Do Blue Jays Travel In Flocks? Yes, blue jays do travel in flocks, especially outside the breeding season. If you are planning a trip to Vietnam and are curious about the local wildlife, SIXT.VN can help you arrange memorable nature excursions. With SIXT.VN, discover Vietnam’s rich biodiversity and plan your bird-watching adventures with ease. Consider SIXT.VN for seamless travel arrangements and discovering Vietnam’s hidden natural treasures.
1. What Exactly is a Blue Jay? A Colorful Introduction
Blue jays ( Cyanocitta cristata) are striking, intelligent birds commonly found across North America. Recognized for their vibrant blue, white, and black plumage, they belong to the corvid family, which also includes crows and ravens. These birds are known for their complex social behaviors, adaptability, and distinctive calls. Encountering them can add a touch of natural wonder to any travel experience, and with SIXT.VN, you can explore diverse habitats that are home to unique avian species.
2. What Does the Social Structure of Blue Jays Look Like?
Blue jays exhibit a fascinating social structure. During the breeding season, they are primarily monogamous, with pairs forming the core social unit. However, they are not strictly territorial and often share feeding grounds with other pairs. Outside of the breeding season, particularly in late summer and winter, blue jays frequently form larger flocks. According to research by Racine and Thompson, stable winter flocks consist of related individuals who return to the same feeding stations year after year.
 Blue jays perched on a snowy branch, showcasing their vibrant plumage and winter adaptability
Blue jays perched on a snowy branch, showcasing their vibrant plumage and winter adaptability
3. Do Blue Jays Migrate? Understanding Their Travel Patterns
The migratory behavior of blue jays is complex and not fully understood. Some blue jays, especially those in the northern United States, migrate south for the winter, while others remain in their nesting areas year-round. Stewart’s meta-analysis of over 8,000 blue jays along the Atlantic Flyway found no single factor determining which jays migrate. The reasons behind these varying migration patterns are still under investigation. For travelers interested in witnessing bird migrations, SIXT.VN offers customizable tours that can align with peak migration seasons.
4. Are There Differences in Social Behavior Between Male and Female Blue Jays?
Yes, there are notable differences in social behavior between male and female blue jays. Males are typically dominant over females, especially during the breeding season. A four-year study by Tarvin and Woolfenden in Florida found that males win the vast majority of interactions with females. However, immediately before the breeding season, females may become more aggressive as they require more nutrients for nesting, though this does not change the overall dominance hierarchy.
5. How Do Blue Jays Communicate?
Blue jays have a diverse range of calls and are known for their ability to mimic other birds, including predators like hawks. This mimicry can be used to deceive other birds and steal their food. Lofton and Clench documented instances of blue jays imitating red-shouldered hawks to scare away other birds from feeding areas. Whether this behavior is primarily for protection or manipulation, it highlights the intelligence and resourcefulness of these birds. Consider capturing these moments with SIXT.VN’s arranged private photography tours in Hanoi’s bird sanctuaries.
6. What Role Do Blue Jays Play in Their Ecosystem?
Blue jays play a crucial role in seed dispersal, particularly for oak and beech trees. They collect nuts and acorns and bury them for later consumption, often forgetting some of these caches. This behavior significantly contributes to the spread of these trees. Johnson and Webb’s research indicates that blue jays are responsible for dispersing 5-6% of the nut crop, making them key players in forest regeneration. Exploring the natural habitats where blue jays contribute to the ecosystem can be a rewarding experience, and SIXT.VN can help you plan eco-friendly tours in Vietnam.
7. How Smart Are Blue Jays? Exploring Their Intelligence
Blue jays are highly intelligent birds. Studies have shown they can use tools to obtain food. In a University of Massachusetts study, blue jays were observed using paper and other materials to reach food pellets that were otherwise inaccessible. Six out of eight jays successfully used tools in this manner, demonstrating their problem-solving abilities and adaptability.
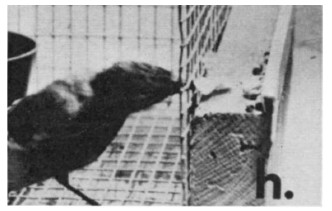 A blue jay using paper as a tool to gather food outside the cage, highlighting their problem-solving skills
A blue jay using paper as a tool to gather food outside the cage, highlighting their problem-solving skills
8. What is the Conservation Status of Blue Jays?
Blue jays are not currently considered threatened or endangered. Their populations are stable across their range. However, habitat loss and degradation can pose a threat to local populations. Supporting conservation efforts and maintaining healthy ecosystems are essential for ensuring their continued survival. By choosing eco-conscious travel options through SIXT.VN, you can contribute to the preservation of natural habitats.
9. How Can Travelers Spot Blue Jays in Vietnam?
While blue jays are native to North America, understanding bird behavior can enhance wildlife viewing wherever you travel. If you’re in Vietnam, keep an eye out for native species that exhibit similar flocking behaviors. Parks, gardens, and nature reserves are prime locations for bird watching. Bring binoculars and a field guide to help identify different species. SIXT.VN can arrange visits to Vietnam’s top bird-watching spots, complete with expert guides.
10. Why Choose SIXT.VN for Your Bird-Watching Trip?
SIXT.VN offers personalized travel services that cater to nature enthusiasts. From arranging transportation to remote bird-watching locations to booking eco-friendly accommodations, SIXT.VN ensures a seamless and responsible travel experience. Their expert local guides can provide valuable insights into the region’s flora and fauna, enhancing your understanding and appreciation of the local ecosystem. With SIXT.VN, you can focus on enjoying the natural wonders of Vietnam while they take care of all the logistics.
11. What Kind of Habitats Do Blue Jays Typically Prefer?
Blue jays are adaptable birds that thrive in various habitats, including forests, woodlands, parks, and suburban areas. They prefer environments with a mix of trees and open spaces, which provide both cover and foraging opportunities. Their ability to adapt to different environments has contributed to their widespread distribution.
12. Do Blue Jays Show Aggressive Behavior?
Yes, blue jays can exhibit aggressive behavior, especially towards other birds when competing for food or defending their territory. They are known to chase away smaller birds from feeders and can be quite vocal in asserting their dominance. However, this aggression is typically limited to specific situations and does not define their overall behavior.
13. How Long Do Blue Jays Live?
The average lifespan of a blue jay in the wild is about 5 to 7 years, although some individuals can live much longer. The oldest recorded blue jay lived for over 26 years. Factors such as habitat quality, food availability, and predation risks can affect their lifespan.
14. What Do Blue Jays Eat?
Blue jays have a varied diet that includes nuts, seeds, insects, fruits, and occasionally small vertebrates. They are opportunistic feeders and will adapt their diet based on what is available. Their fondness for acorns and nuts plays a crucial role in seed dispersal.
 A blue jay perched with a peanut in its beak, illustrating their varied diet and adaptability
A blue jay perched with a peanut in its beak, illustrating their varied diet and adaptability
15. How Do Blue Jays Build Their Nests?
Blue jays build their nests in trees or shrubs, typically at a height of 8 to 30 feet above the ground. The nests are cup-shaped and made of twigs, grass, roots, and mud. Both male and female blue jays participate in nest building, which usually takes about a week to complete.
16. What Are Some Unique Physical Characteristics of Blue Jays?
Blue jays have several unique physical characteristics, including their bright blue plumage, prominent crest, and strong beak. Their plumage does not vary with sex or season, making it easy to identify them year-round. They also have zygodactyl feet, with two toes pointing forward and two toes pointing backward, which helps them grip branches more effectively.
17. What Are Some Threats to Blue Jay Populations?
While blue jay populations are currently stable, they face several potential threats, including habitat loss, pesticide use, and collisions with vehicles and windows. Climate change could also alter their habitat and food availability, posing long-term challenges.
18. How Can People Help Protect Blue Jays?
People can help protect blue jays by preserving their natural habitats, reducing pesticide use, and providing food and water in their backyards. Planting native trees and shrubs can create a welcoming environment for blue jays and other birds. Supporting conservation organizations that work to protect bird habitats is also essential.
19. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About Blue Jays?
One common misconception about blue jays is that they are solely aggressive and domineering birds. While they can exhibit aggressive behavior, they are also intelligent, resourceful, and play a crucial role in their ecosystem. Another misconception is that they only eat nuts and seeds, when in reality, their diet is quite varied.
