Are you curious about how far chipmunks travel? This article explores the fascinating world of chipmunk territories, habits, and how SIXT.VN can help you plan your Vietnam adventure, providing seamless travel experiences and uncovering the best destinations in Vietnam, from airport transfers to tailored tours. So, discover more about these creatures while planning an unforgettable trip.
1. What Is the Average Travel Distance for Chipmunks?
Chipmunks typically travel within a relatively small home range. On average, the travel distance for chipmunks is usually around a quarter of an acre (approximately 0.1 hectares). This area provides them with sufficient resources, including food, shelter, and mates.
- Within this range, chipmunks create intricate burrow systems for nesting and storing food.
- They are most active during the day, foraging for nuts, seeds, and other food items.
- Their territorial behavior keeps them primarily within their established home range.
1.1 What Factors Influence a Chipmunk’s Travel Distance?
Several factors influence how far a chipmunk will travel. These include:
- Availability of Food: Areas with abundant food sources allow chipmunks to meet their needs without venturing too far.
- Predator Presence: High predator activity can limit travel distances as chipmunks stay closer to the safety of their burrows.
- Territory Size: Chipmunks are territorial, and their travel is generally confined within the boundaries of their territory.
- Breeding Season: During breeding season, male chipmunks may travel further to find mates.
- Habitat Quality: A rich, diverse habitat supports all their needs in a small area.
1.2 How Does Habitat Quality Affect Chipmunk Movement?
Habitat quality plays a crucial role in chipmunk behavior. High-quality habitats offer:
- Abundant food sources: Nuts, seeds, fruits, and insects.
- Safe burrowing sites: Areas with soft soil and plenty of cover.
- Protection from predators: Dense vegetation and escape routes.
In areas with poor habitat quality, chipmunks must travel longer distances to find adequate resources, which increases their risk of predation and energy expenditure. According to research, chipmunks in fragmented habitats have larger home ranges due to the need to find resources dispersed over a wider area.
1.3 Do Chipmunks Migrate?
No, chipmunks do not migrate. Instead, they are known for their hoarding behavior to survive the winter months.
- Chipmunks enter a state of torpor during the winter but do not hibernate deeply.
- They rely on their stored food to wake up periodically and sustain themselves.
- Their burrows provide insulation and protection from harsh weather conditions.
1.4 What Is the Typical Size of a Chipmunk’s Territory?
The typical territory size for a chipmunk is around 0.1 hectares or a quarter of an acre. However, this can vary based on habitat quality and population density.
- In areas with plentiful resources, territories may be smaller.
- In areas with scarce resources, chipmunks need to cover larger areas to find enough food.
- Territories are often marked with scent to deter other chipmunks.
1.5 How Do Chipmunks Mark Their Territory?
Chipmunks use a variety of methods to mark their territory:
- Scent Marking: Depositing small amounts of urine or feces to leave their scent.
- Vocalizations: Emitting chirping sounds to warn off intruders.
- Visual Displays: Posturing and chasing to assert dominance.
- Physical Defense: Aggressively defending their territory against other chipmunks.
2. What Is the Daily Routine of a Chipmunk?
The daily routine of a chipmunk is centered around foraging, maintaining their burrows, and avoiding predators.
- Morning: Chipmunks emerge from their burrows to begin foraging for food.
- Daytime: They spend their time gathering nuts, seeds, and insects, storing them in their cheek pouches.
- Afternoon: Chipmunks return to their burrows to cache their food and rest.
- Evening: They may emerge again for a short period before retreating to their burrows for the night.
2.1 How Much Time Do Chipmunks Spend Foraging?
Chipmunks spend a significant portion of their day foraging. They can spend up to 5-8 hours a day searching for food, depending on availability and their energy needs.
- Foraging time increases during the fall as they prepare for winter.
- They use their cheek pouches to transport large quantities of food back to their burrows.
- Efficient foraging helps them build up substantial food stores for the winter months.
2.2 How Do Chipmunks Use Their Cheek Pouches?
Cheek pouches are an essential tool for chipmunks. They can expand to an incredible size, allowing chipmunks to carry large quantities of food at once.
- Chipmunks can fill their cheek pouches with nuts, seeds, and other small items.
- The pouches can expand to three times the size of their head.
- This adaptation allows them to efficiently transport food back to their burrows.
