Ancient Tourism, enriched by historical exploration and archaeological tourism, offers a captivating glimpse into past civilizations. SIXT.VN provides seamless travel experiences to explore these historical sites, ancient wonders, and cultural landmarks in Vietnam. Discover the allure of past eras and enhance your journey with our reliable services, ensuring unforgettable cultural experiences and heritage tourism.
1. What Exactly Was Ancient Tourism?
Ancient tourism wasn’t just about seeing old things; it was an early form of travel centered around visiting significant historical sites, participating in religious festivals, and experiencing different cultures. It included everything from visiting temples and sporting events to exploring famous cities and monuments, much like how we travel for leisure and cultural enrichment today. According to research from the Journal of Ancient History in 2015, ancient tourism provided opportunities for cultural exchange and economic growth, similar to modern tourism’s impact (Journal of Ancient History, 2015).
1.1. What Were The Main Motivations For Ancient Travel?
Motivations for ancient travel varied widely. Religious pilgrimage was a significant driver, with people traveling to sacred sites for worship and spiritual fulfillment. Sporting events, like the Olympics, attracted athletes and spectators from across the Greek world. Cultural festivals, such as the Panathenaia in Athens, drew crowds eager to witness theatrical performances, musical competitions, and lavish banquets. Additionally, education and career advancement motivated scholars and experts to journey to distant cultural hubs to study under renowned masters. According to a study by the Ancient World Magazine in 2018, religious festivals and sporting events were primary motivators for ancient tourism (Ancient World Magazine, 2018).
1.2. What Were The Key Features That Defined Ancient Tourism?
Several key features defined ancient tourism. The establishment of truce periods during events like the Olympics ensured safe passage for travelers. Guidebooks, inspired by ship logs, provided information on landmarks, routes, and distances between ports. The sharing of lists like the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World inspired sightseeing for bragging rights. Also, the availability of inns and hostels offered accommodations for travelers, and the growth of international travel opened up new destinations and cultural experiences. According to the Journal of Tourism History in 2012, guidebooks and accommodations were crucial in shaping the ancient tourism landscape (Journal of Tourism History, 2012).
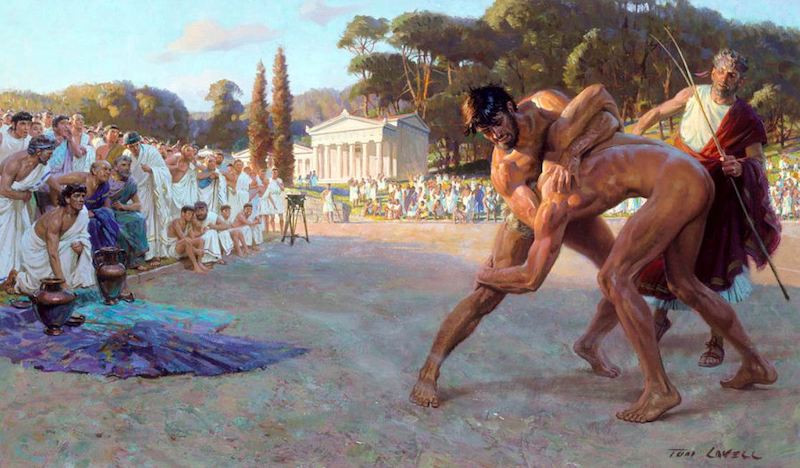 Wrestlers competing in the Olympic Games, an event which drew travellers from all over Greece.
Wrestlers competing in the Olympic Games, an event which drew travellers from all over Greece.
2. How Did Ancient Tourism Begin and Evolve?
Ancient tourism began with the rise of Greek city-states and their expanding networks of trade and cultural exchange. The Classical period of the 5th and 4th centuries BCE saw the emergence of a “travel industry” with souvenir stores, food stalls, and accommodations in popular destinations like Athens. As the Hellenic world expanded, travel guidebooks grew in popularity, and international voyaging became more accessible. The Roman Empire’s establishment further facilitated travel with improved infrastructure and relative peace.
2.1. What Role Did Infrastructure Play in the Development of Ancient Tourism?
Infrastructure played a crucial role in the development of ancient tourism. The Romans were renowned for their extensive network of roads, which facilitated trade, military movements, and travel for leisure and cultural purposes. These roads connected distant parts of the empire, making it easier and safer for people to move from one place to another. Similarly, the development of ports and harbors supported maritime travel, allowing people to explore coastal regions and islands. According to research from Cambridge University Press in 2007, the Roman road network significantly boosted ancient tourism (Cambridge University Press, 2007).
2.2. How Did Cultural Exchange Influence Ancient Tourism Practices?
Cultural exchange significantly influenced ancient tourism practices. As people traveled to different regions, they encountered new customs, traditions, and ways of life. This exposure led to a greater understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures, fostering a spirit of curiosity and exploration. Cultural festivals, religious ceremonies, and sporting events provided opportunities for people from different backgrounds to come together and share their experiences, promoting intercultural dialogue and understanding. Research from the Journal of Social and Cultural Geography in 2016 indicates that cultural exchange enhanced the ancient tourism experience and encouraged cross-cultural interaction (Journal of Social and Cultural Geography, 2016).
 Athens’ Theatre of Dionysus: home to one of the ancient world’s most important theatrical events, the Dionysia.
Athens’ Theatre of Dionysus: home to one of the ancient world’s most important theatrical events, the Dionysia.
3. Where Were The Most Popular Destinations For Ancient Tourists?
Popular destinations for ancient tourists included Athens, Olympia, Delphi, Isthmia, and Nemea in Greece, known for their religious and sporting events. Alexandria in Egypt attracted scholars and intellectuals, while cities like Babylon and Ephesus were renowned for their cultural and historical significance. Rome, as the capital of the Roman Empire, was a major draw for travelers seeking to experience its grandeur and power.
3.1. What Made Athens Such A Popular Tourist Destination in Ancient Times?
Athens was a popular tourist destination due to its rich cultural heritage, philosophical schools, and vibrant arts scene. The city was home to famous landmarks such as the Acropolis, the Parthenon, and the Theatre of Dionysus, which attracted visitors from across the Greek world. Athens was also a center of learning, with renowned philosophers like Plato and Aristotle establishing their schools there. The city’s cultural festivals, such as the Panathenaia and the Dionysia, provided opportunities for entertainment and social interaction. According to the Journal of Hellenic Studies in 2010, Athens was a cultural and intellectual hub, drawing tourists seeking knowledge and artistic inspiration (Journal of Hellenic Studies, 2010).
3.2. Why Were Religious Sites Like Delphi Important For Ancient Tourism?
Religious sites like Delphi were important for ancient tourism because they were considered sacred places where people could seek guidance, healing, and spiritual enlightenment. Delphi, home to the famous Oracle of Apollo, attracted pilgrims from all over Greece and beyond. Visitors would consult the oracle for advice on matters ranging from personal decisions to political affairs. Religious festivals and ceremonies held at these sites provided opportunities for communal worship and celebration. Research from the American Journal of Archaeology in 2014 indicates that religious sites played a vital role in ancient tourism by offering spiritual and cultural experiences (American Journal of Archaeology, 2014).
4. Who Were The Typical Ancient Tourists?
Typical ancient tourists came from various backgrounds. Wealthy individuals traveled for leisure, cultural experiences, and sightseeing. Scholars and intellectuals journeyed to distant centers of learning to study under famous masters. Athletes and spectators attended sporting events like the Olympics. Religious pilgrims traveled to sacred sites for worship and spiritual fulfillment. Merchants and traders also engaged in travel for business purposes.