20. What Role Do Blue Jays Play in Seed Dispersal for Fagaceous Trees?
Blue jays play a vital role in the seed dispersal of fagaceous trees, particularly oak and beech trees, in eastern North America. These birds collect acorns and nuts, caching them in the ground for later consumption. However, they often forget where they buried some of these nuts, allowing them to germinate and grow into new trees. According to research, blue jays are responsible for dispersing 5-6% of the nut crop, making them essential for forest regeneration.
21. How Do Scientists Study the Migration Patterns of Blue Jays?
Scientists study the migration patterns of blue jays through banding programs. These programs involve capturing blue jays, placing a numbered band around their leg, and releasing them back into the wild. When these banded birds are recaptured, scientists can track their movements and gather data on their migration patterns. Stewart’s meta-analysis of over 8,000 recaptured blue jays provided valuable insights into their migratory behavior.
22. What Impact Does Human Development Have on Blue Jay Populations?
Human development can have a significant impact on blue jay populations. Habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization reduces the availability of suitable nesting and foraging areas. Pesticide use can also negatively affect blue jays by reducing their food supply and causing direct toxicity. Additionally, collisions with vehicles and windows are a major cause of mortality for blue jays in urban areas.
23. How Can Urban Planning Help Protect Blue Jays in Cities?
Urban planning can help protect blue jays in cities by incorporating green spaces, planting native trees and shrubs, and creating wildlife corridors. These measures can provide blue jays with suitable habitats and allow them to move safely between different areas. Reducing pesticide use and implementing bird-friendly building designs can also help mitigate the negative impacts of urbanization on blue jay populations.
24. Do Blue Jays Migrate Individually or in Flocks?
Blue jays often migrate in flocks, especially during the fall and winter months. These flocks can consist of related individuals who have formed stable social groups. Migrating in flocks provides blue jays with several benefits, including increased protection from predators and improved foraging efficiency.
25. How Do Blue Jays Adapt to Different Climates?
Blue jays are adaptable birds that can tolerate a wide range of climates. In colder regions, they may migrate south to avoid harsh winter conditions. They also have physiological adaptations that help them conserve heat, such as fluffing up their feathers to create an insulating layer of air.
26. What is the Role of Dominance Behavior in Blue Jay Social Structure?
Dominance behavior plays a significant role in blue jay social structure. Males are typically dominant over females, and older individuals are often dominant over younger ones. Dominance hierarchies help regulate access to resources, such as food and nesting sites. However, dominance relationships can be complex and vary depending on the specific context and individuals involved.
27. How Do Blue Jays Learn to Use Tools?
Blue jays learn to use tools through a combination of observation and trial-and-error. Young blue jays may watch older individuals using tools and then attempt to imitate their behavior. They also learn through their own experiences, discovering which tools and techniques are most effective for obtaining food.
28. What is the Significance of Blue Jay Mimicry?
Blue jay mimicry is a fascinating behavior that serves multiple purposes. By imitating the calls of predators, such as hawks, blue jays can scare away other birds from feeding areas, allowing them to steal their food. Mimicry may also be used as a form of communication, with blue jays imitating the calls of other species to convey specific messages.
29. How Do Blue Jays Contribute to Forest Regeneration?
Blue jays contribute to forest regeneration by dispersing the seeds of various tree species. They collect acorns and nuts, caching them in the ground for later consumption. However, they often forget where they buried some of these nuts, allowing them to germinate and grow into new trees. This process helps maintain the diversity and health of forest ecosystems.
30. What Research is Currently Being Conducted on Blue Jays?
Current research on blue jays focuses on various aspects of their behavior, ecology, and genetics. Scientists are studying their migration patterns, social structure, tool use, and cognitive abilities. They are also investigating the impacts of climate change and habitat loss on blue jay populations.
31. How do Blue Jays contribute to biodiversity?
Blue jays contribute to biodiversity by playing several key ecological roles. Their seed dispersal activities help maintain the diversity of plant species in forests and other ecosystems. They also serve as both predators and prey, influencing the populations of other species. Additionally, their presence can enhance the aesthetic value of natural areas, attracting more visitors and promoting conservation efforts.
32. What is the impact of urbanization on blue jay behavior?
Urbanization can significantly alter blue jay behavior. In urban areas, blue jays may become more habituated to humans and less fearful of them. They may also modify their diet to include more human-provided foods, such as bread and birdseed. Additionally, urbanization can disrupt their social structure and migration patterns.