2.3 What Types of Food Do Chipmunks Typically Eat?
Chipmunks have a varied diet that includes:
- Nuts: Acorns, hickory nuts, and walnuts.
- Seeds: Sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, and grass seeds.
- Fruits: Berries, apples, and other fruits.
- Insects: Grubs, caterpillars, and beetles.
- Fungi: Mushrooms and other fungi.
2.4 How Do Chipmunks Prepare for Winter?
Preparing for winter is a critical task for chipmunks. They focus on:
- Food Storage: Gathering and caching large quantities of food in their burrows.
- Burrow Maintenance: Ensuring their burrows are well-insulated and protected from the elements.
- Building Fat Reserves: Consuming high-calorie foods to build up fat reserves for energy.
- Entering Torpor: Slowing down their metabolism and entering periods of inactivity to conserve energy.
2.5 What Is Torpor, and How Does It Help Chipmunks Survive Winter?
Torpor is a state of decreased physiological activity in an animal, usually marked by reduced body temperature and metabolic rate.
- Chipmunks enter torpor to conserve energy during the winter months.
- They wake up periodically to feed on their stored food.
- This strategy allows them to survive the winter without fully hibernating.
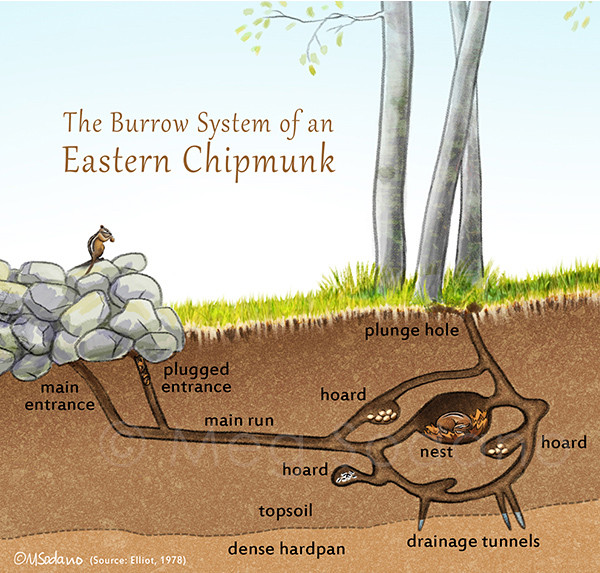
3. Where Do Chipmunks Build Their Burrows?
Chipmunks are meticulous burrow builders, and their burrows are essential for their survival.
- Underground Tunnels: A network of tunnels that can extend several feet below the surface.
- Multiple Entrances: Several entry points, some concealed to avoid predators.
- Nesting Chamber: A cozy, leaf-lined area for sleeping and raising young.
- Food Storage Areas: Separate chambers for caching nuts, seeds, and other food items.
3.1 What Are the Key Features of a Chipmunk Burrow?
The key features of a chipmunk burrow include:
- Multiple Entrances: Some hidden and some obvious, for escape and access.
- Elaborate Tunnel System: Complex networks that can extend up to 30 feet.
- Nesting Chamber: A well-insulated area for sleeping and raising young.
- Food Storage Areas: Separate chambers for storing food.
- Drainage Tunnels: To keep the burrow dry.
3.2 How Deep Do Chipmunk Burrows Typically Go?
Chipmunk burrows can extend several feet below the surface, typically ranging from 1 to 3 feet deep.
- The depth depends on soil conditions and the presence of obstacles like rocks and roots.
- Deeper burrows provide better insulation and protection from predators.
- Some burrows can be more extensive, with tunnels stretching up to 30 feet in length.
3.3 Why Do Chipmunks Have Multiple Entrances to Their Burrows?
Multiple entrances serve several purposes:
- Escape Routes: Providing multiple ways to escape from predators.
- Ventilation: Allowing for air circulation within the burrow system.
- Access Points: Facilitating easier access to different parts of their territory.
- Deception: Confusing predators and making it harder to locate the main nest chamber.
3.4 What Materials Do Chipmunks Use to Build Their Nests?
Chipmunks use a variety of soft, insulating materials to build their nests, including:
- Dry Leaves: Crushed and shredded to create a soft bedding.
- Grass: Dried grass for additional insulation.
- Fur: Animal fur found in their environment.
- Feathers: Soft feathers for added warmth.
3.5 How Do Chipmunks Keep Their Burrows Clean?
Chipmunks are meticulous about keeping their burrows clean. They:
- Remove Waste: Regularly remove feces and urine from the nest chamber.
- Separate Waste Areas: Use specific areas outside the burrow for waste disposal.
- Maintain Food Storage: Keep food storage areas clean to prevent spoilage.
- Replace Nesting Material: Regularly replace old nesting material with fresh materials.
4. How Do Chipmunks Interact With Each Other?
Chipmunks are generally solitary animals, but they do interact with each other, particularly during the breeding season.
- Territorial Defense: Defending their territory against intruders.
- Mating Behavior: Engaging in courtship and mating rituals.
- Communication: Using vocalizations and scent marking to communicate.
- Social Hierarchy: Establishing a social hierarchy within a population.
4.1 Are Chipmunks Social Animals?
No, chipmunks are not typically social animals. They are primarily solitary, except during the breeding season.
- They prefer to live alone in their burrows.
- They only interact with other chipmunks for mating or territorial defense.
- They do not form long-term social bonds or live in groups.
4.2 How Do Chipmunks Communicate With Each Other?
Chipmunks communicate through a variety of methods:
- Vocalizations: Chirps, trills, and alarm calls.
- Scent Marking: Using urine and feces to mark their territory.
- Visual Displays: Posturing, chasing, and other visual signals.
- Tactile Communication: Brief physical contact during mating or territorial disputes.
4.3 What Are the Different Types of Chipmunk Vocalizations?
Chipmunks use several distinct vocalizations:
- Chirp: A high-pitched sound used as a general call or greeting.
- Trill: A rapid series of chirps used as an alarm call.
- Chuck: A low, guttural sound used during territorial defense.
- Scream: A high-pitched scream used when threatened or injured.
4.4 How Do Chipmunks Establish a Social Hierarchy?
Chipmunks establish a social hierarchy through:
- Aggressive Encounters: Fighting and chasing to establish dominance.
- Visual Displays: Posturing and displaying size.
- Scent Marking: Using scent to assert dominance.
- Access to Resources: Dominant chipmunks have greater access to food and mates.
4.5 How Does the Breeding Season Affect Chipmunk Interactions?
During the breeding season, chipmunk interactions become more frequent and intense:
- Male Competition: Males compete for access to females.
- Courtship Rituals: Males engage in courtship displays to attract females.
- Increased Vocalizations: Chipmunks vocalize more frequently to attract mates.
- Territorial Defense: Increased territorial defense to protect mating opportunities.
5. What Are the Predators of Chipmunks?
Chipmunks face threats from various predators, making vigilance essential for their survival.
- Birds of Prey: Hawks and owls.
- Snakes: Various snake species.
- Foxes: Red foxes and gray foxes.
- Coyotes: Coyotes are opportunistic predators.
- Domestic Animals: Cats and dogs.
5.1 How Do Chipmunks Avoid Predators?
Chipmunks employ several strategies to avoid predators:
- Vigilance: Constantly scanning their surroundings for threats.
- Alarm Calls: Emitting alarm calls to warn other chipmunks.
- Burrow Systems: Using their burrows as safe havens.
- Camouflage: Blending in with their environment.
- Agility: Quick and agile movements to evade predators.
5.2 What Types of Alarm Calls Do Chipmunks Use?
Chipmunks use different alarm calls to signal different types of threats:
- High-Pitched Trill: Used to signal the presence of aerial predators like hawks.
- Rapid Chirping: Used to signal the presence of ground predators like foxes.
- Scream: Used when directly threatened or injured.
5.3 How Does Habitat Influence Chipmunk Predation Rates?
Habitat plays a crucial role in chipmunk predation rates:
- Dense Vegetation: Provides cover and hiding places, reducing predation risk.
- Open Areas: Increase predation risk due to lack of cover.
- Proximity to Human Habitation: Can increase predation risk from domestic animals.
- Availability of Food: Abundant food sources can reduce the need to venture into risky areas.
5.4 How Do Chipmunks Protect Their Young From Predators?
Chipmunks protect their young by:
- Concealing Burrows: Hiding burrow entrances to prevent detection.
- Constant Vigilance: Constantly monitoring the area around the burrow.
