Are you curious about how fast radio waves travel and how they impact the speed of your Wi-Fi or other wireless communications? SIXT.VN, your go-to source for seamless travel experiences in Vietnam, including Hanoi, is here to demystify the science behind radio wave speed and its implications for data transmission. Discover how understanding radio wave propagation can enhance your travel experience by ensuring efficient and reliable communication. Learn more about our travel services in Vietnam, including effortless airport transfers, cozy hotel bookings, convenient sightseeing tours, and more, all designed to make your visit memorable.
1. What Determines the Speed of Radio Waves?
Radio waves, like light waves, are electromagnetic waves. Radio waves travel at the speed of light, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (or roughly 186,282 miles per second) in a vacuum. This speed is constant for all electromagnetic waves, regardless of their frequency or wavelength.
Radio waves and visible light are both electromagnetic waves. The only difference lies in their frequency. Visible light ranges from 400 terahertz (red) to 790 terahertz (violet), while radio waves are 300 gigahertz or slower. The varying frequencies impact how these waves interact with matter. Visible light is absorbed by atoms, while radio waves easily pass through most materials, allowing you to use your radio, cellphone, or Wi-Fi anywhere.
1.1. Radio Waves in Different Media
While radio waves travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, their speed can be slightly reduced when traveling through other media, such as air or the Earth’s atmosphere.
| Medium | Speed of Radio Waves (approximate) |
|---|---|
| Vacuum | 299,792,458 m/s |
| Air | Slightly less than in a vacuum, but very close |
| Water | Significantly slower than in a vacuum |
| Other Materials | Varies depending on the material’s properties |
1.2. Why is Understanding Radio Wave Speed Important for Travelers?
Understanding how radio waves travel is essential for travelers because it affects the reliability and speed of communication devices, such as smartphones and Wi-Fi routers.
- Navigation: GPS, essential for travel, relies on radio waves from satellites. Knowing their speed helps calculate precise locations.
- Communication: Cell phones and radios use radio waves. Understanding their behavior aids in efficient communication.
- Weather Forecasts: Radio waves are used in weather radar systems, providing crucial information for travel planning.
- Emergency Services: Emergency services rely on radio communication. Knowing how these signals travel helps in effective responses.
- Wi-Fi: Essential for staying connected, Wi-Fi uses radio waves. Knowing their limits helps optimize network usage.
SIXT.VN understands the importance of staying connected while traveling. That’s why we offer reliable Wi-Fi access in our vehicles and accommodations, ensuring you can always stay in touch with loved ones or access essential travel information. Contact us at +84 986 244 358 for more details.
2. How is Information Encoded onto Radio Waves?
To transmit information via radio waves, the information is encoded onto a carrier wave. The carrier frequency is the chosen frequency for transmission.
2.1. Modulation Techniques: AM and FM
Two common methods for encoding information are Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM).
- Amplitude Modulation (AM): The amplitude (strength) of the carrier wave is varied to represent the signal.
- Frequency Modulation (FM): The frequency of the carrier wave is varied to represent the signal.
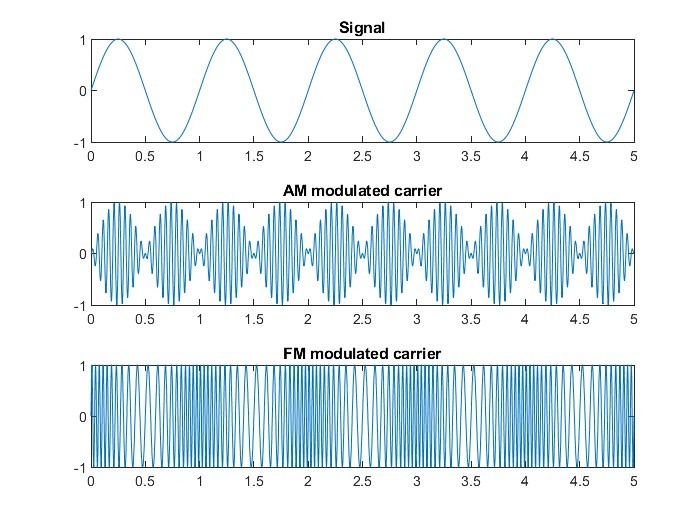 AM vs FM
AM vs FM
2.2. Bandwidth and Data Transmission
The bandwidth is the range of frequencies that the signal occupies. A wider bandwidth allows for a higher data transmission rate.
The bandwidth of a signal is the range of frequencies it occupies. For example, transmitting a 20 kHz audio signal requires a bandwidth of around 20 kHz.