33. How do blue jays interact with other bird species?
Blue jays interact with other bird species in various ways. They may compete with other birds for food and nesting sites. They may also prey on the eggs and nestlings of other birds. However, they can also form mutualistic relationships with other species, such as helping to warn them of approaching predators.
34. What are the key factors that influence blue jay habitat selection?
Key factors that influence blue jay habitat selection include the availability of food, water, and nesting sites. Blue jays prefer habitats with a mix of trees and open spaces, which provide both cover and foraging opportunities. They also require access to a reliable source of water for drinking and bathing.
35. How do blue jays adapt their foraging behavior to different environments?
Blue jays adapt their foraging behavior to different environments by modifying their diet and foraging techniques. In areas where nuts and seeds are abundant, they may focus on caching these items for later consumption. In areas where insects are more readily available, they may spend more time searching for them. They also use different foraging techniques depending on the type of food they are seeking.
36. What is the role of genetics in blue jay behavior?
Genetics plays a significant role in blue jay behavior. Studies have shown that certain behavioral traits, such as migration patterns and tool use, are at least partially influenced by genes. However, environmental factors also play a crucial role in shaping blue jay behavior.
37. How do blue jays respond to climate change?
Blue jays respond to climate change by altering their migration patterns, breeding timing, and habitat selection. As temperatures rise, they may shift their ranges northward and begin breeding earlier in the year. They may also be forced to adapt to new habitats as their traditional habitats become unsuitable.
38. What are the most effective strategies for blue jay conservation?
Effective strategies for blue jay conservation include preserving their natural habitats, reducing pesticide use, and mitigating the impacts of urbanization. Protecting forests and other natural areas is essential for ensuring that blue jays have access to suitable nesting and foraging areas. Reducing pesticide use can help maintain their food supply. Implementing bird-friendly building designs and creating wildlife corridors can help mitigate the negative impacts of urbanization.
39. How Do Blue Jays Benefit from Human-Provided Bird Feeders?
Blue jays benefit from human-provided bird feeders, especially during the winter months when natural food sources are scarce. Bird feeders provide them with a reliable source of energy, helping them survive the cold and maintain their health. However, it is important to clean bird feeders regularly to prevent the spread of diseases.
40. What Are Some Cultural Symbolism and Folklore Associated with Blue Jays?
In some cultures, blue jays are seen as symbols of intelligence, resourcefulness, and adaptability. They may also be associated with communication and sociability, due to their complex social behavior and diverse calls. In folklore, blue jays are sometimes depicted as tricksters or messengers.
 A map showing the distribution of blue jays across the United States, with different colors indicating summer-only, winter-only, and year-round presence
A map showing the distribution of blue jays across the United States, with different colors indicating summer-only, winter-only, and year-round presence
FAQ: Understanding Blue Jay Behavior
-
Do blue jays always travel in flocks?
Blue jays often travel in flocks outside the breeding season, particularly in late summer and winter.
-
Are blue jays migratory birds?
Some blue jays migrate, while others remain in their nesting areas year-round.
-
What is the typical diet of a blue jay?
Blue jays have a varied diet, including nuts, seeds, insects, fruits, and occasionally small vertebrates.
-
How intelligent are blue jays?
Blue jays are highly intelligent birds known for their problem-solving abilities and tool use.
-
What is the conservation status of blue jays?
Blue jays are not currently considered threatened or endangered, with stable populations across their range.
-
How do blue jays communicate with each other?
Blue jays communicate through a diverse range of calls and mimicry of other birds.
-
What is the role of blue jays in seed dispersal?
Blue jays play a crucial role in dispersing the seeds of oak and beech trees.
-
Are blue jays aggressive towards other birds?
Blue jays can exhibit aggressive behavior, especially when competing for food or defending their territory.
-
How can I attract blue jays to my backyard?
You can attract blue jays by providing food, water, and suitable nesting habitats in your backyard.
-
What are the primary threats to blue jay populations?
Primary threats include habitat loss, pesticide use, and collisions with vehicles and windows.
Ready to explore Vietnam and its diverse wildlife? SIXT.VN offers a range of travel services designed to make your trip unforgettable. From airport transfers and hotel bookings to personalized tour itineraries, we’ve got you covered. Contact us today to start planning your adventure!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN



