Are you curious about the potential dangers of traveling with a bullet lodged in your body after an accident in Vietnam? At SIXT.VN, we understand your concerns and offer expert advice on this critical health issue, alongside comprehensive travel assistance for a safe and worry-free experience in Vietnam.
1. What Happens If A Bullet Stays In Your Body?
Yes, a bullet can stay in your body, but whether it should is a complex question. Typically, a bullet remains in the body if removing it poses a greater risk than leaving it in place.
Leaving a bullet in your body can lead to a host of complications. These can include:
- Infection: Bullets aren’t sterile. Introducing a foreign object into the body can cause an infection.
- Lead Poisoning: If the bullet is made of lead, the lead can leach into the body over time, causing lead poisoning.
- Nerve Damage: A bullet near a nerve can cause pain, numbness, or even paralysis.
- Vascular Damage: A bullet near a blood vessel can cause bleeding or blood clots.
- Migration: In rare cases, a bullet can move around inside the body, potentially causing damage to other organs or tissues.
2. Can A Bullet Move Around Inside You?
Yes, bullets can move around inside the body, although it’s rare. This phenomenon, known as bullet migration, occurs when a bullet shifts from its initial location to another part of the body. According to a case study published in the Journal of Medical Case Reports, spontaneous migration of a bullet can occur, potentially leading to neurovascular damage.
Several factors can contribute to bullet migration:
- Muscle Movement: The natural movement of muscles can dislodge a bullet and cause it to shift.
- Blood Flow: Bullets can sometimes enter the bloodstream and travel to distant parts of the body.
- Gravity: Depending on the location of the bullet, gravity can also play a role in its migration.
Bullet migration can lead to a range of complications, including pain, nerve damage, and damage to vital organs.
3. How Far Can A Bullet Travel In The Body?
The distance a bullet can travel in the body varies widely depending on several factors, including the bullet’s size and shape, the angle of entry, and the tissues and organs it encounters. There have been recorded cases of bullets traveling considerable distances, even moving from the extremities to the heart or lungs.
According to a study in the European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery, bullets can migrate along various routes, including intermuscular spaces and blood vessels. In some instances, bullets have been known to travel against the flow of blood, although this is exceedingly rare.
If you’re planning a trip to Vietnam and have concerns about a bullet lodged in your body, SIXT.VN can provide valuable assistance. We offer services such as:
- Medical Travel Insurance: Coverage for medical emergencies, including those related to bullet migration.
- Assistance Finding Medical Care: We can help you locate qualified medical professionals in Vietnam who can assess your condition and provide appropriate treatment.
- Translation Services: Overcome language barriers and communicate effectively with healthcare providers.
4. What Are The Symptoms Of A Migrating Bullet?
The symptoms of a migrating bullet can vary depending on the location of the bullet and the tissues or organs it is affecting. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain: This is often the most common symptom. The pain may be localized to the area where the bullet is located, or it may radiate to other parts of the body.
- Numbness or Tingling: If the bullet is pressing on a nerve, it can cause numbness or tingling in the affected area.
- Weakness: In some cases, a migrating bullet can cause weakness in the muscles of the affected limb.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Function: If the bullet is located in the abdomen, it can cause changes in bowel or bladder function.
- Shortness of Breath: If the bullet migrates to the chest, it can cause shortness of breath.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. A doctor can perform imaging tests to determine the location of the bullet and whether it is migrating.
5. What Happens If A Bullet Is Lodged Near A Nerve?
If a bullet is lodged near a nerve, it can cause a variety of symptoms, depending on the size and location of the bullet, as well as the specific nerve affected.
- Pain: The most common symptom is pain, which can range from mild to severe. The pain may be constant or intermittent, and it may be aggravated by movement or pressure.
- Numbness or Tingling: The bullet can also compress the nerve, causing numbness or tingling in the area that the nerve supplies.
- Weakness: In some cases, the bullet can damage the nerve, leading to weakness or paralysis of the muscles that the nerve controls.
- Muscle Atrophy: Over time, if the nerve is severely damaged, the muscles that it supplies can begin to atrophy or waste away.
6. How Do Doctors Decide To Leave A Bullet In?
Doctors carefully weigh the risks and benefits of removing a bullet before making a decision. Factors that influence this decision include:
- Location of the Bullet: If the bullet is near vital organs, major blood vessels, or nerves, removal may be too risky.
- Depth of the Bullet: Bullets lodged deep within the body may be difficult to remove without causing significant damage.
- Patient’s Overall Health: Patients with underlying health conditions may not be able to tolerate surgery to remove the bullet.
- Symptoms: If the bullet is not causing any symptoms, it may be best to leave it in place.
Leaving a bullet in place is not without risks. Long-term complications can include infection, lead poisoning, and chronic pain.
7. What Are The Risks Of Leaving A Bullet Inside The Body?
Leaving a bullet inside the body can pose several risks, both short-term and long-term. These risks depend on factors such as the bullet’s location, composition, and the individual’s overall health.
Short-Term Risks
- Infection: Bullets can carry bacteria into the body, leading to infections at the entry site or deeper within the tissues.
- Hemorrhage: If the bullet damages blood vessels, it can cause bleeding, which may require immediate medical attention.
- Nerve Damage: Bullets lodged near nerves can cause pain, numbness, tingling, or even paralysis.
- Organ Damage: Depending on the bullet’s trajectory, it can damage vital organs, leading to serious complications.
Long-Term Risks
- Lead Poisoning: Lead bullets can corrode over time, releasing lead into the bloodstream. Lead poisoning can cause a range of symptoms, including abdominal pain, fatigue, headaches, and neurological problems.
- Chronic Pain: Bullets lodged near nerves or joints can cause chronic pain, which can be difficult to manage.
- Arthritis: Bullets lodged in or near joints can cause arthritis, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion.
- Migration: In rare cases, bullets can migrate from their initial location, potentially causing damage to other tissues and organs.
8. How Is Bullet Migration Diagnosed?
Diagnosing bullet migration typically involves a combination of physical examination and imaging techniques.
- Physical Examination: A doctor will perform a thorough physical examination to assess the patient’s symptoms and identify any potential signs of bullet migration, such as pain, numbness, or weakness.
- Imaging Techniques:
- X-rays: X-rays are often the first imaging test used to detect and locate bullets in the body. They can reveal the bullet’s current position and any changes in its location over time.
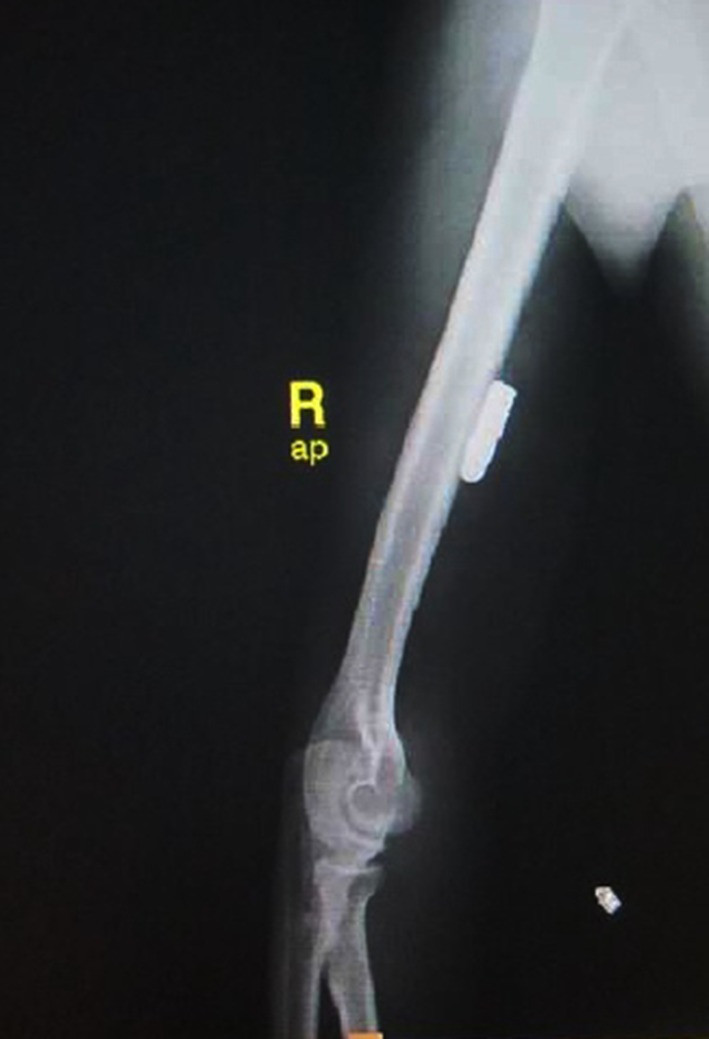 X-rays of the arm taken after the injury showing bullet inside the proximal arm
X-rays of the arm taken after the injury showing bullet inside the proximal arm - Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans provide more detailed images of the body than X-rays. They can help doctors visualize the bullet’s relationship to surrounding tissues and organs.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. It can be particularly useful for visualizing soft tissues, such as nerves and blood vessels, which may be affected by bullet migration.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the body. It can be used to visualize bullets that are located close to the surface of the skin.
- X-rays: X-rays are often the first imaging test used to detect and locate bullets in the body. They can reveal the bullet’s current position and any changes in its location over time.
9. How Is Bullet Migration Treated?
The treatment for bullet migration depends on several factors, including the bullet’s location, size, and the symptoms it is causing. In some cases, no treatment may be necessary. However, in other cases, surgery may be required to remove the bullet.
Non-Surgical Treatment
If the bullet is not causing any symptoms, or if the risks of surgery outweigh the benefits, the doctor may recommend non-surgical treatment. This may include:
- Pain Management: Pain medication may be prescribed to help relieve any pain associated with the bullet migration.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to help improve range of motion and reduce pain.
- Monitoring: The doctor will likely want to monitor the bullet’s location and any symptoms it is causing. This may involve regular X-rays or other imaging tests.
Surgical Treatment
If the bullet is causing significant symptoms, or if there is a risk of serious complications, the doctor may recommend surgery to remove the bullet. The type of surgery will depend on the bullet’s location and size. Some common surgical procedures include:
- Open Surgery: This involves making a large incision to access the bullet.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This involves making several small incisions and using a camera and specialized instruments to remove the bullet.
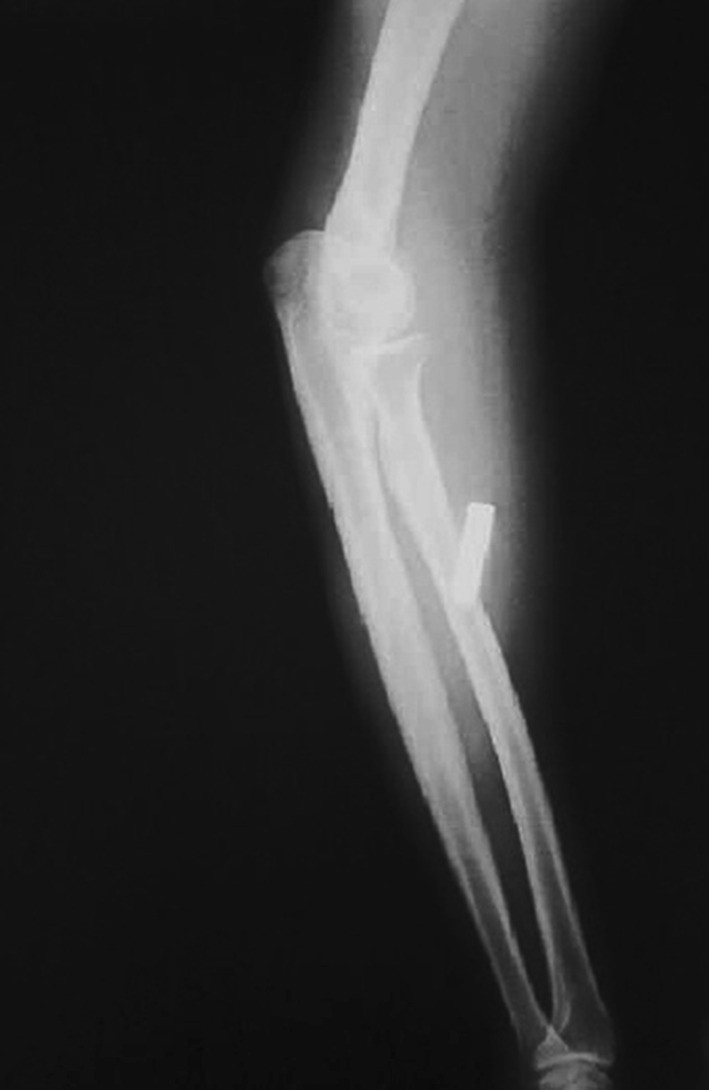 Radiographs taken after 3 months of the injury showing migration of bullet in the proximal forearm
Radiographs taken after 3 months of the injury showing migration of bullet in the proximal forearm - Endovascular Surgery: This involves inserting a catheter into a blood vessel and using it to guide instruments to the bullet.
10. Can Ultrasound Be Used To Remove A Bullet?
Yes, ultrasound can be used to guide the removal of a bullet. This technique, known as ultrasound-guided bullet removal, offers several advantages over traditional open surgery.
How Ultrasound-Guided Bullet Removal Works
- Localization: An ultrasound machine is used to precisely locate the bullet within the body. The ultrasound waves create real-time images of the bullet and surrounding tissues, allowing the surgeon to pinpoint its exact location.
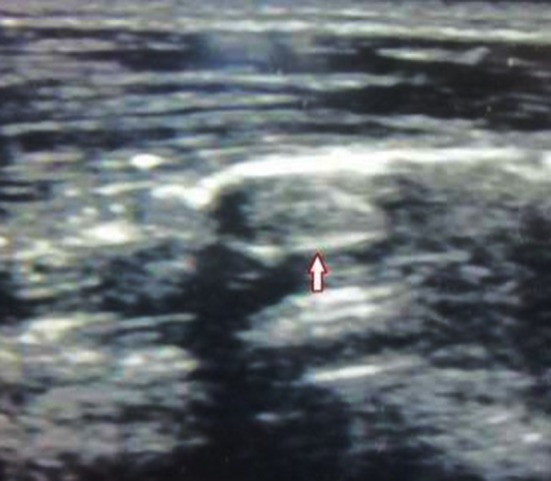 Ultrasonographic localization of the bullet (bullet marked with *arrow*)
Ultrasonographic localization of the bullet (bullet marked with *arrow*) - Minimally Invasive Incision: A small incision is made over the bullet’s location, guided by the ultrasound images.
- Bullet Extraction: Using specialized instruments, the surgeon carefully removes the bullet under continuous ultrasound guidance. This ensures that the bullet is removed safely and efficiently, without damaging surrounding tissues.
Benefits of Ultrasound-Guided Bullet Removal
- Minimally Invasive: This technique requires only a small incision, resulting in less pain, scarring, and recovery time.
- Precise Localization: Ultrasound guidance allows for precise localization of the bullet, minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
- Real-Time Visualization: The surgeon can visualize the bullet and surrounding tissues in real-time, ensuring that the removal process is safe and effective.
- Reduced Risk of Complications: Ultrasound-guided bullet removal is associated with a lower risk of complications compared to traditional open surgery.
Limitations of Ultrasound-Guided Bullet Removal
- Bullet Location: This technique is best suited for bullets that are located close to the surface of the skin.
- Bullet Size: Ultrasound-guided bullet removal may not be appropriate for very large bullets.
- Surgeon Expertise: This technique requires specialized training and expertise.
SIXT.VN: Your Trusted Partner For Safe And Enjoyable Travel In Vietnam
At SIXT.VN, we understand that traveling with health concerns can be stressful. That’s why we offer a range of services to help you plan a safe and enjoyable trip to Vietnam:
- Personalized Travel Itineraries: We can create a customized itinerary that takes into account your specific health needs and preferences.
- Airport Transfer Service: Enjoy seamless transportation from the airport to your hotel with our reliable airport transfer service.
- Hotel Booking: We offer a wide selection of hotels to suit your budget and needs.
- Tours in Ha Noi: Explore the best of Hanoi with our expert-guided tours.
- Flight Booking: We can help you find the best flights to Vietnam at competitive prices.
Contact us today at +84 986 244 358 or visit our website at SIXT.VN to learn more about our services and start planning your dream trip to Vietnam. Our address is 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.



