Are you curious about the science behind waves and how they travel? What Type Of Wave Requires A Medium To Travel Through? Mechanical waves need a medium to travel through, and SIXT.VN is here to help you explore the wonders of Vietnam, where you can witness various wave phenomena firsthand. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of wave mechanics, and discover how SIXT.VN can enhance your travel experiences with seamless planning and convenient services. Understanding how waves behave is the key to the physics of wave phenomena.
1. Understanding Wave Types: A Comprehensive Guide
Waves are categorized in several ways, revealing their diverse properties and behaviors. The primary distinctions lie in their mode of propagation and their ability to transmit energy through different media.
1.1. Transverse, Longitudinal, and Surface Waves
The direction of particle movement relative to the wave’s direction of travel distinguishes these three types of waves.
- Transverse Waves: In transverse waves, particles move perpendicular to the wave’s direction. A classic example is a wave on a string, where the string moves up and down while the wave travels horizontally.
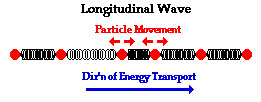
- Longitudinal Waves: Also known as compressional waves, longitudinal waves involve particles moving parallel to the wave’s direction. Sound waves are a prime example, with air particles compressing and expanding in the same direction as the sound travels.
- Surface Waves: These waves exhibit a combination of transverse and longitudinal motions. Particles at the surface move in a circular path. Water waves are a common example, displaying both up-and-down and back-and-forth motion.
 Transverse Wave
Transverse Wave
1.2. Electromagnetic vs. Mechanical Waves
Another critical distinction is whether a wave requires a medium to travel through.
- Electromagnetic Waves: These waves can transmit energy through a vacuum, like the vastness of space. Light, radio waves, and X-rays are all examples of electromagnetic waves, generated by the vibration of charged particles.
- Mechanical Waves: These waves require a medium, such as air, water, or a solid, to transport energy. Sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves are all mechanical waves.
2. What are Mechanical Waves and Why Do They Need a Medium?
Mechanical waves are disturbances that propagate through a medium due to the interaction of its particles. The medium’s particles vibrate and transfer energy to neighboring particles, allowing the wave to travel.
2.1. Definition of Mechanical Waves
A mechanical wave is a type of wave that requires a medium to propagate, meaning it cannot travel through a vacuum. These waves are created by a disturbance or vibration in a medium, which can be a solid, liquid, or gas.
2.2. The Role of a Medium
The medium plays a crucial role in the propagation of mechanical waves. It provides the particles that vibrate and interact with each other to transfer energy. Without a medium, there are no particles to vibrate, and the wave cannot travel.
2.3. Examples of Mechanical Waves
Several types of waves fall under the category of mechanical waves, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
- Sound Waves: Sound waves are perhaps the most familiar type of mechanical wave. They travel through the air by compressing and expanding air molecules, creating areas of high and low pressure.
- Water Waves: Water waves are another common example, formed by disturbances on the surface of the water. These waves can be transverse, longitudinal, or a combination of both, depending on the depth and type of disturbance.
- Seismic Waves: Seismic waves are produced by earthquakes and other geological events. They travel through the Earth’s crust and mantle, providing valuable information about the planet’s internal structure.
- Waves on a String: Waves on a string or rope are often used to demonstrate wave behavior in physics experiments. These waves are typically transverse, with the string moving up and down as the wave travels along its length.
2.4. Why a Medium is Necessary
The necessity of a medium for mechanical waves arises from the fundamental mechanism of energy transfer.
- Particle Interaction: Mechanical waves rely on the interaction between particles in the medium. When one particle is disturbed, it transfers its energy to neighboring particles, which in turn transfer energy to their neighbors, and so on. This chain reaction allows the wave to propagate through the medium.
- Elastic Properties: The medium must possess elastic properties, meaning it can return to its original shape after being deformed. This elasticity is essential for the particles to vibrate and transfer energy efficiently.
- Vacuum Limitation: In a vacuum, there are no particles to vibrate or interact, so mechanical waves cannot propagate. This is why sound cannot travel through space, and why other mechanical waves are limited to traveling through matter.
3. Delving Deeper: Types of Mechanical Waves
Mechanical waves are further classified based on how particles in the medium move relative to the wave’s direction.
3.1. Transverse Mechanical Waves
Transverse mechanical waves are characterized by particle motion perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
- Particle Motion: In a transverse wave, the particles of the medium move up and down or side to side, while the wave itself travels horizontally. This creates a visual pattern of crests and troughs.
- Examples: Waves on a string, such as those created by plucking a guitar string, are classic examples of transverse mechanical waves. The string vibrates up and down, while the wave travels along the string’s length.
- Properties: Transverse waves can exhibit properties such as polarization, where the oscillations are confined to a single plane. This is because the particles are moving in a specific direction perpendicular to the wave’s motion.
3.2. Longitudinal Mechanical Waves
Longitudinal mechanical waves, also known as compressional waves, involve particle motion parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
- Particle Motion: In a longitudinal wave, the particles of the medium move back and forth in the same direction as the wave is traveling. This creates regions of compression (where particles are close together) and rarefaction (where particles are spread apart).
- Examples: Sound waves are the most common example of longitudinal mechanical waves. As a sound wave travels through the air, it compresses and expands the air molecules, creating areas of high and low pressure.
- Properties: Longitudinal waves cannot be polarized because the particle motion is already aligned with the wave’s direction. They are also affected by the medium’s density and elasticity, which determine the speed of the wave.
3.3. Surface Mechanical Waves
Surface mechanical waves occur at the interface between two media, such as water and air.
- Particle Motion: Surface waves exhibit a combination of transverse and longitudinal motion. Particles at the surface move in a circular or elliptical path, with the amplitude of motion decreasing with depth.
- Examples: Water waves are the most familiar type of surface wave. As a water wave travels across the surface, the water particles move in a circular motion, creating the characteristic up-and-down and back-and-forth movement.
- Properties: Surface waves are influenced by factors such as gravity, surface tension, and the depth of the water. They can also exhibit phenomena such as refraction and diffraction, similar to other types of waves.
4. Sound Waves: A Prime Example of Mechanical Waves
Sound waves are the quintessential example of mechanical waves, vividly illustrating their properties and behavior.
4.1. How Sound Waves Travel
Sound waves travel through a medium by compressing and expanding the particles of that medium. This creates a chain reaction, where each particle pushes on its neighboring particle, transferring energy and propagating the wave.
4.2. The Role of Air in Sound Transmission
In the case of sound waves in air, the air molecules act as the medium. When a sound source vibrates, it causes the surrounding air molecules to vibrate as well. These vibrating molecules then collide with other molecules, transferring the energy and creating areas of high and low pressure that travel through the air.
4.3. Sound Cannot Travel in a Vacuum
Because sound waves require a medium to travel, they cannot propagate through a vacuum. In a vacuum, there are no particles to vibrate, so the sound wave cannot transfer energy and cannot be heard. This is why there is no sound in space, as famously depicted in science fiction films.
4.4. Speed of Sound in Different Media
The speed of sound varies depending on the medium through which it travels. Sound travels faster in solids than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in gases. This is because the particles in solids are more tightly packed together, allowing for more efficient energy transfer.
| Medium | Speed of Sound (m/s) |
|---|---|
| Air | 343 |
| Water | 1481 |
| Steel | 5960 |
5. Practical Examples and Applications of Mechanical Waves
Mechanical waves are not just theoretical concepts; they have numerous practical applications in our daily lives.
5.1. Medical Imaging: Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal organs and tissues.
- How it Works: A transducer emits sound waves that travel through the body. When these waves encounter different tissues, they are reflected back to the transducer. By analyzing the reflected waves, a computer can create an image of the internal structures.
- Advantages: Ultrasound is non-invasive, painless, and does not use ionizing radiation, making it safe for pregnant women and children.
- Applications: Ultrasound is used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, including pregnancy monitoring, detecting tumors, and evaluating heart function.
5.2. Geophysics: Seismic Waves and Earthquakes
Seismic waves play a crucial role in understanding the Earth’s structure and monitoring earthquake activity.
- How it Works: Seismographs detect seismic waves generated by earthquakes and other geological events. By analyzing the speed and arrival times of these waves, scientists can determine the location, magnitude, and type of earthquake.
- Applications: Seismic data is used to map the Earth’s internal layers, study plate tectonics, and assess the risk of future earthquakes.
5.3. Music and Musical Instruments
Music relies heavily on sound waves, and musical instruments are designed to produce and manipulate these waves.
- How it Works: Musical instruments create sound waves through various mechanisms, such as vibrating strings (guitars, violins), vibrating air columns (flutes, trumpets), or vibrating membranes (drums).
- Applications: The manipulation of sound waves allows musicians to create different pitches, timbres, and volumes, resulting in a wide range of musical expression.
5.4. Communication: Sonar
Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging) is a technique used to detect objects underwater by emitting sound waves and analyzing the reflected signals.
- How it Works: A sonar device emits sound waves that travel through the water. When these waves encounter an object, they are reflected back to the sonar device. By measuring the time it takes for the waves to return, the distance and location of the object can be determined.
- Applications: Sonar is used in a variety of applications, including submarine detection, fish finding, and underwater mapping.
6. The Importance of Understanding Wave Phenomena
Understanding wave phenomena is crucial for various fields, from technology to natural science.
6.1. Advancements in Technology
A deep understanding of wave behavior has led to significant technological advancements.
- Communication Systems: The development of radio, television, and mobile communication relies on the understanding of electromagnetic waves and their properties.
- Medical Equipment: Medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI utilize different types of waves to create detailed images of the human body.
- Energy Production: Solar panels convert sunlight (electromagnetic waves) into electricity, providing a clean and renewable energy source.
6.2. Understanding Natural Phenomena
Wave phenomena play a critical role in understanding various natural processes.
- Earthquakes and Tsunamis: Studying seismic waves helps scientists understand the Earth’s structure and predict the occurrence of earthquakes and tsunamis.
- Weather Patterns: Understanding how electromagnetic waves interact with the atmosphere is essential for predicting weather patterns and climate change.
- Ocean Currents: Ocean currents are influenced by surface waves, which transport energy and momentum across the ocean.
6.3. Safety and Disaster Preparedness
Knowledge of wave behavior is essential for ensuring safety and preparing for natural disasters.
- Tsunami Warning Systems: Tsunami warning systems rely on the detection of seismic waves and the prediction of tsunami propagation to alert coastal communities.
- Building Design: Engineers must consider the effects of seismic waves on buildings to design structures that can withstand earthquakes.
- Navigation Systems: Navigation systems such as GPS rely on the understanding of radio waves and their behavior to provide accurate location information.
7. SIXT.VN: Your Travel Partner in Exploring Vietnam
Now that you have a better understanding of mechanical waves and their importance, let’s explore how SIXT.VN can enhance your travel experiences in Vietnam.
7.1. Discovering Vietnam’s Natural Wonders
Vietnam boasts a diverse landscape, from stunning beaches to lush mountains, offering ample opportunities to witness wave phenomena firsthand.
- Halong Bay: Explore the mesmerizing Halong Bay, where you can witness the beauty of surface waves as they interact with the iconic limestone karsts.
- Mekong Delta: Cruise through the Mekong Delta, where you can observe the complex interplay of water waves and currents in this vast river system.
- Coastal Cities: Visit coastal cities like Da Nang and Nha Trang, where you can relax on the beach and observe the rhythmic motion of ocean waves.
7.2. SIXT.VN Services for a Seamless Travel Experience
SIXT.VN offers a range of services to make your travel experience in Vietnam smooth and enjoyable.
- Airport Transfer: Start your trip stress-free with SIXT.VN’s reliable airport transfer service. Our professional drivers will pick you up from the airport and take you to your hotel in comfort and style.
- Hotel Booking: Choose from a wide selection of hotels that suits your budget and preferences with SIXT.VN. We offer competitive rates and a hassle-free booking process.
- Sightseeing Tours: Explore Vietnam’s iconic landmarks with SIXT.VN’s sightseeing tours. Our experienced guides will take you on unforgettable journeys to discover the rich culture and history of Vietnam.
- Flight Booking: Book your flights to Vietnam with ease through SIXT.VN. We offer a variety of flight options at competitive prices.
7.3. Why Choose SIXT.VN?
Choosing SIXT.VN as your travel partner offers numerous advantages.
- Convenience: SIXT.VN provides a one-stop platform for all your travel needs, from booking flights and hotels to arranging airport transfers and sightseeing tours.
- Reliability: SIXT.VN partners with reputable service providers to ensure a high level of reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Affordability: SIXT.VN offers competitive rates on all its services, making travel accessible to a wide range of travelers.
- Customer Support: SIXT.VN’s dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any questions or concerns.
8. FAQs About Waves and Travel with SIXT.VN
Here are some frequently asked questions about waves and how SIXT.VN can help you explore Vietnam.
8.1. What is the main difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
Transverse waves have particle motion perpendicular to the wave’s direction, while longitudinal waves have particle motion parallel to the wave’s direction.
8.2. Can sound travel through water?
Yes, sound can travel through water. In fact, sound travels faster in water than in air.
8.3. What are seismic waves?
Seismic waves are waves of energy that travel through the Earth’s crust and mantle, typically caused by earthquakes or other geological events.
8.4. How does SIXT.VN ensure a smooth airport transfer experience?
SIXT.VN provides reliable airport transfer services with professional drivers who are punctual and courteous. We also track your flight to ensure timely pickup, even in case of delays.
8.5. What types of sightseeing tours does SIXT.VN offer in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers a variety of sightseeing tours in Vietnam, including city tours, cultural tours, historical tours, and adventure tours.
8.6. Can I book my entire trip to Vietnam through SIXT.VN?
Yes, SIXT.VN offers a comprehensive platform for booking your entire trip to Vietnam, including flights, hotels, airport transfers, and sightseeing tours.
8.7. What if my flight is delayed? Will SIXT.VN still provide airport transfer?
Yes, SIXT.VN tracks your flight status and adjusts the pickup time accordingly, ensuring that our driver will be there to meet you even if your flight is delayed.
8.8. How can I contact SIXT.VN for assistance during my trip?
You can contact SIXT.VN’s customer support team 24/7 via phone, email, or online chat.
8.9. Are SIXT.VN’s tours customizable?
Yes, SIXT.VN offers customizable tour options to cater to your specific interests and preferences. Contact our customer support team to discuss your requirements.
8.10. What measures does SIXT.VN take to ensure the safety of travelers?
SIXT.VN partners with reputable service providers who adhere to strict safety standards. We also provide travel insurance options for added peace of mind.
9. Conclusion: Explore Vietnam with SIXT.VN
Understanding the science of waves enhances our appreciation of the natural world. With SIXT.VN, exploring Vietnam’s stunning landscapes and cultural treasures becomes a seamless and enriching experience.
9.1. Call to Action
Ready to embark on your Vietnamese adventure? Let SIXT.VN be your trusted travel partner. Book your flights, hotels, airport transfers, and sightseeing tours with us today and discover the beauty of Vietnam with ease and convenience.
- Visit SIXT.VN to explore our travel packages and services.
- Contact our customer support team for personalized assistance.
- Follow us on social media for travel inspiration and exclusive deals.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN



