Radio waves travel through space as electromagnetic radiation, and SIXT.VN is here to guide you through the world of travel, just like radio waves traverse the airwaves. Thinking about your trip to Vietnam? Let us help you navigate your travel needs with ease, offering services like airport transfers, hotel bookings, and exciting Hanoi tours, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable travel experience.
1. What Are Radio Waves and How Do They Relate to Electromagnetic Waves?
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) within the electromagnetic spectrum; they’re essential for wireless communication, broadcasting, and even navigation. Radio waves and other electromagnetic waves transport energy and information without needing a physical medium. SIXT.VN helps transport you, offering seamless travel experiences in Vietnam.
1.1. What Defines Electromagnetic Waves?
Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation. These waves are characterized by their frequency and wavelength, with higher frequency waves having shorter wavelengths and vice versa.
1.2. How Do Radio Waves Fit into the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays, all differing in frequency and wavelength. Radio waves occupy the portion of the spectrum with the lowest frequencies, ranging from a few hertz to several gigahertz.
1.3. What Role Do Radio Waves Play in Everyday Technology?
Radio waves enable countless technologies, including broadcasting (AM/FM radio, television), mobile communications (cell phones, Wi-Fi), satellite communications, radar systems, and remote controls. These technologies facilitate communication and navigation, making our lives more connected and efficient.
2. How Do Radio Waves Propagate Through Space?
Radio waves propagate through space via electromagnetic radiation, enabling wireless communication over long distances. Understanding the different propagation modes—ground waves, sky waves, and space waves—is crucial for optimizing radio communication systems. SIXT.VN is your trusted partner, providing seamless travel solutions to navigate Vietnam effortlessly.
2.1. What Are the Three Main Modes of Radio Wave Propagation?
Radio waves propagate through space via three primary modes: ground waves, sky waves, and space waves. Each mode is influenced by factors such as frequency, atmospheric conditions, and terrain.
- Ground Waves: Ground waves travel along the surface of the Earth, following its curvature. They are most effective at lower frequencies (e.g., AM radio) and are used for short- to medium-distance communication.
- Sky Waves: Sky waves are reflected or refracted by the ionosphere, a layer of charged particles in the upper atmosphere. They are used for long-distance communication, as the waves can “skip” off the ionosphere and travel thousands of kilometers.
- Space Waves: Space waves travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. They are used for satellite communication, microwave links, and line-of-sight communication.
2.2. How Does the Ionosphere Affect Radio Wave Propagation?
The ionosphere, a layer of charged particles in the upper atmosphere, plays a crucial role in reflecting or refracting sky waves, enabling long-distance communication. The density and height of the ionosphere vary with time of day, season, and solar activity, affecting the range and reliability of sky wave communication.
2.3. How Does Terrain Impact Radio Wave Propagation?
Terrain features such as mountains, hills, and buildings can obstruct or reflect radio waves, affecting their propagation. Diffraction, the bending of waves around obstacles, allows radio waves to propagate beyond the line of sight, but signal strength may be reduced.
3. What Factors Influence the Range and Strength of Radio Waves?
The range and strength of radio waves are affected by several factors, including frequency, transmitter power, antenna characteristics, and environmental conditions. Understanding these factors is essential for optimizing radio communication systems and ensuring reliable wireless connectivity. SIXT.VN helps you overcome travel obstacles, offering reliable services for a seamless journey in Vietnam.
3.1. How Does Frequency Affect Radio Wave Range?
Lower frequency radio waves tend to have longer ranges than higher frequency waves. Lower frequency waves can propagate more effectively as ground waves, following the Earth’s curvature. Higher frequency waves are more likely to be absorbed by the atmosphere or blocked by obstacles, limiting their range.
3.2. How Does Transmitter Power Influence Radio Wave Strength?
Transmitter power directly affects the strength of radio waves at a given distance from the transmitter. Higher transmitter power results in stronger signals and longer communication ranges, but it also increases power consumption and may cause interference with other devices.
3.3. What Role Do Antennas Play in Radio Wave Transmission and Reception?
Antennas play a crucial role in both transmitting and receiving radio waves. The design and characteristics of an antenna, such as its gain, radiation pattern, and polarization, affect the efficiency and directionality of radio wave propagation.
3.4. How Do Environmental Conditions Impact Radio Wave Propagation?
Environmental conditions such as atmospheric absorption, precipitation, and temperature inversions can affect radio wave propagation. Atmospheric absorption, caused by water vapor and oxygen, reduces the strength of radio waves, especially at higher frequencies. Precipitation can scatter or absorb radio waves, leading to signal attenuation. Temperature inversions can cause radio waves to bend or refract, affecting their range and direction.
4. How Are Radio Waves Used in Communication Systems?
Radio waves are indispensable in modern communication systems, enabling wireless connectivity across various platforms. Broadcasting, mobile communications, satellite communications, and navigation systems rely on radio waves for transmitting and receiving information. SIXT.VN ensures you stay connected with seamless travel solutions in Vietnam.
4.1. How Do Radio Waves Facilitate Broadcasting?
Radio waves are the backbone of broadcasting, enabling the transmission of audio and video signals to a wide audience. AM and FM radio stations use radio waves to transmit music, news, and talk shows to listeners within their coverage area. Television stations use radio waves to transmit video and audio signals to viewers.
4.2. How Do Radio Waves Enable Mobile Communications?
Radio waves are essential for mobile communications, enabling cell phones, smartphones, and other wireless devices to connect to cellular networks. Cellular networks use a network of base stations to transmit and receive radio waves, allowing mobile devices to communicate with each other and access the internet.
4.3. What Is the Role of Radio Waves in Satellite Communications?
Radio waves are used for satellite communications, enabling communication between ground stations and satellites orbiting the Earth. Satellites use radio waves to transmit and receive data, voice, and video signals, providing communication services to remote areas and enabling global connectivity.
4.4. How Do Navigation Systems Utilize Radio Waves?
Navigation systems such as GPS (Global Positioning System) use radio waves to determine the location and velocity of a receiver on Earth. GPS satellites transmit radio signals containing timing and positioning information. GPS receivers use these signals to calculate their position and provide navigation guidance.
5. What Are Some Interesting Applications of Radio Waves Beyond Communication?
Radio waves have a wide range of applications beyond communication, including radar systems, medical imaging, industrial heating, and scientific research. These applications leverage the unique properties of radio waves for various purposes. SIXT.VN is your travel companion, exploring the wonders of Vietnam beyond the ordinary.
5.1. How Are Radio Waves Used in Radar Systems?
Radar systems use radio waves to detect and track objects, such as aircraft, ships, and weather patterns. Radar systems transmit radio waves and then analyze the reflected signals to determine the distance, speed, and direction of the objects.
5.2. What Is the Role of Radio Waves in Medical Imaging?
Radio waves are used in medical imaging techniques such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI uses radio waves and strong magnetic fields to create detailed images of the human body, enabling doctors to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
5.3. How Are Radio Waves Applied in Industrial Heating?
Radio waves are used in industrial heating processes such as microwave heating and radio frequency (RF) heating. These methods use radio waves to heat materials quickly and efficiently, making them suitable for applications such as food processing, drying, and sterilization.
5.4. How Do Scientists Use Radio Waves in Research?
Scientists use radio waves in various research areas, including astronomy, atmospheric science, and materials science. Radio telescopes use radio waves to study celestial objects such as stars, galaxies, and black holes. Atmospheric scientists use radio waves to study the properties of the atmosphere and ionosphere. Materials scientists use radio waves to investigate the properties of materials and develop new technologies.
6. What Are the Potential Health Effects of Radio Waves?
The potential health effects of radio waves have been a topic of ongoing research and debate. While high levels of radio wave exposure can cause harm, the general consensus is that exposure to low levels of radio waves from common sources such as cell phones and Wi-Fi is not harmful. SIXT.VN cares about your well-being, providing safe and reliable travel services in Vietnam.
6.1. What Are the Known Health Effects of High-Level Radio Wave Exposure?
High-level exposure to radio waves can cause tissue heating, leading to burns and other injuries. This is the principle behind microwave ovens, which use radio waves to heat food. High-level exposure to radio waves can also interfere with electronic devices, such as pacemakers and other medical implants.
6.2. What Is the Evidence Regarding Low-Level Radio Wave Exposure and Health Risks?
The evidence regarding low-level radio wave exposure and health risks is mixed and inconclusive. Some studies have suggested a possible link between low-level radio wave exposure and certain types of cancer, while others have found no evidence of harm. Most scientific organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the National Cancer Institute (NCI), conclude that there is no consistent evidence that low-level radio wave exposure causes adverse health effects.
6.3. What Are Some Ways to Reduce Radio Wave Exposure?
If you are concerned about radio wave exposure, there are several steps you can take to reduce your exposure. These include:
- Using a wired headset instead of holding a cell phone to your ear.
- Keeping cell phones and other wireless devices away from your body when not in use.
- Turning off Wi-Fi and Bluetooth when not needed.
- Maintaining a safe distance from radio transmitters and antennas.
7. How Can I Optimize Radio Wave Reception for Better Connectivity?
Optimizing radio wave reception can improve connectivity for various devices, including radios, cell phones, and Wi-Fi devices. Factors such as antenna placement, interference mitigation, and signal boosting can enhance signal strength and reliability. SIXT.VN ensures you stay connected with travel tips for a smooth experience in Vietnam.
7.1. What Are Some Tips for Improving Radio Reception?
To improve radio reception, consider the following tips:
- Position the radio near a window or outdoors for better signal access.
- Extend the antenna to its full length and adjust its orientation for optimal reception.
- Keep the radio away from electronic devices that may cause interference.
- Use a signal booster or amplifier to enhance the signal strength.
7.2. How Can I Enhance Cell Phone Signal Strength?
Enhancing cell phone signal strength can improve call quality, data speeds, and overall connectivity. Here are some tips for improving cell phone signal strength:
- Move to an area with better coverage, such as outdoors or near a cell tower.
- Remove obstructions that may block the signal, such as walls or buildings.
- Use a cell phone signal booster to amplify the signal strength.
- Update your phone’s software to ensure optimal performance.
7.3. What Are Some Strategies for Improving Wi-Fi Connectivity?
Improving Wi-Fi connectivity can enhance internet speeds, reduce lag, and provide a more reliable wireless experience. Consider these strategies for improving Wi-Fi connectivity:
- Position the Wi-Fi router in a central location, away from walls and obstructions.
- Update the router’s firmware to ensure optimal performance.
- Use a Wi-Fi extender to expand the coverage area.
- Reduce interference from other electronic devices by using the 5 GHz band.
8. What Is the Future of Radio Wave Technology?
The future of radio wave technology is promising, with ongoing innovations in wireless communication, sensing, and energy transfer. Advancements in 5G technology, cognitive radio, and wireless power transfer are poised to transform various industries and enhance our daily lives. SIXT.VN stays ahead, offering innovative travel solutions for your Vietnam journey.
8.1. How Will 5G Technology Impact Radio Wave Communication?
5G technology will revolutionize radio wave communication by providing faster speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. 5G networks use higher frequency radio waves and advanced technologies such as massive MIMO and beamforming to deliver superior performance and support new applications such as virtual reality, autonomous vehicles, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
8.2. What Is Cognitive Radio and How Does It Enhance Radio Wave Efficiency?
Cognitive radio is a technology that enables wireless devices to sense their environment and dynamically adapt their transmission parameters to optimize spectrum utilization. Cognitive radio can identify unused frequency bands and transmit data without interfering with other users, improving radio wave efficiency and spectrum utilization.
8.3. How Will Wireless Power Transfer Utilize Radio Waves?
Wireless power transfer (WPT) uses radio waves to transmit energy wirelessly over short or long distances. WPT technology can power electronic devices without the need for cables or batteries, enabling applications such as wireless charging of mobile devices, electric vehicles, and remote sensors.
9. What Are The Regulations Regarding Radio Waves?
Radio wave regulations are essential for managing the electromagnetic spectrum, preventing interference, and ensuring fair access to radio frequencies. Regulatory bodies such as the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) establish rules and standards for radio wave emissions, licensing, and equipment certification. SIXT.VN ensures compliance, providing reliable travel services that adhere to local regulations in Vietnam.
9.1. Why Is Radio Wave Regulation Important?
Radio wave regulation is crucial for several reasons:
- Preventing Interference: Radio wave regulations prevent interference between different radio systems by establishing limits on emissions and requiring coordination between users.
- Ensuring Fair Access: Radio wave regulations ensure fair access to radio frequencies by allocating spectrum to different services and users based on their needs and priorities.
- Promoting Innovation: Radio wave regulations promote innovation by creating a stable and predictable regulatory environment that encourages investment in new technologies and services.
9.2. Who Regulates Radio Waves Globally and Nationally?
- Globally: The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the primary global organization responsible for coordinating the use of the radio frequency spectrum and developing international standards for radio communication.
- Nationally: Each country has its own regulatory body responsible for regulating radio waves within its borders. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates radio waves. In Europe, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) develops standards for radio communication.
9.3. What Are the Consequences of Violating Radio Wave Regulations?
Violating radio wave regulations can result in various penalties, including fines, equipment confiscation, and license revocation. Regulatory bodies have the authority to enforce regulations and take action against violators to maintain order and prevent interference in the radio frequency spectrum.
10. What Are Some Misconceptions About Radio Waves?
Despite their widespread use, radio waves are often misunderstood. Addressing common misconceptions can help clarify their nature, applications, and potential impacts. SIXT.VN clarifies travel concerns, providing accurate information for your Vietnam adventure.
10.1. Are Radio Waves Harmful to Humans?
This is a common concern, but most scientific evidence suggests that exposure to low levels of radio waves from everyday devices like cell phones and Wi-Fi routers is not harmful.
10.2. Do Radio Waves Require a Physical Medium to Travel?
No, radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation and can travel through the vacuum of space. This is how radio signals are transmitted to and from satellites.
10.3. Are All Radio Waves the Same?
No, radio waves vary in frequency and wavelength. These differences determine their properties and applications. For example, AM radio waves have longer wavelengths than FM radio waves.
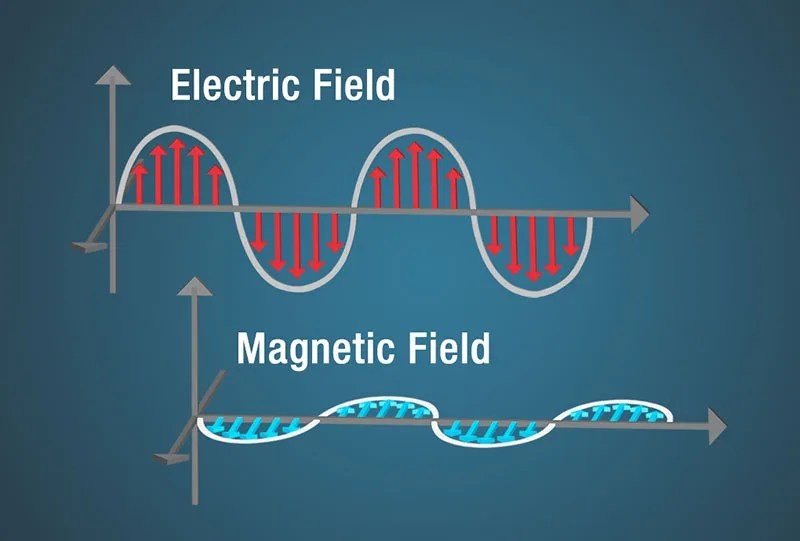 Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic wave and are used in many technologies such as radio, television, and cell phones.
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic wave and are used in many technologies such as radio, television, and cell phones.
FAQs About How Radio Waves Travel
1. How do radio waves travel through walls?
Radio waves can penetrate walls through diffraction, bending around obstacles, or by passing directly through materials depending on their density and composition.
2. Can radio waves travel through water?
Yes, but water absorbs radio waves, especially at higher frequencies, limiting the distance they can travel underwater.
3. Do radio waves travel faster in air or space?
Radio waves travel faster in space because there is no atmosphere to slow them down.
4. How far can radio waves travel?
The distance radio waves can travel depends on factors like frequency, power, antenna height, and atmospheric conditions. Some can travel thousands of miles.
5. Do radio waves travel in a straight line?
While they ideally travel in a straight line, they can be bent or reflected by objects and the ionosphere, allowing them to travel beyond the horizon.
6. Can radio waves be blocked?
Yes, dense materials like metal, concrete, and even some types of foliage can block radio waves.
7. How are radio waves used in aviation?
Radio waves are used for communication between pilots and air traffic control, navigation, and radar systems to detect other aircraft and weather conditions.
8. Are radio waves affected by weather?
Yes, weather conditions like rain, snow, and fog can absorb or scatter radio waves, reducing their range and signal strength.
9. How do radio waves differ from sound waves?
Radio waves are electromagnetic waves that can travel through a vacuum, while sound waves are mechanical waves that require a medium like air or water to travel.
10. What is the role of radio waves in Wi-Fi technology?
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly between devices and a router, enabling internet access without physical cables.
Ready to explore Vietnam? SIXT.VN offers comprehensive travel solutions, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and guided tours. Our dedicated team is here to ensure your trip is seamless and unforgettable. Contact us today to plan your adventure and experience the best of Vietnam with ease!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN



