Are you curious about the nature of sound and how it travels? Do you wonder, can a mechanical wave travel through empty space? SIXT.VN is here to help you navigate the fascinating world of sound waves while planning your trip to Vietnam. Let’s embark on this sonic journey together, exploring sound, mechanics, and even offering travel tips for your Vietnamese adventure!
1. What Exactly Are Mechanical Waves?
The straightforward answer is no, a mechanical wave cannot travel through empty space. Mechanical waves need a medium, whether it’s a solid, liquid, or gas, to propagate. Let’s dive deeper into why this is and explore the nature of mechanical waves in more detail.
1.1. The Need for a Medium
Mechanical waves are disturbances that transfer energy through a medium by causing the particles of that medium to vibrate. Think of it like a chain reaction: one particle bumps into the next, transferring energy along the way. Empty space, by definition, lacks these particles, rendering it impossible for mechanical waves to propagate. Without the medium, the transfer of momentum is impossible.
1.2. Examples of Mechanical Waves
- Sound Waves: These are the most common example. As we will explore in detail, sound travels through air, water, or solids.
- Water Waves: These occur on the surface of liquids, with the water molecules themselves oscillating.
- Seismic Waves: These travel through the Earth’s crust, caused by earthquakes.
- Waves on a String: Pluck a guitar string, and you’ll see a mechanical wave traveling along it.
1.3. The Difference Between Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves
It is helpful to consider what mechanical waves are not. Electromagnetic waves (like light, radio waves, and X-rays) do not require a medium. They can travel through the vacuum of space, which is how sunlight reaches Earth. This fundamental difference lies in their mode of propagation: electromagnetic waves are self-propagating disturbances in electric and magnetic fields.
1.4. Why Does This Matter for Your Trip to Vietnam?
Understanding that sound needs a medium to travel has practical implications for your travel experience. For example:
- Underwater Sounds: If you’re scuba diving or snorkeling in Vietnam’s beautiful coastal waters, remember that sound travels differently underwater than in air. Sounds may seem louder and travel faster.
- Soundproofing: Hotels use soundproofing materials to minimize the transmission of sound waves, ensuring a peaceful stay. SIXT.VN can help you find accommodations that prioritize your comfort.
- Communication: When exploring bustling cities like Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City, remember that sound travels less efficiently through crowded spaces. This can affect communication, especially in noisy environments.
2. Delving into the Characteristics of Sound Waves
Sound waves, a prime example of mechanical waves, exhibit fascinating characteristics. Understanding these properties is crucial to comprehending how sound behaves and how it interacts with its environment.
2.1. Longitudinal Waves
Sound waves are longitudinal waves, which means that the particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of energy transfer. Imagine pushing a slinky – the compression and rarefaction move along the slinky in the same direction as your push.
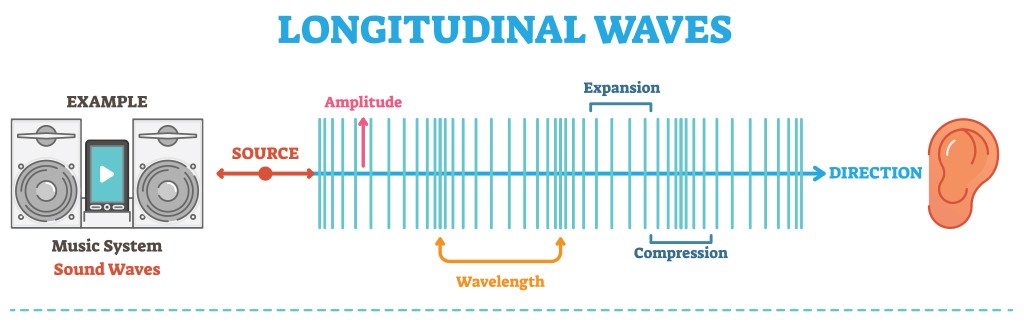 Longitudinal Waves
Longitudinal Waves
2.2. Compression and Rarefaction
As a sound wave travels, it creates areas of compression (where particles are close together) and rarefaction (where particles are spread apart). These alternating regions of high and low pressure propagate through the medium.
2.3. Frequency and Pitch
The frequency of a sound wave, measured in Hertz (Hz), determines its pitch. High-frequency waves correspond to high-pitched sounds, while low-frequency waves correspond to low-pitched sounds. The human ear can typically hear frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz.
2.4. Amplitude and Loudness
The amplitude of a sound wave determines its loudness, which is measured in decibels (dB). A larger amplitude means a louder sound. However, human perception of loudness is also influenced by frequency, as our ears are more sensitive to certain frequencies than others.
2.5. Wavelength
The wavelength of a sound wave is the distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions. It is inversely proportional to frequency: the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength.
2.6. Speed of Sound
The speed of sound depends on the medium through which it travels. It is generally faster in solids than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in gases. It also depends on the temperature and density of the medium. In dry air at 20°C, the speed of sound is approximately 343 meters per second.
2.7. How Can This Information Enhance Your Vietnamese Journey?
- Understanding Vietnamese Music: Vietnamese traditional music often features unique instruments with distinct frequencies and timbres. Understanding the properties of sound can enhance your appreciation of these musical forms.
- Navigating Noisy Environments: Cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City can be quite noisy. Knowing how sound travels can help you find quieter spots or use noise-canceling headphones effectively.
- Appreciating Natural Sounds: From the crashing waves on Nha Trang beach to the sounds of the rainforest in Cuc Phuong National Park, understanding the physics of sound can deepen your connection with nature.
3. Exploring Different Types of Sound Waves
Sound waves aren’t all created equal. They can be categorized based on their frequency relative to the human hearing range.
3.1. Audible Sound Waves
These are the sound waves that humans can hear, with frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz. This range is crucial for communication, music, and our overall perception of the world.
3.2. Infrasonic Waves (Infrasound)
Infrasonic waves have frequencies below 20 Hz, making them inaudible to humans. However, some animals, like elephants, use infrasound to communicate over long distances. Scientists also use infrasound to study earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
3.3. Ultrasonic Waves (Ultrasound)
Ultrasonic waves have frequencies above 20,000 Hz, also beyond human hearing. Bats use ultrasound for echolocation, and medical professionals use it for sonograms. Ultrasound also has industrial applications, such as cleaning and welding.
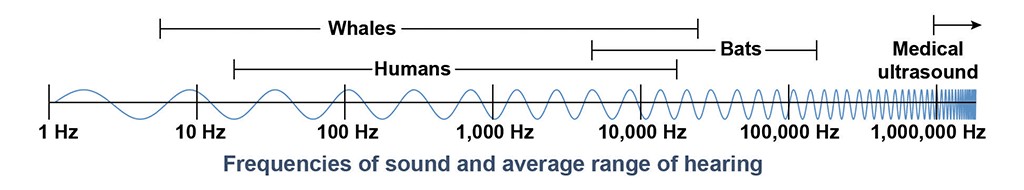 Frequencies of sound and average range of hearing
Frequencies of sound and average range of hearing
3.4. How Does This Relate to Your Vietnam Trip?
- Animal Encounters: If you’re lucky enough to encounter elephants in Vietnam, remember that they may be communicating using infrasound, which you can’t hear.
- Medical Treatments: If you require any medical treatments during your trip, you might encounter ultrasound technology for diagnosis or therapy.
- Technological Applications: Ultrasonic sensors are used in various technologies, such as parking sensors in cars, which you might encounter while using transportation services in Vietnam.
4. Mediums and the Speed of Sound
As mentioned earlier, sound requires a medium to travel. But the properties of that medium significantly affect the speed of sound.
4.1. Solids
Sound travels fastest through solids because the molecules are closely packed together, allowing for efficient energy transfer.
4.2. Liquids
Sound travels slower in liquids than in solids but faster than in gases. The speed of sound in water is about four times faster than in air.
4.3. Gases
Sound travels slowest in gases because the molecules are more spread out. The speed of sound in air depends on temperature, with warmer air allowing for faster sound transmission.
4.4. Density and Temperature
In general, sound travels faster in denser and warmer mediums. This is because denser mediums have more molecules to transmit the sound waves, and warmer mediums have molecules that vibrate more readily.
4.5. Practical Takeaways for Your Vietnam Trip:
- Coastal Sounds: When visiting Vietnam’s beaches, you’ll notice that sound travels differently over the water than over the land. This is because of the differences in density and temperature between the air and the water.
- Mountainous Regions: In mountainous regions, the air is thinner and cooler, which can affect the speed and clarity of sound transmission.
- Architectural Acoustics: The materials used in buildings can affect the way sound travels within them. Ancient temples in Vietnam often have unique acoustic properties due to their construction materials.
5. The Human Ear and Sound Perception
Our ears are remarkable organs that allow us to perceive the world of sound. Understanding how they work can deepen our appreciation for the complexities of sound.
5.1. The Outer Ear
The outer ear, or pinna, collects sound waves and funnels them into the ear canal.
5.2. The Middle Ear
The middle ear contains the eardrum, which vibrates in response to sound waves. These vibrations are amplified by three tiny bones (the malleus, incus, and stapes) and transmitted to the inner ear.
5.3. The Inner Ear
The inner ear contains the cochlea, a fluid-filled structure that contains hair cells. These hair cells convert the vibrations into electrical signals, which are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.
5.4. Brain Interpretation
The brain interprets these electrical signals as sound, allowing us to perceive pitch, loudness, and timbre.
5.5. How to Protect Your Hearing During Your Travels in Vietnam:
- Loud Music: Be mindful of loud music at concerts or clubs. Use earplugs if necessary.
- Traffic Noise: Cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City have heavy traffic. Consider using noise-canceling headphones to protect your hearing.
- Respectful Listening: Be mindful of noise levels in quiet areas, such as temples and pagodas.
6. Applications of Sound Waves
Sound waves are used in a surprising number of applications. Here are a few:
6.1. Medical Imaging
Ultrasound is used in medical imaging to create images of internal organs and tissues. This is a safe and non-invasive way to diagnose a variety of conditions.
6.2. Navigation
Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging) uses sound waves to detect objects underwater. This is used by ships and submarines for navigation and detection.
6.3. Communication
Sound waves are used for communication in a variety of ways, from speech to music to alarms.
6.4. Industrial Applications
Ultrasound is used in industrial applications such as cleaning, welding, and testing materials.
6.5. Entertainment
Sound waves are essential for entertainment, from music to movies to video games.
6.6. Scientific Research
Scientists use sound waves to study a variety of phenomena, from the structure of the Earth to the behavior of animals.
6.7. How Can Understanding Sound Wave Applications Enhance Your Travel Experience?
- Appreciating Technology: Recognizing the use of sound wave technology in various applications, such as medical equipment or transportation systems, can enrich your understanding of modern advancements.
- Enhancing Cultural Experiences: Being aware of how sound is used in cultural performances, religious ceremonies, or traditional practices can deepen your appreciation for the local culture.
- Promoting Responsible Tourism: Understanding the impact of noise pollution on ecosystems and communities can encourage responsible travel practices, such as respecting quiet zones or supporting eco-friendly initiatives.
7. Visiting Vietnam: Let SIXT.VN Be Your Guide
Now that you have a better understanding of sound waves, let’s talk about how SIXT.VN can help you plan your trip to Vietnam.
7.1. Tailored Travel Itineraries
SIXT.VN can create personalized travel itineraries that cater to your interests and preferences. Whether you want to explore the bustling cities, relax on the beaches, or trek through the mountains, we can design the perfect trip for you.
7.2. Airport Transfer Services
Arrive in Vietnam stress-free with SIXT.VN’s reliable airport transfer services. Our professional drivers will greet you at the airport and take you directly to your hotel, ensuring a smooth and comfortable start to your trip.
7.3. Hotel Booking Assistance
SIXT.VN offers a wide range of hotel options to suit every budget and preference. From luxurious resorts to cozy guesthouses, we can help you find the perfect accommodation for your stay in Vietnam.
7.4. Tour and Excursion Bookings
Explore Vietnam’s top attractions with SIXT.VN’s guided tours and excursions. We can arrange visits to historical sites, cultural landmarks, natural wonders, and more, ensuring an enriching and unforgettable experience.
7.5. Flight Booking Services
SIXT.VN can help you find the best deals on flights to and from Vietnam. We work with a network of airlines to offer you a variety of options at competitive prices.
7.6. 24/7 Support
SIXT.VN provides 24/7 support to assist you with any questions or concerns you may have during your trip. Our dedicated team is always available to help you make the most of your Vietnamese adventure.
8. Soundscapes of Vietnam: A Traveler’s Perspective
Vietnam offers a rich tapestry of sounds, from the bustling streets of Hanoi to the tranquil rice paddies of Sapa. Here are some unique soundscapes you might encounter:
8.1. The Rhythms of Hanoi’s Old Quarter
The Old Quarter of Hanoi is a symphony of sounds, from the honking of motorbikes to the chatter of vendors to the clanging of pots and pans.
8.2. The Melodies of Hue’s Imperial City
The Imperial City of Hue is filled with the sounds of traditional music, from the gentle melodies of the dan tranh (zither) to the powerful drums of the royal court.
8.3. The Waves Crashing on Nha Trang Beach
Nha Trang Beach is a haven of relaxation, with the soothing sound of waves crashing on the shore providing the perfect backdrop for a peaceful getaway.
8.4. The Sounds of the Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta is a world of waterways, where the sounds of boats, birds, and bustling markets create a unique and vibrant atmosphere.
8.5. The Echoes of Phong Nha Caves
The caves of Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park are filled with the echoes of dripping water and the calls of bats, creating a mysterious and awe-inspiring experience.
8.6. Immersing Yourself in the Vietnamese Soundscape:
- Engage with Locals: Strike up conversations with locals and learn about the sounds that are meaningful to them.
- Explore Different Environments: Venture beyond the tourist hotspots and discover the diverse soundscapes of rural villages, mountain retreats, and coastal communities.
- Attend Cultural Events: Immerse yourself in traditional music performances, religious ceremonies, or local festivals to experience the authentic sounds of Vietnamese culture.
9. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Sound
Let’s clarify some common misconceptions about sound.
9.1. Sound Travels Faster in Space
This is false. Sound cannot travel in the vacuum of space because it needs a medium to propagate.
9.2. Loudness is the Same as Intensity
While related, loudness is a subjective perception, while intensity is an objective measure of sound wave power.
9.3. Sound is Always Annoying
Not true! Music, nature sounds, and even some human-made sounds can be pleasant and relaxing.
9.4. Debunking Sound Myths to Enhance Your Understanding:
- Myth: Sound travels in straight lines.
- Fact: Sound waves can bend around obstacles and spread out as they travel, especially in enclosed spaces or through complex environments.
- Myth: All sounds are equally audible to everyone.
- Fact: Individual differences in hearing sensitivity, age, and exposure to loud noises can affect how people perceive sounds.
- Myth: Soundproofing eliminates all sound.
- Fact: Soundproofing materials reduce the transmission of sound waves but cannot completely eliminate all sound.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Sound
10.1. What is the difference between sound and noise?
Sound is a general term for any vibration that travels through a medium and is perceived by the ear. Noise is unwanted or unpleasant sound.
10.2. How does temperature affect the speed of sound?
The speed of sound increases with temperature.
10.3. Can sound travel through a vacuum?
No, sound requires a medium to travel.
10.4. What is the range of human hearing?
The typical range of human hearing is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
10.5. What is the unit of measurement for loudness?
Loudness is measured in decibels (dB).
10.6. What is infrasound and ultrasound?
Infrasound is sound with a frequency below 20 Hz, and ultrasound is sound with a frequency above 20,000 Hz.
10.7. How do noise-canceling headphones work?
Noise-canceling headphones use microphones to detect ambient noise and then create sound waves that are the inverse of the noise, effectively canceling it out.
10.8. What is the Doppler effect?
The Doppler effect is the change in frequency of a sound wave due to the motion of the source or the observer.
10.9. What are the different types of sound waves?
Sound waves can be longitudinal, transverse (under specific circumstances), or surface waves.
10.10. How can I protect my hearing?
Avoid exposure to loud noises, use earplugs or noise-canceling headphones in noisy environments, and get regular hearing checkups.
Conclusion: Listen to the Wonders of Vietnam with SIXT.VN
While mechanical waves can’t travel through empty space, you can travel to Vietnam with SIXT.VN and experience the rich and vibrant sounds of this amazing country. From the bustling cities to the serene countryside, Vietnam offers a unique soundscape that will captivate your senses. Contact SIXT.VN today to start planning your unforgettable Vietnamese adventure! Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. Website: SIXT.VN. Let the sounds of Vietnam fill your memories!



