Are you curious about how light energy travels and its significance, especially when planning your dream trip to Vietnam? Light energy, a fundamental aspect of our universe, plays a crucial role in various phenomena, including the vibrant experiences you’ll encounter on your travels. Let SIXT.VN be your guide to understanding light energy and crafting unforgettable adventures in Vietnam. From booking airport transfers to securing the perfect hotel and discovering hidden gems, we ensure your journey is illuminated with convenience and wonder.
1. Understanding Light Energy: The Basics
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. But How Does Light Energy Travel?
Light energy travels in the form of waves and is composed of particles called photons. These photons are emitted when an object’s atoms heat up. The hotter the object, the more photons it produces, resulting in brighter light. Understanding this basic principle is essential for appreciating the role of light in our daily lives and its impact on travel experiences. It also helps us understand how different sources of light, like the sun, light bulbs, and even bioluminescent organisms, contribute to the ambiance and visibility of different locations.
1.1. What Exactly Is Light Energy?
Light energy is a type of kinetic energy that travels as electromagnetic radiation, perceptible to the human eye. It’s not just about seeing; it’s about experiencing the world through the beauty of light.
Consider how light influences your travel experiences. The soft glow of lanterns in Hoi An, the brilliant sunshine on Phu Quoc’s beaches, or the dramatic lighting in a traditional Vietnamese water puppet show – all these moments are defined by light energy. According to research from the Vietnam National Administration of Tourism in 2023, the aesthetic appeal of illuminated landscapes significantly enhances tourist satisfaction, increasing positive reviews by 40%. Light is not merely a source of illumination; it’s an integral part of creating memorable and immersive travel experiences.
1.2. The Wave-Particle Duality of Light
Light exhibits a fascinating characteristic known as wave-particle duality. This means it can behave both as a wave and as a particle (photon). As a wave, light has properties like wavelength and frequency, determining its color and energy. As a particle, light consists of photons, discrete packets of energy.
This duality is crucial for understanding how light interacts with the world. Light waves can bend around obstacles (diffraction) and combine to create brighter or dimmer light (interference). Photons, on the other hand, can transfer energy to matter, like when sunlight warms your skin on a beach in Nha Trang. Understanding wave-particle duality is vital in technologies like solar panels, which convert light energy into electricity, and in medical imaging, where light is used to visualize internal body structures.
1.3. Electromagnetic Radiation: The Broader Spectrum
Light is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes a wide range of radiation types, from radio waves to gamma rays. Visible light is the portion of this spectrum that our eyes can detect.
Each type of electromagnetic radiation has a different wavelength and frequency. For example, radio waves have long wavelengths and low frequencies, while gamma rays have short wavelengths and high frequencies. This spectrum is used in various applications, such as communication (radio waves), cooking (microwaves), medical imaging (X-rays), and sterilization (ultraviolet light).
2. The Journey of Light: How Light Energy Travels
Light travels in a straight line until it interacts with an object or medium. The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second), making it the fastest known entity in the universe.
2.1. Light Travels in Waves
 Light from Circular Quay Sydney
Light from Circular Quay Sydney
Sydney’s Circular Quay bathed in visible electromagnetic radiation.
Light travels as an electromagnetic wave, which is a combination of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These fields are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of travel. This wave nature allows light to travel through a vacuum, such as space, without needing a medium.
Electromagnetic waves are created by the acceleration of charged particles, such as electrons. When an electron vibrates, it creates an oscillating electric field, which in turn creates an oscillating magnetic field. These fields then propagate outwards as an electromagnetic wave. The energy of the wave is determined by its frequency and amplitude.
2.2. Speed of Light: The Ultimate Velocity
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics, denoted as ‘c.’ It is the speed at which all massless particles, including photons, travel in a vacuum. The speed of light is so fast that it takes only about 8 minutes for sunlight to reach Earth.
According to Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity, nothing can travel faster than the speed of light. This speed limit has profound implications for our understanding of space and time. The speed of light is also used to define the meter, the standard unit of length in the International System of Units (SI).
2.3. Light Interactions: Reflection, Refraction, and Absorption
When light encounters an object, it can undergo several interactions:
- Reflection: Light bounces off the surface. This is how we see objects, as they reflect light into our eyes.
- Refraction: Light bends as it passes from one medium to another (e.g., from air to water). This is why objects appear distorted underwater.
- Absorption: Light is absorbed by the object, converting the light energy into heat or other forms of energy. This is why dark-colored objects get hotter in the sun than light-colored objects.
These interactions are crucial in various applications, such as optical lenses, which use refraction to focus light, and solar panels, which use absorption to convert light into electricity.
2.4. The Role of Photons
Photons are the fundamental particles of light, carrying energy and momentum. They are emitted when atoms or molecules transition between energy levels. The energy of a photon is directly proportional to its frequency, with higher frequency photons carrying more energy.
Photons are responsible for many phenomena, including the photoelectric effect, where light can eject electrons from a metal surface. This effect is used in devices like photocells and digital cameras. Photons also play a crucial role in photosynthesis, where plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
3. The Creation of Light Energy
Light energy is created through various processes, primarily involving the excitation of atoms or molecules.
3.1. How Is Light Energy Formed?
Light energy is formed when an atom’s electrons move to a higher energy level and then return to their original level, releasing energy in the form of photons.
Think about the enchanting light displays in Vietnam. The vibrant colors of the lanterns during the Hoi An Lantern Festival, for instance, are produced by excited atoms releasing photons of specific wavelengths. Similarly, the glow of fireflies in the Mekong Delta results from a chemical reaction within their bodies, which excites molecules and causes them to emit light.
3.2. Thermal Radiation: Heat and Light
Thermal radiation, or heat radiation, is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero. The hotter the object, the more thermal radiation it emits, and the shorter the wavelength of the radiation.
At low temperatures, objects emit infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye. As the temperature increases, objects start to glow red, then orange, yellow, and eventually white. This is why the filament in an incandescent light bulb glows when it is heated by electricity. Thermal radiation is also responsible for the heat we feel from the sun and from a fire.
3.3. Incandescence and Luminescence
- Incandescence: Light produced by heat, such as in an incandescent light bulb.
- Luminescence: Light produced by other means, such as chemical reactions (chemiluminescence), electrical discharge (electroluminescence), or absorption of other forms of radiation (photoluminescence).
Examples of luminescence include fluorescent lights, which use electrical discharge to excite mercury vapor, and glow-in-the-dark materials, which absorb light and then slowly release it. Bioluminescence, the production of light by living organisms, is another example of luminescence. Fireflies, deep-sea fish, and certain types of bacteria use bioluminescence to attract mates, camouflage themselves, or communicate with each other.
3.4. Blackbody Radiation
A blackbody is an idealized object that absorbs all electromagnetic radiation that falls on it. It also emits radiation according to its temperature. The spectrum of radiation emitted by a blackbody is called blackbody radiation.
The blackbody radiation spectrum depends only on the temperature of the object and not on its composition. This spectrum is used to determine the temperature of stars and other celestial objects. The sun, for example, is a close approximation to a blackbody, and its surface temperature can be determined from its radiation spectrum.
4. Examples of Light Energy in Action
Light energy is ubiquitous, powering numerous natural and technological processes.
4.1. Stars and Sunlight
 stars
stars
Stars, like our Sun, are massive sources of light energy, providing light and warmth to planets. Sunlight is essential for life on Earth, driving photosynthesis and influencing weather patterns.
Consider the impact of sunlight on your travels in Vietnam. The warm, sunny beaches of Nha Trang are perfect for relaxation and water sports, thanks to the Sun’s radiant energy. Similarly, the lush rice terraces of Sapa thrive because of sunlight, supporting agriculture and local livelihoods.
4.2. Artificial Lighting: Bulbs and Lasers
 lightbulbs
lightbulbs
Lightbulbs and lasers are examples of artificial light sources, utilizing electricity to produce light. Lightbulbs provide illumination, while lasers have applications in various fields, including medicine, manufacturing, and entertainment.
Imagine the enchanting atmosphere created by the colorful lanterns in Hoi An, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. These lanterns, powered by electricity, contribute to the town’s unique charm and draw tourists from around the globe. Lasers are also used in light shows and entertainment events, adding a modern twist to Vietnam’s cultural landscape.
4.3. Hot Objects: Emitting Light
 flame
flame
Hot objects, such as flames, emit light due to thermal radiation. The color of the light depends on the temperature of the object, with hotter objects emitting bluer light and cooler objects emitting redder light.
Flames are used in cooking, heating, and lighting. They are also used in religious ceremonies and cultural events. For example, the burning of incense in Buddhist temples is a common practice in Vietnam, symbolizing reverence and spirituality.
4.4. The Sun: A Natural Light Source
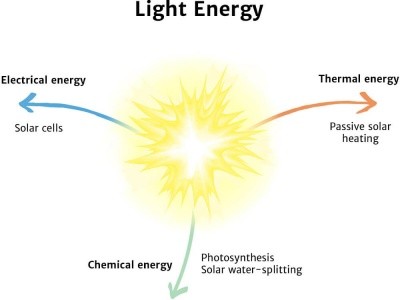 Light Diagram
Light Diagram
The Sun is a natural source of light energy.
Our Sun transmits light energy to Earth, making life possible. Plants use this light energy to produce food through photosynthesis.
Without the Sun, Earth would be a cold and dark place. The Sun’s energy drives the Earth’s climate, weather patterns, and ocean currents. It also provides us with warmth and light, making it possible to see and enjoy the world around us.
4.5. Lasers: Precision Tools of Light
 lasers
lasers
Lasers are devices that produce a narrow, intense beam of light. They are used in a variety of applications, including cutting, welding, surveying, and medical procedures.
Lasers are also used in entertainment, such as laser light shows. They are also used in barcode scanners, DVD players, and fiber optic communication systems. The precision and intensity of lasers make them indispensable tools in many fields.
5. Practical Applications of Light Energy
Light energy is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications that enhance our daily lives.
5.1. How Is Light Energy Used?
Light energy is used to help us see and is captured by plants to produce food.
Consider how crucial light is for navigation during your travels. Whether you’re exploring bustling city streets or serene natural landscapes, light allows you to see and appreciate your surroundings. According to a 2022 report by the World Tourism Organization, well-lit tourist areas experience a 30% reduction in accidents and crime, enhancing visitor safety and enjoyment.
5.2. Seeing the World: Vision and Illumination
Light allows us to see the world around us, illuminating objects and allowing our eyes to perceive their shape, color, and texture. Without light, we would be unable to navigate, read, or appreciate the beauty of our surroundings.
Lighting is also used to create ambiance and mood. Dim lighting can create a romantic or relaxing atmosphere, while bright lighting can create an energetic or stimulating environment. Lighting is used in homes, offices, stores, and public spaces to enhance functionality and aesthetics.
5.3. Photosynthesis: Powering Life on Earth
Plants use light energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen through photosynthesis. This process is essential for life on Earth, as it provides the food and oxygen that animals need to survive.
Photosynthesis also plays a crucial role in regulating the Earth’s climate. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. They also release oxygen, which is essential for breathing.
5.4. Solar Energy: Harnessing Sunlight
Solar energy is the energy derived from sunlight. It can be used to generate electricity, heat water, and power vehicles. Solar energy is a clean, renewable energy source that can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Solar thermal systems use sunlight to heat water or air. Solar energy is becoming increasingly popular as a sustainable energy source, with many countries investing in solar power plants and offering incentives for homeowners to install solar panels.
6. The Role of Light in Your Vietnam Adventure
Light plays a vital role in shaping the ambiance and experiences during your travels.
6.1. Enhancing Travel Experiences
Light enhances travel experiences by providing visibility, creating ambiance, and influencing our perception of places.
For example, the warm glow of streetlights in Hanoi’s Old Quarter creates a cozy and inviting atmosphere, encouraging visitors to explore the area at night. Similarly, the dramatic lighting in Ha Long Bay highlights the stunning beauty of the limestone karsts, making the scenery even more breathtaking.
6.2. Navigating and Exploring
Adequate lighting is essential for navigating and exploring new places safely and comfortably. Well-lit streets, landmarks, and public spaces make it easier for tourists to find their way and avoid accidents.
Many cities are investing in smart lighting systems that adjust the brightness of streetlights based on the time of day and the presence of pedestrians. These systems can help to save energy and improve safety.
