Earth’s journey around the sun, a topic of immense fascination, is a cornerstone of understanding our planet’s place in the cosmos. If you’re planning a trip to explore the wonders of Vietnam, SIXT.VN is here to ensure your journey is as smooth and enriching as the Earth’s orbit. We offer comprehensive travel solutions, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and curated tours, making your Vietnamese adventure unforgettable. Let’s delve into the fascinating details of Earth’s orbital journey.
1. What Is The Duration Of Earth’s Orbit Around The Sun?
Earth completes its orbit around the Sun in approximately 365.25 days. This period is what we define as one year. The extra 0.25 days is why we have a leap year every four years, adding an extra day (February 29th) to keep our calendar aligned with Earth’s orbit.
Earth’s journey around the sun is not just a matter of time; it’s a dance through space that defines our seasons and shapes our understanding of the cosmos. The concept of a year, rooted in this orbital journey, is fundamental to our calendars and the rhythm of life on Earth.
2. Why Does Earth’s Orbit Take Approximately 365.25 Days?
Earth’s orbital period is determined by its distance from the Sun and its orbital speed. According to Kepler’s laws of planetary motion, planets closer to the Sun have shorter orbital periods and travel faster, while planets farther away have longer orbital periods and move slower. Earth’s specific orbital distance and speed result in the 365.25-day year.
- Distance from the Sun: Earth’s average distance from the Sun is about 149.6 million kilometers (93 million miles). This distance influences the time it takes to complete one orbit.
- Orbital Speed: Earth travels at an average speed of about 30 kilometers per second (18.6 miles per second) in its orbit around the Sun.
These factors combine to dictate the length of Earth’s orbital period.
3. What Is The Shape Of Earth’s Orbit?
Earth’s orbit is not perfectly circular; it is an ellipse. This means that the distance between Earth and the Sun varies throughout the year. At its closest point, called perihelion, Earth is about 147.1 million kilometers from the Sun. At its farthest point, called aphelion, Earth is about 152.1 million kilometers from the Sun.
The elliptical shape of Earth’s orbit is significant because it affects the amount of solar radiation that reaches different parts of the planet at different times of the year. This variation in solar radiation contributes to the changing seasons.
4. How Does Earth’s Tilt Affect The Length Of A Year?
Earth’s axial tilt, approximately 23.4 degrees, is a primary factor in the changing seasons. This tilt causes different parts of the Earth to receive more direct sunlight at different times of the year. Without this tilt, we would not experience distinct seasons.
- Summer: When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, it experiences summer with longer days and warmer temperatures.
- Winter: When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, it experiences winter with shorter days and colder temperatures.
The tilt ensures a consistent pattern of seasonal changes as Earth orbits the Sun, defining the annual cycle.
5. What Is The Significance Of The Leap Year?
The leap year is necessary because Earth’s orbit is not exactly 365 days. It’s approximately 365.25 days. Without the leap year, the calendar would drift by about 24 days every century, leading to a significant misalignment between the calendar and the seasons over time.
The addition of a leap day every four years corrects this discrepancy and keeps our calendar synchronized with Earth’s orbit. This alignment is crucial for agriculture, navigation, and many other aspects of human life that depend on the predictability of the seasons.
6. How Fast Does Earth Travel Around The Sun?
Earth travels at an average speed of about 30 kilometers per second (18.6 miles per second) in its orbit around the Sun. This speed varies slightly depending on Earth’s position in its elliptical orbit, being faster at perihelion and slower at aphelion.
The high speed at which Earth orbits the Sun is a testament to the immense gravitational forces at play and the scale of the solar system.
7. What Are The Consequences Of Earth’s Revolution Around The Sun?
Earth’s revolution around the Sun has several important consequences:
- Seasons: The changing seasons are a direct result of Earth’s tilt and its revolution around the Sun.
- Length of Day: The length of daylight hours varies throughout the year due to Earth’s tilt and orbit.
- Climate Patterns: The distribution of solar radiation across the Earth’s surface affects climate patterns and weather systems.
These consequences impact various aspects of life on Earth, from agriculture and ecosystems to human behavior and culture.
8. How Does Earth’s Orbit Influence Timekeeping?
Earth’s orbit is the basis for our calendar system and our understanding of time. The year is defined by Earth’s orbital period, and the seasons are marked by Earth’s position in its orbit.
Accurate timekeeping is essential for navigation, communication, and coordination in modern society. Earth’s orbit provides a reliable and consistent framework for measuring and tracking time.
9. What Is The Perihelion and Aphelion, and How Do They Affect Earth?
Perihelion is the point in Earth’s orbit when it is closest to the Sun, while aphelion is the point when it is farthest from the Sun. Earth reaches perihelion around January 3rd or 4th and aphelion around July 4th or 5th.
- Perihelion: Earth is about 147.1 million kilometers from the Sun.
- Aphelion: Earth is about 152.1 million kilometers from the Sun.
Although the difference in distance between perihelion and aphelion is significant, it has a relatively small impact on Earth’s seasons. The tilt of Earth’s axis is the primary driver of seasonal changes.
10. What Is The Vernal Equinox and Autumnal Equinox?
The vernal equinox (spring equinox) and autumnal equinox (fall equinox) are the two times of the year when the Sun is directly above the Equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night lengths all over the world.
- Vernal Equinox: Occurs around March 20th or 21st in the Northern Hemisphere, marking the beginning of spring.
- Autumnal Equinox: Occurs around September 22nd or 23rd in the Northern Hemisphere, marking the beginning of autumn.
These equinoxes are significant because they represent transitional points in Earth’s orbit and the changing seasons.
11. How Does Earth’s Orbit Impact Navigation?
Earth’s orbit is crucial for accurate navigation, especially in space travel. Understanding Earth’s position and motion in relation to the Sun and other celestial bodies is essential for planning and executing space missions.
Spacecraft navigation relies on precise calculations of Earth’s orbit to determine the position and velocity of the spacecraft and to ensure accurate trajectories.
12. What Role Does Earth’s Orbit Play in Astronomical Observations?
Earth’s orbit influences astronomical observations because it affects the position and visibility of celestial objects in the sky. As Earth moves around the Sun, different constellations and stars become visible at different times of the year.
Astronomers must account for Earth’s orbital motion when making observations and interpreting data from telescopes and other instruments.
13. How Has Understanding Earth’s Orbit Evolved Over Time?
The understanding of Earth’s orbit has evolved significantly over time, from ancient geocentric models to modern heliocentric models.
- Ancient Models: Early civilizations believed that Earth was the center of the universe and that the Sun and other celestial bodies revolved around it.
- Heliocentric Model: Nicolaus Copernicus proposed the heliocentric model in the 16th century, which correctly placed the Sun at the center of the solar system.
- Kepler’s Laws: Johannes Kepler formulated the laws of planetary motion in the early 17th century, which accurately described the elliptical shape of Earth’s orbit and its speed variations.
These advancements have transformed our understanding of the solar system and Earth’s place within it.
14. What Is the Significance of Earth’s Revolution in Cultural and Historical Contexts?
Earth’s revolution around the Sun has profound cultural and historical significance. The changing seasons, which are a direct result of Earth’s orbit, have influenced agriculture, festivals, and mythology in many cultures throughout history.
- Agriculture: The timing of planting and harvesting crops is closely tied to the seasons, which are determined by Earth’s position in its orbit.
- Festivals: Many cultural festivals and celebrations are associated with seasonal changes, such as spring festivals and harvest festivals.
- Mythology: Earth’s orbit and the changing seasons have inspired numerous myths and legends in different cultures.
These cultural and historical connections demonstrate the deep impact of Earth’s revolution on human societies.
15. What Are the Effects of Earth’s Orbit on Climate Change?
Earth’s orbit plays a role in long-term climate variations. Changes in Earth’s orbit, such as variations in its eccentricity (shape of the orbit), axial tilt, and precession (wobble of the axis), can affect the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth and influence climate patterns over thousands of years.
These orbital variations, known as Milankovitch cycles, are believed to have contributed to past ice ages and other climate changes. Understanding these effects is crucial for studying and predicting future climate trends.
16. How Can Travelers Experience and Appreciate Earth’s Orbit and Its Effects?
Travelers can experience and appreciate the effects of Earth’s orbit in various ways:
- Seasonal Travel: Plan trips to experience different seasons in different parts of the world. Visit the Northern Hemisphere in the summer for long days and warm temperatures, or the Southern Hemisphere in the winter for skiing and snow activities.
- Equinox and Solstice Celebrations: Participate in cultural celebrations and festivals associated with the equinoxes and solstices.
- Stargazing: Take advantage of clear nights to observe the stars and constellations that are visible at different times of the year due to Earth’s orbit.
- Visit Observatories: Explore astronomical observatories and learn about the science of Earth’s orbit and its impact on the cosmos.
By engaging with these experiences, travelers can gain a deeper understanding and appreciation for Earth’s place in the solar system.
17. What Is the Connection Between Earth’s Orbit and Daylight Saving Time?
Daylight Saving Time (DST) is a practice of advancing clocks during the summer months to make better use of daylight. While not directly related to Earth’s orbit, DST is implemented to align waking hours with daylight hours, taking advantage of the longer days that occur during summer due to Earth’s tilt and orbit.
DST is typically observed in regions with distinct seasons, where the length of daylight hours varies significantly throughout the year.
18. How Does Earth’s Orbit Affect Plant Growth and Agriculture?
Earth’s orbit and the resulting seasons have a profound impact on plant growth and agriculture. The changing temperatures, sunlight levels, and precipitation patterns that occur throughout the year influence the timing of planting, growing, and harvesting crops.
Farmers and agricultural scientists carefully monitor Earth’s orbit and seasonal changes to optimize crop production and ensure food security.
19. What Is the Role of Earth’s Orbit in the Study of Climate Science?
Earth’s orbit is a critical factor in the study of climate science. Changes in Earth’s orbit, such as variations in its eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession, can affect the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth and influence climate patterns over long periods.
Climate scientists study these orbital variations, known as Milankovitch cycles, to understand past climate changes and to develop models for predicting future climate trends.
20. How Does Understanding Earth’s Orbit Contribute to Space Exploration?
Understanding Earth’s orbit is essential for planning and executing space exploration missions. Space agencies must accurately calculate Earth’s position and motion in relation to the Sun and other celestial bodies to navigate spacecraft and ensure successful missions.
Knowledge of Earth’s orbit is also crucial for launching satellites into specific orbits around Earth and for communicating with spacecraft in deep space.
21. What Is the Impact of Earth’s Orbit on the Tides?
While the Moon’s gravity is the primary cause of tides, Earth’s orbit also plays a role. The changing distance between Earth and the Sun throughout the year affects the gravitational forces acting on Earth’s oceans, which can influence the height and timing of tides.
When the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned (during new and full moons), the combined gravitational forces produce higher tides, known as spring tides. When the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other (during quarter moons), the gravitational forces partially cancel each other out, resulting in lower tides, known as neap tides.
22. How Does Earth’s Orbit Relate to the Concept of a Sidereal Year?
A sidereal year is the time it takes for Earth to complete one orbit around the Sun with respect to the fixed stars. It is slightly longer than a solar year, which is the time it takes for Earth to complete one orbit with respect to the Sun.
The difference between a sidereal year and a solar year is due to the precession of Earth’s axis, which causes the position of the Sun relative to the stars to change over time.
23. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Earth’s Orbit?
There are several common misconceptions about Earth’s orbit:
- Earth’s orbit is perfectly circular: As mentioned earlier, Earth’s orbit is actually an ellipse.
- The seasons are caused by Earth’s distance from the Sun: The seasons are primarily caused by Earth’s axial tilt, not its distance from the Sun.
- The Sun is always directly overhead at noon: The Sun’s position in the sky varies throughout the year due to Earth’s tilt and orbit.
Understanding these misconceptions can help people gain a more accurate understanding of Earth’s orbit and its effects.
24. How Can Individuals Learn More About Earth’s Orbit and Astronomy?
Individuals can learn more about Earth’s orbit and astronomy through various resources:
- Books: Read books on astronomy and astrophysics to learn about Earth’s orbit and other celestial phenomena.
- Websites: Visit websites of space agencies, observatories, and scientific organizations for information and educational resources.
- Planetariums: Attend shows at planetariums to experience immersive simulations of the solar system and learn about Earth’s orbit.
- Astronomy Clubs: Join local astronomy clubs to connect with other enthusiasts and participate in stargazing events.
By exploring these resources, individuals can deepen their knowledge and appreciation of Earth’s place in the cosmos.
25. How Does SIXT.VN Enhance the Travel Experience in Vietnam by Understanding Earth’s Orbit?
While SIXT.VN doesn’t directly use information about Earth’s orbit in its services, understanding the seasons and climate patterns influenced by Earth’s orbit helps us provide better travel recommendations and services to our customers.
- Seasonal Travel Planning: We can advise travelers on the best times to visit different regions of Vietnam based on seasonal weather conditions.
- Cultural Events: We can inform travelers about cultural festivals and celebrations that are associated with seasonal changes in Vietnam.
- Optimal Travel Routes: We can recommend travel routes and activities that are best suited for the current season.
By incorporating this knowledge into our services, SIXT.VN enhances the travel experience for our customers and helps them make the most of their time in Vietnam.
26. What are the Terrestrial Coordinates and How Do They Relate to Earth’s Orbit?
Terrestrial coordinates, including latitude and longitude, are used to specify locations on Earth’s surface. These coordinates are essential for navigation and mapping, and they are indirectly related to Earth’s orbit because they help us understand our planet’s orientation in space.
- Latitude: Measures the north-south position of a location on Earth’s surface relative to the equator.
- Longitude: Measures the east-west position of a location on Earth’s surface relative to the prime meridian.
Understanding terrestrial coordinates is crucial for accurately tracking Earth’s position in its orbit and for making precise astronomical observations.
27. How Does the Rotation of Earth Interact with Its Revolution Around the Sun?
Earth’s rotation on its axis and its revolution around the Sun are two distinct but interconnected motions. Earth’s rotation causes the daily cycle of day and night, while its revolution around the Sun causes the annual cycle of seasons.
The combination of these two motions creates the complex patterns of daylight hours, temperature variations, and weather systems that we experience on Earth.
28. What is Precession and Nutation, and How Do They Affect Our Understanding of Earth’s Orbit?
Precession and nutation are two additional motions of Earth that affect its orientation in space.
- Precession: A slow, conical wobble of Earth’s axis with a period of about 26,000 years.
- Nutation: A smaller, nodding motion superimposed on precession with a period of about 18.6 years.
These motions are caused by the gravitational forces of the Sun and Moon acting on Earth’s oblate shape. Understanding precession and nutation is important for making precise astronomical measurements and for accurately tracking Earth’s position in its orbit over long periods.
29. How do Epochs Relate to Tracking Earth’s Orbit and Other Celestial Bodies?
Epochs are specific moments in time used as reference points for astronomical measurements. Because Earth’s orbit and the positions of other celestial bodies are constantly changing, astronomers use epochs to define a fixed coordinate system for making observations.
The standard reference epoch is currently J2000.0, which refers to the mean equator and equinox of the year 2000. Using epochs allows astronomers to compare observations made at different times and to accurately track the motions of celestial objects.
30. How Does SIXT.VN Utilize Knowledge of Earth’s Movements to Benefit Travelers in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN leverages an understanding of Earth’s movements, including its rotation and revolution, to enhance the travel experience for visitors to Vietnam:
- Optimized Airport Transfers: We ensure punctual airport transfers, accounting for the time of day and traffic patterns influenced by daily cycles.
- Tailored Tour Recommendations: Our tour itineraries consider seasonal variations, recommending activities that are best enjoyed at specific times of the year. For example, we suggest visiting the beaches during the dry season or exploring the rice terraces during the harvest season.
- Strategic Hotel Bookings: We advise on hotel locations that offer optimal access to attractions based on the time of year and anticipated weather conditions.
By integrating these considerations, SIXT.VN provides travelers with a seamless and enriching experience, ensuring they can fully appreciate the beauty and diversity of Vietnam, regardless of the time of year. Contact SIXT.VN today at Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. Website: SIXT.VN to book your next adventure!
31. What Is the Role of Spacecraft Navigation in Understanding Earth’s Orbit?
Spacecraft navigation relies heavily on a precise understanding of Earth’s orbit. To send spacecraft to other planets or celestial bodies, scientists must accurately calculate Earth’s position and motion in space. This requires detailed knowledge of Earth’s orbital parameters, including its semi-major axis, eccentricity, inclination, and longitude of ascending node.
By tracking spacecraft and analyzing their trajectories, scientists can also refine their understanding of Earth’s orbit and improve their ability to predict its future position.
32. How Does Earth’s Orbit Affect the Visibility of Stars and Constellations?
Earth’s orbit around the Sun causes the apparent positions of stars and constellations to change throughout the year. As Earth moves around the Sun, different stars become visible in the night sky. This is why certain constellations are associated with specific seasons.
For example, the constellation Orion is best seen in the winter months in the Northern Hemisphere, while the constellation Sagittarius is best seen in the summer months. By understanding Earth’s orbit, astronomers can predict which stars and constellations will be visible at any given time of the year.
33. What Are the Milankovitch Cycles and How Do They Relate to Earth’s Orbit?
The Milankovitch cycles are long-term variations in Earth’s orbit that affect the amount of solar radiation reaching the planet. These cycles include:
- Eccentricity: Changes in the shape of Earth’s orbit from nearly circular to more elliptical.
- Obliquity: Changes in the tilt of Earth’s axis.
- Precession: Changes in the direction of Earth’s axis of rotation.
These cycles can influence Earth’s climate over tens of thousands of years and are believed to have played a role in past ice ages.
34. How Can Travelers Use Knowledge of Earth’s Orbit to Enhance Their Travel Experiences in Vietnam?
Travelers can use knowledge of Earth’s orbit and its effects to plan more meaningful and enriching experiences in Vietnam. For example:
- Timing Visits with Seasonal Events: Plan trips to coincide with seasonal events and festivals, such as the Tet Nguyen Dan (Lunar New Year) in the spring or the Mid-Autumn Festival in the fall.
- Optimizing Travel for Weather Conditions: Choose destinations and activities that are best suited for the current season. Visit the northern mountains in the cooler months for hiking and trekking, or the coastal areas in the dry season for swimming and sunbathing.
- Appreciating Cultural Practices Related to Earth’s Cycles: Learn about traditional Vietnamese practices and beliefs that are connected to Earth’s cycles, such as lunar calendars and agricultural practices.
By incorporating this knowledge into their travel plans, visitors can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural and cultural heritage of Vietnam.
35. How Does SIXT.VN Provide Information About Seasonal Weather Patterns to Travelers in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN provides travelers with up-to-date information about seasonal weather patterns in Vietnam to help them plan their trips effectively. This information includes:
- Average Temperatures and Rainfall: Data on average temperatures and rainfall for different regions of Vietnam throughout the year.
- Seasonal Weather Forecasts: Predictions about upcoming weather conditions based on historical data and current weather patterns.
- Recommendations for Appropriate Clothing and Gear: Advice on what to pack for different seasons and activities.
This information helps travelers make informed decisions about when and where to travel in Vietnam and ensures that they are prepared for the weather conditions they are likely to encounter.
36. What Is the Connection Between Earth’s Orbit and Lunar Eclipses?
Lunar eclipses occur when Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon. The timing and frequency of lunar eclipses are related to Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the Moon’s orbit around Earth.
Lunar eclipses can only occur during a full moon, when the Moon is on the opposite side of Earth from the Sun. The exact alignment of the Sun, Earth, and Moon must be precise for a lunar eclipse to occur.
37. How Does Earth’s Orbit Influence the Aurora Borealis and Aurora Australis?
The aurora borealis (northern lights) and aurora australis (southern lights) are natural light displays in the sky, typically seen in high-latitude regions. These auroras are caused by charged particles from the Sun interacting with Earth’s magnetic field.
While Earth’s orbit does not directly cause auroras, it does influence the frequency and intensity of solar activity, which in turn affects the likelihood of auroras occurring. Periods of high solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, are more likely to produce auroras.
38. What Role Does Earth’s Orbit Play in the Search for Extraterrestrial Life?
Earth’s orbit is relevant to the search for extraterrestrial life because it helps us understand the conditions necessary for life to exist on other planets. By studying Earth’s orbit and its effects on climate, temperature, and other factors, scientists can identify planets that may be habitable.
The habitable zone around a star is the region where a planet could have liquid water on its surface, which is considered essential for life as we know it. Earth’s orbit places it within the Sun’s habitable zone, making it a suitable place for life.
39. How Can Travelers Use Knowledge of Earth’s Orbit to Appreciate the Night Sky in Vietnam?
Travelers can use knowledge of Earth’s orbit to enhance their appreciation of the night sky in Vietnam by:
- Identifying Constellations: Learn to identify constellations that are visible at different times of the year due to Earth’s orbit.
- Observing Meteor Showers: Plan trips to coincide with meteor showers, which occur when Earth passes through streams of debris left behind by comets.
- Stargazing in Dark Locations: Seek out dark locations away from city lights to get the best view of the stars and planets.
By taking these steps, travelers can gain a deeper connection to the cosmos and appreciate the beauty of the night sky in Vietnam.
40. How Does SIXT.VN Provide Information About Stargazing Opportunities in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN provides information about stargazing opportunities in Vietnam to help travelers make the most of their time in the country. This information includes:
- Recommended Stargazing Locations: Suggestions for locations with minimal light pollution and clear views of the night sky.
- Information About Upcoming Celestial Events: Details about meteor showers, lunar eclipses, and other celestial events that will be visible from Vietnam.
- Links to Astronomy Resources: Links to websites and organizations that provide information about astronomy and stargazing.
By providing this information, SIXT.VN helps travelers connect with the natural world and experience the wonders of the universe during their travels in Vietnam.
41. How Does Earth’s Speed Vary in Its Orbit Around the Sun?
Earth’s speed in its orbit around the Sun is not constant. According to Kepler’s Second Law of Planetary Motion, a planet moves faster when it is closer to the Sun and slower when it is farther away. This means that Earth travels slightly faster during the perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) and slightly slower during the aphelion (farthest distance from the Sun).
The difference in speed is relatively small, but it does affect the length of the seasons. Because Earth is moving faster in its orbit during the winter months in the Northern Hemisphere, winter is slightly shorter than summer.
42. What Is the Significance of Earth’s Axial Tilt (Obliquity) in Relation to Its Orbit?
Earth’s axial tilt, also known as obliquity, is the angle between Earth’s rotational axis and its orbital plane. This tilt is currently about 23.4 degrees, but it varies slightly over long periods due to gravitational interactions with other planets.
Earth’s axial tilt is responsible for the changing seasons. Without axial tilt, there would be no distinct seasons, and the climate would be more uniform throughout the year.
43. How Does Earth’s Orbit Affect Long-Term Climate Variability?
Earth’s orbit plays a significant role in long-term climate variability through the Milankovitch cycles. These cycles, which involve changes in Earth’s eccentricity, obliquity, and precession, can affect the amount and distribution of solar radiation reaching Earth and influence climate patterns over tens of thousands of years.
The Milankovitch cycles are believed to have contributed to past ice ages and other major climate changes. Understanding these cycles is crucial for studying and predicting future climate trends.
44. How Can Travelers Use Knowledge of Earth’s Orbit to Plan Unique Travel Experiences in Vietnam?
Travelers can use knowledge of Earth’s orbit and its effects to plan unique and memorable travel experiences in Vietnam, such as:
- Chasing the Seasons: Plan a multi-trip to experience different seasons in various regions of Vietnam.
- Equinox and Solstice Celebrations: Participate in local festivals and celebrations that are connected to the equinoxes and solstices.
- Stargazing Adventures: Embark on stargazing tours in remote areas of Vietnam with minimal light pollution.
By incorporating these experiences into their travel plans, visitors can gain a deeper connection to the natural world and create lasting memories.
45. How Does SIXT.VN Help Travelers Find and Participate in Local Festivals and Celebrations Related to Earth’s Orbit?
SIXT.VN assists travelers in discovering and participating in local festivals and celebrations that are related to Earth’s orbit by:
- Providing a Calendar of Events: Offering a calendar of events that highlights seasonal festivals and celebrations in different regions of Vietnam.
- Offering Tour Packages: Designing tour packages that include opportunities to experience local customs and traditions.
- Providing Information on the Cultural Significance of Events: Sharing information about the cultural and historical significance of various festivals and celebrations.
By providing these services, SIXT.VN helps travelers immerse themselves in the local culture and create meaningful travel experiences.
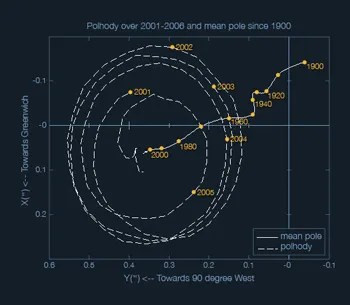 Movement of Earth's rotational poles 2001 to 2006, and the mean pole location from the year 1900 to 2000
Movement of Earth's rotational poles 2001 to 2006, and the mean pole location from the year 1900 to 2000
46. What Is the Significance of Earth’s Orbital Plane (Ecliptic)?
The ecliptic is the plane of Earth’s orbit around the Sun. It is an important reference plane in astronomy because the other planets in our solar system orbit the Sun in roughly the same plane.
The ecliptic also defines the path that the Sun appears to take across the sky throughout the year. The zodiac constellations are located along the ecliptic, and the Sun passes through each of these constellations at different times of the year.
47. How Does Earth’s Orbit Affect the Length of Day and Night?
Earth’s orbit, combined with its axial tilt, causes the length of day and night to vary throughout the year. During the summer solstice, the hemisphere tilted towards the Sun experiences the longest day and shortest night, while the opposite hemisphere experiences the shortest day and longest night.
During the winter solstice, the opposite occurs: the hemisphere tilted away from the Sun experiences the shortest day and longest night, while the opposite hemisphere experiences the longest day and shortest night. During the equinoxes, both hemispheres experience roughly equal lengths of day and night.
48. What Role Does Earth’s Orbit Play in Predicting Solar Eclipses?
Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Sun and Earth, blocking the Sun’s light. The timing and frequency of solar eclipses are related to Earth’s orbit around the Sun and the Moon’s orbit around Earth.
Predicting solar eclipses requires precise knowledge of the positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon. Astronomers use sophisticated models of Earth’s orbit and the Moon’s orbit to predict when and where solar eclipses will occur.
49. How Can Travelers Experience the Effects of Earth’s Orbit on Seasonal Changes in Vietnam?
Travelers can experience the effects of Earth’s orbit on seasonal changes in Vietnam by:
- Visiting Different Regions at Different Times of the Year: Explore the northern mountains during the cooler months for hiking and trekking, or the coastal areas during the dry season for swimming and sunbathing.
- Observing Changes in Flora and Fauna: Notice how the vegetation and animal life change with the seasons.
- Participating in Local Festivals: Immerse themselves in local festivals and celebrations that are related to the changing seasons.
By paying attention to these details, travelers can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural cycles that shape the Vietnamese landscape and culture.
50. How Does SIXT.VN Provide Travelers with Information About the Best Times to Visit Different Regions of Vietnam Based on Seasonal Weather Patterns?
SIXT.VN provides travelers with information about the optimal times to visit various regions of Vietnam based on seasonal weather conditions, including:
- Detailed Weather Guides: Providing comprehensive weather guides for different regions of Vietnam, highlighting average temperatures, rainfall, and humidity levels throughout the year.
- Recommendations for Activities and Attractions: Suggesting activities and attractions that are best suited for each season.
- Personalized Travel Advice: Offering personalized travel advice based on individual preferences and interests.
By offering these services, SIXT.VN ensures that travelers can make informed decisions about when and where to travel in Vietnam, maximizing their enjoyment and comfort.
In conclusion, understanding how long Earth takes to travel around the Sun, and the myriad effects this journey has on our planet, enriches our travel experiences. With SIXT.VN, exploring Vietnam becomes more than just a trip; it’s an immersive journey through a land shaped by the very cosmos we inhabit. Let us guide you to the best experiences Vietnam has to offer, ensuring your adventure is both memorable and seamless. From airport services to tailored tours, we are here to make your travel dreams a reality. Visit SIXT.VN, your gateway to the wonders of Vietnam.