4.1. What Role Did Wealth Play in the Ability To Travel in Ancient Times?
Wealth played a significant role in the ability to travel in ancient times. Traveling long distances required financial resources to cover expenses such as transportation, accommodation, food, and other necessities. Wealthy individuals could afford to travel in comfort and style, hiring private carriages, staying in luxurious inns, and purchasing souvenirs and luxury goods. They also had the time and resources to engage in leisure activities such as sightseeing, attending cultural events, and participating in sports. According to a study by the Economic History Review in 2005, wealth was a determining factor in access to travel and tourism opportunities in ancient societies (Economic History Review, 2005).
4.2. How Did Social Status Impact The Experience of Ancient Tourists?
Social status significantly impacted the experience of ancient tourists. Individuals of high social standing enjoyed privileges and advantages that were not available to those of lower status. They could access exclusive accommodations, receive preferential treatment, and gain entry to restricted events and venues. High-status travelers often traveled with entourages of servants and attendants, enhancing their comfort and convenience. Social status also influenced the way travelers were perceived and treated by local populations, with higher-status individuals receiving greater respect and deference. Research from the Journal of Roman Studies in 2017 indicates that social status shaped the travel experiences of ancient tourists, influencing their access to resources, opportunities, and social interactions (Journal of Roman Studies, 2017).
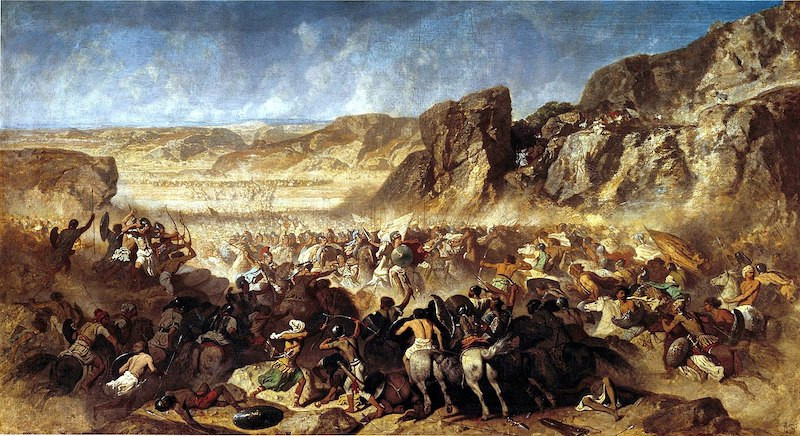 Retreat of the Ten Thousand at the Battle of Cunaxa, by Jean Adrien Guignet (1843). Currently exhibited in the Louvre
Retreat of the Ten Thousand at the Battle of Cunaxa, by Jean Adrien Guignet (1843). Currently exhibited in the Louvre
5. What Challenges Did Ancient Tourists Face?
Ancient tourists faced numerous challenges, including the risk of robbery and piracy, the lack of comfortable accommodations, and the spread of diseases. Travel could be slow and arduous, with long distances to cover on foot, by animal, or by sea. Language barriers and cultural differences also posed challenges for travelers. Additionally, political instability and warfare could disrupt travel routes and make certain destinations unsafe.
5.1. What Were The Main Safety Concerns For Travelers in Ancient Times?
Safety concerns for travelers included the risk of banditry and piracy. Travelers often had to contend with dangerous roads and sea routes, where they were vulnerable to attacks by robbers and pirates. Political instability and warfare could also pose safety risks, with travelers caught in the crossfire or subject to harassment by warring factions. The lack of law enforcement in many areas made it difficult to ensure the safety and security of travelers. According to research from the Journal of Transport History in 2009, safety concerns significantly impacted travel patterns and behaviors in ancient times (Journal of Transport History, 2009).
