Planning a trip to Vietnam and curious about its rich history? How Close Could Viet Minh Forces Get To The Command Bunker? The proximity varied greatly depending on the location, security measures, and specific time period during the conflict. With SIXT.VN, exploring Vietnam’s historical sites is easy and convenient, offering insights into the strategic landscape of the war. Discover the stories behind Vietnam’s historical events.
1. Understanding the Viet Minh and Their Tactics
To understand how close the Viet Minh forces could get to command bunkers, it’s essential to know who they were and the strategies they employed. The Viet Minh was a Vietnamese national independence coalition formed in 1941.
1.1. Who Were the Viet Minh?
The Viet Minh, short for Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh Hoi (League for the Independence of Vietnam), were primarily focused on achieving Vietnamese independence from French colonial rule. According to historical records, the Viet Minh were adept at guerilla warfare, utilizing the terrain and local support to their advantage (Traas, 2010). Their ranks included farmers, laborers, and intellectuals, united by a strong sense of nationalism.
1.2. Guerilla Warfare: The Viet Minh’s Primary Tactic
The Viet Minh relied heavily on guerilla warfare tactics, which involved small, mobile groups engaging in ambushes, sabotage, and raids. This approach was highly effective against the better-equipped French forces.
According to a study by the Center of Military History, the Viet Minh’s guerilla warfare tactics were instrumental in their success against the French. The element of surprise was key to their operations.
1.3. The Significance of Local Support for the Viet Minh
Local support was crucial for the Viet Minh. They often operated in areas where they had strong ties to the local population, who provided them with food, shelter, and intelligence.
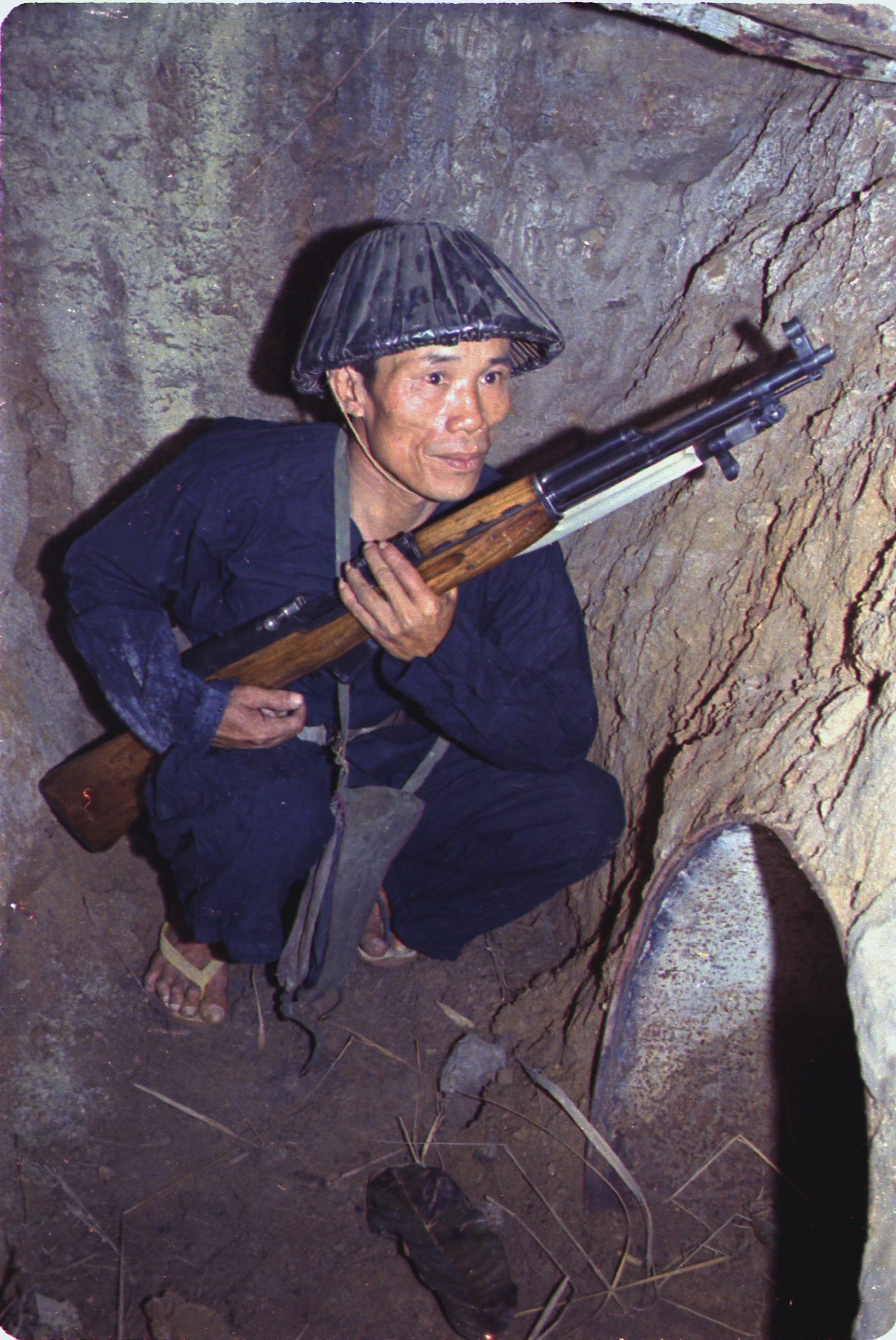 Viet Cong soldier crouched in a tunnel holding a rifle outside the entrance to a smaller tunnel.
Viet Cong soldier crouched in a tunnel holding a rifle outside the entrance to a smaller tunnel.
1.4. Infiltration and Espionage Tactics
The Viet Minh also used infiltration and espionage tactics to gather intelligence and disrupt enemy operations. They had networks of spies who provided valuable information about enemy movements and plans. This network allowed them to stay one step ahead.
1.5. The Viet Minh’s Resourcefulness in Overcoming Obstacles
Resourcefulness was a defining characteristic of the Viet Minh. They often used improvised weapons and tactics, turning everyday items into tools of war.
2. What Was a Command Bunker?
Command bunkers were critical installations for military operations during the Vietnam War, serving as fortified centers for strategic decision-making and communication. These bunkers were designed to protect key personnel and equipment from enemy attacks, ensuring the continuity of command and control even under intense combat conditions. Understanding their construction, purpose, and security levels helps to assess the Viet Minh’s potential to infiltrate or compromise these vital assets.
2.1. The Purpose and Function of Command Bunkers
Command bunkers served as secure locations where military leaders could coordinate operations, analyze intelligence, and issue commands. These bunkers typically housed communication equipment, maps, and other essential resources necessary for managing military campaigns.
2.2. Construction and Design of Command Bunkers
Command bunkers were typically constructed using reinforced concrete and steel, designed to withstand heavy bombardment. They were often located underground or partially buried to provide additional protection.
2.3. Security Measures Surrounding Command Bunkers
Security around command bunkers was typically very tight, with multiple layers of defense to prevent enemy infiltration. This included perimeter fences, guard posts, and patrols. According to military protocols from the era, access to command bunkers was strictly controlled, with personnel required to undergo thorough security checks.
2.4. Vulnerabilities of Command Bunkers
Despite their robust construction and security measures, command bunkers were not invulnerable. Vulnerabilities included:
- Infiltration: The Viet Minh’s ability to infiltrate enemy lines posed a constant threat.
- Sabotage: Enemy agents could potentially sabotage critical systems within the bunker.
- Direct Attack: While bunkers were designed to withstand bombardment, a sustained and concentrated attack could potentially breach their defenses.
2.5. How Command Bunkers Supported Military Strategies
Command bunkers played a critical role in supporting military strategies by providing a secure and reliable platform for command and control. They allowed military leaders to make informed decisions based on the latest intelligence and to effectively coordinate operations across different units and regions.
3. How Close Could Viet Minh Forces Get?
The proximity of Viet Minh forces to command bunkers varied significantly, influenced by factors such as geographical location, the intensity of conflict in the area, and the specific tactics employed by both sides. Historical accounts reveal instances where Viet Minh forces managed to penetrate the outer defenses of command bunkers, while in other cases, they were kept at a considerable distance. Understanding these variations provides insight into the challenges faced by both sides during the war.
3.1. Factors Influencing Proximity to Command Bunkers
Several factors influenced how close the Viet Minh could get to command bunkers:
- Geographical Location: Bunkers located in remote or contested areas were more vulnerable.
- Security Measures: The effectiveness of security measures played a crucial role.
- Intelligence: Accurate intelligence about enemy movements was essential for defense.
3.2. Instances of Viet Minh Forces Breaching Outer Defenses
There were instances where Viet Minh forces managed to breach the outer defenses of command bunkers, often through infiltration or surprise attacks. According to historical accounts, these breaches typically resulted in intense firefights and significant casualties on both sides. In some cases, the Viet Minh were able to inflict damage on the bunkers or capture valuable intelligence.
3.3. Cases Where Viet Minh Forces Were Kept at a Distance
In other cases, the Viet Minh were kept at a distance from command bunkers due to effective security measures and strong defensive positions. These bunkers were often located in well-defended areas with multiple layers of protection.
3.4. Impact of Proximity on Military Operations
The proximity of Viet Minh forces to command bunkers had a significant impact on military operations. When the Viet Minh were able to get close, it disrupted command and control, making it more difficult for military leaders to coordinate operations effectively. This could lead to delays, miscommunications, and ultimately, setbacks on the battlefield.
3.5. How U.S. and Allied Forces Adapted to the Threat
To counter the threat posed by the Viet Minh, U.S. and allied forces adapted their tactics and strategies. This included:
- Strengthening Security: Implementing stricter security measures around command bunkers.
- Improving Intelligence: Enhancing intelligence gathering capabilities.
- Conducting Counter-Insurgency Operations: Launching operations to disrupt Viet Minh activities in the surrounding areas.
4. The Role of Tunnels in Viet Minh Tactics
Tunnels played a crucial role in Viet Minh tactics, providing them with a network of underground pathways for movement, communication, and concealment. These tunnels allowed the Viet Minh to operate undetected, launch surprise attacks, and evade enemy forces. Exploring the structure, function, and strategic importance of these tunnels sheds light on the challenges faced by U.S. and allied forces in countering the Viet Minh’s guerilla warfare tactics.
4.1. Structure and Function of Viet Minh Tunnels
Viet Minh tunnels were often complex networks of interconnected passages, chambers, and bunkers. They served multiple purposes:
- Movement: Allowing troops to move undetected.
- Storage: Providing storage for supplies and weapons.
- Shelter: Offering shelter from enemy attacks.
4.2. How Tunnels Facilitated Infiltration and Surprise Attacks
The tunnels allowed the Viet Minh to infiltrate enemy territory and launch surprise attacks from unexpected locations. This gave them a significant advantage on the battlefield. The Viet Cong tunnels allowed for surprise attacks.
4.3. The Cu Chi Tunnels: A Prime Example
The Cu Chi tunnels are a prime example of the Viet Minh’s tunnel warfare tactics. This vast network of tunnels, located near Saigon, played a crucial role in the Viet Minh’s operations during the war. According to historical accounts, the Cu Chi tunnels were used to house troops, store supplies, and launch attacks against U.S. and allied forces.
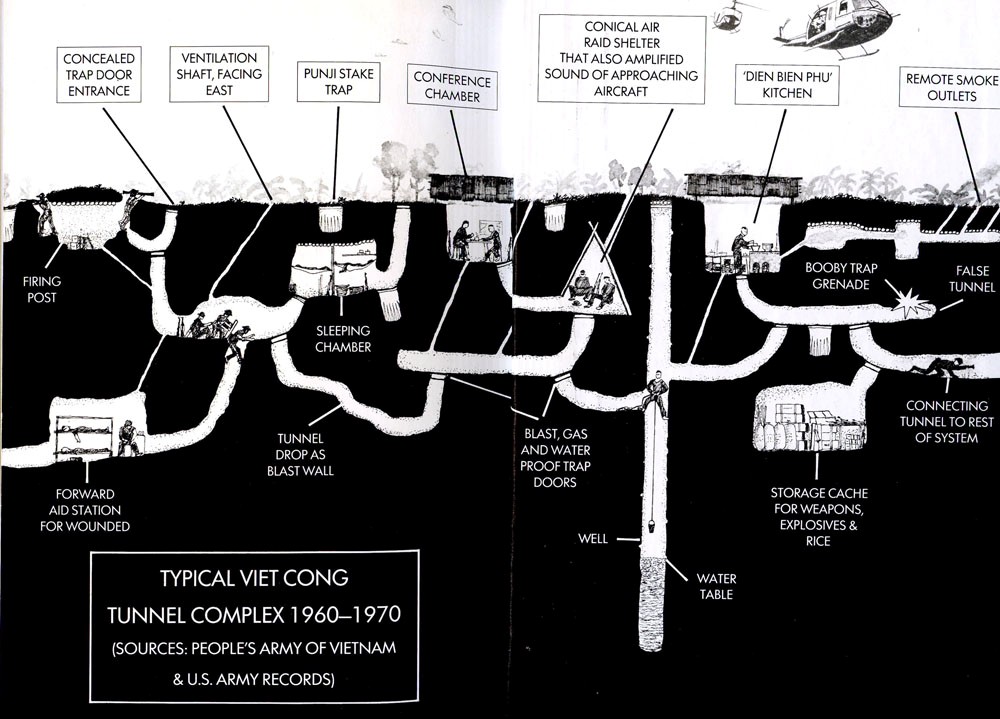 diagram of tunnels showing underground living quarters, aid stations, and storage rooms
diagram of tunnels showing underground living quarters, aid stations, and storage rooms
4.4. Challenges Posed by Tunnels for U.S. and Allied Forces
The tunnels posed significant challenges for U.S. and allied forces. They were difficult to detect, navigate, and clear.
4.5. The “Tunnel Rats”: Specialized Soldiers Tasked with Clearing Tunnels
To counter the threat posed by the tunnels, the U.S. Army created specialized units known as “tunnel rats.” These soldiers were tasked with entering the tunnels to search for enemy troops, supplies, and intelligence.
5. Notable Battles and Events Involving Viet Minh Near Bunkers
Several notable battles and events highlighted the Viet Minh’s ability to get close to command bunkers and other strategic locations. These incidents provide valuable insights into the tactics employed by both sides and the challenges faced by U.S. and allied forces in defending their positions. Examining these specific events helps to illustrate the broader dynamics of the conflict and the strategic importance of command bunkers.
5.1. The Tet Offensive: A Major Turning Point
The Tet Offensive of 1968 was a major turning point in the Vietnam War. During this coordinated series of attacks, Viet Minh forces targeted numerous cities and military installations throughout South Vietnam, including command bunkers. The offensive caught U.S. and allied forces by surprise and demonstrated the Viet Minh’s ability to strike at the heart of enemy territory.
5.2. The Battle of Khe Sanh: A Prolonged Siege
The Battle of Khe Sanh was another significant event in the Vietnam War. During this prolonged siege, Viet Minh forces surrounded a U.S. Marine base in Khe Sanh, subjecting it to intense bombardment and ground attacks. While the Viet Minh did not directly assault the base’s command bunker, their proximity and sustained pressure created a constant threat.
5.3. Other Significant Engagements Near Command Bunkers
There were numerous other significant engagements near command bunkers throughout the Vietnam War. These incidents highlight the ongoing struggle between the Viet Minh and U.S. and allied forces for control of key strategic locations.
5.4. Tactical Innovations and Adaptations During These Battles
These battles led to tactical innovations and adaptations on both sides. U.S. and allied forces developed new strategies for defending their positions and countering Viet Minh tactics. The Viet Minh, in turn, refined their guerilla warfare techniques and tunnel warfare tactics.
5.5. Lessons Learned from These Encounters
These encounters provided valuable lessons about the nature of guerilla warfare, the importance of intelligence, and the need for adaptability in the face of evolving threats. These lessons continue to inform military doctrine and training to this day.
6. The Impact on U.S. Military Strategy
The Viet Minh’s ability to get close to command bunkers and other strategic locations had a significant impact on U.S. military strategy. It forced the U.S. military to adapt its tactics, strengthen its defenses, and invest in new technologies and training programs. Examining these strategic shifts reveals how the Viet Minh’s guerilla warfare tactics influenced the course of the war.
6.1. Changes in Defensive Strategies
The U.S. military implemented several changes in its defensive strategies in response to the Viet Minh threat. This included:
- Strengthening Perimeter Security: Enhancing security measures around military installations.
- Improving Intelligence Gathering: Investing in intelligence gathering capabilities.
- Conducting Counter-Insurgency Operations: Launching operations to disrupt Viet Minh activities.
6.2. Investments in New Technologies and Training Programs
The U.S. military also invested in new technologies and training programs to counter the Viet Minh threat. This included:
- Tunnel Detection Equipment: Developing equipment to detect underground tunnels.
- Specialized Training: Training soldiers in tunnel warfare tactics.
- Advanced Weaponry: Deploying advanced weaponry to counter guerilla warfare tactics.
6.3. The Role of Air Power in Countering Guerilla Warfare
Air power played a crucial role in countering guerilla warfare tactics. The U.S. military used air strikes to target Viet Minh strongholds, disrupt supply lines, and provide support for ground operations.
6.4. The Use of Agent Orange and Its Controversial Legacy
The U.S. military’s use of Agent Orange, a defoliant chemical, remains a controversial aspect of the Vietnam War. While it was intended to clear vegetation and deny the Viet Minh cover, it had devastating effects on the environment and human health.
6.5. Long-Term Strategic Implications of the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War had long-term strategic implications for the United States. It led to a reassessment of U.S. foreign policy and military strategy.
7. Personal Accounts from Soldiers
Personal accounts from soldiers who served in Vietnam provide valuable insights into the challenges and dangers of the war. These stories offer a firsthand perspective on the experiences of those who fought on the front lines and shed light on the human cost of conflict.
7.1. Stories from “Tunnel Rats”
“Tunnel rats” faced unique challenges and dangers as they ventured into the underground world of Viet Minh tunnels. Their stories offer a glimpse into the claustrophobic and perilous conditions they faced. One tunnel rat, Harold Roper, recalled feeling more fear than he had ever felt before or since (Gorner, 1985).
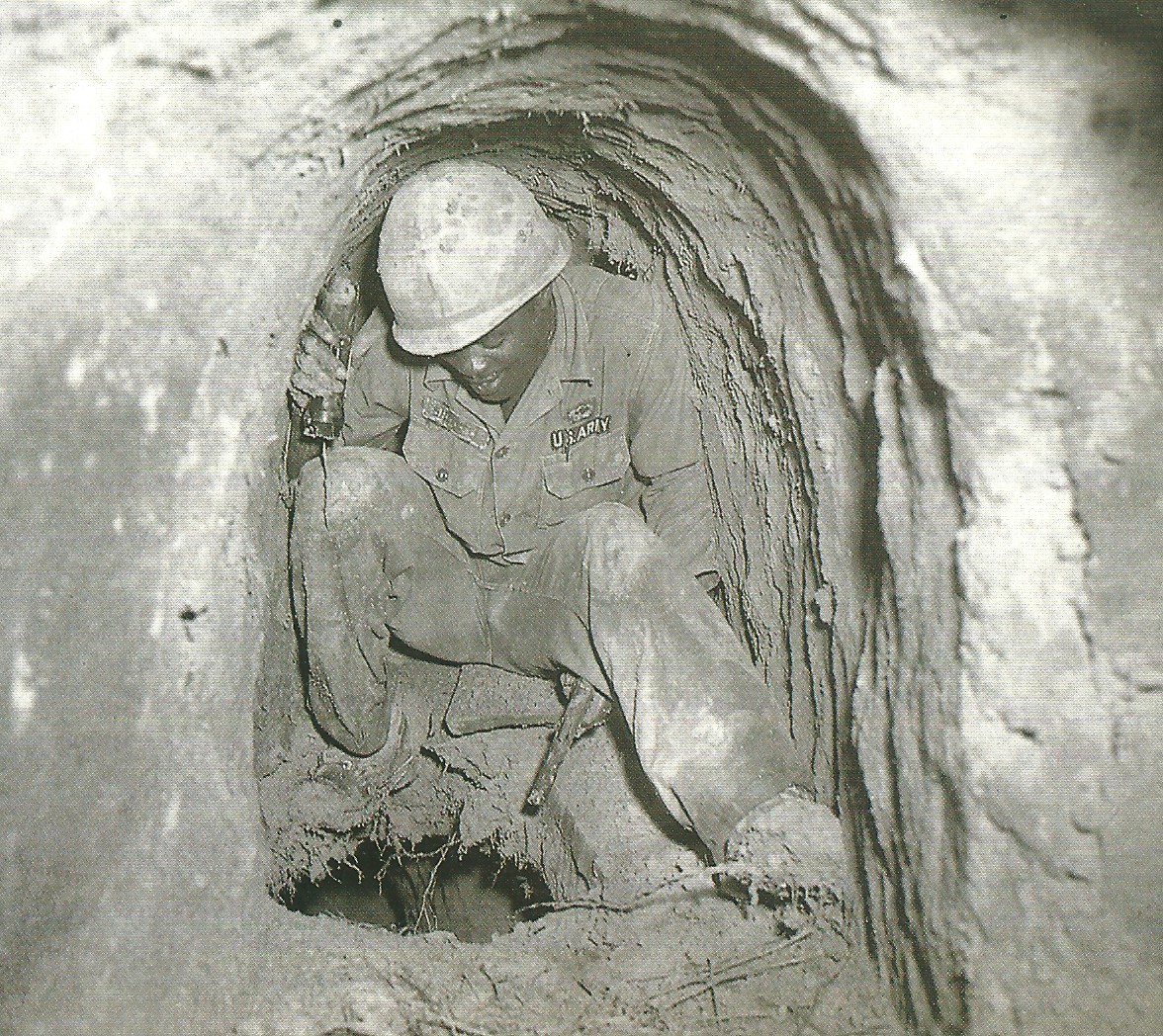 Man in uniform huddled in a tunnel over a hole in the ground holding a flashlight in his left hand and a pistol in his right hand, both pointed at the hole.
Man in uniform huddled in a tunnel over a hole in the ground holding a flashlight in his left hand and a pistol in his right hand, both pointed at the hole.
7.2. Experiences of Soldiers Defending Command Bunkers
Soldiers tasked with defending command bunkers faced a different set of challenges. They had to remain vigilant against enemy attacks while maintaining the security of their positions.
7.3. The Psychological Impact of Constant Threat
The constant threat of attack took a heavy toll on the psychological well-being of soldiers. The stress of combat, the fear of death, and the trauma of witnessing violence left lasting scars on many veterans.
7.4. How Soldiers Adapted and Survived
Despite the challenges they faced, soldiers found ways to adapt and survive. They relied on their training, their camaraderie, and their resilience to overcome adversity.
7.5. The Lasting Legacy of Their Service
The service of these soldiers left a lasting legacy. Their sacrifices helped to shape the course of history.
8. Visiting Historical Sites in Vietnam Today
Today, visitors to Vietnam can explore numerous historical sites that offer insights into the Vietnam War. These sites provide a tangible connection to the past and allow visitors to learn more about the events that shaped the country.
8.1. The Cu Chi Tunnels: A Popular Tourist Destination
The Cu Chi Tunnels are one of the most popular tourist destinations in Vietnam. Visitors can explore the tunnels, learn about their history, and gain a deeper understanding of the Viet Minh’s tunnel warfare tactics. SIXT.VN can arrange guided tours to this location.
8.2. War Remnants Museum in Ho Chi Minh City
The War Remnants Museum in Ho Chi Minh City offers a sobering look at the Vietnam War. The museum features exhibits on the war’s impact on Vietnamese civilians, as well as displays of military equipment and artifacts.
8.3. Other Significant War-Related Sites
Other significant war-related sites in Vietnam include:
- The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone): The former border between North and South Vietnam.
- The Khe Sanh Combat Base: The site of a major battle during the war.
- The My Lai Memorial: A memorial to the victims of the My Lai Massacre.
8.4. Tips for Planning a Historical Tour of Vietnam
Here are some tips for planning a historical tour of Vietnam:
- Research: Research the sites you want to visit and learn about their history.
- Plan: Plan your itinerary carefully, taking into account travel times and the opening hours of the sites.
- Hire a Guide: Consider hiring a local guide who can provide valuable insights and context.
8.5. How SIXT.VN Can Enhance Your Travel Experience
SIXT.VN can enhance your travel experience by providing convenient and reliable transportation services. We offer a range of options to suit your needs, including airport transfers, private car hire, and guided tours.
9. Analyzing the Viet Minh’s Successes and Failures
Analyzing the Viet Minh’s successes and failures provides valuable lessons about the nature of guerilla warfare, the importance of local support, and the challenges of fighting a determined and resourceful enemy. By examining the factors that contributed to their victories and defeats, we can gain a deeper understanding of the Vietnam War.
9.1. Factors Contributing to Viet Minh Successes
Several factors contributed to the Viet Minh’s successes:
- Guerilla Warfare Tactics: Their effective use of guerilla warfare tactics.
- Local Support: The strong support they received from the local population.
- Determination: Their unwavering determination to achieve Vietnamese independence.
9.2. Key Challenges and Setbacks Faced by the Viet Minh
The Viet Minh also faced key challenges and setbacks:
- Superior Firepower: The superior firepower of U.S. and allied forces.
- Internal Divisions: Internal divisions and rivalries within the Viet Minh leadership.
- Losses: Significant losses in key battles and campaigns.
9.3. The Role of International Support in the Viet Minh’s Efforts
International support played a crucial role in the Viet Minh’s efforts. They received aid and assistance from communist countries such as China and the Soviet Union.
9.4. How the Viet Minh Adapted to Changing Circumstances
The Viet Minh demonstrated a remarkable ability to adapt to changing circumstances. They modified their tactics, refined their strategies, and overcame numerous obstacles.
9.5. The Long-Term Impact of the Viet Minh’s Struggle
The Viet Minh’s struggle had a long-term impact on Vietnam and the world. Their victory led to the reunification of Vietnam under communist rule.
10. Modern Perspectives on the Vietnam War
Modern perspectives on the Vietnam War continue to evolve as new information emerges and historical interpretations shift. The war remains a subject of intense debate and scrutiny, with scholars and historians offering diverse perspectives on its causes, consequences, and legacy.
10.1. Evolving Interpretations of the War’s Causes and Consequences
Evolving interpretations of the war’s causes and consequences reflect changing social, political, and cultural contexts. New research and analysis continue to shed light on the complexities of the conflict.
10.2. The War’s Impact on Vietnamese Society and Culture
The Vietnam War had a profound impact on Vietnamese society and culture. It led to widespread destruction, displacement, and loss of life.
10.3. The War’s Influence on American Politics and Culture
The Vietnam War also had a significant influence on American politics and culture. It led to widespread protests, social unrest, and a reassessment of U.S. foreign policy.
10.4. The Role of Media and Propaganda in Shaping Public Opinion
The role of media and propaganda in shaping public opinion about the war remains a subject of debate.
10.5. Commemorating and Remembering the War Today
Today, the Vietnam War is commemorated and remembered in various ways. Memorials, museums, and educational programs help to ensure that the lessons of the war are not forgotten.
FAQ: Viet Minh Forces and Command Bunkers
-
How close could the Viet Minh forces get to command bunkers?
The proximity varied; sometimes they breached outer defenses, other times they were kept at a distance.
-
What tactics did the Viet Minh use to approach command bunkers?
They primarily used guerilla warfare, infiltration, and surprise attacks.
-
What were command bunkers used for during the Vietnam War?
They served as secure locations for military leaders to coordinate operations and issue commands.
-
How were command bunkers constructed to withstand attacks?
They were built with reinforced concrete and steel, often located underground for added protection.
-
What role did tunnels play in the Viet Minh’s strategy?
Tunnels facilitated infiltration, surprise attacks, and provided storage and shelter.
-
Who were the “tunnel rats” and what was their mission?
They were specialized soldiers tasked with entering and clearing Viet Minh tunnels.
-
How did the Tet Offensive impact the security of command bunkers?
It demonstrated the Viet Minh’s ability to strike at the heart of enemy territory, including command bunkers.
-
What were some challenges faced by U.S. and allied forces in defending command bunkers?
Challenges included infiltration, sabotage, and the constant threat of attack.
-
How did the U.S. military adapt its strategies in response to the Viet Minh’s tactics?
They strengthened perimeter security, improved intelligence gathering, and invested in new technologies.
-
Can tourists visit former command bunker sites in Vietnam today?
While direct access to former command bunkers may be limited, many war-related sites like the Cu Chi Tunnels and War Remnants Museum are open to visitors.
Ready to explore Vietnam’s historical sites? Let SIXT.VN take care of your travel needs with our convenient services. Contact us today to plan your unforgettable journey. Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. Visit our Website: SIXT.VN.



