Traveling the cosmos is a dream, but the vast distances can be daunting; thus, exploring Vietnam with SIXT.VN is your practical gateway to adventure. Understanding the light year as a unit of cosmic distance is essential for grasping the scale of the universe, and Vietnam offers its own unique, earthly adventures. Let SIXT.VN be your guide to discovering the beauty and culture of Vietnam while you contemplate the vastness of space, providing seamless travel experiences with airport transfers, hotel bookings, and tours.
1. What Exactly is a Light Year?
A light year is the distance light travels in one Earth year, which is approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers (5.88 trillion miles). To put it another way, because light moves at a finite pace, a light year quantifies this enormous distance by calculating how far a beam of light can travel in a single year. This measurement is useful for comprehending the colossal distances that separate celestial entities in the cosmos, such as stars and galaxies. According to NASA, light travels at about 300,000 kilometers (186,000 miles) per second in a vacuum. Over a year, this adds up to nearly 9.46 trillion kilometers.
1.1. Why Do Astronomers Use Light Years?
Astronomers employ light years to measure interstellar distances because they are more practical than miles or kilometers. Light years allow scientists to better understand the scale of the universe by expressing the vast distances between stars and galaxies in understandable terms. According to research from the International Astronomical Union in 2018, the light-year unit has become indispensable for astronomy because it enables simple communication and comprehension of cosmic distances.
1.2. How Does a Light Year Relate to Time?
A light year not only measures distance but also serves as a measure of time. When we look at an object one light-year away, we are seeing it as it was one year ago because that is how long it took the light to reach us. For example, the light we see from a star 50 light-years away started its journey 50 years ago. This principle is vital for studying the universe’s history. According to a study published in the “Astrophysical Journal” in 2020, light allows astronomers to reconstruct the universe’s timeline.
1.3. What is the Size of the Observable Universe in Light Years?
The observable universe has a radius of about 46.5 billion light years. This means that the farthest objects we can detect are so far away that their light has taken 46.5 billion years to reach us. The size of the observable universe is constantly expanding, making it a fascinating subject of study for cosmologists and astrophysicists. According to research by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2021, the observable universe contains billions of galaxies, each with billions of stars.
2. What Factors Determine Travel Time to Reach One Light Year?
The time it would take to travel one light year is determined by factors such as speed and propulsion technology. Even the fastest spacecraft ever built would take thousands of years to travel a single light year. Considering current technological limitations, interstellar travel remains a significant challenge.
2.1. How Fast Can Current Spacecraft Travel?
The fastest spacecraft ever built, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe, can reach speeds of up to 692,000 kilometers per hour (430,000 miles per hour). However, even at this speed, it would take thousands of years to travel one light year. According to NASA’s official data from 2023, the Parker Solar Probe’s speed is a major achievement, but it is still a small fraction of the speed of light.
2.2. What Role Does Propulsion Technology Play in Space Travel?
Propulsion technology is critical in determining how quickly a spacecraft can travel through space. Traditional chemical rockets are limited in terms of speed and efficiency. Advanced propulsion systems, such as ion drives and nuclear propulsion, can potentially achieve higher speeds. According to a 2019 report by the Space Technology Mission Directorate, advanced propulsion systems are essential for future deep-space missions.
2.3. What Are the Theoretical Possibilities for Faster-Than-Light Travel?
Faster-than-light travel is currently theoretical, but scientists are investigating several possibilities, including warp drives and wormholes. Warp drives would involve manipulating spacetime to allow a spacecraft to travel faster than light, while wormholes would involve creating tunnels through spacetime that connect two distant points. According to theoretical physicist Dr. Miguel Alcubierre, warp drives are based on Einstein’s theory of general relativity but would require exotic matter with negative mass-energy density, which has yet to be discovered.
3. How Long Would it Take to Travel One Light Year With Current Technology?
Traveling one light year with current technology would take thousands of years, far beyond a human lifespan. Even the fastest spacecraft would require tens of thousands of years to cover such a vast distance. This underscores the challenges of interstellar travel with current capabilities.
3.1. How Many Years Would it Take a Spaceship to Travel One Light Year?
A spaceship traveling at 692,000 kilometers per hour (the speed of the Parker Solar Probe) would take approximately 1,550 years to travel one light year. This calculation illustrates the immense distances involved and the limitations of current spacecraft speeds. According to calculations based on NASA data, the time required highlights the need for significant advancements in propulsion technology.
3.2. What is the Impact of Space Travel on Human Lifespan?
The vast distances involved in interstellar travel pose significant challenges to human lifespan. Even if a spacecraft could travel at a significant fraction of the speed of light, the journey to even the nearest stars would take decades, if not centuries. This necessitates considering life support systems, radiation shielding, and the psychological effects of prolonged space travel. According to a study published in “Acta Astronautica” in 2022, mitigating the effects of space travel on human health is crucial for future interstellar missions.
3.3. What Challenges Would Astronauts Face on a Journey of a Light Year?
Astronauts embarking on a journey of one light year would face numerous challenges, including exposure to cosmic radiation, the need for closed-loop life support systems, and the psychological impact of long-duration spaceflight. Maintaining physical and mental health during such a journey would be critical. According to research by the National Space Biomedical Research Institute, radiation exposure and psychological stress are major concerns for long-duration space missions.
4. What Technologies Could Potentially Reduce Travel Time to a Light Year?
Several technologies could potentially reduce travel time to a light year, including advanced propulsion systems, such as fusion rockets, and theoretical concepts like warp drives and wormholes. These technologies are in various stages of development, but they hold the promise of significantly faster interstellar travel.
4.1. How Could Fusion Rockets Revolutionize Space Travel?
Fusion rockets could revolutionize space travel by providing significantly higher thrust and efficiency compared to traditional chemical rockets. Fusion power, which involves fusing light atomic nuclei to release energy, could potentially propel spacecraft to much higher speeds. According to a 2020 report by the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory, fusion propulsion could reduce travel times to nearby stars from thousands of years to decades.
4.2. What is the Concept Behind Warp Drives?
Warp drives are a theoretical concept that involves manipulating spacetime to allow a spacecraft to travel faster than light. This would involve creating a “warp bubble” around the spacecraft, contracting space in front and expanding space behind, effectively moving the spacecraft without violating the laws of physics. According to theoretical physicist Dr. Miguel Alcubierre, warp drives are based on Einstein’s theory of general relativity but would require exotic matter with negative mass-energy density, which has yet to be discovered.
4.3. How Do Wormholes Potentially Shorten Space Journeys?
Wormholes, also known as Einstein-Rosen bridges, are theoretical tunnels through spacetime that could potentially connect two distant points in the universe. Traveling through a wormhole could allow a spacecraft to bypass the normal constraints of space and time, effectively shortening the distance between two points. According to theoretical physicist Dr. Kip Thorne, wormholes are allowed by Einstein’s theory of general relativity but would require exotic matter to keep them open and stable.
5. What Are the Nearest Stars and How Long Would It Take to Reach Them?
The nearest star system to our solar system is Alpha Centauri, which is approximately 4.37 light years away. Reaching Alpha Centauri with current technology would take tens of thousands of years. However, future technologies like fusion rockets or warp drives could potentially reduce this travel time to decades or even years.
5.1. How Far Away is Alpha Centauri?
Alpha Centauri is approximately 4.37 light years away from Earth. This makes it the closest star system to our solar system. Alpha Centauri is composed of three stars: Alpha Centauri A, Alpha Centauri B, and Proxima Centauri. According to NASA’s data, Proxima Centauri is slightly closer to Earth at 4.2465 light-years.
5.2. How Long Would It Take to Reach Proxima Centauri With Current Technology?
Traveling to Proxima Centauri, the closest star to our Sun at about 4.2465 light-years away, would take approximately 73,000 years using current spacecraft speeds, such as those achieved by the Voyager probes. According to data from NASA, Voyager 1, one of the fastest spacecraft, travels at roughly 17 kilometers per second.
5.3. What Are the Possibilities of Finding Habitable Planets Around Nearby Stars?
The possibility of finding habitable planets around nearby stars like Proxima Centauri has spurred significant interest in exoplanet research. Proxima Centauri hosts a planet, Proxima Centauri b, which is within the star’s habitable zone, meaning it could potentially support liquid water on its surface. According to a 2016 study in “Nature,” the discovery of Proxima Centauri b has ignited efforts to understand its atmosphere and potential for habitability.
6. What Role Does Time Dilation Play in Interstellar Travel?
Time dilation, a concept from Einstein’s theory of relativity, becomes significant at very high speeds. As a spacecraft approaches the speed of light, time slows down for the occupants relative to observers on Earth. This means that while decades might pass on Earth, the astronauts on the spacecraft might experience significantly less time.
6.1. How Does Einstein’s Theory of Relativity Affect Time During Space Travel?
Einstein’s theory of relativity postulates that time is relative and depends on the observer’s speed. As a spacecraft approaches the speed of light, time dilation occurs, causing time to slow down for the astronauts relative to observers on Earth. According to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, this effect becomes more pronounced as the spacecraft’s speed increases.
6.2. What is the Twin Paradox and How Does It Apply to Space Travel?
The twin paradox is a thought experiment in which one twin travels into space at high speed while the other remains on Earth. Due to time dilation, the traveling twin ages more slowly than the Earth-bound twin. This paradox illustrates the counterintuitive effects of relativity. According to a detailed explanation in “Relativity: The Special and the General Theory” by Albert Einstein, the paradox arises from the asymmetry in the twins’ experiences, as the traveling twin undergoes acceleration during the journey.
6.3. How Could Time Dilation Benefit or Hinder Interstellar Missions?
Time dilation could both benefit and hinder interstellar missions. On one hand, it could allow astronauts to travel vast distances within a human lifetime, as they would experience less time than observers on Earth. On the other hand, it could lead to significant differences in aging between the astronauts and their loved ones back on Earth, potentially causing emotional and social challenges. According to a study published in the “Journal of the British Interplanetary Society” in 2018, understanding and managing the effects of time dilation are critical for planning interstellar missions.
7. What Are the Ethical Considerations of Long-Duration Space Travel?
Long-duration space travel raises several ethical considerations, including the psychological and physical well-being of astronauts, the potential impact on their families, and the allocation of resources for such ambitious missions. Balancing the pursuit of scientific knowledge with the ethical treatment of space travelers is essential.
7.1. What Are the Psychological Effects of Long-Duration Spaceflight?
Long-duration spaceflight can have significant psychological effects on astronauts, including isolation, confinement, stress, and changes in cognitive function. Maintaining mental health during prolonged space missions requires careful planning and support. According to research by the NASA Human Research Program, psychological support and countermeasures are essential for mitigating the negative effects of long-duration spaceflight.
7.2. How Does Isolation Impact Astronauts on Long Journeys?
Isolation is a major challenge for astronauts on long journeys, as they are separated from their families, friends, and familiar environments. The lack of social interaction and the monotony of spaceflight can lead to feelings of loneliness and depression. According to a study published in “Frontiers in Psychology” in 2021, social support and virtual reality technologies can help mitigate the effects of isolation on astronauts.
7.3. What Are the Resource Allocation Considerations for Interstellar Missions?
Interstellar missions require significant resources, including funding, technology, and human capital. Allocating these resources raises ethical considerations about the balance between space exploration and other societal needs, such as healthcare, education, and environmental protection. According to a report by the National Research Council, careful consideration of resource allocation is essential for ensuring the long-term sustainability of space exploration.
8. What Would a Multi-Generational Spacecraft Entail?
A multi-generational spacecraft is a concept where a spacecraft would travel for many generations, with the original crew and their descendants continuing the journey. This approach would be necessary for reaching distant stars with current or near-future technology, as the journey would exceed a single human lifespan.
8.1. How Would a Society Function on a Multi-Generational Spaceship?
A society on a multi-generational spaceship would need to be self-sustaining and capable of maintaining its population, resources, and social structure over many generations. This would require careful planning and management of resources, as well as a robust social and cultural framework. According to a study published in “Acta Astronautica” in 2020, creating a stable and resilient society on a multi-generational spaceship would be a complex and challenging undertaking.
8.2. What Genetic Considerations Arise in a Limited Gene Pool?
A limited gene pool on a multi-generational spacecraft could lead to genetic problems over time, such as increased risk of genetic disorders and reduced adaptability to changing environmental conditions. Managing the genetic diversity of the population would be crucial for ensuring its long-term health and survival. According to a report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, genetic screening and gene therapy could help mitigate the risks associated with a limited gene pool.
8.3. What Cultural and Educational Strategies Would Be Needed?
Maintaining cultural continuity and providing education for future generations would be essential on a multi-generational spacecraft. This would require developing educational programs, cultural traditions, and social institutions that can be passed down through the generations. According to a study published in “Futures” in 2019, cultural and educational strategies are critical for ensuring the success of multi-generational space missions.
9. How Could Space Travel Change Our Understanding of the Universe?
Space travel has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe by allowing us to directly explore other planets, stars, and galaxies. This could lead to new discoveries about the origins of the universe, the nature of life, and the potential for extraterrestrial civilizations.