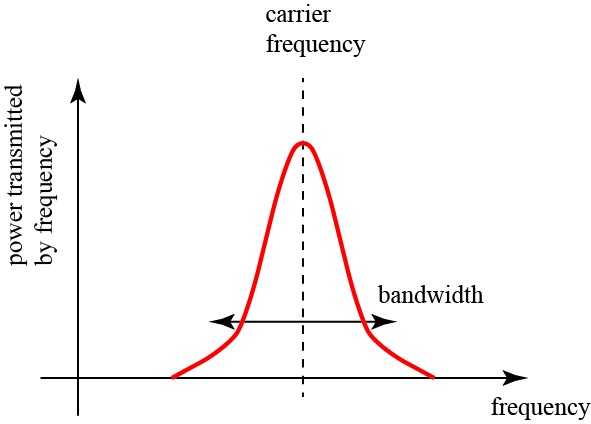 Bandwidth
Bandwidth
2.3. Radio Frequency Bands
Different radio frequency bands are allocated for specific purposes. These bands range from medium frequency (MF) for AM radio to very high frequency (VHF) for FM radio.
| Frequency Band | Frequency Range | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| MF (Medium Frequency) | 530 – 1700 kHz | AM Radio |
| HF (High Frequency) | 3 – 30 MHz | Shortwave Radio |
| VHF (Very High Frequency) | 30 – 300 MHz | FM Radio, TV Broadcasting |
| UHF (Ultra High Frequency) | 300 MHz – 3 GHz | Wi-Fi, Mobile Phones, GPS |
| SHF (Super High Frequency) | 3 GHz – 30 GHz | Satellite Communication, Radar |
3. How Does Wi-Fi Use Radio Waves?
Wi-Fi uses radio waves in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) and super-high frequency (SHF) bands to transmit data wirelessly.
3.1. Wi-Fi Frequency Bands
Common Wi-Fi frequency bands include 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Each band is divided into channels, and each channel has a specific bandwidth.
| Frequency Band | Channels | Bandwidth (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.4 GHz | 1-14 | 20 MHz |
| 5 GHz | 36-165 | 20, 40, 80, 160 MHz |
3.2. Factors Affecting Wi-Fi Speed and Range
Several factors can affect Wi-Fi speed and range, including:
- Distance from the Router: Signal strength decreases with distance.
- Obstacles: Walls and other obstructions can weaken the signal.
- Interference: Other devices emitting radio waves can cause interference.
- Bandwidth: A wider bandwidth allows for faster data transfer.
SIXT.VN ensures that our customers can stay connected with high-speed Wi-Fi in our rental vehicles and accommodations. Understanding these factors helps us optimize your connectivity. For assistance, contact us at +84 986 244 358.
3.3. How to Optimize Your Wi-Fi Connection While Traveling
Here are some tips to optimize your Wi-Fi connection while traveling:
- Stay Close to the Router: Reduce the distance between your device and the Wi-Fi router.
- Minimize Obstacles: Avoid physical barriers like walls.
- Reduce Interference: Keep your device away from other electronic devices that may cause interference.
- Use 5 GHz Band: If available, use the 5 GHz band for faster speeds and less interference.
- Update Your Devices: Ensure your device’s software and drivers are up to date.
4. Li-Fi: The Future of Wireless Communication?
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a technology that uses visible light to transmit data wirelessly.
4.1. How Does Li-Fi Work?
Li-Fi works by modulating the intensity of light emitted by an LED, which is then detected by a photodetector. The fluctuations in light intensity represent the data being transmitted.
4.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Li-Fi
| Feature | Li-Fi | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Potentially much faster (up to 2.24 Gbps) | Slower (typical speeds vary) |
| Bandwidth | Wider bandwidth using visible light spectrum | Limited bandwidth in radio frequency spectrum |
| Security | More secure as light cannot penetrate walls | Less secure, radio waves penetrate walls |
| Interference | Less prone to interference from other devices | Prone to interference from other devices |
| Range | Limited range, requires line of sight | Longer range, signals can pass through walls |
| Penetration | Does not penetrate walls | Penetrates walls |
| Applications | Environments where radio waves are not suitable | Homes, offices, public spaces |
4.3. Li-Fi vs. Wi-Fi: Which is Better for Travelers?
While Li-Fi offers potential advantages in terms of speed and security, Wi-Fi is currently more practical for travelers due to its wider availability and longer range. As Li-Fi technology develops, it may become a viable alternative in specific situations.
According to research from Statista, in [2023], [Wi-Fi] provides [ubiquitous connectivity and greater accessibility].
