Traveling to Africa is an exciting prospect, filled with unique landscapes and diverse cultures. If you’re wondering, “Can You Travel To Africa Without Vaccinations?” the answer is nuanced and depends on several factors. SIXT.VN can help you navigate these complexities, providing up-to-date information and resources to ensure a safe and enjoyable trip, including travel advice, visa requirements, and local customs. By understanding the specific health risks in your destination and taking appropriate precautions, you can minimize health risks.
1. Understanding the Basics: Travel to Africa and Vaccinations
The question of whether you can travel to Africa without vaccinations involves understanding the health landscape of the continent and the specific requirements of each country.
1.1 Why Vaccinations Are Often Recommended
Many African countries have health risks not commonly found in other parts of the world. Vaccinations protect you from these diseases, ensuring a safer travel experience.
1.2 Factors Influencing Vaccination Needs
Your need for vaccinations depends on several factors:
- Destination: Different countries have different health risks.
- Duration of Stay: Longer stays may increase exposure risks.
- Activities: Activities like camping or hiking may require additional precautions.
- Personal Health: Your health history and current health status matter.
1.3 Common Diseases in Africa
Some diseases prevalent in Africa include:
- Yellow Fever: A viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes.
- Malaria: A parasitic disease also transmitted by mosquitoes.
- Hepatitis A and B: Liver infections spread through contaminated food, water, or bodily fluids.
- Typhoid: A bacterial infection spread through contaminated food and water.
- Meningitis: An inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes.
2. Official Guidelines: WHO and CDC Recommendations
For reliable information, consult the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). These organizations offer comprehensive guidelines on vaccinations and health precautions for travelers.
2.1 World Health Organization (WHO)
The WHO provides detailed information on required and recommended vaccinations for each country.
According to the World Health Organization, vaccinations are crucial for preventing the spread of infectious diseases globally. WHO emphasizes that vaccines are among the safest and most effective ways to protect against serious illnesses.
2.2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
The CDC offers similar advice, tailored to US travelers.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that vaccinations have significantly reduced the incidence of vaccine-preventable diseases, promoting public health worldwide.
2.3 Navigating Conflicting Information
It’s crucial to cross-reference information from multiple sources and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
3. Country-Specific Requirements and Recommendations
Vaccination requirements vary significantly across African countries. Some countries mandate specific vaccinations for entry, while others only recommend them.
3.1 Yellow Fever Vaccination: Mandatory vs. Recommended
- Mandatory: Some countries require proof of yellow fever vaccination for entry, especially if you’re arriving from a country with a risk of yellow fever transmission.
- Recommended: Even if not mandatory, yellow fever vaccination is often recommended due to the prevalence of the disease.
3.2 Examples of Country-Specific Requirements
- Kenya: Requires yellow fever vaccination if arriving from a country with yellow fever risk.
- South Africa: Recommends several vaccinations, including hepatitis A and typhoid.
- Uganda: Requires yellow fever vaccination and recommends malaria prophylaxis.
3.3 Utilizing Online Resources
Websites like SIXT.VN, the WHO, and the CDC offer country-specific information to help you plan accordingly.
4. Risks of Traveling Unvaccinated
Traveling to Africa without recommended vaccinations carries potential health risks that can impact your trip and long-term well-being.
4.1 Contracting Preventable Diseases
Without vaccinations, you’re at a higher risk of contracting diseases like yellow fever, malaria, and hepatitis.
4.2 Potential Health Complications
These diseases can lead to severe health complications, including hospitalization and long-term health issues.
4.3 Impact on Travel Plans
Contracting a disease can disrupt your travel plans, requiring medical treatment and potentially preventing you from continuing your trip.
5. Alternatives to Vaccinations: Minimizing Risks
If you choose not to get vaccinated, there are alternative measures you can take to minimize your risk of infection.
5.1 Preventative Measures
- Insect Repellent: Use insect repellent with DEET to protect against mosquito bites.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves and pants to minimize skin exposure.
- Mosquito Nets: Sleep under mosquito nets, especially in areas with high mosquito activity.
- Safe Food and Water: Consume only safe, properly cooked food and bottled or purified water.
5.2 Consulting with Healthcare Professionals
Discuss your travel plans with a healthcare professional to get personalized advice on minimizing risks.
5.3 Travel Insurance
Ensure you have comprehensive travel insurance that covers medical emergencies and evacuation.
6. Legal and Entry Requirements
Even if vaccinations are not mandatory, understanding the legal and entry requirements of your destination is crucial.
6.1 Entry Requirements for Unvaccinated Travelers
Some countries may have specific requirements or restrictions for unvaccinated travelers.
6.2 Potential Quarantine Measures
Be aware that you may be subject to quarantine measures if you arrive without required vaccinations.
6.3 Importance of Checking Official Sources
Always check the official government websites of your destination country for the most up-to-date information.
7. Personal Experiences and Anecdotes
Hearing from other travelers can provide valuable insights, but it’s essential to consider personal experiences with caution.
7.1 Stories from Vaccinated Travelers
Vaccinated travelers often report feeling more secure and confident during their trip.
7.2 Stories from Unvaccinated Travelers
Some unvaccinated travelers have had positive experiences using preventative measures, while others have faced health challenges.
7.3 Balancing Personal Stories with Expert Advice
Use personal stories to inform your decisions, but always prioritize expert advice from healthcare professionals and official sources.
8. Special Considerations: Children, Pregnant Women, and Individuals with Health Conditions
Certain groups require special considerations when it comes to vaccinations and travel to Africa.
8.1 Children
Children may require different vaccinations or dosages than adults.
8.2 Pregnant Women
Pregnant women should consult with their doctor before traveling to Africa, as some vaccinations are not safe during pregnancy.
8.3 Individuals with Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing health conditions should seek personalized advice from their healthcare provider.
9. Debunking Common Myths About Vaccinations
Misinformation about vaccinations can lead to unnecessary anxiety and poor decision-making.
9.1 Addressing Common Misconceptions
- Myth: Vaccinations cause autism.
- Fact: This has been disproven by numerous scientific studies.
- Myth: Natural immunity is always better than vaccination.
- Fact: Vaccination provides safe and effective protection against diseases.
9.2 Providing Evidence-Based Information
Rely on reputable sources like the WHO and CDC for accurate information about vaccinations.
9.3 Emphasizing the Importance of Informed Decisions
Make informed decisions based on evidence and expert advice, not on myths and misinformation.
10. Practical Tips for a Healthy Trip to Africa
Whether you choose to get vaccinated or not, there are several practical tips you can follow to stay healthy during your trip to Africa.
10.1 Before You Go
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss your travel plans and health concerns with your healthcare provider.
- Pack a Travel Health Kit: Include essentials like insect repellent, sunscreen, and medications.
- Get Travel Insurance: Ensure you have comprehensive travel insurance that covers medical emergencies.
10.2 During Your Trip
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of bottled or purified water to prevent dehydration.
- Practice Food Safety: Eat only properly cooked food from reputable sources.
- Avoid Mosquito Bites: Use insect repellent, wear protective clothing, and sleep under mosquito nets.
- Monitor Your Health: Be aware of any symptoms and seek medical attention if needed.
10.3 Additional Resources
Websites like SIXT.VN, the WHO, and the CDC offer valuable resources and tips for staying healthy while traveling in Africa.
11. The Role of Travel Clinics
Travel clinics specialize in providing travel-related health advice and vaccinations.
11.1 Benefits of Visiting a Travel Clinic
- Personalized Advice: Travel clinics offer personalized advice based on your destination and health history.
- Vaccination Services: They provide required and recommended vaccinations.
