Are you curious about wave phenomena during your Vietnam adventure? This comprehensive guide, brought to you by SIXT.VN, dives deep into the world of mechanical waves and vacuum propagation. Discover the fascinating science behind wave travel and how it relates to your travel experiences.
1. What Are Mechanical Waves and Their Need for a Medium?
No, mechanical waves cannot travel through a vacuum because they require a medium to propagate. Mechanical waves, such as sound waves or water waves, are disturbances that transfer energy through a material medium by causing the particles of the medium to vibrate.
A medium is any substance – solid, liquid, gas, or plasma – that can transmit energy through particle interaction. Think of it like a crowd doing “the wave” at a sporting event. Each person needs to bump into the next to keep the wave going. If there’s a gap in the crowd, the wave stops. Similarly, without a medium, there are no particles for the energy to pass through, so the mechanical wave cannot travel. This is why you can’t hear sounds in the vacuum of space, despite the potential for spectacular explosions happening!
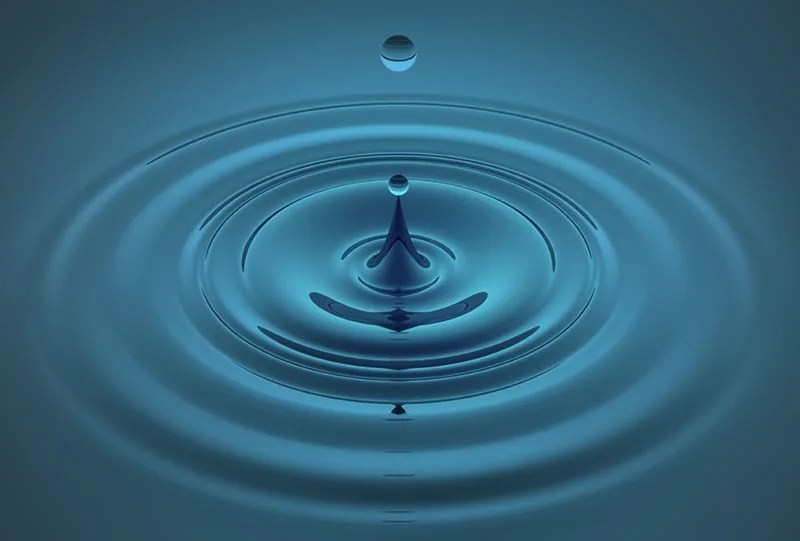 A photograph of a drop of water leaving ripples in a pool.
A photograph of a drop of water leaving ripples in a pool.
Water ripples demonstrating a mechanical wave.
1.1 Examples of Mechanical Waves
Here are some examples of mechanical waves and their respective mediums:
- Sound Waves: These travel through air (gas), water (liquid), or solids. When you speak, your vocal cords vibrate, creating pressure waves in the air that travel to someone else’s ear.
- Water Waves: These travel through water (liquid). A stone thrown into a pond creates disturbances that propagate as ripples on the surface.
- Seismic Waves: These travel through the Earth (solid). Earthquakes generate seismic waves that travel through the Earth’s layers, providing information about the planet’s interior.
- Waves on a String: These travel through a string (solid). When you pluck a guitar string, you create a wave that travels along the string’s length, producing sound.
1.2 How Mechanical Waves Transfer Energy
Mechanical waves transfer energy through a medium via particle interaction. This interaction typically involves:
- Elasticity: The ability of the medium to return to its original shape after being deformed.
- Inertia: The tendency of the particles in the medium to resist changes in their motion.
When a disturbance occurs, it causes the first particle in the medium to vibrate. This vibration then affects the neighboring particles due to the elastic forces between them. The energy is transferred from one particle to another, creating a wave that propagates through the medium. The inertia of the particles ensures that the wave continues to propagate until the energy is dissipated through friction or other damping mechanisms.
2. Electromagnetic Waves: The Exception to the Rule
Electromagnetic waves are unique because they can travel through a vacuum. Unlike mechanical waves, they don’t need a medium. This is because they are created by oscillating electric and magnetic fields, which can sustain each other even in empty space.
Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that encompasses radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. All these forms of radiation are part of the electromagnetic spectrum and travel at the speed of light in a vacuum.
2.1 How Electromagnetic Waves Propagate Through a Vacuum
Electromagnetic waves propagate through a vacuum because they are self-propagating disturbances in electric and magnetic fields. According to Maxwell’s equations, a changing electric field creates a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field creates an electric field. This coupling between the electric and magnetic fields allows electromagnetic waves to propagate through space without the need for a medium.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Generating Fields: An accelerating charged particle creates a changing electric field around it.
- Induced Magnetic Field: This changing electric field, in turn, creates a changing magnetic field perpendicular to it.
- Self-Sustaining Cycle: The changing magnetic field then creates another changing electric field, and this process continues indefinitely.
This self-sustaining cycle of electric and magnetic fields propagating together is what constitutes an electromagnetic wave. Because the fields are intrinsic properties of space, they don’t require a material medium to exist or propagate.
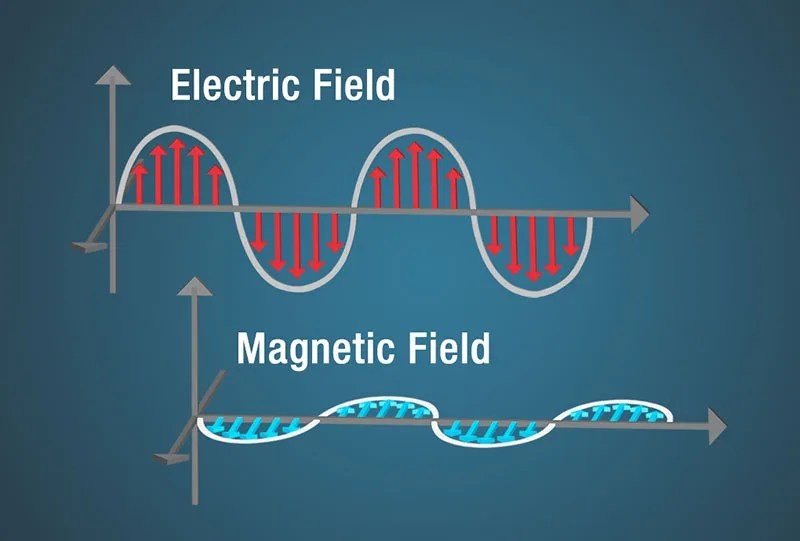 A diagram of an electric field shown as a sine wave with red arrows beneath the curves and a magnetic field shown as a sine wave with blue arrows perpendicular to the electric field.
A diagram of an electric field shown as a sine wave with red arrows beneath the curves and a magnetic field shown as a sine wave with blue arrows perpendicular to the electric field.
Electric and magnetic fields of an electromagnetic wave.
2.2 Examples of Electromagnetic Waves
Here are some common examples of electromagnetic waves:
- Light: Visible light from the sun or a light bulb. This is how we see the world around us.
- Radio Waves: Used for radio and television broadcasting. They carry information over long distances.
- Microwaves: Used in microwave ovens for cooking and in communication systems.
- X-rays: Used in medical imaging to see inside the body.
- Gamma Rays: Emitted by radioactive materials and used in cancer treatment.
3. Key Differences Between Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves
To summarize, here’s a table highlighting the key distinctions between mechanical and electromagnetic waves:
| Feature | Mechanical Waves | Electromagnetic Waves |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Required | Yes | No |
| Nature | Disturbance in a material medium | Oscillating electric and magnetic fields |
| Examples | Sound waves, water waves, seismic waves | Light, radio waves, microwaves, X-rays |
| Speed | Varies depending on the medium | Constant in a vacuum (speed of light) |
| Energy Transfer | Through particle interaction in the medium | Through self-propagation of fields |
| Travel in Vacuum | No | Yes |
| Polarization | Can exhibit polarization, but not always | Can be polarized |
| Creation | Disturbance or vibration in matter | Accelerating charged particles or changing fields |
4. Understanding the Implications for Your Vietnam Travel Experience
While the physics of wave propagation might seem abstract, it has real-world implications for your travels in Vietnam. Consider these points:
- Communication: Radio waves, a type of electromagnetic wave, are essential for communication devices like smartphones and radios. You can stay connected with family and friends, access navigation apps, and receive important travel updates thanks to these waves traveling through the air (and even through space if communicating via satellite).
- Weather Forecasting: Weather forecasts rely on satellite imagery and radar, both of which use electromagnetic waves to gather data. Understanding the weather helps you plan your itinerary and pack accordingly.
- Medical Services: X-rays, another type of electromagnetic wave, are used in hospitals and clinics. Should you need medical attention during your trip, X-ray technology can help diagnose and treat various conditions.
- Photography: Cameras use visible light, a form of electromagnetic radiation, to capture images. The quality of light can greatly affect the outcome of your photos, so understanding how light behaves can help you take stunning travel photos.
5. The Importance of Electromagnetic Waves in Space Exploration
The fact that electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum is crucial for space exploration. Without them, we wouldn’t be able to communicate with spacecraft, study distant stars and galaxies, or explore the universe beyond our planet.
- Communication with Spacecraft: Radio waves are used to send commands to spacecraft and receive data back from them. This allows scientists to monitor spacecraft performance, conduct experiments, and explore other planets and celestial bodies.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites use various types of electromagnetic radiation to study the Earth’s surface, atmosphere, and oceans. This data is used for weather forecasting, climate monitoring, environmental management, and disaster response.
- Astronomy: Telescopes use electromagnetic radiation to observe distant stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects. By studying the properties of electromagnetic radiation, astronomers can learn about the composition, temperature, and motion of these objects.
6. Exploring Wave Properties: Frequency, Wavelength, and Energy
Understanding the properties of waves, whether mechanical or electromagnetic, helps you appreciate the world around you. Key properties include frequency, wavelength, and energy.
6.1 Frequency
Frequency refers to the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz). One Hertz equals one cycle per second.
- High Frequency: Waves with high frequencies have short wavelengths and carry more energy. Examples include gamma rays and X-rays.
- Low Frequency: Waves with low frequencies have long wavelengths and carry less energy. Examples include radio waves and microwaves.
6.2 Wavelength
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave, typically measured in meters.
- Short Wavelength: Waves with short wavelengths have high frequencies and carry more energy.
- Long Wavelength: Waves with long wavelengths have low frequencies and carry less energy.
