The tourism product life cycle explains the stages a destination or tourism product goes through, from initial exploration to potential decline or rejuvenation, and SIXT.VN can help you navigate each stage with expert travel solutions in Vietnam. Understanding this cycle allows for strategic planning and sustainable tourism development, ensuring long-term benefits for both visitors and local communities with services like airport transfers, hotel bookings, and curated tours. Key factors include market trends, destination management, and evolving traveler preferences.
1. Understanding the Tourism Product Life Cycle (TPLC)
The Tourism Product Life Cycle (TPLC) describes the evolution of a tourist destination or product through various stages, much like the life cycle of a manufactured product. Understanding the TPLC is crucial for sustainable tourism development, as it allows destinations to anticipate changes, adapt their strategies, and ensure long-term viability.
1.1. What is the Tourism Product Life Cycle?
The Tourism Product Life Cycle (TPLC) is a framework that illustrates the different stages a tourist destination or product experiences over time. It is similar to the product life cycle used in marketing, but it is applied to the context of tourism. The TPLC helps destinations understand their current position, predict future trends, and develop strategies to manage their resources and attract visitors sustainably.
1.2. Why is Understanding the Tourism Product Life Cycle Important?
Understanding the TPLC is essential for several reasons:
- Strategic Planning: It helps destinations plan for the future by anticipating changes in visitor numbers, market trends, and the overall appeal of the destination.
- Sustainable Development: It allows destinations to manage their resources more effectively, minimizing negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
- Marketing and Promotion: It informs marketing strategies, ensuring that the destination is promoted in a way that aligns with its current stage in the life cycle.
- Investment Decisions: It guides investment decisions, helping to allocate resources to the areas that will have the greatest impact on the destination’s long-term success.
- Competitive Advantage: It enables destinations to differentiate themselves from competitors and maintain a unique appeal to visitors.
By understanding the TPLC, destinations can make informed decisions that support sustainable tourism development and ensure long-term economic, social, and environmental benefits. SIXT.VN is here to provide expert travel solutions, ensuring you navigate Vietnam’s destinations effectively.
1.3. What are the Key Stages of the Tourism Product Life Cycle?
The Tourism Product Life Cycle typically consists of six key stages, each with its own characteristics and challenges:
1. Exploration:
- Characteristics: This is the initial stage when a destination is relatively unknown and unspoiled. A small number of adventurous travelers, often seeking unique experiences, visit the area.
- Challenges: Lack of infrastructure, limited services, and minimal involvement from the local community.
- Opportunities: The chance to develop the destination in a sustainable way, preserving its natural and cultural assets.
2. Involvement:
- Characteristics: As word spreads about the destination, the number of visitors starts to increase. Local communities begin to recognize the potential benefits of tourism and start to get involved in providing services and facilities.
- Challenges: Balancing the needs of tourists with the needs of the local community, managing growth in a sustainable way.
- Opportunities: Creating local jobs, improving infrastructure, and enhancing the quality of life for residents.
3. Development:
- Characteristics: The destination becomes more popular, attracting significant investment from both domestic and international companies. Hotels, restaurants, and other tourist facilities are developed, and the destination becomes more accessible.
- Challenges: Managing the impacts of mass tourism, preserving the destination’s unique character, and ensuring that local communities benefit from the growth.
- Opportunities: Boosting the local economy, creating jobs, and improving infrastructure.
4. Consolidation:
- Characteristics: The destination becomes a well-established tourist destination, with a large number of visitors and a mature tourism industry.
- Challenges: Maintaining the destination’s appeal, managing the impacts of tourism on the environment and local communities, and competing with other destinations.
- Opportunities: Diversifying the tourism product, improving the quality of services, and promoting sustainable tourism practices.
5. Stagnation:
- Characteristics: The destination starts to lose its appeal as it becomes overcrowded, overdeveloped, and loses its unique character. Visitor numbers start to decline, and the local economy suffers.
- Challenges: Addressing the negative impacts of tourism, revitalizing the destination, and attracting new visitors.
- Opportunities: Rebranding the destination, developing new attractions, and promoting sustainable tourism practices.
6. Decline or Rejuvenation:
- Characteristics: The destination either enters a period of decline, with visitor numbers continuing to fall, or it undergoes a process of rejuvenation, with new investment and a renewed focus on sustainable tourism.
- Challenges: Overcoming the negative image of the destination, attracting investment, and implementing sustainable tourism practices.
- Opportunities: Creating a new vision for the destination, developing innovative tourism products, and promoting responsible tourism.
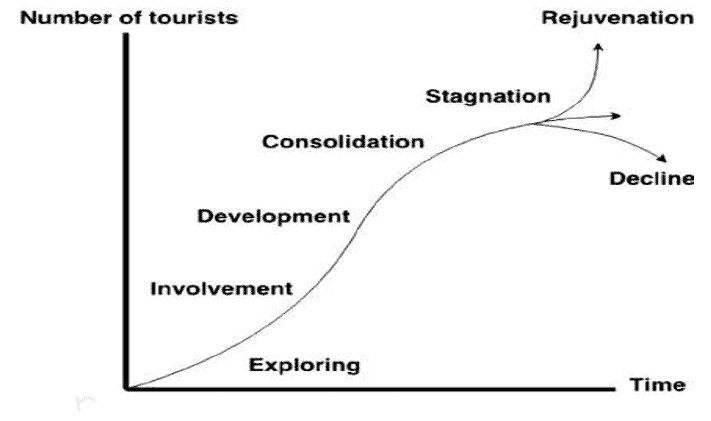 Tourism product life cycle stages
Tourism product life cycle stages
2. The Exploration Stage: Discovering New Destinations
The exploration stage is the initial phase of the tourism product life cycle, where a destination is relatively untouched and attracts a small number of adventurous travelers. Understanding this stage is crucial for destinations aiming to develop sustainably and maintain their unique appeal.
2.1. What Happens During the Exploration Stage?
During the exploration stage, a destination is typically characterized by:
- Low Visitor Numbers: Only a few adventurous travelers, often seeking unique and authentic experiences, visit the destination.
- Limited Infrastructure: The destination has minimal tourist facilities, such as hotels, restaurants, and transportation options.
- Unspoiled Environment: The natural and cultural resources of the destination are largely intact.
- Local Community Involvement: The local community may have limited awareness of tourism and its potential benefits.
- Adventure Seekers: According to a study by the Adventure Travel Trade Association (ATTA) in 2023, destinations in the exploration stage are primarily visited by adventure seekers looking for unique and off-the-beaten-path experiences.
2.2. What are the Key Characteristics of the Exploration Stage?
The key characteristics of the exploration stage include:
- Authenticity: The destination offers a unique and authentic experience that is not found in more developed tourist areas.
- Natural Beauty: The destination is often characterized by its stunning natural landscapes, such as mountains, beaches, or forests.
- Cultural Richness: The destination has a rich cultural heritage, with unique traditions, customs, and historical sites.
- Limited Accessibility: The destination may be difficult to reach, with limited transportation options and poor infrastructure.
- Basic Accommodation: Accommodation options are typically basic, such as guesthouses, homestays, or campsites.
SIXT.VN ensures you can explore Vietnam’s hidden gems with reliable transport and local insights, making even the most remote destinations accessible.
2.3. What are the Challenges and Opportunities in the Exploration Stage?
Challenges:
- Lack of Infrastructure: The limited infrastructure can make it difficult for tourists to access the destination and enjoy their stay.
- Limited Services: The lack of tourist services, such as restaurants, shops, and tour operators, can make it challenging for visitors to plan and organize their trip.
- Environmental Impact: The influx of even a small number of tourists can have a negative impact on the environment, particularly if waste management and conservation efforts are lacking.
- Local Community Engagement: Ensuring that the local community benefits from tourism and is involved in decision-making can be challenging.
Opportunities:
- Sustainable Development: The exploration stage offers the opportunity to develop the destination in a sustainable way, minimizing negative impacts on the environment and local communities.
- Unique Experiences: The destination can offer unique and authentic experiences that are not found in more developed tourist areas.
- Community Empowerment: Tourism can empower local communities, creating jobs, generating income, and improving the quality of life.
- Conservation Efforts: Tourism can provide funding for conservation efforts, protecting the destination’s natural and cultural resources.
2.4. How Can Destinations Manage the Exploration Stage Effectively?
To manage the exploration stage effectively, destinations should:
- Develop a Sustainable Tourism Plan: This plan should outline the destination’s vision for tourism development, with a focus on sustainability and community involvement.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Investing in basic infrastructure, such as roads, water, and electricity, can improve accessibility and the quality of life for both tourists and residents.
