Are you curious about the environmental and health impact of agricultural chemicals? Discover the truth with SIXT.VN and explore sustainable tourism in Vietnam. We will address your questions directly, providing insights and solutions to promote responsible travel.
Agricultural chemicals, while boosting crop production, significantly impact both the environment and human health. SIXT.VN offers eco-friendly travel options in Vietnam, ensuring your journey supports sustainable practices and minimizes environmental harm. Explore Vietnam responsibly with us and discover the beauty of local communities while supporting their well-being through eco-friendly initiatives.
1. What Are Agricultural Chemicals and Why Are They Used?
Agricultural chemicals, also known as agrochemicals, are substances used in agriculture to enhance crop production. They include pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, and growth regulators. These chemicals are crucial for increasing yields, controlling pests, and improving the quality of crops. However, their widespread use raises serious concerns about their impact on the environment and human health.
1.1. Types of Agricultural Chemicals
- Pesticides: Used to control insects, fungi, and other pests that damage crops.
- Herbicides: Used to control weeds that compete with crops for nutrients and sunlight.
- Fertilizers: Used to provide essential nutrients to plants, promoting growth and productivity.
- Growth Regulators: Used to modify plant growth and development, affecting flowering, fruiting, and ripening.
1.2. Benefits of Using Agricultural Chemicals
According to a report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) in 2020, the use of agricultural chemicals has contributed to a significant increase in global food production, ensuring food security for a growing population. These chemicals help protect crops from pests and diseases, reduce crop losses, and improve overall agricultural productivity.
 Pesticide Sprayers Working in a Lush Green Paddy Field
Pesticide Sprayers Working in a Lush Green Paddy Field
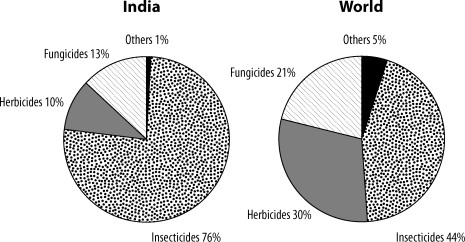
Agricultural Chemical Consumption Patterns
2. What Are the Environmental Impacts of Agricultural Chemicals?
The use of agricultural chemicals has far-reaching effects on the environment, including soil degradation, water contamination, and biodiversity loss. These impacts can disrupt ecosystems and pose long-term threats to environmental sustainability.
2.1. Soil Contamination
Pesticides and fertilizers can accumulate in the soil, altering its chemical composition and affecting soil microorganisms. This contamination can lead to reduced soil fertility and the disruption of natural nutrient cycles, impacting the long-term health of agricultural lands. According to a study published in the “Journal of Environmental Quality” in 2018, excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to soil acidification and the release of greenhouse gases.
2.2. Water Contamination
Agricultural runoff containing pesticides and fertilizers can contaminate surface and groundwater sources. This contamination poses risks to aquatic ecosystems and can affect the quality of drinking water. A report by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 2019 highlighted that agricultural runoff is a major source of nutrient pollution in rivers and lakes, leading to eutrophication and harming aquatic life.
2.3. Biodiversity Loss
Pesticides can harm non-target species, including beneficial insects, birds, and other wildlife. This loss of biodiversity can disrupt ecosystems and reduce their resilience to environmental changes. A study in “Biological Conservation” in 2020 found that neonicotinoid pesticides have been linked to declines in bee populations, which are crucial for pollination.
Table: Environmental Impacts of Agricultural Chemicals
| Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Soil Contamination | Accumulation of chemicals in the soil, reducing fertility and disrupting nutrient cycles. |
| Water Contamination | Runoff pollutes surface and groundwater, harming aquatic ecosystems and affecting drinking water quality. |
| Biodiversity Loss | Harm to non-target species, disrupting ecosystems and reducing resilience. |
3. How Do Agricultural Chemicals Affect Human Health?
Exposure to agricultural chemicals can have significant health implications, ranging from acute poisoning to chronic diseases. Certain populations, such as agricultural workers and children, are particularly vulnerable.
3.1. Acute Poisoning
Direct exposure to high concentrations of pesticides can cause acute poisoning, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and in severe cases, death. A report by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2020 estimated that there are around 385 million cases of unintentional pesticide poisoning each year, resulting in approximately 11,000 deaths.
3.2. Chronic Diseases
Long-term exposure to low levels of agricultural chemicals has been linked to chronic diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and reproductive problems. A study published in “Environmental Health Perspectives” in 2017 found associations between pesticide exposure and increased risk of certain cancers.
3.3. Vulnerable Populations
Agricultural workers, who handle pesticides directly, are at higher risk of exposure and related health effects. Children are also more vulnerable due to their developing bodies and higher exposure rates. A report by the EPA in 2021 emphasized the need for stricter regulations to protect these vulnerable populations.
4. What Are the Specific Health Risks Associated with Different Agricultural Chemicals?
Different agricultural chemicals pose unique health risks, depending on their toxicity and exposure pathways. Understanding these risks is crucial for implementing effective safety measures.
4.1. Organophosphates
Organophosphates are insecticides that can affect the nervous system, causing symptoms such as muscle weakness, confusion, and respiratory failure. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), exposure to organophosphates can inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme essential for nerve function.
4.2. Carbamates
Carbamates are another class of insecticides that can also affect the nervous system. Similar to organophosphates, they inhibit acetylcholinesterase, leading to neurological symptoms. A study in “Toxicological Sciences” in 2018 found that carbamate exposure can have long-term effects on cognitive function.
4.3. Glyphosate
Glyphosate is a widely used herbicide that has been the subject of much debate regarding its potential health risks. Some studies have linked glyphosate exposure to an increased risk of cancer, while others have not found a definitive association. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) classified glyphosate as “probably carcinogenic to humans” in 2015.
Table: Health Risks of Specific Agricultural Chemicals
| Chemical | Health Risks |
|---|---|
| Organophosphates | Affects nervous system, causing muscle weakness, confusion, respiratory failure. |
| Carbamates | Affects nervous system, leading to neurological symptoms. |
| Glyphosate | Potential link to cancer, subject of ongoing debate. |
5. What Regulations and Policies Are in Place to Manage Agricultural Chemicals?
To mitigate the risks associated with agricultural chemicals, various regulations and policies have been implemented at both national and international levels.
5.1. National Regulations
Many countries have established regulations to control the use of agricultural chemicals, including registration requirements, usage restrictions, and monitoring programs. In the United States, the EPA regulates pesticides under the Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA).
5.2. International Agreements
Several international agreements aim to reduce the risks associated with agricultural chemicals, including the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) and the Rotterdam Convention on Prior Informed Consent. These agreements promote the safe management and disposal of hazardous chemicals.
5.3. Enforcement Challenges
Despite the existence of regulations and policies, enforcement can be challenging, particularly in developing countries with limited resources. Strengthening regulatory frameworks and improving enforcement mechanisms are crucial for protecting the environment and human health.
6. What Sustainable Alternatives Exist to Reduce Reliance on Agricultural Chemicals?
Reducing reliance on agricultural chemicals is essential for promoting sustainable agriculture and protecting the environment and human health. Various alternative approaches can be adopted, including organic farming, integrated pest management, and precision agriculture.
6.1. Organic Farming
Organic farming relies on natural methods to enhance soil fertility, control pests, and manage weeds. These methods include crop rotation, composting, and the use of biological pest controls. According to the Organic Trade Association, organic farming practices promote biodiversity, conserve water, and reduce pollution.
6.2. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM involves using a combination of strategies to manage pests, including biological controls, cultural practices, and targeted use of pesticides. IPM aims to minimize pesticide use while maintaining effective pest control. A report by the FAO in 2018 highlighted the benefits of IPM in reducing pesticide use and promoting sustainable agriculture.
6.3. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture uses technology to optimize the use of inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides, based on real-time data about soil conditions and crop needs. This approach can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and minimize environmental impacts. A study in “Computers and Electronics in Agriculture” in 2020 found that precision agriculture can significantly reduce fertilizer and pesticide use while maintaining or increasing crop yields.
Table: Sustainable Alternatives to Agricultural Chemicals
| Alternative | Description |
|---|---|
| Organic Farming | Natural methods to enhance soil fertility and control pests. |
| Integrated Pest Management | Combination of strategies to manage pests while minimizing pesticide use. |
| Precision Agriculture | Technology to optimize the use of inputs based on real-time data. |
7. What Is the Role of Consumers in Reducing the Impact of Agricultural Chemicals?
Consumers play a crucial role in reducing the impact of agricultural chemicals by making informed purchasing decisions and supporting sustainable farming practices.
7.1. Buying Organic Products
Choosing organic products supports farmers who use sustainable farming practices and reduces exposure to pesticides and other harmful chemicals. Look for organic certification labels when shopping for food and other agricultural products.
7.2. Supporting Local and Sustainable Farms
Buying from local and sustainable farms helps promote environmentally friendly farming practices and reduces the environmental footprint associated with transportation and distribution. Visit local farmers’ markets and support community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs.
7.3. Reducing Food Waste
Reducing food waste helps minimize the demand for agricultural production, which can reduce the overall use of agricultural chemicals. Plan meals carefully, store food properly, and compost food scraps.
8. How Is Vietnam Addressing the Challenges of Agricultural Chemicals?
Vietnam, like many agricultural countries, faces significant challenges related to the use of agricultural chemicals. The government and various organizations are working to promote sustainable agricultural practices and mitigate the negative impacts of these chemicals.
8.1. Government Initiatives
The Vietnamese government has implemented several initiatives to promote the safe and sustainable use of agricultural chemicals, including regulations on pesticide registration, usage, and monitoring. The Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) has also launched programs to promote organic farming and integrated pest management.
8.2. Community-Based Approaches
Community-based approaches, such as farmer field schools, are being used to educate farmers about sustainable agricultural practices and the risks associated with agricultural chemicals. These programs empower farmers to make informed decisions and adopt environmentally friendly farming methods.
8.3. Challenges and Opportunities
Despite these efforts, challenges remain, including weak enforcement of regulations, limited access to information and resources, and the prevalence of outdated farming practices. However, there are also opportunities for promoting sustainable agriculture and reducing reliance on agricultural chemicals through policy reforms, technological innovations, and increased consumer awareness.
9. What Can Tourists Do to Support Sustainable Agriculture in Vietnam?
As a tourist in Vietnam, you can support sustainable agriculture by making responsible travel choices and supporting local communities that prioritize environmental stewardship.
9.1. Choosing Eco-Friendly Tours and Accommodations
Select tours and accommodations that are committed to sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and supporting local communities. Look for certifications and labels that indicate environmental sustainability. SIXT.VN offers eco-friendly travel options that ensure your journey supports sustainable practices and minimizes environmental harm.
9.2. Visiting Organic Farms and Markets
Visit organic farms and markets to learn about sustainable farming practices and support local farmers who are committed to environmental stewardship. Participate in farm tours and workshops to gain a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing Vietnamese farmers.
9.3. Buying Local and Organic Products
When shopping for food and souvenirs, choose local and organic products to support sustainable agriculture and reduce your environmental footprint. Look for products that are certified organic or that come from local farms that use environmentally friendly farming practices.
10. How Does SIXT.VN Promote Sustainable Tourism in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN is committed to promoting sustainable tourism in Vietnam by offering eco-friendly travel options, supporting local communities, and minimizing environmental impacts.
10.1. Eco-Friendly Travel Options
SIXT.VN offers a range of eco-friendly travel options, including transportation, accommodations, and tours that are designed to minimize environmental impacts. We partner with local businesses that are committed to sustainable practices and support initiatives that promote environmental conservation.
10.2. Supporting Local Communities
SIXT.VN works with local communities to promote sustainable tourism development and ensure that tourism benefits local residents. We support community-based tourism initiatives that empower local communities to manage their resources and preserve their cultural heritage.
10.3. Minimizing Environmental Impacts
SIXT.VN is committed to minimizing the environmental impacts of our operations by reducing waste, conserving water, and promoting responsible energy use. We also support environmental conservation projects that protect Vietnam’s natural resources and biodiversity.
Why choose SIXT.VN for your sustainable travel in Vietnam?
- Eco-Friendly Options: We offer a range of eco-friendly travel choices.
- Community Support: We support local communities and their sustainable initiatives.
- Environmental Conservation: We actively minimize our environmental footprint.
FAQ: Agricultural Chemicals and Their Impact
Here are some frequently asked questions about the impact of agricultural chemicals on the environment and health:
-
What are the main types of agricultural chemicals?
Agricultural chemicals include pesticides, herbicides, fertilizers, and growth regulators. These substances are used to enhance crop production and protect crops from pests and diseases.
-
How do agricultural chemicals contaminate water sources?
Agricultural runoff containing pesticides and fertilizers can contaminate surface and groundwater sources. This contamination poses risks to aquatic ecosystems and can affect the quality of drinking water.
-
What are the acute health effects of pesticide exposure?
Direct exposure to high concentrations of pesticides can cause acute poisoning, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and in severe cases, death.
-
Can long-term exposure to agricultural chemicals cause chronic diseases?
Yes, long-term exposure to low levels of agricultural chemicals has been linked to chronic diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, and reproductive problems.
-
What is organic farming, and how does it reduce the use of agricultural chemicals?
Organic farming relies on natural methods to enhance soil fertility, control pests, and manage weeds. These methods include crop rotation, composting, and the use of biological pest controls, reducing the need for synthetic chemicals.
-
What is integrated pest management (IPM)?
IPM involves using a combination of strategies to manage pests, including biological controls, cultural practices, and targeted use of pesticides, aiming to minimize pesticide use while maintaining effective pest control.
-
How can consumers support sustainable agriculture?
Consumers can support sustainable agriculture by buying organic products, supporting local and sustainable farms, and reducing food waste.
-
What are the benefits of precision agriculture?
Precision agriculture uses technology to optimize the use of inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides, based on real-time data about soil conditions and crop needs, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
-
What is Vietnam doing to address the challenges of agricultural chemicals?
Vietnam has implemented initiatives to promote the safe and sustainable use of agricultural chemicals, including regulations on pesticide registration, usage, and monitoring, and programs to promote organic farming and integrated pest management.
-
How can tourists support sustainable agriculture in Vietnam?
Tourists can support sustainable agriculture in Vietnam by choosing eco-friendly tours and accommodations, visiting organic farms and markets, and buying local and organic products.
Ready to explore Vietnam sustainably? Contact SIXT.VN today to book your eco-friendly tour, find accommodations that support local communities, and discover the beauty of responsible travel. Visit SIXT.VN or call +84 986 244 358 for personalized travel plans and support. Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.