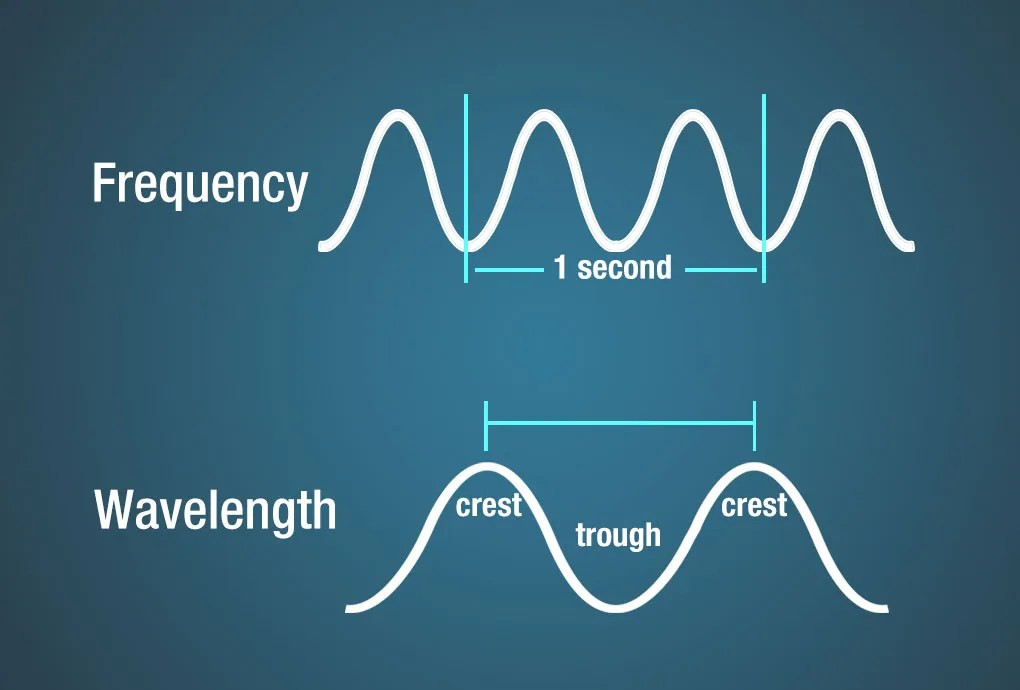 Diagram showing frequency as the measurement of the number of wave crests that pass a given point in a second. Wavelength is measured as the distance between two crests.
Diagram showing frequency as the measurement of the number of wave crests that pass a given point in a second. Wavelength is measured as the distance between two crests.
Wavelength and frequency relationship.
6.3 Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work, and for electromagnetic waves, it is directly proportional to the frequency. It’s often measured in electron volts (eV).
- High Energy: Waves with high frequencies and short wavelengths carry more energy. These can be harmful, like gamma rays, which can damage cells.
- Low Energy: Waves with low frequencies and long wavelengths carry less energy. These are generally harmless, like radio waves used for communication.
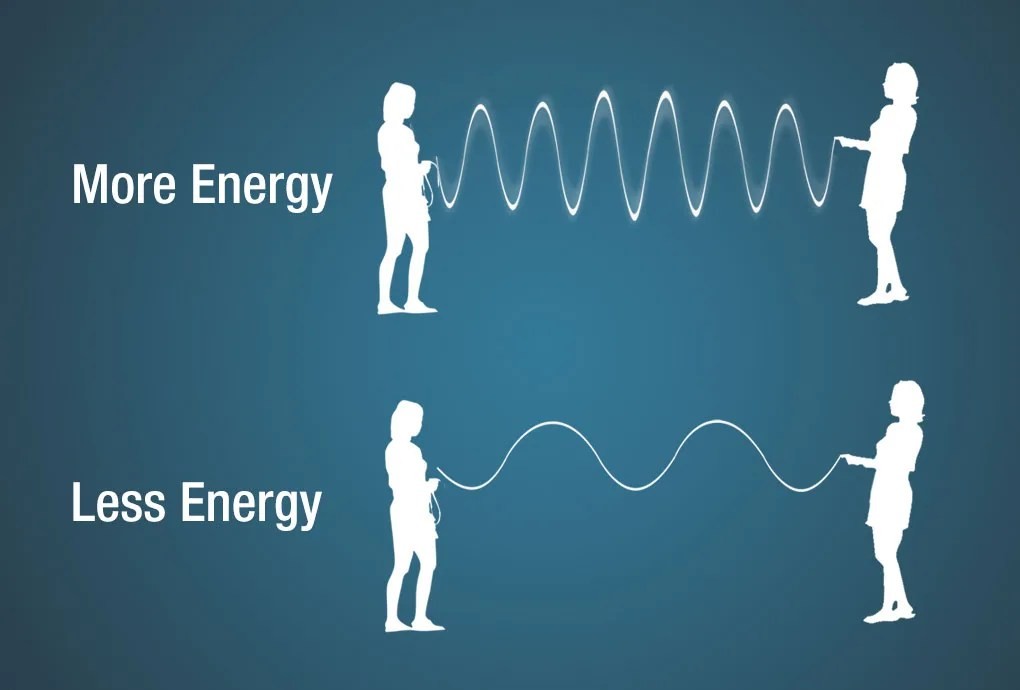 An illustration showing a jump rope with each end being held by a person. As the people move the jump rope up and down very fast – adding MORE energy – the more wave crests appear, thus shorter wavelengths. When the people move the jump rope up and down slower, there are fewer wave crests within the same distance, thus longer wavelengths.