- Promote Responsible Tourism Practices: Encouraging tourists to respect the environment, support local businesses, and engage with the local community can help minimize negative impacts.
- Engage the Local Community: Involving the local community in decision-making and ensuring that they benefit from tourism can foster a sense of ownership and support for tourism development.
- Monitor and Evaluate Impacts: Regularly monitoring and evaluating the impacts of tourism can help identify potential problems and ensure that the destination is developing in a sustainable way.
By carefully managing the exploration stage, destinations can ensure that tourism benefits both visitors and the local community, while preserving the destination’s unique character and natural resources. SIXT.VN provides seamless services that help manage these early stages, ensuring sustainable tourism development.
3. The Involvement Stage: Local Communities Get Involved
The involvement stage is the second phase of the tourism product life cycle, where local communities begin to recognize the potential benefits of tourism and start to participate in related activities. This stage is crucial for fostering sustainable tourism and ensuring that local residents benefit from the growth of the industry.
3.1. What Happens During the Involvement Stage?
During the involvement stage, a destination typically experiences:
- Increased Visitor Numbers: The number of tourists starts to grow as word spreads about the destination’s unique attractions and experiences.
- Local Community Engagement: Local residents begin to recognize the economic opportunities presented by tourism and start to provide services and facilities to visitors.
- Emerging Infrastructure: Basic infrastructure, such as roads, accommodation, and restaurants, starts to develop to cater to the growing number of tourists.
- Entrepreneurial Activities: Local entrepreneurs start to establish businesses to serve tourists, such as guesthouses, tour operators, and handicraft shops.
- Community-Based Tourism: According to a 2022 report by the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), destinations in the involvement stage often see a rise in community-based tourism initiatives, where local communities manage and benefit directly from tourism activities.
3.2. What are the Key Characteristics of the Involvement Stage?
The key characteristics of the involvement stage include:
- Local Ownership: Local residents take ownership of tourism development, playing an active role in providing services and facilities to visitors.
- Economic Opportunities: Tourism creates new economic opportunities for local residents, such as jobs, income, and business ventures.
- Cultural Exchange: Tourists and local residents interact, fostering cultural exchange and understanding.
- Environmental Awareness: Local communities become more aware of the importance of protecting the environment and natural resources to sustain tourism.
- Small-Scale Development: Tourism development is typically small-scale, with a focus on preserving the destination’s unique character and authenticity.
With SIXT.VN, you’re supporting local businesses and sustainable tourism, creating a positive impact on Vietnamese communities during your travels.
3.3. What are the Challenges and Opportunities in the Involvement Stage?
Challenges:
- Managing Growth: The increasing number of tourists can put a strain on local resources, such as water, electricity, and waste management.
- Preserving Authenticity: As tourism develops, there is a risk of losing the destination’s unique character and authenticity.
- Ensuring Equitable Distribution of Benefits: Ensuring that all members of the local community benefit from tourism can be challenging, particularly if development is concentrated in certain areas or controlled by a few individuals.
- Protecting the Environment: The increasing number of tourists can have a negative impact on the environment, particularly if sustainable practices are not implemented.
Opportunities:
- Economic Development: Tourism can drive economic development, creating jobs, generating income, and improving the quality of life for local residents.
- Community Empowerment: Tourism can empower local communities, giving them a voice in decision-making and control over their own development.
- Cultural Preservation: Tourism can help preserve local culture and traditions, as tourists are often interested in experiencing authentic cultural experiences.
- Environmental Conservation: Tourism can provide funding for environmental conservation efforts, protecting the destination’s natural resources.
3.4. How Can Destinations Manage the Involvement Stage Effectively?
To manage the involvement stage effectively, destinations should:
- Develop a Community-Based Tourism Plan: This plan should outline the destination’s vision for tourism development, with a focus on community involvement and sustainable practices.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Investing in basic infrastructure, such as water, electricity, and waste management, can help manage the increasing number of tourists and protect the environment.
- Promote Sustainable Tourism Practices: Encouraging tourists and local businesses to adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and respecting local culture, can help minimize negative impacts.
- Support Local Entrepreneurs: Providing training, funding, and other resources to local entrepreneurs can help them establish successful tourism businesses.
- Engage the Local Community: Involving the local community in decision-making and ensuring that they benefit from tourism can foster a sense of ownership and support for tourism development.
By carefully managing the involvement stage, destinations can ensure that tourism benefits both visitors and the local community, while preserving the destination’s unique character and natural resources. SIXT.VN supports destinations by promoting local engagement and sustainable tourism initiatives.
4. The Development Stage: Investment and Infrastructure Growth
The development stage is the third phase of the tourism product life cycle, marked by significant investment, infrastructure growth, and increased marketing efforts. This stage sees a destination evolve into a more structured and accessible tourist spot.
4.1. What Happens During the Development Stage?
During the development stage, a destination typically experiences:
- Increased Tourist Arrivals: A sharp rise in the number of tourists, driven by increased awareness and improved accessibility.
- Foreign Investment: Attracts significant foreign investment, leading to the construction of hotels, resorts, and other tourist facilities.
- Infrastructure Development: Improvement in infrastructure such as roads, airports, and public transportation to accommodate the growing number of visitors.
- Marketing Campaigns: Large-scale marketing and promotional campaigns to attract even more tourists.
- Emergence of Large-Scale Tourism Operations: According to a 2023 report by the Pacific Asia Travel Association (PATA), the development stage often sees the rise of large-scale tourism operations, including international hotel chains and tour operators.
4.2. What are the Key Characteristics of the Development Stage?
The key characteristics of the development stage include:
- Mass Tourism: Transition from niche tourism to mass tourism, catering to a broader range of visitors.
- Standardization of Services: Standardization of tourist services and facilities to meet the expectations of international visitors.
- Increased Competition: Increased competition among tourism businesses to attract customers.
- Environmental Concerns: Growing concerns about the environmental impact of tourism, such as pollution, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity.
- Social and Cultural Impacts: Potential social and cultural impacts on local communities, such as changes in traditional lifestyles and values.
4.3. What are the Challenges and Opportunities in the Development Stage?
Challenges:
- Environmental Degradation: The increased number of tourists can lead to environmental degradation, such as pollution, deforestation, and loss of biodiversity.
- Loss of Authenticity: The standardization of services and facilities can lead to a loss of the destination’s unique character and authenticity.
- Social and Cultural Disruptions: Tourism can disrupt local communities, leading to changes in traditional lifestyles and values.
- Economic Leakage: A significant portion of tourism revenue may leak out of the local economy, as international companies and suppliers capture a large share of the profits.
Opportunities:
- Economic Growth: Tourism can drive economic growth, creating jobs, generating income, and improving the quality of life for local residents.
- Infrastructure Development: Tourism can stimulate infrastructure development, improving transportation, communication, and other essential services.
- Cultural Exchange: Tourism can promote cultural exchange, fostering understanding and appreciation between visitors and local communities.
- Environmental Awareness: Tourism can raise awareness of environmental issues, encouraging sustainable practices and conservation efforts.
SIXT.VN contributes to sustainable development by partnering with eco-friendly accommodations and promoting responsible travel practices, ensuring long-term benefits for Vietnam’s destinations.
4.4. How Can Destinations Manage the Development Stage Effectively?
To manage the development stage effectively, destinations should:
- Implement Sustainable Tourism Policies: Enact policies that promote sustainable tourism practices, such as environmental protection, waste management, and energy conservation.
- Invest in Infrastructure: Invest in infrastructure that supports sustainable tourism, such as public transportation, renewable energy, and water conservation.
- Promote Responsible Tourism Practices: Encourage tourists and businesses to adopt responsible tourism practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and respecting local culture.
- Support Local Businesses: Provide support to local businesses, helping them compete with international companies and capture a larger share of the tourism revenue.
- Engage the Local Community: Involve the local community in decision-making and ensure that they benefit from tourism development.
By carefully managing the development stage, destinations can maximize the economic benefits of tourism while minimizing the negative impacts on the environment and local communities. SIXT.VN helps manage this stage by promoting responsible travel practices and supporting local businesses, ensuring sustainable growth for Vietnam’s destinations.
5. The Consolidation Stage: Maturation and Market Saturation
The consolidation stage represents the fourth phase in the tourism product life cycle, characterized by a mature market, established infrastructure, and a large volume of tourists. However, it also brings challenges such as market saturation and the risk of losing destination appeal.
5.1. What Happens During the Consolidation Stage?
During the consolidation stage, a destination typically experiences:
- High Tourist Volume: A steady flow of tourists, with the destination becoming a well-known and popular choice.
- Established Infrastructure: Well-developed infrastructure, including a wide range of accommodation options, transportation networks, and tourist facilities.
- Mature Market: A mature tourism market, with a high level of competition among businesses and a focus on maintaining market share.
- Brand Recognition: Strong brand recognition and a well-defined image in the tourism market.
- Dependence on Tourism: According to a 2024 study by Tourism Economics, destinations in the consolidation stage often become heavily dependent on tourism revenue, making them vulnerable to economic downturns or shifts in traveler preferences.
5.2. What are the Key Characteristics of the Consolidation Stage?
The key characteristics of the consolidation stage include:
- Mass Tourism: Continued reliance on mass tourism, with a focus on attracting large numbers of visitors.
- Standardized Experiences: A tendency towards standardized tourist experiences, with less emphasis on unique or authentic offerings.
- Increased Marketing Efforts: Intensified marketing efforts to maintain market share and attract new visitors.
- Environmental Pressures: Increased environmental pressures due to the high volume of tourists, including pollution, congestion, and resource depletion.
- Socio-Cultural Impacts: Potential socio-cultural impacts on local communities, such as overcrowding, loss of cultural identity, and increased commercialization.
5.3. What are the Challenges and Opportunities in the Consolidation Stage?
Challenges:
- Market Saturation: The risk of market saturation, with the destination becoming overcrowded and losing its appeal to tourists.
- Environmental Degradation: Increased environmental pressures, such as pollution, congestion, and resource depletion.
- Socio-Cultural Impacts: Potential socio-cultural impacts on local communities, such as overcrowding, loss of cultural identity, and increased commercialization.
- Economic Dependence: High dependence on tourism revenue, making the destination vulnerable to economic downturns or shifts in traveler preferences.
Opportunities:
- Diversification of Tourism Products: The opportunity to diversify tourism products, offering new and unique experiences to attract a wider range of visitors.
- Sustainable Tourism Practices: The chance to implement sustainable tourism practices, reducing environmental impacts and preserving the destination’s natural and cultural resources.
- Community Involvement: The opportunity to involve local communities in tourism development, ensuring that they benefit from the industry and have a voice in decision-making.
- Destination Management: The need for effective destination management, coordinating the efforts of various stakeholders to ensure the long-term sustainability of tourism.
SIXT.VN offers eco-friendly transport options and supports local cultural preservation initiatives, contributing to the sustainability of Vietnam’s consolidated destinations.
5.4. How Can Destinations Manage the Consolidation Stage Effectively?
To manage the consolidation stage effectively, destinations should:
- Diversify Tourism Products: Develop new and unique tourism products, catering to a wider range of interests and attracting different types of visitors.
- Implement Sustainable Tourism Practices: Adopt sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and promoting responsible behavior among tourists.
- Engage Local Communities: Involve local communities in tourism development, ensuring that they benefit from the industry and have a voice in decision-making.
- Invest in Infrastructure Improvements: Invest in infrastructure improvements, such as public transportation, waste management, and renewable energy, to reduce environmental impacts and improve the quality of life for residents.
- Promote Destination Management: Establish effective destination management organizations, coordinating the efforts of various stakeholders to ensure the long-term sustainability of tourism.
By carefully managing the consolidation stage, destinations can maintain their appeal, minimize negative impacts, and ensure the long-term sustainability of tourism. SIXT.VN helps manage this stage by promoting diversified tourism products, responsible travel, and supporting local communities, ensuring sustainable growth for Vietnam’s destinations.
6. The Stagnation Stage: Decline in Popularity and Appeal
The stagnation stage is the fifth phase in the tourism product life cycle, where a destination begins to lose its appeal and popularity, often due to overdevelopment, environmental degradation, or a lack of innovation.
6.1. What Happens During the Stagnation Stage?
During the stagnation stage, a destination typically experiences:
- Decreasing Tourist Numbers: A decline in the number of tourists, as the destination loses its appeal and faces increased competition from other destinations.
- Aging Infrastructure: Deterioration of infrastructure, such as hotels, roads, and tourist facilities, due to lack of investment and maintenance.
- Environmental Degradation: Worsening environmental problems, such as pollution, congestion, and loss of natural resources.
- Loss of Authenticity: A decline in the destination’s unique character and authenticity, as it becomes more commercialized and standardized.
- Economic Decline: According to a 2022 report by the Sustainable Tourism Research Institute (STRI), destinations in the stagnation stage often experience economic decline, as tourism revenue decreases and local businesses struggle to survive.
6.2. What are the Key Characteristics of the Stagnation Stage?
The key characteristics of the stagnation stage include:
- Overdevelopment: Excessive development of tourist facilities, leading to overcrowding, congestion, and loss of natural beauty.
- Environmental Problems: Worsening environmental problems, such as pollution, waste disposal, and loss of biodiversity.
- Lack of Innovation: A lack of new attractions, activities, or experiences to keep tourists interested and attract new visitors.
- Negative Image: A negative image in the tourism market, as the destination becomes known for its problems and loses its appeal to tourists.
- Dependence on Repeat Visitors: A reliance on repeat visitors, as the destination struggles to attract new tourists.
SIXT.VN is committed to revitalizing Vietnam’s destinations by supporting sustainable initiatives and promoting lesser-known attractions, helping to steer away from stagnation.
6.3. What are the Challenges and Opportunities in the Stagnation Stage?
Challenges:
- Reversing Negative Trends: The difficulty of reversing negative trends, such as declining tourist numbers, environmental degradation, and loss of authenticity.
- Attracting Investment: The challenge of attracting investment for revitalization efforts, as the destination’s negative image may deter potential investors.
- Changing Perceptions: The difficulty of changing perceptions and convincing tourists that the destination has improved.
- Competition: Intense competition from other destinations, which may be more attractive and offer better experiences.
Opportunities:
- Rebranding: The opportunity to rebrand the destination, creating a new image and attracting a different type of tourist.
- Sustainable Tourism Development: The chance to implement sustainable tourism practices, addressing environmental problems and preserving the destination’s natural and cultural resources.
- Community Involvement: The opportunity to involve local communities in revitalization efforts, ensuring that they benefit from tourism and have a voice in decision-making.
- Innovation: The chance to innovate and develop new attractions, activities, or experiences that will appeal to tourists and set the destination apart from its competitors.
6.4. How Can Destinations Manage the Stagnation Stage Effectively?
To manage the stagnation stage effectively, destinations should:
- Develop a Revitalization Plan: Create a comprehensive plan for revitalizing the destination, addressing its problems and outlining strategies for attracting new tourists.
- Invest in Infrastructure Improvements: Invest in infrastructure improvements, such as modernizing hotels, upgrading roads, and improving public transportation.
- Implement Sustainable Tourism Practices: Implement sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, and promoting responsible behavior among tourists.
- Engage Local Communities: Involve local communities in revitalization efforts, ensuring that they benefit from tourism and have a voice in decision-making.
- Promote Innovation: Encourage innovation and develop new attractions, activities, or experiences that will appeal to tourists and set the destination apart from its competitors.
By carefully managing the stagnation stage, destinations can reverse negative trends, revitalize their economies, and regain their appeal to tourists. SIXT.VN helps manage this stage by supporting revitalization efforts, promoting sustainable practices, and encouraging innovation in Vietnam’s destinations.
7. The Decline or Rejuvenation Stage: A Crossroads for Tourism
The decline or rejuvenation stage is the final phase of the tourism product life cycle, representing a critical juncture where a destination either faces a downward spiral or undergoes a transformative revival.
7.1. What Happens During the Decline or Rejuvenation Stage?
During this stage, a destination’s trajectory diverges significantly:
Decline:
- Continued Drop in Tourist Arrivals: A sustained decrease in tourist numbers, leading to economic hardship for local businesses and communities.
- Closure of Tourist Facilities: Hotels, restaurants, and other tourist facilities may close down due to lack of business.
- Environmental Neglect: Further environmental degradation, as resources are depleted and conservation efforts are abandoned.
- Loss of Community Support: A decline in community support for tourism, as residents become disillusioned with its negative impacts.
Rejuvenation:
- Renewed Investment: Significant investment in infrastructure improvements, new attractions, and sustainable tourism initiatives.
- Rebranding Efforts: A comprehensive rebranding strategy to create a new image and attract a different type of tourist.
- Community Engagement: Active involvement of local communities in tourism development, ensuring that they benefit from the industry and have a voice in decision-making.
- Sustainable Practices: Implementation of sustainable tourism practices, such as environmental conservation, waste reduction, and cultural preservation.
- Increased Tourist Arrivals: A gradual increase in tourist numbers, as the destination regains its appeal and attracts new visitors.
7.2. What are the Key Characteristics of the Decline or Rejuvenation Stage?
The key characteristics depend on the path the destination takes:
Decline:
- Negative Reputation: A negative reputation in the tourism market, as the destination becomes known for its problems and loses its appeal to tourists.
- Economic Hardship: Economic hardship for local businesses and communities, as tourism revenue declines and unemployment rises.
- Environmental Degradation: Continued environmental degradation, leading to a loss of natural resources and biodiversity.
- Social Problems: Social problems, such as crime, poverty, and social unrest.
Rejuvenation:
- Positive Image: A positive image in the tourism market, as the destination becomes known for its sustainable practices, unique experiences, and community involvement.
- Economic Growth: Economic growth for local businesses and communities, as tourism revenue increases and new opportunities are created.
- Environmental Protection: Environmental protection, leading to a restoration of natural resources and biodiversity.
- Community Empowerment: Community empowerment, as local residents take ownership of tourism development and benefit from the industry.
SIXT.VN plays a pivotal role in the rejuvenation of Vietnam’s destinations by promoting sustainable travel and supporting community-based tourism initiatives.
7.3. What are the Challenges and Opportunities in the Decline or Rejuvenation Stage?
Challenges:
- Overcoming Negative Perceptions: The difficulty of overcoming negative perceptions and convincing tourists that the destination has changed for the better.
- Securing Investment: The challenge of securing investment for revitalization efforts, as the destination may be seen as a risky investment.
- Balancing Economic, Social, and Environmental Goals: The need to balance economic, social, and environmental goals, ensuring that tourism development is sustainable and benefits all stakeholders.
Opportunities:
- Creating a Unique Identity: The opportunity to create a unique identity for the destination, differentiating it from its competitors and attracting a specific type of tourist.
- Promoting Sustainable Tourism: The chance to promote sustainable tourism practices, attracting environmentally conscious travelers and preserving the destination’s natural and cultural resources.
- Empowering Local Communities: The opportunity to empower local communities, giving them a voice in decision-making and ensuring that they benefit from tourism development.
7.4. How Can Destinations Manage the Decline or Rejuvenation Stage Effectively?
To manage the decline or rejuvenation stage effectively, destinations should:
- Conduct a Thorough Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the destination’s problems, identifying the root causes of its decline and the opportunities for rejuvenation.
- Develop a Comprehensive Plan: Develop a comprehensive plan for revitalization, outlining strategies for attracting investment, improving infrastructure, promoting sustainable tourism, and empowering local communities.
- Engage Stakeholders: Engage all stakeholders in the planning process, including government agencies, local businesses, community organizations, and residents.
- Implement Sustainable Practices: Implement sustainable tourism practices, such as reducing waste, conserving water, protecting natural resources, and promoting cultural preservation.
- Monitor Progress: Monitor progress regularly, tracking key indicators such as tourist arrivals, economic performance, environmental quality, and community satisfaction.
By carefully managing the decline or rejuvenation stage, destinations can reverse negative trends, revitalize their economies, and create a sustainable tourism industry that benefits both visitors and local communities. SIXT.VN helps manage this stage by supporting sustainable tourism initiatives, promoting responsible travel, and connecting travelers with unique and authentic experiences in Vietnam’s destinations.
8. Real-World Examples of the Tourism Product Life Cycle
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into how the Tourism Product Life Cycle (TPLC) operates and how destinations can effectively manage its different stages.
8.1. Case Study 1: Bali, Indonesia
- Early Stages (Exploration & Involvement): Bali initially attracted surfers and backpackers drawn to its natural beauty and unique culture.
- Development & Consolidation: Mass tourism boomed with significant infrastructure development, attracting a wide range of visitors.
- Stagnation: Overcrowding, environmental degradation, and commercialization began to threaten Bali’s appeal.
- Rejuvenation: Efforts are now focused on sustainable tourism, promoting cultural preservation, and developing eco-friendly attractions.
8.2. Case Study 2: Amsterdam, Netherlands
- Development & Consolidation: Amsterdam became a popular destination, known for its canals, museums, and liberal culture.
- Stagnation: Over-tourism led to overcrowding, rising housing costs, and negative impacts on local communities.
- Rejuvenation: The city is implementing measures to manage tourist flows, promote sustainable tourism, and prioritize the needs of residents.
8.3. Case Study 3: Cancun, Mexico
- Early Stages (Exploration & Involvement): Cancun started as a pristine beach destination attracting adventurous travelers.
- Development & Consolidation: Extensive resort development and marketing campaigns transformed Cancun into a mass tourism hotspot.
- Stagnation: Environmental concerns, such as coral reef damage and water pollution, began to emerge.
- Rejuvenation: Efforts are underway to promote eco-tourism, protect natural resources, and diversify the tourism product.
8.4. Case Study 4: Ha Long Bay, Vietnam
- Early Stages (Exploration & Involvement): Ha Long Bay initially attracted adventurous travelers who came to see its stunning natural beauty.
- Development & Consolidation: Increased development and promotion led to a boom in tourist numbers, with improved infrastructure to accommodate the growth.
- Stagnation: Concerns have grown regarding pollution, waste management, and the impact on the bay’s unique ecosystem.
- Rejuvenation: Current strategies include sustainable tourism initiatives, environmental protection measures, and promoting community-based tourism to preserve the bay’s natural beauty and benefit local communities. With SIXT.VN, you can explore Ha Long Bay responsibly, supporting local conservation efforts and enjoying sustainable travel options.
SIXT.VN actively supports these initiatives by partnering with eco-conscious providers, promoting responsible tourism practices, and offering transportation solutions that minimize environmental impact.
9. Benefits of Using SIXT.VN for Your Vietnam Tourism Needs
Choosing SIXT.VN for your Vietnam tourism needs offers numerous advantages, ensuring a seamless, enjoyable, and sustainable travel experience.
9.1. Convenience and Ease of Booking
SIXT.VN provides a user-friendly platform for booking all your travel needs in Vietnam. Whether you need airport transfers, hotel reservations, or tour packages, our website and mobile app offer a hassle-free booking process.
9.2. Wide Range of Services
From private airport transfers to guided tours of Hanoi, SIXT.VN offers a comprehensive range of services to cater to all your travel requirements. We partner with trusted local providers to ensure high-quality experiences.
9.3. Reliable and Professional Service
SIXT.VN is committed to providing reliable and professional service to all our customers. Our drivers are experienced and knowledgeable, and our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any questions or concerns.
9.4. Sustainable Tourism Practices
SIXT.VN is dedicated to promoting sustainable tourism practices in Vietnam. We partner with eco-friendly accommodations, support local communities, and offer transportation options that minimize environmental impact.
9.5. Local Expertise
As a local company, SIXT.VN has in-depth knowledge of Vietnam’s destinations, culture, and customs. We can provide valuable insights and recommendations to help you plan the perfect trip.
9.6. Competitive Pricing
SIXT.VN offers competitive pricing on all our services, ensuring that you get the best value for your money.
9.7. Support for Local Communities
By choosing SIXT.VN, you are supporting local communities in Vietnam. We partner with local businesses and community organizations to ensure that tourism benefits local residents.
SIXT.VN helps you explore Vietnam responsibly, contributing to the sustainable development of its destinations and the well-being of its communities.
10. FAQs About the Tourism Product Life Cycle
Here are some frequently asked questions about the Tourism Product Life Cycle (TPLC) to help you better understand this important concept.
10.1. What is the main purpose of the Tourism Product Life Cycle?
The main purpose of the Tourism Product Life Cycle is to provide a framework for understanding how tourist destinations evolve over time. It helps destinations anticipate changes, plan for the future, and manage their resources sustainably.
10.2. How can destinations use the TPLC to improve their tourism offerings?
Destinations can use the TPLC to identify their current stage of development, anticipate future challenges, and develop strategies for sustainable growth, diversification, and rejuvenation.
10.3. What are some strategies for extending the life cycle of a tourism destination?
Strategies for extending the life cycle of a tourism destination include:
- Diversifying tourism products: Offering new and unique experiences to attract a wider range of visitors.
- Implementing sustainable tourism practices: Reducing environmental impacts and preserving natural and cultural resources.
- Engaging local communities: Involving local residents in tourism development and ensuring that they benefit from the industry.
- Investing in infrastructure improvements: Modernizing facilities and enhancing the overall visitor experience.
- Rebranding the destination: Creating a new image and attracting a different type



