Are you curious about how quickly radio waves travel and how this affects data transmission? SIXT.VN is here to guide you through the fascinating world of electromagnetic waves and their role in modern communication. Discover the factors influencing data speeds and explore the potential of light-based communication technologies for your next adventure in Vietnam!
1. Understanding Electromagnetic Waves: Radio vs. Light
What are electromagnetic waves, and how do radio waves and light differ?
Electromagnetic waves are combined oscillations of electric and magnetic fields. The primary difference between radio waves and light is their frequency of oscillation. Visible light has frequencies ranging from 400 terahertz (THz) for red to 790 THz for violet, while radio waves oscillate at 300 gigahertz (GHz) or slower. According to research from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that travels through space.
 Electromagnetic Spectrum Showing Radio Waves and Visible Light
Electromagnetic Spectrum Showing Radio Waves and Visible Light
1.1 Interaction with Matter
How do radio waves and light interact with matter differently?
Visible light is strongly emitted and absorbed by individual atoms, interacting strongly with matter. Radio waves, however, do not strongly interact with individual atoms and tend to pass through most matter with ease. This property makes radio waves useful for communication through walls and other barriers.
1.2 Practical Applications
Why are radio waves suitable for certain applications, and light for others?
Radio waves are ideal for applications where signals need to pass through obstacles, such as in-home Wi-Fi or mobile communication. Light, on the other hand, is being explored for high-speed, line-of-sight data transmission, like Li-Fi, although it requires a clear path between the transmitter and receiver.
2. Encoding Information on Waves: Carrier Frequency and Modulation
How is information encoded onto a wave for transmission?
Information is encoded by choosing a wave frequency to transmit over, known as the carrier frequency. This carrier wave, ideally a perfect sinusoidal wave, is then distorted slightly to carry the information. These distortions represent the data we want to transmit, whether it’s audio signals for traditional radio or binary data for internet signals.
2.1 Amplitude Modulation (AM) vs. Frequency Modulation (FM)
What are the key differences between AM and FM radio encoding?
In Amplitude Modulation (AM), the signal creates a change in the amplitude of the carrier wave. In Frequency Modulation (FM), the signal creates a change in the frequency of the carrier wave. FM is generally preferred for music due to its higher bandwidth, which allows for better audio quality.
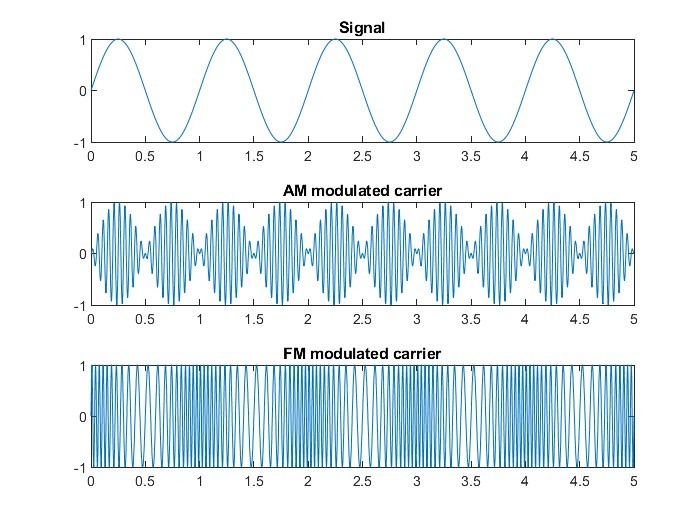 Comparison of Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM)
Comparison of Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM)
2.2 Bandwidth and Signal Quality
How does bandwidth affect the quality and amount of information transmitted?
Bandwidth refers to the range of frequency components in a signal. A wider bandwidth allows for more information to be transmitted at a higher rate. For example, transmitting a 20 kHz audio signal requires a bandwidth of around 20 kHz. According to the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), bandwidth is a critical factor in determining the amount of data that can be transmitted.
3. Radio Frequency Bands and Their Uses
What are the different radio frequency bands, and what are they used for?
Different radio frequency bands are designated for specific purposes. The AM radio band ranges from 530 to 1700 kHz, while the FM radio band ranges from 87.5 to 108 MHz. High-frequency radio (3-30 MHz) is used for shortwave communication.
3.1 AM vs. FM Bandwidth
Why is FM radio preferred for music over AM radio?