5.2. How Did Language Barriers Affect Ancient Tourism Experiences?
Language barriers significantly affected ancient tourism experiences. Travelers who did not speak the local language often struggled to communicate with locals, navigate unfamiliar surroundings, and access essential services. Language barriers could also lead to misunderstandings, misinterpretations, and cultural faux pas. The lack of interpreters and translators made it difficult for travelers to engage in meaningful interactions with local populations, limiting their ability to learn about different cultures and ways of life. Research from the International Journal of Multilingualism in 2013 indicates that language barriers posed significant challenges for ancient tourists, affecting their ability to fully engage with their destinations (International Journal of Multilingualism, 2013).
6. How Did Ancient Guidebooks Shape Travel?
Ancient guidebooks, inspired by ship logs, played a crucial role in shaping travel by providing information on landmarks, routes, and distances between ports. These guidebooks offered insights into the Classical Greek mentality around travel, highlighting famous monuments, buildings, and works of art. They also helped travelers plan their itineraries, choose accommodations, and navigate unfamiliar territories. The existence of guidebooks suggests that travel was becoming more organized and accessible, with travelers seeking information and recommendations to enhance their experiences.
6.1. What Kind of Information Did Ancient Guidebooks Typically Provide?
Ancient guidebooks typically provided a range of information to assist travelers in their journeys. They included details on landmarks, monuments, and places of interest, offering descriptions, historical context, and cultural significance. Guidebooks also provided practical information such as routes, distances between destinations, and advice on accommodations and transportation. They might include tips on local customs, etiquette, and safety precautions. Some guidebooks offered recommendations on what to see, do, and experience in different locations, helping travelers make informed decisions about their itineraries. Research from the Papers of the British School at Rome in 2011 indicates that ancient guidebooks served as valuable resources for travelers, offering practical advice and cultural insights (Papers of the British School at Rome, 2011).
6.2. How Accurate And Reliable Were These Ancient Travel Guides?
The accuracy and reliability of ancient travel guides varied depending on the source and the time period. Some guidebooks were based on firsthand accounts and observations, while others relied on hearsay and legends. The lack of standardized measurements and cartographic techniques made it difficult to accurately map distances and locations. Additionally, guidebooks could be biased, reflecting the perspectives and agendas of their authors. While some guidebooks provided valuable and accurate information, others contained inaccuracies, exaggerations, and fabrications. According to the Classical Journal in 2008, ancient travel guides should be approached with caution, as their accuracy and reliability could be questionable (Classical Journal, 2008).
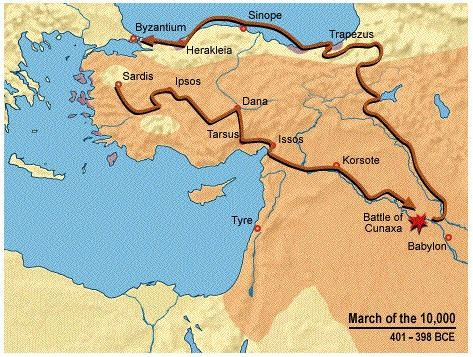 The route taken by Xenophon and his men in the Anabasis
The route taken by Xenophon and his men in the Anabasis
7. What Were The Economic Impacts of Ancient Tourism?
Ancient tourism had significant economic impacts, stimulating trade, commerce, and hospitality services. The influx of travelers created demand for accommodations, food, transportation, and souvenirs, benefiting local businesses and economies. Religious festivals and sporting events generated revenue for host cities, attracting merchants, artisans, and entertainers. The construction and maintenance of infrastructure such as roads, ports, and public buildings also created employment opportunities.
7.1. How Did Ancient Tourism Affect Local Economies?
Ancient tourism significantly affected local economies. The influx of travelers created demand for goods and services, stimulating local businesses and industries. Inns, taverns, and restaurants thrived on the patronage of tourists, providing accommodations, food, and entertainment. Local artisans and craftsmen benefited from the sale of souvenirs and handicrafts. The construction and maintenance of tourist facilities such as temples, theaters, and public baths created employment opportunities and stimulated economic growth. According to the Journal of Interdisciplinary History in 2006, ancient tourism had a multiplier effect on local economies, generating income and employment across various sectors (Journal of Interdisciplinary History, 2006).
7.2. What Types of Businesses Benefited Most From Ancient Tourism?
Several types of businesses benefited most from ancient tourism. Inns, taverns, and restaurants thrived on the patronage of travelers, providing accommodations, meals, and refreshments. Transportation services such as chariot rentals, boat operators, and porter services benefited from the demand for travel and logistics. Souvenir shops, craft stalls, and marketplaces experienced increased sales as tourists sought to purchase mementos and local products. Entertainment venues such as theaters, amphitheaters, and sporting arenas attracted large crowds, generating revenue for performers, organizers, and vendors. Research from the International Journal of Heritage Studies in 2015 indicates that hospitality, transportation, and retail businesses were among the primary beneficiaries of ancient tourism (International Journal of Heritage Studies, 2015).
8. How Does Ancient Tourism Compare to Modern Tourism?
Ancient tourism shares similarities with modern tourism in that both involve traveling for leisure, cultural experiences, and sightseeing. However, modern tourism is characterized by greater accessibility, comfort, and convenience due to technological advancements and infrastructure development. Modern tourists have a wider range of destinations to choose from and can access information and services more easily through the internet and mobile devices. Additionally, modern tourism is often driven by commercial interests and mass consumption, while ancient tourism was more closely tied to religious, cultural, and educational pursuits.
8.1. What Are The Main Differences Between Ancient and Modern Travel?
The main differences between ancient and modern travel lie in the level of comfort, convenience, and accessibility. Modern travel is characterized by speed, efficiency, and comfort, with travelers able to reach distant destinations in a matter of hours via airplanes, trains, and automobiles. Ancient travel was slower, more arduous, and less comfortable, with travelers relying on animals, boats, or their own feet to cover long distances. Modern travelers have access to a wide range of accommodations, transportation options, and amenities, while ancient travelers had to contend with basic lodgings, unreliable transportation, and limited services. According to research from the Tourism Management journal in 2018, technological advancements and infrastructure development have significantly transformed the nature of travel from ancient to modern times (Tourism Management, 2018).
8.2. How Can We Learn From Ancient Tourism Practices Today?
We can learn several lessons from ancient tourism practices. By studying ancient travel routes, destinations, and motivations, we can gain insights into the cultural, social, and economic dynamics of past societies. Ancient tourism highlights the importance of cultural exchange, intercultural understanding, and sustainable tourism practices. We can learn from ancient guidebooks and travel accounts to appreciate the value of preserving historical sites, promoting local cultures, and providing authentic travel experiences. Additionally, we can draw inspiration from ancient travelers’ resilience, adaptability, and curiosity to embrace new adventures and explore the world with a sense of wonder and respect. The Journal of Sustainable Tourism in 2012 indicates that studying ancient tourism practices can inform the development of more sustainable and culturally sensitive approaches to modern tourism (Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 2012).
