Are you planning a trip to Vietnam and curious about the science of sound and light? Let SIXT.VN be your guide! Mechanical waves, unlike electromagnetic waves, need a medium to travel. This article dives deep into why mechanical waves can’t travel through empty space, exploring their properties and contrasting them with electromagnetic waves, ensuring you’re well-informed for your Vietnamese adventure. Think of SIXT.VN as your trusted travel companion, offering seamless services from airport transfers to hotel bookings, and guided tours, making your exploration of Vietnam smooth and enjoyable.
1. What Are Mechanical Waves and Why Do They Need a Medium?
Mechanical waves, such as sound waves and water waves, require a medium like air, water, or a solid to travel. These waves are disturbances that propagate through a medium due to the interaction of its particles.
Think of it like a crowd doing “the wave” at a stadium. People (particles) need to stand next to each other to pass the wave along. If there are gaps, the wave stops. Similarly, mechanical waves rely on the particles of a medium to transfer energy.
1.1. Types of Mechanical Waves
There are two main types of mechanical waves:
- Transverse Waves: The particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation (e.g., water waves).
- Longitudinal Waves: The particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of wave propagation (e.g., sound waves).
1.2. The Role of a Medium in Mechanical Wave Propagation
A medium provides the necessary physical connection between particles for the energy of a mechanical wave to be transferred. Without a medium, there’s nothing to vibrate or oscillate, and therefore no wave propagation.
According to the Physics Classroom, mechanical waves require a medium to transport their energy. This distinguishes them from electromagnetic waves, which can travel through the vacuum of space.
2. Why Can’t Mechanical Waves Travel Through Empty Space?
Empty space, or a vacuum, lacks the necessary particles or medium required for mechanical waves to propagate. In the absence of a medium, there are no particles to vibrate or interact with each other, preventing the transfer of energy.
2.1. The Absence of Particles in Empty Space
Empty space is defined by its lack of matter. Without any particles, there can be no vibrations or disturbances to propagate as a wave.
Imagine trying to play a game of dominoes without any dominoes. You can set up the starting position, but without the actual dominoes, there’s no chain reaction or wave of falling pieces. Similarly, mechanical waves can’t exist in empty space because there’s nothing to “fall” or vibrate.
2.2. The Need for Intermolecular Interaction
Mechanical waves rely on the interaction between molecules or particles in a medium. These interactions allow energy to be transferred from one particle to another, creating the wave motion. In empty space, there are no molecules to interact, so no wave propagation can occur.
3. What Are Electromagnetic Waves and How Do They Differ?
Electromagnetic waves, such as light, radio waves, and X-rays, are a form of energy that can travel through both a medium and empty space. They are created by the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields, which are self-propagating and do not require a medium.
3.1. The Nature of Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. This unique property allows them to travel through the vacuum of space.
3.2. Electromagnetic Waves Don’t Need a Medium
Unlike mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium to travel. They can propagate through the vacuum of space because the oscillating electric and magnetic fields generate each other, allowing the wave to move forward without relying on the interaction of particles.
As NASA explains, electromagnetic waves can travel through the vacuum of space because they do not require a medium. This is why we can see light from the sun, even though there is no air in space.
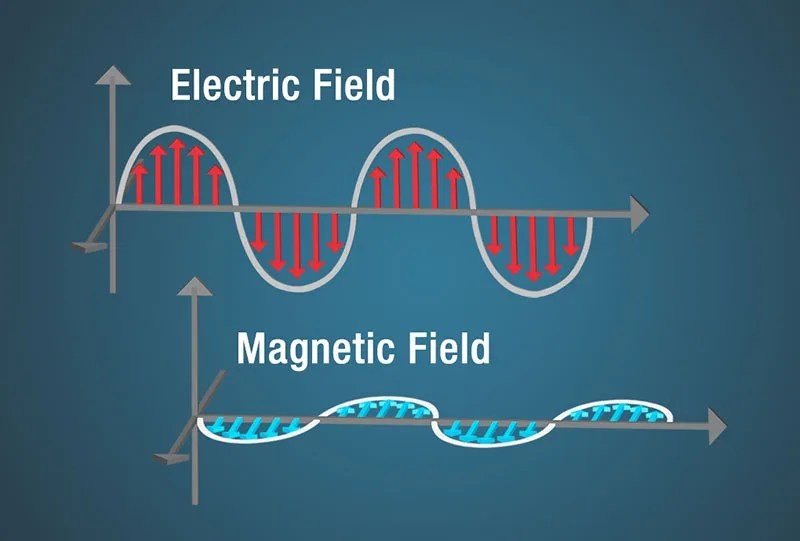 Electric field and magnetic field diagram showing electromagnetic waves traveling through space
Electric field and magnetic field diagram showing electromagnetic waves traveling through space
Caption: Electric field and magnetic field diagram showing electromagnetic waves traveling through space. This illustrates how electromagnetic waves can propagate without a medium.
4. Exploring the Properties of Sound Waves
Sound waves are a type of mechanical wave that travels through a medium by causing particles to vibrate. The speed of sound depends on the properties of the medium, such as density and elasticity.
4.1. How Sound Waves Travel
Sound waves are created by vibrations that cause particles in a medium to compress and expand. These compressions and expansions propagate through the medium as a wave.
4.2. Sound Waves and Their Dependence on a Medium
Since sound waves are mechanical waves, they require a medium to travel. The absence of a medium, such as in empty space, prevents the propagation of sound waves.
4.3. Examples of Sound Waves in Different Media
- Air: Sound travels through air by causing air molecules to vibrate.
- Water: Sound travels through water by causing water molecules to vibrate.
- Solids: Sound travels through solids by causing the atoms or molecules in the solid to vibrate.
5. Exploring the Properties of Light Waves
Light waves are electromagnetic waves that do not require a medium to travel. They are created by the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields and can travel through the vacuum of space.
5.1. How Light Waves Travel
Light waves are created by accelerating charged particles, which generate oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These fields propagate through space as a wave.
5.2. Light Waves and Their Ability to Travel Through Empty Space
Since light waves are electromagnetic waves, they can travel through the vacuum of space. The oscillating electric and magnetic fields generate each other, allowing the wave to move forward without relying on the interaction of particles.
5.3. Examples of Light Waves in Different Media
- Vacuum: Light travels through the vacuum of space at its maximum speed, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
- Air: Light travels through air at a slightly slower speed than in a vacuum.
- Water: Light travels through water at a significantly slower speed than in a vacuum.
6. Comparing Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves in a Table
| Feature | Mechanical Waves | Electromagnetic Waves |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Required | Yes | No |
| Examples | Sound waves, water waves | Light waves, radio waves, X-rays |
| Energy Transfer | Through particle interaction | Through oscillating electric and magnetic fields |
| Speed | Depends on the medium | Constant in a vacuum (approximately 299,792,458 m/s) |
| Travel in Empty Space | No | Yes |
| Wave Type | Transverse or longitudinal | Transverse |
| Creation | Vibration or disturbance in a medium | Acceleration of charged particles |
| Interaction | Particles of the medium vibrate | Electric and magnetic fields regenerate each other |
| Applications | Sound systems, sonar | Communication, medical imaging, astronomy |
| Frequency Range | Wide range depending on the type of wave | Broad spectrum from radio waves to gamma rays |
| Wavelength Range | Varies with frequency and medium | Covers a vast range from meters to picometers |
| Detection | Ears, seismographs | Eyes, radio receivers, X-ray detectors |
7. Real-World Applications: Why This Matters for Travelers
Understanding the difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves has practical implications, especially for travelers. Here’s how:
7.1. Communication in Space
Astronauts rely on radio waves (electromagnetic) to communicate with Earth because sound (mechanical) cannot travel through the vacuum of space.
7.2. Understanding Sonar Technology
Sonar uses sound waves to detect objects underwater. This technology is crucial for navigation and underwater exploration.
7.3. Implications for Space Travel
Spacecraft use electromagnetic radiation for propulsion, such as solar sails that harness the pressure of sunlight to accelerate.
7.4. Everyday Technologies
Many technologies we use daily, such as cell phones, Wi-Fi, and GPS, rely on electromagnetic waves to function.
8. The Significance of Wave Properties in Technology and Nature
Wave properties play a crucial role in numerous technologies and natural phenomena. Understanding these properties helps us develop advanced technologies and gain insights into the workings of the universe.
8.1. Medical Imaging
Medical imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI use electromagnetic waves to create detailed images of the human body.
8.2. Wireless Communication
Wireless communication systems, such as cell phones and Wi-Fi, rely on radio waves to transmit information wirelessly.
8.3. Astronomy
Astronomers use telescopes to observe electromagnetic radiation from distant objects in space, providing valuable information about the universe.
8.4. Optical Technology
Optical technologies, such as lenses and fiber optics, use the properties of light waves to focus and transmit light.
9. Why You Should Choose SIXT.VN for Your Vietnam Trip
Planning a trip to Vietnam? SIXT.VN offers a range of services to make your travel experience seamless and enjoyable.
9.1. Airport Transfer Services
Arrive in Vietnam stress-free with SIXT.VN’s reliable airport transfer services. Our professional drivers will pick you up from the airport and take you to your hotel in comfort.
9.2. Hotel Booking Assistance
SIXT.VN provides assistance with booking hotels to suit your budget and preferences. We partner with a wide range of hotels to offer you the best options.
9.3. Tour Packages
Explore Vietnam with SIXT.VN’s curated tour packages. Whether you’re interested in cultural tours, historical sites, or natural landscapes, we have a tour package for you.
9.4. Car Rental Services
Enjoy the freedom to explore Vietnam at your own pace with SIXT.VN’s car rental services. We offer a wide range of vehicles to suit your needs.
9.5. Flight Booking Services
SIXT.VN helps you find the best deals on flights to Vietnam. Our flight booking services ensure you get the most convenient and affordable options.
9.6. Local Expertise
Leverage SIXT.VN’s local expertise for personalized recommendations and insights, enhancing your travel experience with authentic cultural and culinary experiences.
9.7. 24/7 Support
Enjoy peace of mind with SIXT.VN’s round-the-clock customer support, ready to assist with any queries or issues during your trip.
9.8. Streamlined Booking Process
SIXT.VN’s user-friendly platform ensures a seamless booking experience for all your travel needs, from accommodations to transportation.
9.9. Comprehensive Travel Solutions
From visa assistance to travel insurance, SIXT.VN offers comprehensive solutions, ensuring a hassle-free and secure journey throughout Vietnam.
10. Conclusion: Embracing the Science and Planning Your Trip with SIXT.VN
Understanding the fundamental difference between mechanical and electromagnetic waves not only enhances your scientific knowledge but also provides practical insights into various technologies and natural phenomena. Planning your trip to Vietnam with SIXT.VN ensures a seamless and enjoyable experience, allowing you to explore the country’s rich culture and stunning landscapes without any hassle.
Ready to explore Vietnam? SIXT.VN is here to help! Contact us today to plan your perfect trip!
Contact Information:
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can sound travel through space?
No, sound cannot travel through space because it is a mechanical wave and requires a medium to propagate.
2. What type of wave is light?
Light is an electromagnetic wave, which means it can travel through both a medium and empty space.
3. Why do astronauts use radio waves to communicate?
Astronauts use radio waves because they are electromagnetic waves and can travel through the vacuum of space, unlike sound waves.
4. What is a medium in the context of wave propagation?
A medium is a substance or material that allows mechanical waves to travel through it by vibrating or oscillating its particles.
5. How do electromagnetic waves travel?
Electromagnetic waves travel through the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields, which generate each other and propagate through space.
6. What are some examples of mechanical waves?
Examples of mechanical waves include sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves.
7. What are some examples of electromagnetic waves?
Examples of electromagnetic waves include light waves, radio waves, X-rays, and microwaves.
8. How does temperature affect the speed of sound?
The speed of sound increases with temperature. In warmer temperatures, air molecules move faster, allowing sound waves to travel more quickly.
9. What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
10. How do sunglasses use polarization to reduce glare?
Sunglasses use polarized lenses to block horizontally polarized light, which is a major component of glare reflected off surfaces like water or roads. The lenses only allow vertically polarized light to pass through, reducing the intensity of glare.



