Light speed embodies the universe’s ultimate velocity, and SIXT.VN helps you explore Vietnam with unmatched efficiency. It only takes a fraction of a second for light to circle Earth, yet exploring Vietnam’s rich culture and stunning landscapes can be just as swift and seamless with our premium travel services. Unlock seamless travel experiences and discover the beauty of Vietnam with SIXT.VN, your trusted travel companion.
1. What Is the Speed of Light and How Does It Relate to Traveling Around the Earth?
The speed of light, a universal constant, is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (or about 186,282 miles per second). In simpler terms, light travels incredibly fast. It is so fast that a beam of light can travel around the entire Earth in a mere fraction of a second. Understanding this concept helps appreciate how swiftly information and energy can propagate across vast distances. This understanding allows us to improve travel options in Vietnam.
1.1. Breaking Down the Speed of Light
To truly grasp the speed of light, let’s break it down:
- Meters per Second: Light travels 299,792,458 meters every second. This is the standard scientific measurement.
- Miles per Second: In more familiar units, this equates to about 186,282 miles per second.
- Circumference of Earth: The Earth’s circumference is approximately 24,901 miles.
When you divide the Earth’s circumference by the speed of light, you find that light can travel around the world in roughly 0.13 seconds.
1.2. The Significance of This Speed
The fact that light can circle the Earth so quickly highlights its immense speed. This speed is not just a number; it is a fundamental aspect of how the universe operates. It affects everything from communication to astronomy.
- Communication: Modern communication systems, such as fiber optic cables, rely on the speed of light to transmit data across continents almost instantaneously.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use the speed of light to measure distances in space. A light-year, for example, is the distance light travels in one year.
1.3. How Fast Does Light Travel Around the Earth Compared to Other Speeds?
To put the speed of light into perspective, consider these comparisons:
- Speed of Sound: The speed of sound is about 767 miles per hour (about 343 meters per second). Light is vastly faster, making sound seem slow in comparison.
- Commercial Airplane: A typical commercial airplane travels at around 500-600 miles per hour. Light is hundreds of thousands of times faster.
- Fastest Bullet: Even the fastest bullet travels at speeds of around 2,700 miles per hour, which is still a tiny fraction of the speed of light.
These comparisons illustrate just how unparalleled the speed of light is, dwarfing everyday speeds that we experience.
2. How Is the Calculation Made to Determine the Travel Time of Light Around the Earth?
Calculating how quickly light travels around the Earth involves a simple yet insightful formula: dividing the Earth’s circumference by the speed of light. This calculation underscores the immense velocity at which light propagates, making it an essential concept in physics and travel.
2.1. Understanding the Formula
The basic formula to calculate the travel time of light around the Earth is:
Time = Distance / Speed
Where:
- Distance is the circumference of the Earth.
- Speed is the speed of light.
2.2. Earth’s Circumference
The Earth is not a perfect sphere. Its circumference varies depending on where you measure it. However, for the purpose of this calculation, we use the average circumference:
- Average Circumference: Approximately 40,075 kilometers (24,901 miles)
This measurement provides a standard distance for our calculation.
2.3. Speed of Light
The speed of light is a constant, denoted as c, and is approximately:
- Speed of Light (c): 299,792,458 meters per second (186,282 miles per second)
This constant is crucial for various calculations in physics and astronomy.
2.4. Step-by-Step Calculation
-
Convert Units: Ensure that the units are consistent. Since the speed of light is often given in meters per second, convert the Earth’s circumference to meters:
- 40,075 kilometers = 40,075,000 meters
-
Apply the Formula: Use the formula Time = Distance / Speed:
- Time = 40,075,000 meters / 299,792,458 meters per second
-
Calculate: Perform the division:
- Time ≈ 0.134 seconds
Thus, light can travel around the Earth in approximately 0.134 seconds.
2.5. Practical Implications of This Calculation
While this calculation may seem purely theoretical, it has several practical implications:
- Global Communication: Understanding the speed at which signals travel helps in optimizing global communication networks.
- Satellite Technology: The delay in signals sent to and from satellites is influenced by the speed of light, affecting satellite communication and navigation systems.
- Travel Planning: Though humans cannot travel at the speed of light, appreciating its speed highlights the efficiency of modern travel methods. SIXT.VN leverages this understanding to provide seamless and efficient travel services in Vietnam.