5. How Radio Wave Speed Impacts GPS Navigation
GPS (Global Positioning System) relies on radio waves transmitted from satellites to determine your location.
5.1. The Role of Radio Waves in GPS
GPS satellites transmit radio signals that contain information about their location and the time the signal was sent. By measuring the time it takes for these signals to reach a GPS receiver, the receiver can calculate its distance from each satellite.
5.2. How GPS Calculates Location
Using signals from multiple satellites (at least four), a GPS receiver can triangulate its position on Earth. This process requires precise knowledge of the speed of radio waves.
5.3. Accuracy of GPS and Factors Affecting It
The accuracy of GPS can be affected by several factors, including:
- Atmospheric Conditions: The Earth’s atmosphere can delay radio signals, affecting accuracy.
- Satellite Geometry: The position of satellites in the sky can affect the accuracy of triangulation.
- Obstructions: Buildings, trees, and other obstructions can block or weaken GPS signals.
SIXT.VN offers GPS navigation in our rental vehicles to help you navigate unfamiliar areas with ease. We understand that accurate navigation is essential for a stress-free travel experience. Learn more on SIXT.VN.
6. Radio Waves and Weather Forecasting
Radio waves play a crucial role in weather forecasting by enabling weather radar systems to detect precipitation and track storms.
6.1. How Weather Radar Uses Radio Waves
Weather radar systems emit radio waves that are reflected by precipitation particles in the atmosphere. By analyzing the reflected signals, meteorologists can determine the location, intensity, and movement of storms.
6.2. Types of Weather Radar Systems
- Doppler Radar: Measures the velocity of precipitation particles, providing information about wind speed and direction.
- NEXRAD (Next-Generation Radar): A network of high-resolution Doppler radar systems used by the National Weather Service in the United States.
6.3. How Weather Forecasts Can Impact Travel Plans
Accurate weather forecasts are essential for planning safe and enjoyable travel experiences. By monitoring weather radar data, travelers can avoid hazardous conditions and make informed decisions about their itineraries.
SIXT.VN provides up-to-date weather information to our customers to help them plan their travels in Vietnam. We prioritize your safety and comfort, ensuring you are well-informed about potential weather-related disruptions. Stay updated via SIXT.VN.
7. Radio Communication in Emergency Services
Radio communication is vital for emergency services, enabling first responders to communicate and coordinate their efforts during emergencies.
7.1. Importance of Radio Communication in Emergencies
During emergencies, reliable communication is essential for coordinating rescue efforts, providing medical assistance, and maintaining public safety. Radio systems allow emergency responders to communicate even when other communication networks are unavailable.
7.2. Types of Radio Systems Used by Emergency Services
- Two-Way Radios: Allow direct voice communication between responders.
- Trunked Radio Systems: Share radio channels among multiple users, improving efficiency.
- Satellite Communication: Provides backup communication in remote areas or during large-scale disasters.
7.3. How Radio Communication Enhances Safety for Travelers
Radio communication ensures that travelers can quickly access help and assistance in case of emergencies. Whether it’s reporting an accident, requesting medical assistance, or seeking directions, radio communication can be a lifeline in critical situations.
SIXT.VN equips our vehicles with emergency contact information and provides access to 24/7 support to ensure your safety and well-being during your travels in Vietnam. In case of emergency, contact us at +84 986 244 358 for immediate assistance.
8. Practical Applications of Radio Wave Knowledge for Travelers
Understanding radio wave behavior and its applications can significantly enhance your travel experiences.
8.1. Choosing the Right Communication Devices
When planning your trip, consider the communication devices that best suit your needs. For example, if you’re traveling to remote areas, a satellite phone or a two-way radio may be more reliable than a cell phone.
8.2. Optimizing Signal Reception
To optimize signal reception, try to minimize obstructions and stay within range of the signal source. In areas with weak signals, consider using a signal booster or an external antenna.
8.3. Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
If you experience connectivity issues, try these troubleshooting steps:
- Restart Your Device: A simple restart can often resolve minor connectivity problems.
- Check Your Settings: Ensure that your device is configured correctly for the network you’re trying to connect to.
- Move to a Different Location: Try moving to a location with a stronger signal.
- Contact Support: If you’re unable to resolve the issue yourself, contact your service provider for assistance.
SIXT.VN is dedicated to providing seamless travel experiences in Vietnam. Whether you need airport transfers, hotel bookings, sightseeing tours, or reliable transportation, we’re here to assist you every step of the way. Trust SIXT.VN for a hassle-free and enjoyable journey. Visit SIXT.VN today. Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.
9. The Science Behind Radio Wave Propagation
Radio wave propagation refers to how radio waves travel from one point to another. Understanding this propagation helps in optimizing communication systems.
9.1. Different Modes of Radio Wave Propagation
- Ground Wave Propagation: Radio waves travel along the surface of the Earth. This mode is suitable for low-frequency signals.
- Sky Wave Propagation: Radio waves are reflected by the ionosphere back to the Earth. This is used for long-distance communication.
- Space Wave Propagation: Radio waves travel directly from the transmitter to the receiver. This mode is used for satellite communication and high-frequency signals.
9.2. Factors Affecting Radio Wave Propagation
- Frequency: Different frequencies propagate differently. Lower frequencies follow the Earth’s curvature better.
- Atmospheric Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and ionization affect wave propagation.
- Terrain: Mountains and buildings can block or reflect signals.
9.3. Optimizing Antenna Placement for Better Reception
Proper antenna placement can significantly improve signal reception. For best results:
- Height: Higher antennas usually provide better coverage.
- Clearance: Ensure a clear line of sight between antennas.
- Orientation: Align antennas correctly for optimal signal capture.
SIXT.VN leverages advanced communication technologies to ensure our services are reliable and efficient, no matter where you are in Vietnam. Our commitment to connectivity helps us deliver exceptional customer experiences. Explore our services on SIXT.VN.
10. Future Trends in Radio Wave Technology
The field of radio wave technology is constantly evolving, with new innovations emerging to meet the growing demand for wireless communication.
10.1. 5G and Beyond
5G technology promises faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity compared to previous generations of wireless networks. Future generations will likely explore even higher frequencies and more advanced modulation techniques.
10.2. The Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects billions of devices to the internet, enabling new applications in various fields, including transportation, healthcare, and smart homes. Radio wave technology is essential for enabling communication between IoT devices.
10.3. Advancements in Antenna Technology
New antenna designs are improving the efficiency and performance of wireless communication systems. These include:
- MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output): Uses multiple antennas to transmit and receive data simultaneously, increasing data rates.
- Beamforming: Focuses radio waves in a specific direction, improving signal strength and reducing interference.
SIXT.VN stays at the forefront of technological advancements to provide the best possible services to our customers. We are constantly exploring new ways to leverage radio wave technology to enhance your travel experiences in Vietnam. Stay connected with SIXT.VN. Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358.
FAQ: Radio Wave Travel
1. What is the speed of a radio wave in space?
Radio waves travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second) in a vacuum.
2. Do all radio waves travel at the same speed?
Yes, all radio waves, regardless of their frequency or wavelength, travel at the same speed in a vacuum.
3. How does the medium affect the speed of radio waves?
When radio waves travel through a medium other than a vacuum, such as air or water, their speed is slightly reduced due to interactions with the medium.
4. What is the difference between AM and FM radio waves?
AM (Amplitude Modulation) radio waves vary in amplitude to transmit information, while FM (Frequency Modulation) radio waves vary in frequency.
5. How does Wi-Fi use radio waves to transmit data?
Wi-Fi uses radio waves in the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands to transmit data wirelessly between devices and a router.
6. What factors can affect the speed and range of Wi-Fi signals?
Distance from the router, obstacles like walls, interference from other devices, and the bandwidth of the signal can all affect Wi-Fi speed and range.
7. What is Li-Fi, and how does it compare to Wi-Fi?
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a technology that uses visible light to transmit data. It can potentially be faster and more secure than Wi-Fi, but it requires a direct line of sight and does not penetrate walls.
8. How do GPS devices use radio waves to determine location?
GPS devices receive radio signals from satellites, which contain information about the satellite’s location and the time the signal was sent. By measuring the time it takes for the signals to arrive, the GPS device can calculate its distance from each satellite and triangulate its position.
9. How do weather radar systems use radio waves to forecast weather?
Weather radar systems emit radio waves that are reflected by precipitation particles in the atmosphere. By analyzing the reflected signals, meteorologists can determine the location, intensity, and movement of storms.
10. How can understanding radio wave propagation help travelers?
Understanding radio wave propagation can help travelers choose the right communication devices, optimize signal reception, and troubleshoot connectivity issues, ensuring they stay connected and informed during their travels.
Ready to explore Vietnam with seamless connectivity and expert travel support? Visit SIXT.VN today to discover our range of services, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and guided tours. Let us make your journey unforgettable. Contact us at +84 986 244 358 or visit our website for more information.