- Relocating Young: Moving young to different burrows if they sense danger.
- Aggressive Defense: Defending their young against predators.
5.5 What Role Do Humans Play in Chipmunk Predation?
Humans can indirectly influence chipmunk predation rates:
- Habitat Destruction: Removing vegetation and reducing cover.
- Introducing Predators: Domestic animals like cats and dogs.
- Providing Food Sources: Attracting predators to areas where chipmunks live.
- Creating Unsafe Environments: Altering landscapes in ways that make chipmunks more vulnerable.
6. How Does Climate Change Affect Chipmunks?
Climate change poses several challenges to chipmunks, affecting their behavior, distribution, and survival.
- Changes in Food Availability: Altered timing of nut and seed production.
- Habitat Alteration: Changes in vegetation and forest composition.
- Increased Extreme Weather Events: More frequent and intense storms and droughts.
- Shifts in Predator-Prey Dynamics: Altered relationships with predators and prey.
6.1 How Does Climate Change Impact Chipmunk Food Sources?
Climate change affects chipmunk food sources in several ways:
- Altered Timing of Nut Production: Warmer temperatures can cause trees to produce nuts earlier in the year.
- Changes in Seed Availability: Shifts in precipitation patterns can affect seed production.
- Increased Pest Outbreaks: Warmer temperatures can lead to increased pest outbreaks, damaging food crops.
- Habitat Loss: Climate change can lead to habitat loss, reducing the availability of food sources.
6.2 How Does Climate Change Affect Chipmunk Burrowing Habits?
Climate change can affect chipmunk burrowing habits:
- Changes in Soil Conditions: Altered precipitation patterns can affect soil moisture and stability.
- Increased Flooding Risk: More frequent and intense storms can increase the risk of burrow flooding.
- Altered Insulation: Changes in temperature can affect the insulation properties of their burrows.
- Habitat Shifts: Climate change can cause shifts in suitable habitat, forcing chipmunks to relocate their burrows.
6.3 How Do Chipmunks Adapt to Changing Climatic Conditions?
Chipmunks can adapt to changing climatic conditions in several ways:
- Shifting Activity Patterns: Adjusting their foraging and activity patterns to match changes in food availability.
- Altering Burrowing Habits: Building burrows in different locations to avoid flooding or other hazards.
- Changing Diet: Adapting their diet to include new or different food sources.
- Relocating: Moving to new areas with more suitable climatic conditions.
6.4 What Is the Long-Term Impact of Climate Change on Chipmunk Populations?
The long-term impact of climate change on chipmunk populations is uncertain, but potential effects include:
- Population Declines: Reduced survival and reproduction rates due to altered food availability and habitat loss.
- Range Shifts: Changes in geographic distribution as chipmunks move to more suitable areas.
- Increased Extinction Risk: Greater risk of extinction for populations that are unable to adapt to changing conditions.
- Altered Ecosystem Dynamics: Changes in the roles chipmunks play in their ecosystems.
6.5 How Can Humans Help Chipmunks Cope With Climate Change?
Humans can help chipmunks cope with climate change by:
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Taking steps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to slow down climate change.
- Protecting and Restoring Habitat: Protecting and restoring natural habitats to provide chipmunks with suitable living conditions.
- Providing Supplemental Food: Providing supplemental food sources during times of scarcity.
- Creating Safe Environments: Creating safe environments for chipmunks by reducing the use of pesticides and other harmful chemicals.
 Chipmunk Burrow
Chipmunk Burrow
7. What Role Do Chipmunks Play in Their Ecosystems?
Chipmunks play several important roles in their ecosystems.
- Seed Dispersal: Help disperse seeds by caching nuts and seeds in different locations.
- Soil Aeration: Their burrowing activity helps aerate the soil.
- Prey Species: Serve as a food source for various predators.
- Nutrient Cycling: Contribute to nutrient cycling through their feeding and waste disposal habits.
7.1 How Do Chipmunks Contribute to Seed Dispersal?
Chipmunks contribute to seed dispersal by:
- Caching Nuts and Seeds: Burying nuts and seeds in different locations for later consumption.
- Forgetting Caches: Failing to retrieve all of their cached food, allowing seeds to germinate and grow.
- Moving Seeds Over Long Distances: Transporting seeds over long distances, helping to colonize new areas.
- Promoting Plant Diversity: Dispersing a variety of different plant species.
7.2 How Does Chipmunk Burrowing Aerate the Soil?
Chipmunk burrowing aerates the soil by:
- Creating Tunnels: Creating tunnels that allow air and water to penetrate the soil.
- Mixing Soil Layers: Mixing different layers of soil, improving soil structure.
- Increasing Drainage: Improving soil drainage, preventing waterlogging.
- Enhancing Root Growth: Creating conditions that are favorable for root growth.
7.3 How Do Chipmunks Serve as a Prey Species?
Chipmunks serve as a prey species by:
- Providing a Food Source: Serving as a food source for various predators, including hawks, snakes, and foxes.
- Supporting Predator Populations: Helping to support predator populations in their ecosystems.
- Influencing Predator Behavior: Influencing predator behavior and distribution.
- Maintaining Ecosystem Balance: Contributing to the overall balance and stability of their ecosystems.
7.4 How Do Chipmunks Contribute to Nutrient Cycling?
Chipmunks contribute to nutrient cycling by:
- Consuming Plants and Seeds: Consuming plants and seeds, extracting nutrients from them.
- Excreting Waste: Excreting waste products that contain nutrients.
- Decomposing Organic Matter: Contributing to the decomposition of organic matter in their burrows.
- Returning Nutrients to the Soil: Returning nutrients to the soil, promoting plant growth.
7.5 What Would Happen if Chipmunks Disappeared From an Ecosystem?
If chipmunks disappeared from an ecosystem, several things might happen:
- Reduced Seed Dispersal: Decreased seed dispersal, leading to changes in plant distribution and diversity.
- Decreased Soil Aeration: Reduced soil aeration, leading to poorer soil quality.
- Impact on Predator Populations: Reduced food supply for predators, potentially leading to population declines.
- Altered Ecosystem Dynamics: Changes in the overall structure and function of the ecosystem.
8. How Can You Attract Chipmunks to Your Yard?
If you want to attract chipmunks to your yard, you can take several steps to make it more inviting.
- Provide Food Sources: Offer nuts, seeds, and fruits.
- Create Burrowing Habitat: Provide areas with loose soil and cover.
- Offer Water Sources: Provide a shallow dish of water.
- Avoid Pesticides: Avoid using pesticides that could harm chipmunks.
8.1 What Types of Food Should You Offer to Chipmunks?
You can offer a variety of foods to attract chipmunks, including:
- Nuts: Acorns, walnuts, and hazelnuts.
- Seeds: Sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds.
- Fruits: Berries and apples.
- Vegetables: Carrots and corn.
8.2 How Can You Create Suitable Burrowing Habitat for Chipmunks?
You can create suitable burrowing habitat for chipmunks by:
- Providing Loose Soil: Offering areas with loose, well-drained soil.
- Adding Cover: Providing cover with rocks, logs, and shrubs.
- Creating Rock Piles: Building rock piles to provide shelter and burrowing opportunities.
- Leaving Leaf Litter: Leaving leaf litter on the ground to provide nesting material.
8.3 How Can You Protect Chipmunks From Predators in Your Yard?
You can protect chipmunks from predators by:
- Providing Cover: Offering plenty of cover with shrubs and trees.
- Installing Fencing: Installing fencing to keep out predators like cats and dogs.
- Removing Hazards: Removing hazards like traps and poisons.
- Supervising Pets: Supervising pets to prevent them from hunting chipmunks.
8.4 Should You Be Concerned About Chipmunks Damaging Your Garden?
Chipmunks can sometimes cause damage to gardens, but the damage is usually minimal.
- Eating Plants: They may eat some plants, but they usually prefer nuts and seeds.
- Digging Holes: They may dig small holes, but these are usually not a major problem.
- Storing Food: They may store food in gardens, but this is usually not a significant issue.
8.5 Are There Any Risks Associated With Attracting Chipmunks to Your Yard?
There are some risks associated with attracting chipmunks to your yard:
- Disease Transmission: Chipmunks can carry diseases that can be transmitted to humans.
- Pest Attraction: Attracting chipmunks can also attract other pests, such as rodents and insects.
- Increased Predation: Attracting chipmunks can increase the risk of predation by cats and other predators.
- Property Damage: Chipmunks can cause minor property damage, such as digging holes in lawns and gardens.
9. What Are Some Interesting Facts About Chipmunks?
Chipmunks are fascinating creatures with many interesting behaviors and adaptations.
- Cheek Pouches: They can store large quantities of food in their cheek pouches.
- Burrow Systems: They build complex burrow systems with multiple entrances and chambers.
- Torpor: They enter a state of torpor during the winter months.
- Vocalizations: They use a variety of vocalizations to communicate with each other.
- Agility: They are quick and agile, making them difficult for predators to catch.
9.1 How Much Food Can a Chipmunk Store in Its Cheek Pouches?
Chipmunks can store an incredible amount of food in their cheek pouches:
- Quantity: They can carry up to one-third of their body weight in food in their cheek pouches.
- Size: Their cheek pouches can expand to three times the size of their head.
- Efficiency: This allows them to efficiently transport food back to their burrows.
- Adaptation: This is an adaptation that helps them survive the winter months.
9.2 How Long Do Chipmunks Typically Live?
Chipmunks typically live for:
- Lifespan: 2 to 3 years in the wild.
- Factors: Their lifespan can be affected by factors such as predation, disease, and habitat conditions.
- Captivity: They can live longer in captivity, where they are protected from predators and provided with food and shelter.
- Environment: Their lifespan is also affected by the environment they live in.
9.3 Are Chipmunks Considered Pests?
Whether or not chipmunks are considered pests depends on the context:
- Gardens: They can be considered pests if they cause damage to gardens or property.
- Ecosystems: They play important roles in their ecosystems, such as seed dispersal and soil aeration.
- Perspective: Whether they are viewed as pests depends on individual perspectives and experiences.
- Management: In some cases, it may be necessary to manage chipmunk populations to prevent damage.
9.4 What Is the Conservation Status of Chipmunks?
The conservation status of chipmunks is generally:
- Least Concern: Most chipmunk species are listed as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Threats: They face some threats, such as habitat loss and climate change, but their populations are generally stable.
- Monitoring: It is important to monitor chipmunk populations and protect their habitats to ensure their long-term survival.
- Conservation: Conservation efforts can help to ensure the continued presence of chipmunks in their ecosystems.
9.5 What Are the Different Species of Chipmunks?
There are several different species of chipmunks, including:
- Eastern Chipmunk: Found in eastern North America.
- Western Chipmunk: Found in western North America.
- Least Chipmunk: The smallest chipmunk species.
- Yellow-Pine Chipmunk: Found in pine forests.
- Alpine Chipmunk: Found in high-altitude areas.
10. Planning Your Vietnam Trip with SIXT.VN
Now that you know more about chipmunks and their habits, let’s focus on planning your unforgettable trip to Vietnam. SIXT.VN offers a comprehensive suite of services to ensure your journey is smooth, enjoyable, and tailored to your preferences.
- Customized Itineraries: Tailored travel plans to match your interests and schedule.
- Airport Transfers: Safe and convenient transportation from the airport to your hotel.
- Hotel Booking: Wide selection of hotels to fit your budget and location preferences.
- Sightseeing Tours: Expert-led tours to explore Hanoi and surrounding regions.
- Flight Booking: Assistance with booking flights at competitive prices.
10.1 How Can SIXT.VN Help You Plan Your Trip to Vietnam?
SIXT.VN simplifies your travel planning with a range of services designed to meet your specific needs:
- Expert Advice: Get personalized recommendations for the best places to visit and things to do in Vietnam.
- Convenient Booking: Easily book hotels, flights, and tours through our user-friendly platform.
- Reliable Transportation: Ensure smooth airport transfers and transportation within Vietnam.
- Multilingual Support: Receive assistance in multiple languages to address any questions or concerns.
- 24/7 Customer Service: Access round-the-clock support to handle any issues that may arise during your trip.
10.2 What Types of Travel Services Does SIXT.VN Offer?
SIXT.VN offers a variety of travel services to cater to different types of travelers:
- Tour Packages: Comprehensive tour packages that cover multiple destinations and activities.
- Custom Tours: Tailored tours designed to match your specific interests and preferences.
- City Tours: Guided tours of Hanoi and other major cities in Vietnam.
- Adventure Tours: Thrilling adventure tours, including trekking, cycling, and kayaking.
- Cultural Tours: Immersive cultural experiences to explore Vietnam’s rich heritage.
10.3 How Can You Book Airport Transfers With SIXT.VN?
Booking airport transfers with SIXT.VN is easy and convenient:
- Online Booking: Visit our website and select the airport transfer service.
- Enter Details: Provide your flight details, arrival time, and destination.
- Choose Vehicle: Select the vehicle type that best suits your needs.
- Confirm Booking: Confirm your booking and receive a confirmation email.
- Meet Driver: Our driver will meet you at the airport upon arrival.
10.4 What Are the Benefits of Booking Hotels Through SIXT.VN?
Booking hotels through SIXT.VN offers numerous benefits:
- Wide Selection: Access a wide selection of hotels in various locations and price ranges.
- Competitive Prices: Find competitive prices and special deals on hotel bookings.
- Easy Booking: Easily book hotels through our user-friendly platform.
- Secure Payment: Enjoy secure payment options for your hotel bookings.
- Customer Support: Receive customer support to assist with any hotel-related queries.
10.5 How Can You Create a Custom Tour With SIXT.VN?
Creating a custom tour with SIXT.VN is simple:
- Contact Us: Reach out to our travel experts to discuss your interests and preferences.
- Share Ideas: Share your ideas for the places you want to visit and activities you want to do.
- Receive Proposal: Receive a customized tour proposal that matches your requirements.
- Customize Itinerary: Customize the itinerary to fit your specific needs and budget.
- Confirm Booking: Confirm your booking and prepare for your unforgettable adventure.
Planning a trip to Vietnam? SIXT.VN is your premier partner for seamless travel experiences. With a focus on personalized service, convenience, and reliability, SIXT.VN ensures your adventure is unforgettable. From airport transfers to custom tours, our expert team caters to every detail, allowing you to explore the beauty and culture of Vietnam with ease.
Ready to explore Vietnam? Contact SIXT.VN today to start planning your dream trip!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN
FAQ: Understanding Chipmunk Behavior and Travel
1. How do chipmunks navigate their territory?
Chipmunks navigate their territory using a combination of spatial memory, scent marking, and visual cues. They remember the locations of food sources and landmarks within their home range, allowing them to efficiently find their way around.
2. What happens if a chipmunk is displaced from its territory?
If a chipmunk is displaced from its territory, it may struggle to survive. It will need to find a new area with sufficient food, shelter, and protection from predators. It may also face competition from resident chipmunks.
3. Do chipmunks travel more during certain times of the year?
Chipmunks generally travel more during the fall as they prepare for winter. They need to gather and cache large quantities of food in their burrows, requiring them to spend more time foraging.
4. How do chipmunks react to human presence in their territory?
Chipmunks typically react to human presence by becoming more cautious and alert. They may freeze in place, emit alarm calls, or retreat to their burrows. Over time, they may become habituated to human presence if they do not perceive humans as a threat.
5. Can chipmunks travel in urban environments?
Yes, chipmunks can travel and survive in urban environments. They can adapt to living in parks, gardens, and other green spaces within cities. However, they may face increased risks from traffic, domestic animals, and habitat fragmentation.
6. What is the longest distance a chipmunk has been recorded traveling?
While chipmunks typically stay within a quarter-acre territory, some may venture further in search of food or mates. However, there is no specific record for the longest distance traveled, as it varies depending on individual circumstances and habitat conditions.
7. How do young chipmunks learn to navigate their environment?
Young chipmunks learn to navigate their environment by following their mother and observing her foraging behavior. They gradually explore their surroundings, learning the locations of food sources, shelter, and potential threats.
8. What are the signs that a chipmunk is stressed or threatened?
Signs that a chipmunk is stressed or threatened include:
- Rapid breathing
- Trembling
- Freezing in place
- Emitting alarm calls
- Aggressive behavior
9. Do chipmunks travel differently in different types of habitats?
Yes, chipmunks may travel differently in different types of habitats. In dense forests, they may travel shorter distances due to the abundance of food and shelter. In fragmented habitats, they may need to travel longer distances to find resources.
10. How does urbanization affect chipmunk travel patterns?
Urbanization can significantly affect chipmunk travel patterns by fragmenting their habitats and reducing the availability of natural resources. Chipmunks may need to travel longer distances to find food and shelter, increasing their risk of predation and other hazards.