9.1. How Would Exploring Other Planets Change Our Perspective?
Exploring other planets could change our perspective by providing new insights into the diversity of planetary environments and the potential for life beyond Earth. This could challenge our assumptions about the uniqueness of Earth and our place in the universe. According to a report by the Planetary Science Decadal Survey, exploring other planets is essential for understanding the formation and evolution of planetary systems.
9.2. How Would Contact With Extraterrestrial Life Impact Humanity?
Contact with extraterrestrial life would have a profound impact on humanity, potentially transforming our understanding of biology, technology, and philosophy. It could also raise ethical and social questions about our relationship with other intelligent species. According to a study published in “Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A” in 2017, preparing for the possibility of contact with extraterrestrial life is essential for ensuring a positive outcome.
9.3. How Can Studying Space Help Solve Problems on Earth?
Studying space can help solve problems on Earth by providing new technologies, scientific knowledge, and a broader perspective on global challenges. Space-based technologies have led to advances in areas such as communication, navigation, and environmental monitoring. According to a report by the Space Foundation, space exploration has significant economic and societal benefits.
10. What is SIXT.VN and How Can It Help With Your Travel Plans?
While interstellar travel remains a distant dream, SIXT.VN can make your earthly travels a reality, especially when exploring Vietnam. With services like airport transfers, hotel bookings, and curated tours, SIXT.VN ensures a smooth and enjoyable travel experience. Whether you’re a solo traveler, a family, or a business traveler, SIXT.VN offers convenient and reliable solutions for your travel needs.
10.1. What Services Does SIXT.VN Offer for Travelers to Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services for travelers to Vietnam, including:
- Airport Transfers: Ensuring a hassle-free arrival and departure.
- Hotel Bookings: Providing a variety of options to suit different budgets and preferences.
- Tours: Offering curated tours to explore the best of Vietnam.
These services are designed to make your trip to Vietnam as seamless and enjoyable as possible.
10.2. How Can SIXT.VN Simplify Your Travel Planning Process?
SIXT.VN simplifies your travel planning process by offering a one-stop platform for all your travel needs. From booking airport transfers to finding the perfect hotel and arranging tours, SIXT.VN takes care of the details so you can focus on enjoying your trip.
10.3. Why Choose SIXT.VN for Your Next Trip to Vietnam?
Choose SIXT.VN for your next trip to Vietnam for a convenient, reliable, and enjoyable travel experience. With a focus on customer satisfaction and a wide range of services, SIXT.VN is your ideal travel partner in Vietnam.
SIXT.VN is ready to assist you with all your travel needs in Vietnam. From airport transfers to hotel bookings and tours, SIXT.VN ensures a seamless and enjoyable experience. Contact us today to start planning your dream trip to Vietnam!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN
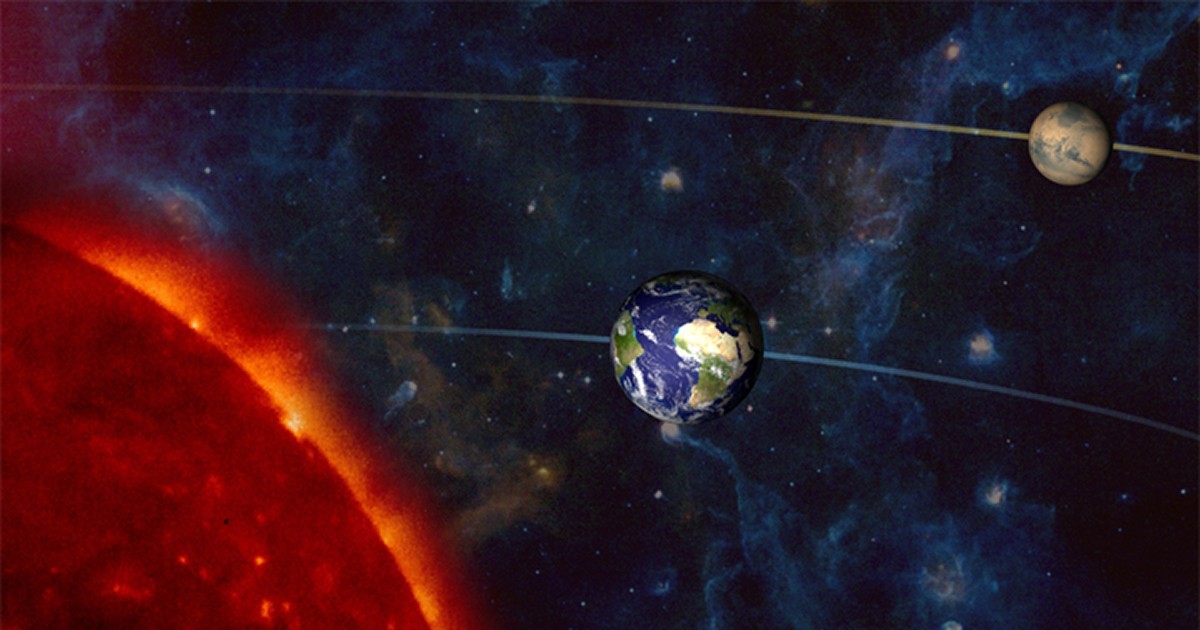 Earth's distance from the Sun is 1AU, but to describe much larger distances across the cosmos we need much bigger values. This is where the lightyear comes in
Earth's distance from the Sun is 1AU, but to describe much larger distances across the cosmos we need much bigger values. This is where the lightyear comes in
FAQ: Understanding Light Years and Space Travel
1. What is a light year?
A light year is the distance light travels in one Earth year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers (5.88 trillion miles).
2. Why do astronomers use light years instead of miles or kilometers?
Light years are more practical for measuring the vast distances between stars and galaxies.
3. How long would it take to travel one light year with current technology?
It would take tens of thousands of years to travel one light year with current technology.
4. What is the fastest spacecraft ever built?
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe is the fastest spacecraft, reaching speeds of up to 692,000 kilometers per hour (430,000 miles per hour).
5. What technologies could potentially reduce travel time to a light year?
Technologies like fusion rockets, warp drives, and wormholes could potentially reduce travel time.
6. What is Alpha Centauri?
Alpha Centauri is the nearest star system to our solar system, approximately 4.37 light years away.
7. What is time dilation?
Time dilation is a concept from Einstein’s theory of relativity where time slows down for objects moving at very high speeds relative to a stationary observer.
8. What is a multi-generational spacecraft?
A multi-generational spacecraft is a concept where a spacecraft would travel for many generations, with the original crew and their descendants continuing the journey.
9. How can space travel change our understanding of the universe?
Space travel can revolutionize our understanding by allowing us to directly explore other planets, stars, and galaxies, leading to new discoveries about the universe.
10. How can SIXT.VN assist with travel plans in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers services like airport transfers, hotel bookings, and tours, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable travel experience in Vietnam.
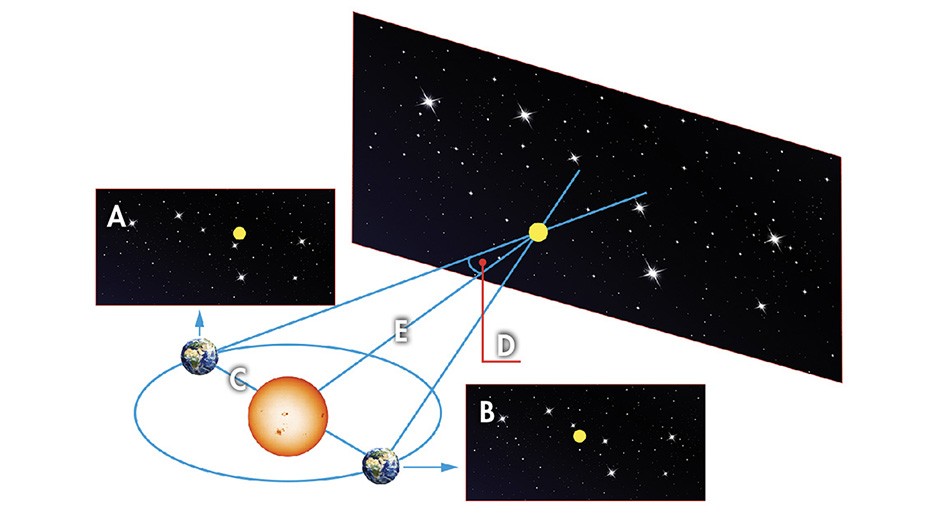 A diagram showing parallax. A and B show how a nearby star appears to move against its background when Earth is at different positions. C is equal to 1 AU. D is a parallax angle of one arcsecond. E is a parsec
A diagram showing parallax. A and B show how a nearby star appears to move against its background when Earth is at different positions. C is equal to 1 AU. D is a parallax angle of one arcsecond. E is a parsec
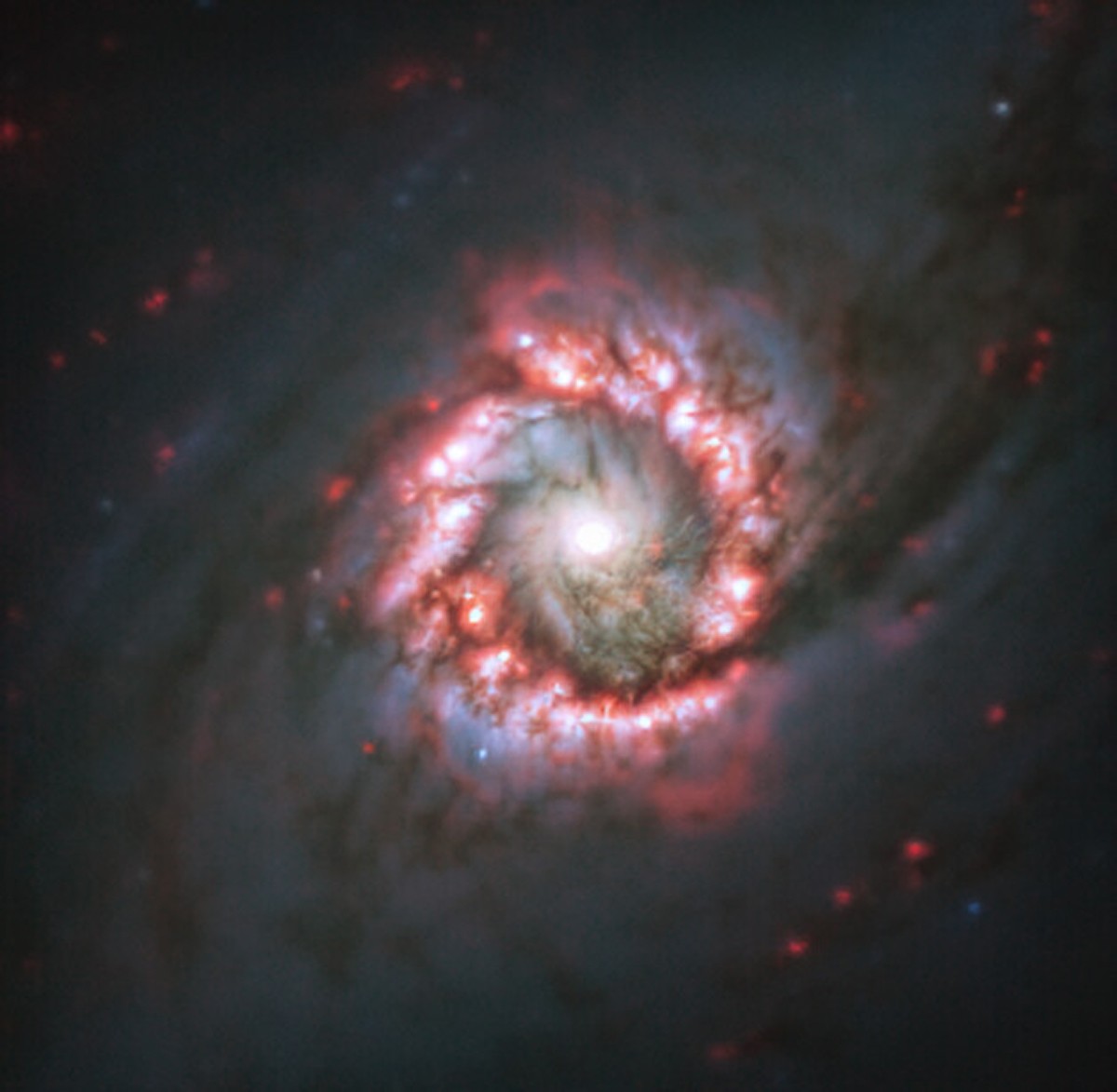 Galaxy NGC 1097 is 45 million lightyears from Earth, meaning we see it as it existed 45 million years ago. Credit: ESO/TIMER Survey
Galaxy NGC 1097 is 45 million lightyears from Earth, meaning we see it as it existed 45 million years ago. Credit: ESO/TIMER Survey