- Preventative Medications: They can prescribe preventative medications like malaria prophylaxis.
11.2 Finding a Reputable Travel Clinic
Look for travel clinics certified by reputable organizations and staffed by experienced healthcare professionals.
11.3 Preparing for Your Visit
Bring your travel itinerary and health records to your appointment to help the healthcare provider provide the best advice.
12. Understanding Malaria Risks and Prevention
Malaria is a significant health risk in many parts of Africa, and understanding how to prevent it is essential.
12.1 How Malaria is Transmitted
Malaria is transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
12.2 Malaria Prevention Strategies
- Antimalarial Medications: Take antimalarial medications as prescribed by your doctor.
- Insect Repellent: Use insect repellent with DEET.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves and pants.
- Mosquito Nets: Sleep under mosquito nets.
12.3 Recognizing Malaria Symptoms
Symptoms of malaria include fever, chills, headache, and muscle aches. Seek medical attention immediately if you experience these symptoms.
13. Staying Safe from Waterborne and Foodborne Illnesses
Waterborne and foodborne illnesses are common in Africa, but you can take steps to minimize your risk.
13.1 Common Waterborne and Foodborne Illnesses
- Traveler’s Diarrhea: Caused by consuming contaminated food or water.
- Hepatitis A: A liver infection spread through contaminated food and water.
- Typhoid: A bacterial infection spread through contaminated food and water.
13.2 Tips for Preventing Illnesses
- Drink Bottled or Purified Water: Avoid tap water, ice, and unpasteurized beverages.
- Eat Properly Cooked Food: Avoid raw or undercooked meats, seafood, and vegetables.
- Wash Your Hands: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water.
- Choose Reputable Restaurants: Eat at restaurants with good hygiene practices.
13.3 What to Do if You Get Sick
If you experience symptoms of a waterborne or foodborne illness, seek medical attention and stay hydrated.
14. Understanding Altitude Sickness
If your travel plans include visiting high-altitude areas, be aware of the risks of altitude sickness.
14.1 Symptoms of Altitude Sickness
Symptoms of altitude sickness include headache, nausea, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
14.2 Preventing Altitude Sickness
- Ascend Gradually: Avoid rapid ascents to allow your body to adjust to the altitude.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water.
- Avoid Alcohol and Caffeine: These can worsen symptoms of altitude sickness.
- Medications: Consult your doctor about medications to prevent altitude sickness.
14.3 What to Do if You Develop Altitude Sickness
If you experience symptoms of altitude sickness, descend to a lower altitude and seek medical attention if needed.
15. Preparing for Common Travel Ailments
Being prepared for common travel ailments can help you manage them effectively.
15.1 Common Travel Ailments
- Traveler’s Diarrhea
- Motion Sickness
- Sunburn
- Insect Bites
- Minor Injuries
15.2 Essential Items for Your Travel Health Kit
- Insect Repellent
- Sunscreen
- Antidiarrheal Medication
- Motion Sickness Medication
- Pain Relievers
- Antiseptic Wipes
- Bandages
15.3 Managing Ailments on the Go
Know how to manage common ailments and when to seek medical attention.
16. The Importance of Comprehensive Travel Insurance
Travel insurance is essential for protecting yourself against unexpected medical expenses and emergencies.
16.1 What to Look for in a Travel Insurance Policy
- Medical Coverage: Ensure the policy covers medical expenses, hospitalization, and evacuation.
- Trip Cancellation Coverage: Look for coverage in case you need to cancel your trip due to illness or other reasons.
- Lost or Stolen Baggage Coverage: Ensure the policy covers lost or stolen baggage.
- 24/7 Assistance: Look for a policy that provides 24/7 assistance in case of emergencies.
16.2 Understanding Policy Exclusions
Be aware of any exclusions in the policy, such as pre-existing conditions or high-risk activities.
16.3 Filing a Claim
Know how to file a claim and what documents you need to provide.
17. Staying Informed About Health Advisories
Staying informed about current health advisories can help you make informed decisions about your travel plans.
17.1 How to Stay Updated
- Check Official Websites: Regularly check the websites of the WHO and CDC for health advisories.
- Sign Up for Alerts: Sign up for email or text alerts from travel health organizations.
- Follow News Sources: Stay informed about health news from reputable news sources.
17.2 Responding to Health Advisories
If a health advisory is issued for your destination, follow the recommendations and take appropriate precautions.
17.3 Making Informed Decisions
Use health advisories to make informed decisions about your travel plans and protect your health.
18. Mental Health and Travel
Traveling to a new and unfamiliar place can bring excitement but also stress and anxiety. Taking care of your mental health while traveling is as important as physical health.
18.1 Managing Travel Anxiety
Plan Ahead: Research your destination, transportation, and accommodation to ease uncertainty.
Stay Connected: Keep in touch with family and friends for emotional support.
Relaxation Techniques: Practice deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to reduce stress.
18.2 Combating Loneliness
Join Tours and Activities: Participate in group activities to meet new people.
Engage with Locals: Interact with locals to learn about their culture and make connections.
Use Social Media: Connect with other travelers through online groups and forums.
18.3 Seeking Professional Help
If you experience persistent anxiety, depression, or other mental health issues, seek professional help from a therapist or counselor. Many online resources offer virtual therapy sessions.
19. Sustainable and Responsible Travel
Traveling responsibly is essential for preserving the environment and supporting local communities.
19.1 Eco-Friendly Practices
Reduce Waste: Use reusable water bottles, shopping bags, and containers.
Conserve Energy: Turn off lights and air conditioning when leaving your accommodation.
Choose Eco-Friendly Tours: Support tour operators that follow sustainable practices.
19.2 Supporting Local Communities
Shop Locally: Buy souvenirs and products from local artisans and businesses.
Eat at Local Restaurants: Try traditional dishes and support local food vendors.
Respect Local Customs: Learn about and respect the customs and traditions of the local culture.
19.3 Ethical Wildlife Encounters
Avoid Animal Exploitation: Do not participate in activities that harm or exploit animals, such as riding elephants or taking photos with captive wildlife.
Visit Sanctuaries: Support ethical wildlife sanctuaries that rescue and rehabilitate animals.
Observe Wildlife Responsibly: Maintain a safe distance and avoid disturbing wildlife in their natural habitat.
20. Travel in the Post-COVID World
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the landscape of travel. Staying informed about the latest guidelines and protocols is crucial for safe travel.
20.1 Vaccination and Testing Requirements
Check Entry Requirements: Stay updated on the vaccination and testing requirements for your destination.
Carry Vaccination Proof: Keep a copy of your vaccination certificate or test results with you.
20.2 Hygiene and Safety Measures
Wear Masks: Follow local guidelines on mask-wearing in public spaces.
Practice Hand Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently with soap and water or use hand sanitizer.
Maintain Social Distance: Keep a safe distance from others to reduce the risk of transmission.
20.3 Travel Insurance and Flexibility
Purchase Comprehensive Travel Insurance: Ensure your policy covers COVID-19-related medical expenses and trip cancellations.
Stay Flexible: Be prepared to adjust your travel plans in response to changing circumstances and restrictions.
Conclusion: Making an Informed Decision
Ultimately, the decision of whether to travel to Africa without vaccinations is a personal one. However, it’s essential to make an informed decision based on reliable information, expert advice, and a thorough understanding of the risks involved. SIXT.VN is here to assist you with travel planning, providing reliable and safe travel experiences.
SIXT.VN: Your Partner for Safe and Enjoyable Travel to Vietnam
At SIXT.VN, we understand the importance of safe and well-informed travel. Whether you need airport transfer, hotel booking, Hanoi tours or flight booking, we’re here to assist you every step of the way, ensuring you have a smooth and memorable experience.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN
 Elephants in Central Serengeti National Park, Tanzania, Africa
Elephants in Central Serengeti National Park, Tanzania, Africa
Elephants grazing peacefully in the Central Serengeti, showcasing the raw beauty of African wildlife.