An illustration showing a jump rope with each end being held by a person. As the people move the jump rope up and down very fast – adding MORE energy – the more wave crests appear, thus shorter wavelengths. When the people move the jump rope up and down slower, there are fewer wave crests within the same distance, thus longer wavelengths.
Energy and wavelength relationship.
7. Polarization: A Unique Property of Light
Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves that describes the orientation of the electric field’s oscillation. Light waves are transverse waves, meaning their oscillations occur perpendicular to the direction of propagation. In unpolarized light, the electric field oscillates in all directions perpendicular to the wave’s direction. Polarized light, on the other hand, has its electric field oscillating in a single plane.
7.1 How Polarization Works
Imagine shaking a rope up and down. The wave travels horizontally, but the rope moves vertically. If you pass the rope through a vertical slit, the wave continues. But if you turn the slit sideways (horizontally), the wave stops. This is similar to how polarized light works. A polarizing filter only allows light waves vibrating in a specific direction to pass through.
7.2 Applications of Polarization
- Sunglasses: Polarized sunglasses reduce glare by blocking horizontally polarized light reflected from surfaces like water or roads.
- Photography: Polarizing filters can enhance colors and reduce reflections in photos, especially in outdoor settings.
- LCD Screens: Liquid crystal displays (LCDs) use polarized light to create images. The liquid crystals control the amount of light that passes through the screen, creating different colors and brightness levels.
- 3D Movies: 3D glasses use polarized lenses to separate the images projected for the left and right eyes, creating a sense of depth.
8. Navigating Hanoi: Utilizing Waves for a Smooth Journey with SIXT.VN
Understanding how waves function can even subtly enhance your travel experience, especially in a bustling city like Hanoi.
8.1 SIXT.VN’s Services and How Waves Play a Role
SIXT.VN offers a range of services to make your travel in Vietnam seamless. Consider how different types of waves contribute to the functionality of these services:
- Airport Transfer:
- GPS Navigation: GPS relies on radio waves (electromagnetic waves) transmitted from satellites to your device, guiding your driver to your location for prompt pick-up.
- Communication: Radio waves enable communication between you and your driver, ensuring smooth coordination.
- Hotel Booking:
- Internet Access: Accessing SIXT.VN’s website to book your hotel involves the transmission of data via electromagnetic waves through Wi-Fi or cellular networks.
- Tours and Activities:
- Information Access: Researching and booking tours online requires the use of electromagnetic waves to access websites, read reviews, and make reservations.
8.2 Leveraging Waves for a Better Trip
Here’s how understanding waves can indirectly improve your trip:
- Optimize Communication: Be aware of factors that can affect radio wave signals, such as tall buildings or geographical obstacles. Try to stay in open areas for better signal strength.
- Stay Informed: Utilize weather forecasts (based on electromagnetic wave data) to plan your daily activities and pack accordingly.
- Capture Memories: Use polarized sunglasses and camera filters to enhance your photography and capture stunning visuals of Vietnam.
9. Vietnam Travel Tips and Insights
Enhance your trip to Vietnam with these practical tips and insights, keeping in mind how wave-related technologies can assist you:
9.1 Entry Requirements and Visa Information
- Visa Requirements: Check the latest visa requirements for your nationality before traveling. Most nationalities can apply for an e-visa online.
- Passport Validity: Ensure your passport is valid for at least six months beyond your intended stay.
Source: Vietnam Immigration Department
9.2 Transportation Options in Hanoi
- Taxis and Ride-Hailing Apps: Taxis are readily available, and ride-hailing apps like Grab are popular and convenient. Use GPS navigation (radio waves) to track your route.
- Motorbike Taxis (Xe Om): A quick and affordable way to get around, but negotiate the price beforehand.
- Public Buses: An extensive network covering most of the city. Use online maps (accessed via electromagnetic waves) to plan your route.
9.3 Accommodation Options
Hanoi offers a wide range of accommodation options to suit every budget:
- Luxury Hotels: Offering world-class amenities and services.
- Boutique Hotels: Charming and stylish hotels with a local touch.
- Hostels: Budget-friendly options perfect for solo travelers and backpackers.
Use SIXT.VN to compare prices and book the perfect accommodation.
9.4 Must-Visit Attractions in Hanoi
- Hoan Kiem Lake: A scenic lake in the heart of Hanoi, surrounded by temples and pagodas.
- Old Quarter: A bustling historic district with narrow streets, traditional shops, and delicious street food.
- Ho Chi Minh Mausoleum: The final resting place of Ho Chi Minh, the former president of Vietnam.
- Temple of Literature: Vietnam’s first university, founded in 1070.
9.5 Local Customs and Etiquette
- Dress Code: Dress modestly when visiting temples and pagodas.
- Greetings: Use both hands to offer and receive items as a sign of respect.
- Tipping: Tipping is not customary but is appreciated for good service.
9.6 Safety Tips
- Be Aware of Your Surroundings: Watch out for pickpockets, especially in crowded areas.
- Drink Bottled Water: Avoid drinking tap water.
- Cross the Street with Caution: Traffic can be chaotic; use crosswalks and be patient.
9.7 Currency and Payment Methods
- Currency: The Vietnamese currency is the Dong (VND).
- Payment Methods: Credit cards are accepted in major hotels and restaurants, but cash is preferred in local markets and smaller establishments.
9.8 Food and Drink Recommendations
- Pho: A traditional Vietnamese noodle soup.
- Banh Mi: A Vietnamese sandwich with various fillings.
- Bun Cha: Grilled pork with rice noodles and dipping sauce.
- Egg Coffee: A unique Hanoi specialty made with coffee and egg yolks.
9.9 Best Time to Visit Hanoi
- Autumn (September to November): Pleasant weather with mild temperatures and clear skies.
- Spring (March to April): Warm and sunny days with occasional showers.
9.10 Packing Essentials
- Lightweight Clothing: Vietnam has a tropical climate, so pack light, breathable clothing.
- Comfortable Shoes: You’ll be doing a lot of walking, so comfortable shoes are essential.
- Sunscreen and Insect Repellent: Protect yourself from the sun and mosquitoes.
- Adapter: Vietnam uses Type A and Type C plugs, so bring an adapter if necessary.
10. SIXT.VN: Your Partner for Seamless Vietnam Travel
Planning a trip to Vietnam involves numerous details, from arranging airport transfers to booking accommodations and exploring the local attractions. SIXT.VN is dedicated to simplifying your travel experience, offering a comprehensive range of services to meet all your needs.
10.1 Comprehensive Travel Solutions
SIXT.VN provides a one-stop platform for all your travel arrangements, ensuring a smooth and stress-free journey:
- Airport Transfer Services:
- Convenient Pick-Up and Drop-Off: Start your trip with ease with our reliable airport transfer services. Our professional drivers will greet you upon arrival and ensure you reach your destination safely and comfortably.
- Wide Range of Vehicles: Choose from a variety of vehicles to suit your needs, from sedans to minivans, perfect for solo travelers or larger groups.
- Hotel Booking Assistance:
- Extensive Hotel Options: Find the perfect accommodation with our wide selection of hotels, ranging from budget-friendly options to luxurious resorts.
- Competitive Prices: Enjoy competitive prices and exclusive deals, ensuring you get the best value for your money.
- Tour and Activity Bookings:
- Curated Tour Packages: Discover the best of Vietnam with our curated tour packages, designed to showcase the country’s rich culture, history, and natural beauty.
- Customized Itineraries: Create a personalized itinerary based on your interests and preferences, ensuring you experience exactly what you want.
10.2 Advantages of Using SIXT.VN
Choosing SIXT.VN for your Vietnam travel needs comes with numerous benefits:
- Convenience:
- User-Friendly Platform: Our easy-to-navigate website allows you to quickly find and book the services you need.
- 24/7 Customer Support: Our dedicated customer support team is available around the clock to assist you with any questions or concerns.
- Reliability:
- Trusted Service Providers: We partner with reputable and reliable service providers to ensure you receive top-quality service.
- Transparent Pricing: Our pricing is transparent and upfront, with no hidden fees or surprises.
- Personalization:
- Customized Travel Plans: We work with you to create a travel plan that matches your specific needs and preferences.
- Local Expertise: Benefit from our local expertise and insider tips to discover hidden gems and authentic experiences.
10.3 How to Book with SIXT.VN
Booking with SIXT.VN is quick and easy. Follow these simple steps to plan your Vietnam adventure:
- Visit SIXT.VN: Open your web browser and go to the SIXT.VN website.
- Select Your Services: Choose from our range of services, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and tour packages.
- Enter Your Details: Provide the necessary information, such as your travel dates, destination, and preferences.
- Review and Confirm: Review your booking details and confirm your reservation.
- Make Payment: Securely make your payment using our trusted payment gateway.
- Receive Confirmation: Receive instant confirmation of your booking via email.
10.4 Contact Information
For any inquiries or assistance, please feel free to contact us:
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/WhatsApp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
FAQ: Mechanical Waves and Vacuum
1. Can mechanical waves travel through a vacuum?
No, mechanical waves cannot travel through a vacuum because they require a medium to propagate.
2. What is a medium in the context of wave propagation?
A medium is any substance (solid, liquid, gas, or plasma) that can transmit energy through particle interaction.
3. What are some examples of mechanical waves?
Examples include sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves.
4. Can electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum?
Yes, electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum because they are self-propagating disturbances in electric and magnetic fields.
5. What are some examples of electromagnetic waves?
Examples include light, radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.
6. What is the key difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves?
The key difference is that mechanical waves require a medium to propagate, while electromagnetic waves do not.
7. How do electromagnetic waves propagate through a vacuum?
Electromagnetic waves propagate through a vacuum because changing electric fields create magnetic fields, and vice versa, allowing the waves to sustain themselves.
8. What is frequency in the context of waves?
Frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a given point per unit of time, typically measured in Hertz (Hz).
9. What is wavelength in the context of waves?
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of a wave, typically measured in meters.
10. What is polarization, and how does it relate to light?
Polarization is a property of electromagnetic waves describing the orientation of the electric field’s oscillation. Polarized light has its electric field oscillating in a single plane, while unpolarized light oscillates in all directions.
Conclusion: Embrace the Science and the Adventure with SIXT.VN
Understanding the science behind wave propagation, particularly the distinction between mechanical and electromagnetic waves, enriches your travel experience by giving you a deeper appreciation of the technologies and natural phenomena that shape your journey. Whether it’s relying on radio waves for GPS navigation, capturing stunning photos with polarized lenses, or simply enjoying the convenience of online booking, waves are integral to modern travel. Let SIXT.VN be your trusted partner in exploring Vietnam, ensuring a seamless, informed, and memorable adventure. Visit SIXT.VN today to plan your perfect Vietnam getaway!