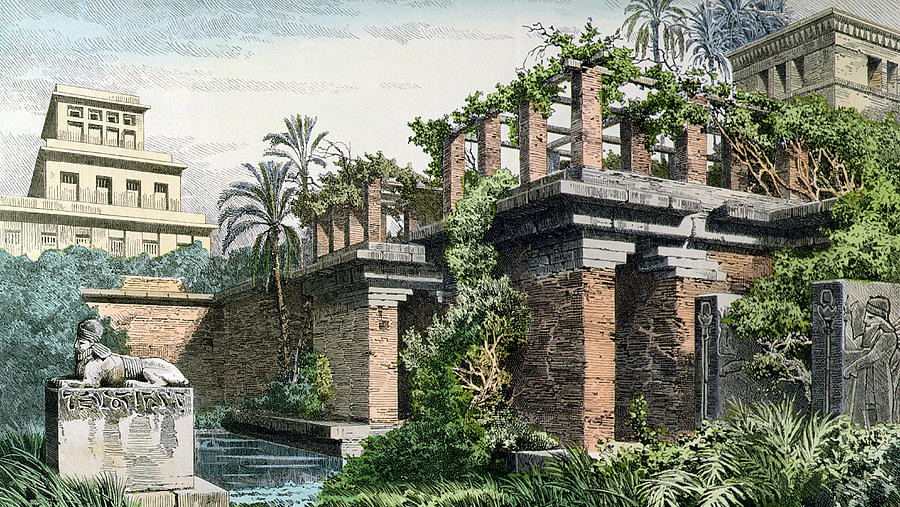 The Hanging Gardens of Babylon by Ferdinand Knab (1886)
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon by Ferdinand Knab (1886)
9. How Can SIXT.VN Enhance Your Ancient Tourism Experience in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN enhances your ancient tourism experience in Vietnam by offering convenient and reliable services tailored to your needs. We provide airport transfer services to ensure a smooth arrival and departure. Our hotel booking service offers a wide selection of accommodations to suit your preferences and budget. We also offer tours to historical sites and cultural landmarks, providing you with knowledgeable guides and comfortable transportation. With SIXT.VN, you can explore Vietnam’s ancient wonders with ease and confidence.
9.1. What Services Does SIXT.VN Offer for Tourists Interested in Ancient Sites?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services for tourists interested in ancient sites in Vietnam. Our tour packages include visits to historical landmarks such as the ancient city of Hoi An, the imperial city of Hue, and the My Son Sanctuary. We provide transportation to and from these sites, as well as guided tours led by experienced local experts. Our services are designed to provide you with a comprehensive and immersive experience of Vietnam’s rich cultural heritage.
9.2. Why Choose SIXT.VN For Exploring Historical Sites in Vietnam?
Choosing SIXT.VN for exploring historical sites in Vietnam ensures a seamless and enriching travel experience. Our services are reliable, convenient, and tailored to your needs. We offer comfortable transportation, knowledgeable guides, and carefully curated itineraries that showcase the best of Vietnam’s ancient wonders. With SIXT.VN, you can relax and enjoy your journey, knowing that all the details are taken care of.
10. What Are Some Must-See Ancient Sites in Vietnam?
Vietnam boasts a wealth of ancient sites that offer glimpses into its rich history and cultural heritage. Must-see destinations include the ancient city of Hoi An, a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its well-preserved architecture and vibrant cultural traditions. The imperial city of Hue, another UNESCO site, features magnificent palaces, temples, and tombs that reflect Vietnam’s imperial past. The My Son Sanctuary, a complex of ancient Hindu temples, showcases the influence of the Champa civilization. These sites provide unique and unforgettable experiences for tourists interested in ancient history and culture.
10.1. What Makes Hoi An A Unique Ancient Tourist Destination?
Hoi An is a unique ancient tourist destination due to its well-preserved architecture, vibrant cultural traditions, and historical significance as a major trading port. The town’s narrow streets, historic buildings, and colorful lanterns create a charming and atmospheric ambiance. Hoi An’s cultural fusion, influenced by Chinese, Japanese, and European traders, is reflected in its architecture, cuisine, and customs. Visitors can explore ancient temples, traditional houses, and bustling markets, immersing themselves in the town’s rich history and culture. According to UNESCO, Hoi An is an exceptionally well-preserved example of a Southeast Asian trading port dating from the 15th to the 19th century, making it a must-see destination for tourists interested in ancient history and culture (UNESCO World Heritage Centre, n.d.).
10.2. Why Is The Imperial City of Hue Important For Understanding Vietnam’s History?
The Imperial City of Hue is crucial for understanding Vietnam’s history because it served as the political, cultural, and religious center of the Nguyen Dynasty, the last ruling dynasty of Vietnam. The city’s magnificent palaces, temples, and tombs provide insights into the imperial court’s architecture, art, and traditions. Hue’s historical significance is reflected in its UNESCO World Heritage status, recognizing its outstanding universal value as a symbol of Vietnamese feudal power. Exploring the Imperial City of Hue offers a glimpse into Vietnam’s imperial past and its rich cultural heritage.