 A winding path through lush green highlands, offering a glimpse into the diverse landscapes of Africa
A winding path through lush green highlands, offering a glimpse into the diverse landscapes of Africa
A serene walking trail through the African highlands, highlighting the continent’s varied and picturesque terrains.
 The Best Places to Go on Safari in 2025
The Best Places to Go on Safari in 2025
An inviting banner promoting the best safari destinations for 2025, enticing travelers with the promise of unforgettable wildlife encounters.
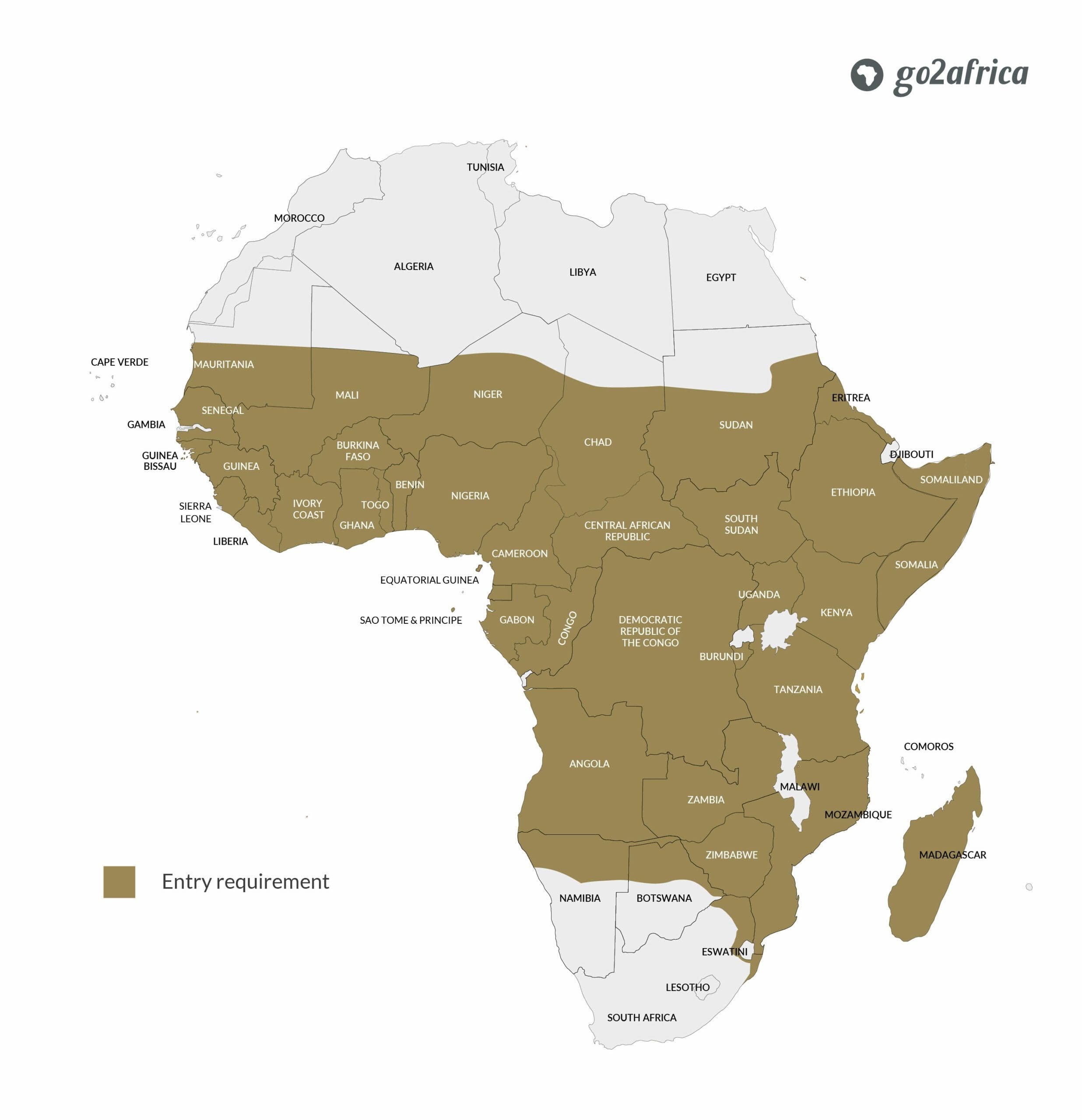 Illustration of malaria-carrying mosquitoes, highlighting the risk of malaria in some African regions
Illustration of malaria-carrying mosquitoes, highlighting the risk of malaria in some African regions
A visual representation of malaria-carrying mosquitoes, emphasizing the importance of malaria prevention during travels in Africa.