The allotted bandwidth for FM radio is significantly larger than that for AM radio. FM radio has a bandwidth of about 20 million Hertz, compared to AM radio’s 1 million Hertz. This larger bandwidth allows FM stations to transmit more audio signals simultaneously and with higher quality.
3.2 Carrier Frequency Importance
How does carrier frequency affect data transmission?
A higher carrier frequency provides more room to fit more channels with a higher rate of data transfer. If you want to transfer data at 300k bits per second, you would need a 300 kHz bandwidth available.
4. Wi-Fi Technology: Frequency Bands and Data Rates
Which radio frequency bands are used for Wi-Fi, and how do they affect performance?
Wi-Fi uses various radio frequency bands, including the 2.4 GHz range. This range includes 14 channels spaced 5 MHz apart, with each channel broadcasting over about 25 MHz. Higher-frequency Wi-Fi systems have reduced interference problems, enhancing performance.
4.1 Wi-Fi Frequencies
What are the different Wi-Fi frequency bands, and how do they perform?
Wi-Fi broadcasts in the “ultra-high frequency” (300 MHz to 3 GHz) or “super-high frequency” (3 GHz to 30 GHz) radio bands. These signals can pass through walls but are attenuated more, making them suitable for in-home Wi-Fi.
4.2 Overcoming Interference
How do higher-frequency Wi-Fi systems reduce interference?
Higher-frequency Wi-Fi systems reduce interference by utilizing less crowded channels and more advanced encoding methods. This allows for better performance, especially in densely populated areas where multiple devices are competing for bandwidth.
5. Li-Fi: The Future of Data Transmission?
What is Li-Fi, and how does it compare to Wi-Fi in terms of data transmission rates?
Li-Fi is a technology that uses visible light to transmit wireless data. Visible light encompasses a 390 THz range of frequencies, roughly 1000 times larger than the entire radio frequency spectrum. This means that Li-Fi could potentially have data transmission rates more than 1000 times greater than Wi-Fi.
5.1 Advantages of Li-Fi
What are the potential benefits of using Li-Fi over traditional Wi-Fi?
Li-Fi offers the potential for much higher data transmission rates due to its use of the visible light spectrum. According to a report by Grand View Research, the Li-Fi market is expected to grow significantly due to its high-speed data capabilities and increased security.
5.2 Limitations of Li-Fi
What are the limitations and challenges associated with Li-Fi technology?
Li-Fi requires a line of sight between the transmitter and receiver, as light cannot pass through walls. This means that devices must be in the same room as the transmitter to receive data. Additionally, the speed is limited by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
6. Factors Influencing Data Transmission Speed
What factors determine the speed at which data can be transmitted via electromagnetic waves?
The rate at which data can be transmitted is strongly dependent on the carrier frequency being used and the available bandwidth. Higher frequencies and wider bandwidths allow for faster data transmission.
6.1 Carrier Frequency and Bandwidth
How do carrier frequency and bandwidth individually impact data transmission speed?
Carrier frequency determines the number of oscillations per second, allowing for more data to be encoded. Bandwidth, on the other hand, determines the amount of frequency range available for transmitting the signal. Both factors are crucial for achieving high data transmission speeds.
6.2 Practical Limits
What are the practical limits to increasing bandwidth and frequency for data transmission?
There are practical limits to simply increasing bandwidth and frequency. Very high-frequency radio signals are more impacted by barriers, and extremely high frequencies like ultraviolet or X-rays can be harmful to humans.
7. Exploring Hanoi with SIXT.VN
Planning a trip to Hanoi? SIXT.VN offers a range of services to make your travel experience seamless and enjoyable.
7.1 Airport Transfers
How can SIXT.VN help with airport transfers in Hanoi?
SIXT.VN provides reliable and convenient airport transfer services. Ensure a stress-free arrival and departure with our professional drivers and comfortable vehicles. We offer punctual and safe transportation to and from Noi Bai International Airport.
7.2 Hotel Bookings
What types of hotel accommodations can SIXT.VN assist with in Hanoi?
SIXT.VN assists with hotel bookings, offering a variety of options to suit your budget and preferences. From luxury hotels to budget-friendly accommodations, we can help you find the perfect place to stay in Hanoi.
7.3 Tours and Activities
What tours and activities does SIXT.VN offer in Hanoi?
SIXT.VN offers a variety of tours and activities to explore Hanoi’s rich culture and history. Discover iconic landmarks, vibrant markets, and delicious cuisine with our expertly guided tours.
8. Benefits of Using SIXT.VN for Your Vietnam Trip
What are the advantages of using SIXT.VN for your travel needs in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN provides convenient, reliable, and comprehensive travel services. Benefit from our easy booking process, professional support, and extensive local knowledge. We offer personalized service to ensure your trip is unforgettable.
8.1 Convenience and Reliability
How does SIXT.VN ensure convenience and reliability for travelers?
SIXT.VN ensures convenience and reliability through our user-friendly website, 24/7 customer support, and partnerships with trusted local service providers. We handle all the details so you can focus on enjoying your trip.
8.2 Comprehensive Travel Services
What range of travel services does SIXT.VN offer to customers?
SIXT.VN offers a comprehensive range of travel services, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, tours, and activities. We are your one-stop shop for all your travel needs in Vietnam.
9. Overcoming Travel Challenges in Vietnam
What common challenges do travelers face in Vietnam, and how can SIXT.VN help?
Travelers in Vietnam may face challenges such as language barriers, transportation difficulties, and uncertainty about finding reliable services. SIXT.VN helps overcome these challenges by providing English-speaking support, reliable transportation options, and a curated selection of trusted service providers.
9.1 Language Barriers
How does SIXT.VN assist with language barriers for foreign tourists?
SIXT.VN provides English-speaking support to assist with communication and ensure a smooth travel experience. Our team is available to answer questions, provide recommendations, and help with any issues that may arise.
9.2 Reliable Transportation
What reliable transportation options does SIXT.VN offer in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers reliable transportation options, including airport transfers and private car services. Our professional drivers are experienced and knowledgeable, ensuring safe and efficient travel throughout Vietnam.
10. Call to Action: Plan Your Vietnam Adventure with SIXT.VN
Ready to explore Vietnam? Visit SIXT.VN today to discover our comprehensive travel services and start planning your unforgettable adventure!
10.1 Explore Our Services
What specific services should potential customers explore on the SIXT.VN website?
Explore our airport transfer services for seamless transportation, browse our hotel selection for the perfect accommodation, and discover our exciting tours and activities to make the most of your trip.
10.2 Contact Us for Support
How can customers contact SIXT.VN for personalized travel assistance?
Contact our friendly customer support team via phone or WhatsApp at +84 986 244 358 for personalized travel assistance. We are here to help you plan every detail of your Vietnam adventure.
FAQ: Radio Waves and Data Transmission
1. How fast do radio waves travel in space?
Radio waves travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (or about 186,282 miles per second) in a vacuum.
2. Does the medium affect the speed of radio waves?
Yes, the medium through which radio waves travel can affect their speed. They travel slightly slower in air than in a vacuum, and their speed can be further reduced when traveling through other materials.
3. What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional. The higher the frequency of a wave, the shorter its wavelength, and vice versa. This relationship is described by the equation: speed of light = frequency × wavelength.
4. How does bandwidth affect the amount of data that can be transmitted?
Bandwidth refers to the range of frequencies available for transmitting a signal. A wider bandwidth allows for more data to be transmitted in a given amount of time, increasing the data transmission rate.
5. What is the difference between radio waves and microwaves?
Radio waves and microwaves are both part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Microwaves have a higher frequency range (typically between 300 MHz and 300 GHz) compared to radio waves (3 kHz to 300 MHz).
6. What are some common applications of radio waves?
Radio waves are used in a wide range of applications, including broadcasting (AM and FM radio), television, mobile communication (cell phones), Wi-Fi, satellite communication, and radar systems.
7. How do Wi-Fi routers transmit data using radio waves?
Wi-Fi routers modulate data onto radio waves and transmit them wirelessly. Devices with Wi-Fi adapters can receive and demodulate these signals to access the internet or communicate with other devices on the network.
8. What is Li-Fi, and how does it differ from Wi-Fi?
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a technology that uses visible light to transmit data, unlike Wi-Fi, which uses radio waves. Li-Fi can potentially offer higher data transmission rates and increased security but requires a direct line of sight between the transmitter and receiver.
9. Are there any health concerns associated with exposure to radio waves?
Regulatory agencies set safety limits on exposure to radiofrequency (RF) radiation to protect the public.
10. How can I improve my Wi-Fi signal strength at home?
To improve Wi-Fi signal strength, you can try the following:
- Position your router in a central location.
- Keep your router away from obstacles like walls and metal objects.
- Update your router’s firmware.
- Use a Wi-Fi extender or mesh network.
- Reduce interference from other electronic devices.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/WhatsApp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN



