporary Closures: In extreme cases, airports may temporarily close until conditions improve.
2.3. What Types of Vehicles are Most Suited for Driving in Lake-Effect Snow?
Some vehicles are better suited for driving in lake-effect snow than others:
- Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) Vehicles: 4WD vehicles provide better traction on snow-covered roads compared to two-wheel drive vehicles.
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Vehicles: AWD vehicles automatically distribute power to all wheels, providing enhanced stability and traction.
- Vehicles with Winter Tires: Winter tires have a special tread pattern and rubber compound that provide superior grip on snow and ice.
- SUVs and Trucks: SUVs and trucks generally have higher ground clearance, which can be helpful in deep snow.
2.4. What Should You Do If You Get Stranded in Your Car During Lake-Effect Snow?
If you get stranded in your car during lake-effect snow, follow these steps:
- Stay in Your Vehicle: Unless you can see a safe place nearby, stay in your vehicle.
- Call for Help: Call 911 or your local emergency number and provide your location.
- Run the Engine Sparingly: Run the engine for about 10 minutes each hour to stay warm. Make sure the exhaust pipe is clear of snow to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning.
- Stay Visible: Turn on your hazard lights and tie a bright-colored cloth to your antenna or window.
- Stay Warm: Use blankets, extra clothing, and floor mats to stay warm. Huddle together if you are traveling with others.
- Stay Awake: If possible, stay awake to avoid the risk of hypothermia.
2.5. What are the Economic Impacts of Lake-Effect Snow on the Region?
Lake-effect snow can have significant economic impacts on the Great Lakes region:
- Transportation Costs: Increased transportation costs due to delays, road closures, and accidents.
- Business Disruptions: Business closures and reduced productivity due to employees being unable to get to work.
- Retail Losses: Reduced retail sales as people stay home to avoid the weather.
- Tourism Impacts: Negative impacts on tourism as visitors cancel trips or avoid the region altogether.
- Snow Removal Costs: Increased costs for snow removal and road maintenance.
- Accident-Related Expenses: Costs associated with accidents, including medical expenses, vehicle repairs, and insurance claims.
 Heavy snowfall in Pennsylvania obscures visibility
Heavy snowfall in Pennsylvania obscures visibility
3. What Safety Precautions Should Travelers Take During Lake-Effect Snow?
When traveling in the Great Lakes region during winter, it’s crucial to be aware of the potential for lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous, and to take appropriate safety precautions. According to the National Safety Council, being prepared and informed can significantly reduce the risks associated with winter driving. Travelers should monitor weather forecasts, avoid unnecessary travel during severe weather, and ensure their vehicles are properly equipped for winter conditions.
3.1. How Should You Prepare Your Vehicle for Lake-Effect Snow?
Before traveling in areas prone to lake-effect snow, it’s important to prepare your vehicle:
- Install Winter Tires: Winter tires provide superior traction on snow and ice compared to all-season tires.
- Check Tire Pressure: Ensure your tires are properly inflated. Low tire pressure can reduce traction.
- Top Off Fluids: Check and top off essential fluids, including antifreeze, windshield washer fluid, and oil.
- Inspect Brakes: Make sure your brakes are in good working order.
- Check Battery: Have your battery tested to ensure it can handle cold weather conditions.
- Replace Wiper Blades: Replace worn wiper blades to ensure good visibility.
- Test Lights: Check all lights, including headlights, taillights, brake lights, and turn signals.
3.2. What Essential Items Should You Carry in Your Car During Winter?
When traveling in winter, it’s wise to carry an emergency kit in your car:
- First-Aid Kit: Include bandages, antiseptic wipes, pain relievers, and any personal medications.
- Blankets: Pack warm blankets to stay warm if you get stranded.
- Flashlight: Carry a flashlight with extra batteries.
- Jumper Cables: Keep jumper cables in case your battery dies.
- Cell Phone Charger: Bring a cell phone charger to keep your phone powered.
- Snacks: Pack non-perishable snacks and water in case you get stranded.
- Ice Scraper: An ice scraper is essential for removing ice and snow from your windows.
- Shovel: A small shovel can help you dig your car out if it gets stuck.
- Sand or Kitty Litter: Sand or kitty litter can provide traction if your tires get stuck in snow or ice.
- Warning Devices: Carry flares or reflective triangles to warn other drivers if you have to stop on the side of the road.
3.3. How Should You Drive in Lake-Effect Snow?
Driving in lake-effect snow requires special techniques:
- Reduce Speed: Slow down and drive well below the posted speed limit.
- Increase Following Distance: Increase your following distance to allow more time to react.
- Use Headlights: Turn on your headlights to increase visibility.
- Avoid Sudden Movements: Avoid sudden braking, accelerating, or steering.
- Brake Gently: If you need to brake, do so gently and gradually.
- Steer Smoothly: Steer smoothly and avoid jerky movements.
- Be Aware of Black Ice: Be aware of the potential for black ice, which is a thin, transparent layer of ice that can be difficult to see.
- Watch for Snowplows: Give snowplows plenty of room and avoid passing them.
3.4. How Can You Stay Informed About Weather Conditions During Travel?
Staying informed about weather conditions is critical:
- Monitor Weather Forecasts: Check the weather forecast before you travel and during your trip.
- Use Weather Apps: Use weather apps on your smartphone to get real-time weather updates.
- Listen to Weather Radio: Tune into a weather radio station for the latest weather information.
- Check Road Conditions: Check road conditions on state Department of Transportation websites or apps.
- Follow Social Media: Follow local news and weather accounts on social media for updates.
3.5. What are the Signs of Hypothermia and Frostbite?
Recognizing the signs of hypothermia and frostbite is crucial in cold weather:
- Hypothermia Signs:
- Shivering
- Confusion
- Slurred Speech
- Drowsiness
- Loss of Coordination
- Frostbite Signs:
- Numbness
- Pale or Bluish Skin
- Hard or Waxy Skin
- If You Suspect Hypothermia or Frostbite:
- Seek medical attention immediately.
- Move the person to a warm place.
- Remove wet clothing.
- Warm the person gradually with blankets or body heat.
- Do not rub frostbitten areas.
 Deep snowdrifts make travel treacherous
Deep snowdrifts make travel treacherous
4. What Role Do Local Governments Play in Managing Lake-Effect Snow?
Local governments play a critical role in managing the impacts of lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous. According to the American Public Works Association (APWA), effective snow and ice control programs are essential for maintaining safe transportation and minimizing economic disruptions. Local governments are responsible for snow removal, road maintenance, and emergency response during lake-effect snow events.
4.1. How Do Cities and Towns Prepare for Lake-Effect Snow?
Cities and towns take several steps to prepare for lake-effect snow:
- Snow Removal Equipment: Cities and towns maintain a fleet of snowplows, salt trucks, and other snow removal equipment.
- Salt and Sand Supplies: They stockpile salt and sand to treat roads and improve traction.
- Weather Monitoring: Local governments monitor weather forecasts and radar to track incoming storms.
- Emergency Plans: They develop emergency plans to coordinate snow removal and emergency response efforts.
- Public Information: They provide information to the public about road closures, travel advisories, and safety tips.
4.2. What Types of Snow Removal Equipment Do They Use?
Local governments use a variety of snow removal equipment:
- Snowplows: Snowplows are used to clear snow from roads and highways.
- Salt Trucks: Salt trucks spread salt on roads to melt ice and snow.
- Sand Trucks: Sand trucks spread sand on roads to improve traction.
- Snow Blowers: Snow blowers are used to remove snow from sidewalks and other areas.
- Graders: Graders are used to smooth out snow and ice on roads.
4.3. How Do They Decide When to Close Roads?
Local authorities decide when to close roads based on several factors:
- Snowfall Rate: If the snowfall rate is too high, roads may be closed to allow for snow removal.
- Visibility: If visibility is severely reduced, roads may be closed to prevent accidents.
- Road Conditions: If roads are too snow-covered or icy, they may be closed for safety reasons.
- Emergency Situations: Roads may be closed to allow emergency vehicles to access accident scenes or other emergencies.
- Travel Bans: In severe cases, travel bans may be implemented, prohibiting all non-essential travel.
4.4. How Do They Communicate with the Public During Snow Events?
Local governments use various methods to communicate with the public during snow events:
- Website Updates: They post updates on their websites about road closures, travel advisories, and safety tips.
- Social Media: They use social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook to provide real-time updates.
- Local News: They work with local news media to disseminate information to the public.
- Emergency Alerts: They use emergency alert systems to send out warnings and advisories.
- Roadside Signs: They post signs along roads to warn drivers about hazardous conditions.
4.5. How Do Local Governments Coordinate with State and Federal Agencies?
Local governments coordinate with state and federal agencies to manage lake-effect snow events:
- State Departments of Transportation: They work with state DOTs to coordinate snow removal efforts and share information about road conditions.
- National Weather Service: They coordinate with the NWS to monitor weather forecasts and receive warnings about incoming storms.
- Emergency Management Agencies: They work with state and federal emergency management agencies to coordinate emergency response efforts.
- Federal Highway Administration: They may receive funding and technical assistance from the FHWA for snow and ice control programs.
 Poor visibility makes driving dangerous
Poor visibility makes driving dangerous
5. Are There Technological Solutions to Help Mitigate the Impact of Lake-Effect Snow?
Yes, there are several technological solutions to help mitigate the impact of lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous. According to the Transportation Research Board (TRB), advanced technologies can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of snow and ice control operations.
5.1. What is Road Weather Information Systems (RWIS)?
Road Weather Information Systems (RWIS) are networks of sensors that collect real-time weather and road condition data. These systems provide valuable information for snow and ice control operations:
- Sensors: RWIS stations include sensors that measure air temperature, pavement temperature, wind speed, wind direction, precipitation, and other weather parameters.
- Data Collection: The data collected by the sensors is transmitted to a central location for analysis.
- Decision Support: RWIS data is used to make informed decisions about when and where to apply salt and other de-icing chemicals.
- Real-Time Information: RWIS provides real-time information to drivers and transportation agencies, helping them make informed decisions about travel.
5.2. How Does De-icing Technology Work?
De-icing technology involves the use of chemicals to melt ice and snow on roads.
- Salt (Sodium Chloride): Salt is the most common de-icing chemical. It lowers the freezing point of water, causing ice and snow to melt.
- Calcium Chloride: Calcium chloride is effective at lower temperatures than salt.
- Magnesium Chloride: Magnesium chloride is another de-icing chemical that is effective at low temperatures.
- Liquid De-icers: Liquid de-icers are sprayed on roads to prevent ice from forming.
5.3. What is Anti-icing and How Does It Help?
Anti-icing is a proactive approach to snow and ice control that involves applying de-icing chemicals before a storm hits.
- Preventative Measures: Anti-icing prevents ice and snow from bonding to the pavement, making it easier to remove after the storm.
- Reduced Chemical Use: Anti-icing can reduce the amount of de-icing chemicals needed, saving money and reducing environmental impacts.
- Improved Safety: Anti-icing can improve safety by preventing ice from forming on roads.
5.4. How Does GPS Technology Aid in Snow Removal Operations?
GPS technology is used to track snowplows and other snow removal equipment:
- Real-Time Tracking: GPS allows transportation agencies to track the location of snowplows in real-time.
- Route Optimization: GPS data can be used to optimize snowplow routes and improve efficiency.
- Performance Monitoring: GPS data can be used to monitor the performance of snowplow operators and identify areas for improvement.
5.5. What Role Do Weather Forecasting Models Play in Mitigating Lake-Effect Snow?
Weather forecasting models are used to predict lake-effect snow:
- Numerical Weather Prediction: Numerical weather prediction models use mathematical equations to simulate the atmosphere and predict future weather conditions.
- High-Resolution Models: High-resolution models are used to predict lake-effect snow with greater accuracy.
- Ensemble Forecasting: Ensemble forecasting involves running multiple weather models to assess the range of possible outcomes.
- Improved Forecasting: Improved weather forecasting models can help transportation agencies and the public prepare for lake-effect snow events.
6. Can Climate Change Affect Lake-Effect Snow?
Yes, climate change can affect lake-effect snow, although the specific impacts are complex and not fully understood. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), climate change is expected to alter precipitation patterns and temperatures, which could influence the frequency and intensity of lake-effect snow events.
6.1. How Might Warmer Lake Temperatures Impact Lake-Effect Snow?
Warmer lake temperatures could potentially increase the amount of lake-effect snow in the short term:
- Increased Evaporation: Warmer lake temperatures could lead to increased evaporation, providing more moisture for lake-effect snow.
- More Intense Snowfall: Increased moisture could result in more intense snowfall rates.
- Longer Snow Season: A later freeze-up of the lakes could extend the lake-effect snow season.
6.2. How Might Changes in Air Temperature Affect Snowfall?
Changes in air temperature could have both positive and negative effects on lake-effect snow:
- Warmer Air: Warmer air temperatures could reduce the amount of snowfall, as more precipitation falls as rain instead of snow.
- Colder Air: If cold air outbreaks become more frequent or intense, lake-effect snow could increase.
6.3. What are the Potential Long-Term Impacts of Climate Change on Lake-Effect Snow?
The long-term impacts of climate change on lake-effect snow are uncertain:
- Reduced Snowfall: Some studies suggest that lake-effect snow will decrease in the long term as temperatures continue to rise.
- Changes in Snowfall Patterns: Climate change could alter the spatial patterns of lake-effect snow, with some areas receiving more snow and others receiving less.
- More Extreme Events: Climate change could lead to more extreme lake-effect snow events, with very heavy snowfall rates and significant impacts on travel and infrastructure.
6.4. How Can Communities Adapt to Potential Changes in Lake-Effect Snow Due to Climate Change?
Communities can take several steps to adapt to potential changes in lake-effect snow:
- Infrastructure Improvements: Invest in infrastructure improvements to handle more extreme snow events.
- Improved Forecasting: Improve weather forecasting capabilities to better predict lake-effect snow.
- Public Education: Educate the public about the risks of lake-effect snow and how to prepare for it.
- Climate Action Plans: Develop climate action plans to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
6.5. What Research is Being Done to Better Understand the Impacts of Climate Change on Lake-Effect Snow?
Researchers are actively studying the impacts of climate change on lake-effect snow:
- Climate Modeling: Climate models are being used to simulate the effects of climate change on lake-effect snow.
- Data Analysis: Researchers are analyzing historical weather data to identify trends in lake-effect snow.
- Field Studies: Field studies are being conducted to study the physical processes that drive lake-effect snow.
- Collaboration: Researchers are collaborating with transportation agencies and local governments to develop strategies for adapting to changes in lake-effect snow.
7. How Has Lake-Effect Snow Impacted the Great Lakes Region in Recent Years?
Lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous, and in recent years, it has caused significant disruptions, leading to state of emergencies, travel bans, and numerous accidents. Recent events underscore the ongoing challenges faced by communities in the Great Lakes region due to lake-effect snow.
7.1. What Were the Impacts of the November 2022 Lake-Effect Snowstorm in Buffalo, NY?
In November 2022, Buffalo, NY, experienced a historic lake-effect snowstorm that had devastating impacts:
- Record Snowfall: Some areas received over 6 feet of snow in a short period.
- Travel Bans: Travel bans were implemented, and many roads were closed.
- Power Outages: Thousands of people lost power due to heavy snow.
- Economic Impacts: Businesses were forced to close, and there were significant economic losses.
- Fatalities: Tragically, several people died due to the storm.
7.2. How Did the December 2020 Lake-Effect Snow Event Affect Travel in Pennsylvania?
In December 2020, a lake-effect snow event impacted travel in Pennsylvania:
- Heavy Snowfall: Erie, PA, and surrounding areas received significant snowfall.
- Road Closures: Numerous roads were closed due to snow-covered conditions.
- Travel Delays: Travelers experienced significant delays due to slow traffic and road closures.
- Accidents: There were numerous accidents due to icy roads and reduced visibility.
7.3. What Measures Were Taken During the January 2019 Lake-Effect Snowstorm in Michigan?
During a January 2019 lake-effect snowstorm in Michigan, the following measures were taken:
- State of Emergency: A state of emergency was declared in some counties.
- Snow Removal Efforts: Extensive snow removal efforts were undertaken to clear roads.
- Travel Advisories: Travel advisories were issued, urging people to avoid unnecessary travel.
- Shelters: Shelters were opened for people who needed a warm place to stay.
7.4. How Did These Events Highlight the Need for Better Preparedness and Response?
These events highlighted the need for:
- Improved Forecasting: More accurate and timely weather forecasts.
- Better Communication: Improved communication with the public about weather conditions and safety tips.
- Enhanced Snow Removal: More efficient and effective snow removal operations.
- Infrastructure Resilience: Infrastructure that is resilient to extreme weather events.
- Public Awareness: Increased public awareness about the risks of lake-effect snow and how to prepare for it.
7.5. What Lessons Have Been Learned from Past Lake-Effect Snow Events?
Lessons learned from past lake-effect snow events include:
- Importance of Planning: The importance of having a well-developed plan for responding to lake-effect snow events.
- Coordination is Key: The need for coordination among local, state, and federal agencies.
- Public Education Saves Lives: The importance of educating the public about the risks of lake-effect snow and how to stay safe.
- Investing in Infrastructure Pays Off: The value of investing in infrastructure that is resilient to extreme weather events.
- Technology Can Help: The potential of technology to improve forecasting, snow removal, and communication.
8. What are Some Interesting Facts About Lake-Effect Snow?
Lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous, but it is also a fascinating weather phenomenon.
8.1. What is the “Snowbelt”?
The “snowbelt” refers to the areas downwind of the Great Lakes that receive significant lake-effect snow.
8.2. Which Great Lake Produces the Most Lake-Effect Snow?
Lake Ontario typically produces the most lake-effect snow due to its depth and orientation.
8.3. What is “Thundersnow”?
“Thundersnow” is a rare phenomenon where thunder and lightning occur during a snowstorm.
8.4. How Does Lake-Effect Snow Compare to Other Types of Snowstorms?
Lake-effect snow is more localized and can produce higher snowfall rates than many other types of snowstorms.
8.5. Can Lake-Effect Snow Occur in Other Parts of the World?
Yes, lake-effect snow can occur in other parts of the world with large lakes or bodies of water.
9. What Resources are Available for Travelers to Stay Safe During Lake-Effect Snow?
To stay safe during lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous, travelers can utilize various resources.
9.1. Government Weather Websites
These websites provide official weather forecasts and warnings:
- National Weather Service (NWS): https://www.weather.gov/
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA): https://www.noaa.gov/
9.2. State and Local Government Websites
These websites offer road conditions, travel advisories, and emergency information:
- New York Department of Transportation (NYSDOT): https://www.dot.ny.gov/
- Pennsylvania Department of Transportation (PennDOT): https://www.penndot.gov/
- Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT): https://www.michigan.gov/mdot
- Ohio Department of Transportation (ODOT): https://www.dot.state.oh.us/
9.3. Mobile Apps for Weather and Traffic
Various mobile apps provide real-time weather and traffic updates:
- The Weather Channel
- AccuWeather
- Google Maps
- Waze
9.4. Emergency Alert Systems
Sign up for local emergency alert systems to receive warnings and advisories:
- Wireless Emergency Alerts (WEA)
- Local Emergency Management Agencies
9.5. Travel Insurance
Consider purchasing travel insurance to protect against weather-related disruptions:
- Travel Insurance Providers
10. What are Some Common Misconceptions About Lake-Effect Snow?
There are several common misconceptions about lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous, which can lead to underestimation of its risks.
10.1. Misconception: Lake-Effect Snow is Just Like Any Other Snowstorm
Fact: Lake-effect snow is different due to its localized nature and high snowfall rates.
10.2. Misconception: All-Season Tires are Good Enough for Driving in Lake-Effect Snow
Fact: Winter tires provide superior traction and are recommended for driving in lake-effect snow.
10.3. Misconception: Four-Wheel Drive Guarantees Safety in Lake-Effect Snow
Fact: Four-wheel drive can improve traction, but it does not guarantee safety. Drivers still need to drive cautiously.
10.4. Misconception: If the Sun is Shining, It’s Safe to Travel
Fact: Lake-effect snow can develop rapidly, even when the sun is shining.
10.5. Misconception: Weather Forecasts are Always Accurate
Fact: Weather forecasts are not always accurate, especially for localized phenomena like lake-effect snow.
FAQ About Lake-Effect Snow
-
What causes lake-effect snow?
Lake-effect snow is caused when cold, dry air passes over warmer lake waters, picking up moisture and creating localized, heavy snowfall downwind.
-
Where does lake-effect snow typically occur?
It primarily affects areas downwind of the Great Lakes, including western New York, northwestern Pennsylvania, northeastern Ohio, and Michigan.
-
Why is lake-effect snow so dangerous?
It leads to high snowfall rates, reduced visibility, icy roads, and localized impacts, making travel conditions hazardous and unpredictable.
-
How can I prepare my vehicle for lake-effect snow?
Install winter tires, check tire pressure, top off fluids, inspect brakes, and ensure your battery is in good condition.
-
What essential items should I carry in my car during winter?
Include a first-aid kit, blankets, flashlight, jumper cables, cell phone charger, snacks, ice scraper, shovel, and sand or kitty litter.
-
How should I drive in lake-effect snow?
Reduce speed, increase following distance, use headlights, avoid sudden movements, brake gently, and steer smoothly.
-
What are the signs of hypothermia and frostbite?
Hypothermia signs include shivering, confusion, and slurred speech; frostbite signs include numbness and pale or bluish skin.
-
How do local governments manage lake-effect snow?
They use snow removal equipment, stockpile salt and sand, monitor weather forecasts, develop emergency plans, and communicate with the public.
-
What technological solutions help mitigate the impact of lake-effect snow?
Road Weather Information Systems (RWIS), de-icing technology, anti-icing measures, GPS tracking for snowplows, and advanced weather forecasting models are all helpful.
-
Can climate change affect lake-effect snow?
Yes, climate change may alter precipitation patterns and temperatures, potentially impacting the frequency and intensity of lake-effect snow events, with uncertain long-term effects.
Navigating the Great Lakes region during winter can be daunting, but with proper preparation and awareness, travelers can mitigate the risks associated with lake-effect snow across the Great Lakes region makes travel treacherous. SIXT.VN offers services tailored to ensure your journey in Vietnam is seamless and stress-free. From airport pick-ups to personalized travel itineraries, SIXT.VN is your trusted companion for a memorable travel experience. Contact us today to explore our range of services and let us help you plan your perfect adventure! Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. Website: SIXT.VN.
Let SIXT.VN take the stress out of your travel plans, offering reliable airport transfers, comfortable hotel bookings, and exciting tour options. With SIXT.VN, you can focus on enjoying your trip, knowing that all the details are taken care of. Don’t let winter weather hold you back—explore the beauty of Vietnam with SIXT.VN! Secure your booking now and embrace the ease and convenience of traveling with SIXT.VN.