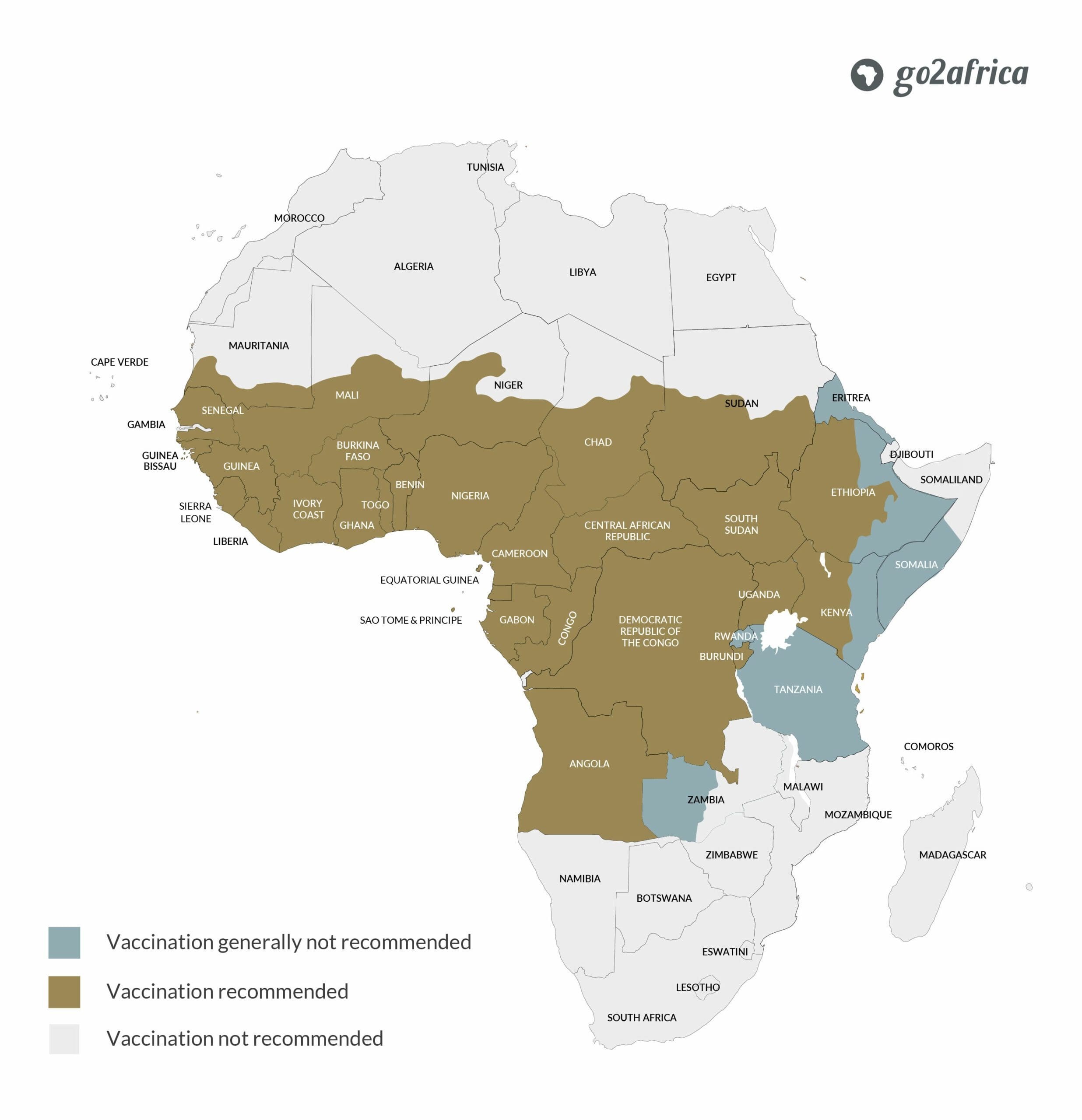 Illustration of yellow fever virus
Illustration of yellow fever virus
An informational illustration about the yellow fever virus, highlighting the significance of vaccination and preventive measures.
FAQ: Traveling to Africa Without Vaccinations
1. Is it mandatory to have vaccinations to travel to Africa?
No, vaccinations are not always mandatory for travel to Africa, but it depends on the country you’re visiting and your country of origin. Some countries require proof of yellow fever vaccination, especially if you are coming from a region with a risk of yellow fever transmission. It’s always best to check the specific requirements for your destination.
2. What are the most common recommended vaccinations for travelers to Africa?
The most commonly recommended vaccinations include those for yellow fever, hepatitis A and B, typhoid, meningitis, and polio. Depending on the region and your activities, your doctor may also recommend vaccinations for rabies or cholera.
3. Can I get vaccinated for yellow fever at any clinic?
No, only authorized travel clinics can administer the yellow fever vaccine and issue the International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), which serves as proof of vaccination.
4. What should I do if I decide not to get vaccinated before traveling to Africa?
If you choose not to get vaccinated, it’s crucial to take extra precautions. Use insect repellent with DEET, wear protective clothing, sleep under mosquito nets, practice strict food and water safety, and ensure you have comprehensive travel insurance. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice is also recommended.
5. How can I stay safe from mosquito bites in Africa?
To stay safe from mosquito bites, use insect repellent containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus. Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants, especially during dawn and dusk when mosquitoes are most active. Sleep under a mosquito net, and consider using mosquito coils or vaporizers in your room.
6. Is it safe to drink tap water in Africa?
In many parts of Africa, it is not safe to drink tap water due to the risk of contamination. Always drink bottled or purified water. Avoid ice cubes, and be cautious when consuming beverages from street vendors.
7. How can I prevent traveler’s diarrhea while in Africa?
To prevent traveler’s diarrhea, practice strict food and water safety. Eat only thoroughly cooked food from reputable sources. Avoid raw or undercooked meats, seafood, and vegetables. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, and carry hand sanitizer.
8. What should I include in a travel health kit for a trip to Africa?
A travel health kit should include insect repellent, sunscreen, antidiarrheal medication, pain relievers, antiseptic wipes, bandages, any personal prescription medications, and a thermometer.
9. How important is travel insurance when traveling to Africa?
Travel insurance is extremely important when traveling to Africa. It can protect you from unexpected medical expenses, trip cancellations, lost or stolen baggage, and other emergencies. Ensure your policy includes coverage for medical evacuation, which can be very costly if needed.
10. Where can I find the most up-to-date health advisories for Africa?
You can find the most up-to-date health advisories for Africa on the websites of the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Regularly check these sources for the latest information before and during your trip.