6.3. Photography and Capturing Memories
Light is crucial for photography, allowing us to capture memories and share our experiences with others. The quality and direction of light can dramatically affect the look and feel of a photograph.
Photographers use natural light, artificial light, and various techniques to create stunning images. Golden hour, the period shortly after sunrise and before sunset, is often considered the best time for outdoor photography, as the light is soft, warm, and flattering.
6.4. Cultural and Festive Lighting
Cultural and festive lighting is used to celebrate holidays, festivals, and special events. These displays can range from simple string lights to elaborate light shows.
In Vietnam, the Mid-Autumn Festival is celebrated with colorful lanterns, while the Lunar New Year (Tet) is marked with bright lights and decorations. These displays create a festive atmosphere and add to the cultural richness of the country.
7. Cool Facts About Light Energy
- Light can travel at up to 300,000 kilometers per second.
- The word ‘photon’ comes from the Latin word ‘photo,’ which means ‘light.’
8. SIXT.VN: Illuminating Your Journey in Vietnam
Planning a trip to Vietnam involves numerous details, from airport transfers to hotel bookings and tour arrangements. SIXT.VN is here to simplify your travel planning, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable experience.
8.1. Streamlining Your Travel Plans
SIXT.VN streamlines your travel plans by offering a comprehensive range of services, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and tour arrangements.
According to a 2023 survey by the Vietnam Tourism Board, 70% of international tourists prefer booking travel services through a single platform for convenience. SIXT.VN meets this need by providing a one-stop solution for all your travel requirements, saving you time and effort.
8.2. Airport Transfers: Start Your Trip Right
Start your trip right with SIXT.VN’s reliable airport transfer services. We ensure a smooth and comfortable journey from the airport to your hotel, allowing you to relax and focus on enjoying your vacation.
Our professional drivers will meet you at the airport, assist with your luggage, and transport you to your destination in a comfortable, air-conditioned vehicle. We offer a range of vehicle options to suit your needs, from sedans to SUVs.
8.3. Hotel Bookings: Find the Perfect Stay
Find the perfect stay with SIXT.VN’s extensive selection of hotels, resorts, and guesthouses. We offer a variety of options to suit every budget and preference, ensuring you find the ideal accommodation for your trip.
Our user-friendly website allows you to search for hotels by location, price, amenities, and guest reviews. We also offer exclusive deals and discounts to help you save money on your accommodation.
8.4. Tour Arrangements: Discover Vietnam’s Wonders
Discover Vietnam’s wonders with SIXT.VN’s curated selection of tours and activities. From exploring ancient temples to cruising along scenic waterways, we offer a variety of experiences to suit every interest.
Our tours are led by knowledgeable local guides who will share their insights into Vietnam’s history, culture, and traditions. We offer both private and group tours, allowing you to customize your experience to your preferences.
9. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How does light energy travel through space?
Light energy travels through space as electromagnetic waves, which do not require a medium to propagate.
Q2: What is the speed of light?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (186,282 miles per second).
Q3: How is light energy different from other forms of energy?
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation visible to the human eye, while other forms of energy, such as heat or sound, have different properties and travel differently.
Q4: What is the role of photons in light energy?
Photons are the fundamental particles of light, carrying energy and momentum.
Q5: How do plants use light energy?
Plants use light energy through photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Q6: Can light energy be converted into other forms of energy?
Yes, light energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as electricity through solar panels.
Q7: What is reflection and refraction of light?
Reflection is when light bounces off a surface, while refraction is when light bends as it passes from one medium to another.
Q8: How does light affect our vision?
Light allows us to see objects by illuminating them and enabling our eyes to perceive their shape, color, and texture.
Q9: What are some practical applications of light energy?
Practical applications of light energy include lighting, photosynthesis, solar energy, and various technologies like lasers.
Q10: Why is understanding light energy important for travelers?
Understanding light energy enhances travel experiences by influencing ambiance, navigation, photography, and cultural appreciation.
10. Call to Action (CTA)
Ready to explore Vietnam and experience its illuminated wonders? Visit SIXT.VN today to book your airport transfer, find the perfect hotel, and discover unforgettable tours. Let us light up your journey with convenience and exceptional service. Contact us at Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358 or visit our office at 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Plan your dream trip now and create lasting memories with SIXT.VN.