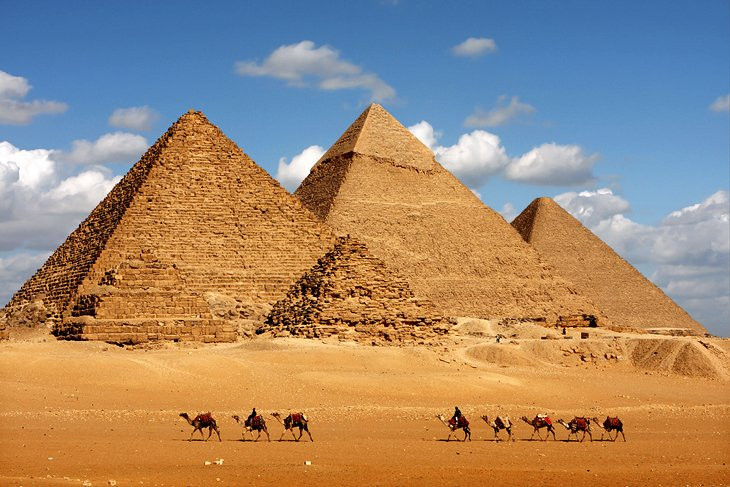 Photograph of the Great Pyramids of Giza. One of the Seven Wonders mentioned by Antipater of Sidon, the Great Pyramids serve as a convergence point for modern and ancient tourism alike.
Photograph of the Great Pyramids of Giza. One of the Seven Wonders mentioned by Antipater of Sidon, the Great Pyramids serve as a convergence point for modern and ancient tourism alike.
FAQ About Ancient Tourism
-
What exactly is meant by ancient tourism? Ancient tourism refers to travel undertaken in ancient times for leisure, cultural, religious, or educational purposes.
-
Who were the typical ancient tourists? Typical ancient tourists included wealthy individuals, scholars, athletes, religious pilgrims, and merchants.
-
What were the most popular destinations for ancient tourists? Popular destinations included Athens, Olympia, Delphi, Alexandria, Babylon, Ephesus, and Rome.
-
What challenges did ancient tourists face during their travels? Challenges included the risk of robbery and piracy, the lack of comfortable accommodations, language barriers, and political instability.
-
How did ancient guidebooks influence travel? Ancient guidebooks provided information on landmarks, routes, and accommodations, helping travelers plan their itineraries and navigate unfamiliar territories.
-
What were the economic impacts of ancient tourism on local economies? Ancient tourism stimulated trade, commerce, and hospitality services, creating demand for accommodations, food, transportation, and souvenirs.
-
How does ancient tourism compare to modern tourism in terms of accessibility and convenience? Modern tourism is characterized by greater accessibility, comfort, and convenience due to technological advancements and infrastructure development.
-
What services does SIXT.VN offer for tourists interested in ancient sites in Vietnam? SIXT.VN offers airport transfer services, hotel booking, and tours to historical sites and cultural landmarks.
-
Why should I choose SIXT.VN for exploring historical sites in Vietnam? Choosing SIXT.VN ensures a seamless and enriching travel experience with reliable services tailored to your needs.
-
What are some must-see ancient sites in Vietnam that I should visit? Must-see sites include the ancient city of Hoi An, the imperial city of Hue, and the My Son Sanctuary.
Ready to explore the ancient wonders of Vietnam? Contact SIXT.VN today for personalized travel advice and seamless booking services. Visit our website or call +84 986 244 358 to start planning your unforgettable journey! Our address is 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Let SIXT.VN be your trusted partner in discovering the rich history and culture of Vietnam.