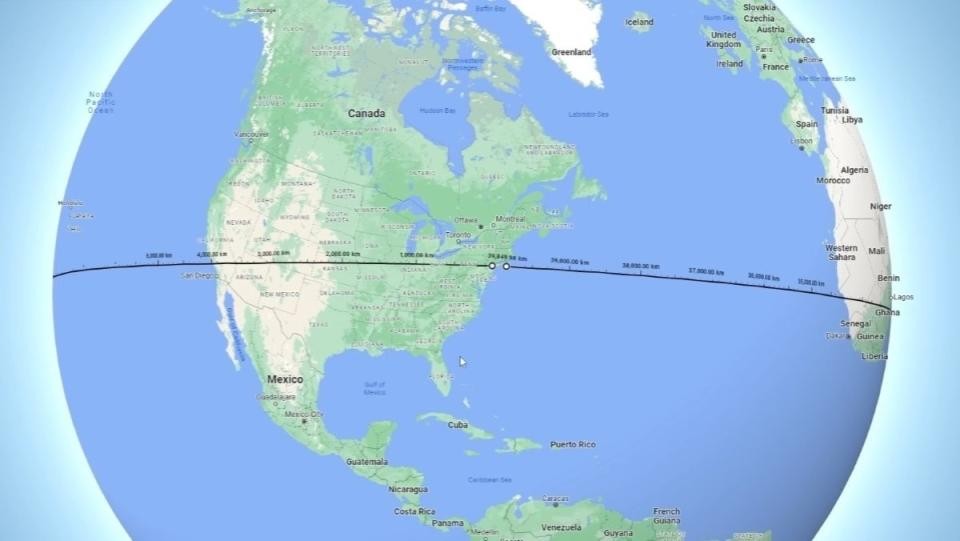 A Google Earth image showing a line from New York City going around the Earth
A Google Earth image showing a line from New York City going around the Earth
Alt: A line from New York City encircling the Earth, illustrating the concept of light traveling around the globe, promoting global connectivity and efficient travel planning.
3. What Are Some Common Misconceptions About the Speed of Light?
Despite being a fundamental concept in physics, the speed of light is often misunderstood. Addressing these misconceptions can lead to a better appreciation of its true nature. It can also improve travel within Vietnam.
3.1. Misconception 1: Light Travels Instantly
Reality: While light travels incredibly fast, it does not travel instantly. It has a finite speed, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
- Explanation: The idea that light is instantaneous is intuitive because, in our everyday experiences, light seems to appear immediately. However, precise measurements have proven that it takes time for light to travel, especially over vast distances.
3.2. Misconception 2: Nothing Can Travel Faster Than Light
Reality: According to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, nothing that has mass can travel faster than light in a vacuum.
- Explanation: This is a cornerstone of modern physics. Objects with mass require infinite energy to reach the speed of light, making it impossible. However, there are some exceptions. For example, in certain mediums (like water), particles can travel faster than the speed of light in that medium, although they are still slower than light in a vacuum.
3.3. Misconception 3: Light Always Travels at the Same Speed
Reality: The speed of light is constant in a vacuum, but it can slow down when traveling through different mediums, such as air, water, or glass.
- Explanation: When light enters a medium, it interacts with the atoms and molecules, causing it to slow down. This is why refraction occurs when light passes through a prism. The speed of light in a vacuum is the absolute maximum.
3.4. Misconception 4: Light Is Only Important in Physics and Astronomy
Reality: Light plays a crucial role in many areas of science and technology, including communication, medicine, and engineering.
- Explanation: Fiber optic cables use light to transmit data, medical imaging techniques rely on light, and lasers are used in manufacturing and surgery. The properties of light are fundamental to these technologies.
3.5. Misconception 5: The Speed of Light Has Always Been Known
Reality: The speed of light was not always known. It took centuries of scientific inquiry to measure it accurately.
- Explanation: Early attempts to measure the speed of light were made by Galileo in the 17th century. However, the first successful measurement was made by Ole Rømer in 1676, who observed variations in the timing of eclipses of Jupiter’s moon Io.
4. What Practical Applications Exist That Are Based on the Speed of Light?
The speed of light is not just a theoretical concept; it has numerous practical applications that impact our daily lives and technological advancements. Understanding these applications illustrates its importance beyond academic circles. SIXT.VN applies this knowledge to improve travel.
4.1. Fiber Optic Communication
Application: Transmitting data over long distances using light signals through glass or plastic fibers.
- Explanation: Fiber optic cables use the speed of light to transmit information quickly and efficiently. These cables are used for internet, telephone, and cable television services. The high speed of light allows for minimal delays in data transmission, making real-time communication possible across continents.
- Relevance: According to research from Fiber Optics Association in 2023, fiber optic networks provide faster and more reliable internet connections, which are crucial for modern communication.
4.2. Satellite Communication
Application: Communicating with satellites in orbit around the Earth.
- Explanation: The speed of light affects the time it takes for signals to travel to and from satellites. This is important for satellite television, GPS navigation, and weather forecasting. Engineers must account for the delay caused by the finite speed of light when designing and operating satellite systems.
- Relevance: According to a report by the Global Satellite Industry Association in 2022, satellite communication is vital for remote areas and global connectivity, relying on the speed of light for timely data transmission.
4.3. Medical Imaging
Application: Using light-based technologies for medical diagnostics.
- Explanation: Techniques like endoscopy, laser surgery, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) rely on the properties of light. These technologies allow doctors to see inside the human body without invasive procedures, diagnose diseases, and perform precise treatments.
- Relevance: According to the National Institutes of Health in 2021, medical imaging technologies based on light offer non-invasive diagnostic tools that improve patient outcomes.
4.4. Laser Technology
Application: Utilizing lasers in various industries, including manufacturing, entertainment, and research.
- Explanation: Lasers use focused beams of light for cutting, welding, barcode scanning, and creating special effects. The precision and speed of lasers make them invaluable in these applications. Lasers also play a crucial role in scientific research, such as in spectroscopy and quantum computing.
- Relevance: According to a study by the Laser Institute of America in 2023, laser technology enhances manufacturing precision and efficiency, leading to higher quality products and reduced costs.
4.5. GPS Navigation
Application: Determining location using signals from GPS satellites.
- Explanation: GPS satellites send signals to receivers on Earth, and the time it takes for these signals to arrive is used to calculate the receiver’s location. The accuracy of GPS depends on knowing the speed of light and accounting for the small delays caused by atmospheric effects.
- Relevance: According to a report by the European Global Navigation Satellite Systems Agency in 2022, GPS navigation relies on accurate timing signals, which are dependent on the constant speed of light for precise location determination.
4.6. Astronomy and Space Exploration
Application: Measuring distances in space and studying celestial objects.
- Explanation: Astronomers use the speed of light to measure vast distances in the universe. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, which is about 9.46 trillion kilometers. By observing the light from distant stars and galaxies, astronomers can learn about their composition, age, and motion.
- Relevance: According to NASA in 2023, the speed of light is essential for understanding the scale of the universe and for studying distant celestial objects, enabling discoveries about the cosmos.
5. How Does the Speed of Light Influence Our Understanding of Time and Space?
The speed of light has profoundly influenced our understanding of time and space, particularly through Einstein’s theory of special relativity. This theory has revolutionized physics and our comprehension of the universe. SIXT.VN embraces new understanding of time and space to improve travel.
5.1. Einstein’s Theory of Special Relativity
Key Concept: Einstein’s theory, published in 1905, postulates that the speed of light in a vacuum is the same for all observers, regardless of the motion of the light source.
- Implications: This seemingly simple idea has radical implications:
- Time Dilation: Time can pass differently for observers in relative motion. If you are moving close to the speed of light, time slows down for you relative to a stationary observer.
- Length Contraction: The length of an object moving at high speed appears shorter in the direction of motion to an observer who is at rest.
- Mass Increase: As an object approaches the speed of light, its mass increases, requiring more energy to accelerate it further.
5.2. Time Dilation Explained
Scenario: Imagine an astronaut traveling in a spaceship at a significant fraction of the speed of light.
- Observation: For the astronaut, time passes normally. However, for an observer on Earth, time passes more slowly for the astronaut. This effect is known as time dilation.
- Formula: The time dilation effect is described by the formula:
- t’ = t / √(1 – v²/c²)
- Where t’ is the time observed by the stationary observer, t is the time experienced by the moving astronaut, v is the astronaut’s speed, and c is the speed of light.
5.3. Length Contraction Explained
Scenario: Consider the same astronaut traveling at high speed.
- Observation: To an observer on Earth, the spaceship appears shorter in the direction of motion. This is length contraction.
- Formula: The length contraction effect is described by the formula:
- L’ = L * √(1 – v²/c²)
- Where L’ is the length observed by the stationary observer, L is the original length of the spaceship, v is the astronaut’s speed, and c is the speed of light.
5.4. Mass Increase Explained
Scenario: As the astronaut accelerates, the spaceship becomes more massive.
- Observation: The mass increase is not noticeable at everyday speeds, but it becomes significant as the speed approaches the speed of light.
- Formula: The mass increase is described by the formula:
- m’ = m / √(1 – v²/c²)
- Where m’ is the mass observed at high speed, m is the rest mass, v is the speed, and c is the speed of light.
5.5. Implications for Space Travel
Challenge: Reaching even a fraction of the speed of light requires immense amounts of energy.
- Practicality: While the effects of time dilation and length contraction could make interstellar travel feasible for astronauts, the energy requirements are currently beyond our technological capabilities.
- Future Prospects: Research into advanced propulsion systems, such as fusion rockets or warp drives, may one day make faster-than-light travel a reality.
5.6. Real-World Applications
GPS Satellites: The effects of special relativity must be accounted for in GPS satellite systems.
- Accuracy: Without correcting for time dilation, GPS systems would quickly become inaccurate, leading to errors in navigation.
- Technology: Atomic clocks on GPS satellites experience time dilation due to their motion relative to observers on Earth, requiring precise corrections.
6. What Role Does the Speed of Light Play in Astronomy?
In astronomy, the speed of light is more than just a constant; it’s a fundamental tool for measuring distances, understanding the age of the universe, and studying celestial objects. Grasping its role allows astronomers to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.
6.1. Measuring Cosmic Distances
Light-Year: A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers (5.88 trillion miles).
- Usage: Astronomers use light-years to measure distances to stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects.
- Example: The nearest star system to our Sun, Alpha Centauri, is about 4.37 light-years away. This means it takes light 4.37 years to travel from Alpha Centauri to Earth.
Parsec: Another unit of distance used in astronomy is the parsec, which is approximately 3.26 light-years.
- Definition: A parsec is defined as the distance at which an object has a parallax angle of one arcsecond.
- Application: Parsecs are used to measure the distances to more distant objects within our galaxy and beyond.
6.2. Determining the Age of the Universe
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): The CMB is the afterglow of the Big Bang, the event that created the universe.
- Observation: By studying the CMB, astronomers can determine the age of the universe.
- Age: The current estimate for the age of the universe is about 13.8 billion years, based on observations of the CMB and other cosmological data.
Redshift: Redshift is the phenomenon where light from distant galaxies is stretched, causing its wavelength to increase.
- Explanation: This stretching is due to the expansion of the universe. The greater the redshift, the farther away the galaxy and the faster it is receding from us.
- Application: By measuring the redshift of galaxies, astronomers can estimate their distances and study the expansion rate of the universe.
6.3. Studying Celestial Objects
Spectroscopy: Spectroscopy is the study of the light emitted or absorbed by celestial objects.
- Analysis: By analyzing the spectrum of light, astronomers can determine the object’s composition, temperature, density, and motion.
- Technique: Each element has a unique spectral fingerprint, allowing astronomers to identify the elements present in stars, planets, and nebulae.
Time Delay: The finite speed of light means that when we observe distant objects, we are seeing them as they were in the past.
- Implication: For example, when we look at a galaxy that is 10 billion light-years away, we are seeing it as it was 10 billion years ago.
- Advantage: This allows astronomers to study the evolution of the universe over cosmic time scales.
6.4. Gravitational Lensing
Phenomenon: Gravitational lensing occurs when the gravity of a massive object, such as a galaxy or black hole, bends the path of light from a more distant object.
- Effect: This can magnify and distort the image of the distant object, making it easier to study.
- Application: Astronomers use gravitational lensing to study faint and distant galaxies that would otherwise be too difficult to observe.
6.5. Implications for Understanding the Cosmos
Cosmology: The speed of light plays a central role in cosmology, the study of the origin, evolution, and structure of the universe.
- Models: Cosmological models are based on the laws of physics, including the constancy of the speed of light.
- Advancements: These models help astronomers understand the large-scale structure of the universe, the distribution of galaxies, and the nature of dark matter and dark energy.
7. How Can Understanding the Speed of Light Enhance Travel Experiences?
While humans can’t travel at the speed of light, understanding it indirectly enhances travel experiences by influencing technology, logistics, and our appreciation of distances. SIXT.VN uses these principles to enhance travel.
7.1. Improving Communication
Global Connectivity: The speed of light enables fast and reliable communication across the globe, which is crucial for travel.
- Real-Time Information: Travelers can access real-time information about flights, weather, and local conditions, ensuring they are always informed.
- Staying Connected: Tourists can easily stay in touch with family and friends, sharing their experiences and staying safe.
Fiber Optic Networks: Fiber optic cables transmit data at the speed of light, facilitating seamless communication.
- Benefits: This results in faster internet speeds and more reliable connections, making it easier to book accommodations, navigate unfamiliar areas, and access online resources.
- SIXT.VN Advantage: With reliable communication, SIXT.VN can promptly address any travel concerns or queries, ensuring a smooth experience.
7.2. Enhancing Navigation
GPS Technology: The Global Positioning System (GPS) relies on signals from satellites that travel at the speed of light.
- Precision: GPS allows travelers to pinpoint their location accurately, making it easier to navigate unfamiliar cities and rural areas.
- SIXT.VN Navigation: SIXT.VN integrates GPS technology into its services, providing accurate directions for airport transfers, hotel bookings, and sightseeing tours.
Real-Time Traffic Updates: GPS data is used to provide real-time traffic updates, helping travelers avoid congestion and delays.
- Efficiency: This ensures that travelers reach their destinations quickly and efficiently, maximizing their time for exploration.
- SIXT.VN Efficiency: SIXT.VN uses real-time traffic data to optimize routes for its transportation services, guaranteeing punctual and stress-free travel.
7.3. Advancing Transportation Technology
Airplane Technology: Understanding aerodynamics and propulsion, influenced by the speed of light, has led to the development of faster and more efficient airplanes.
- Reduced Travel Time: Modern aircraft can cover vast distances in a matter of hours, connecting people and cultures like never before.
- SIXT.VN Partnerships: SIXT.VN partners with airlines to offer competitive flight deals, enabling travelers to reach Vietnam quickly and comfortably.
High-Speed Trains: High-speed trains, which travel at hundreds of miles per hour, are another example of how technology has reduced travel time.
- Convenience: These trains offer a convenient and eco-friendly alternative to air travel, allowing travelers to explore multiple destinations within a country.
- SIXT.VN Connectivity: SIXT.VN provides seamless connections to high-speed rail networks, making it easy for travelers to explore Vietnam’s diverse regions.
7.4. Appreciating Distances and Time
Perspective: Understanding the speed of light gives travelers a greater appreciation for the vast distances involved in global travel.
- Cultural Exchange: It highlights how technology has shrunk the world, making it easier to experience different cultures and connect with people from all walks of life.
- SIXT.VN Exploration: SIXT.VN encourages travelers to embrace this global perspective, offering curated tours and experiences that showcase Vietnam’s unique cultural heritage.
Time Management: By understanding the speed at which information travels, travelers can better manage their time and plan their itineraries efficiently.
- Efficient Planning: This allows them to make the most of their trip, seeing more sights and engaging in more activities.
- SIXT.VN Planning Tools: SIXT.VN provides comprehensive travel planning tools, including customizable itineraries, to help travelers optimize their time in Vietnam.
7.5. Inspiring Future Travel Technologies
Space Tourism: While still in its infancy, space tourism holds the potential to revolutionize travel, offering unparalleled views of Earth and the cosmos.
- Technological Advancements: Advances in propulsion systems and spacecraft design, inspired by the speed of light, are making space tourism a reality.
- SIXT.VN Vision: SIXT.VN envisions a future where space travel is accessible to a wider audience, offering unforgettable experiences beyond our planet.
Hypothetical Technologies: Concepts like warp drives and wormholes, while currently theoretical, inspire scientists and engineers to push the boundaries of what is possible in travel.
- Innovation: These ideas fuel innovation and may one day lead to breakthroughs that dramatically reduce travel time.
- SIXT.VN Innovation: SIXT.VN remains at the forefront of travel innovation, exploring new technologies and partnerships to enhance the travel experience for its customers.
8. What Are Some Examples of Science Fiction Concepts Related to the Speed of Light?
Science fiction often explores concepts related to the speed of light, pushing the boundaries of imagination and inspiring scientific inquiry. Here are some notable examples:
8.1. Warp Drive (Star Trek)
Concept: A technology that allows spacecraft to travel faster than light by warping space-time around them.
- Description: In Star Trek, the warp drive creates a “bubble” of space-time that surrounds the ship, allowing it to move at multiples of the speed of light without violating the laws of physics.
- Impact: The warp drive is a staple of Star Trek, enabling exploration of distant galaxies and encounters with diverse alien civilizations.
Scientific Basis: While currently theoretical, scientists are exploring the possibility of warp drives using concepts from general relativity.
- Challenges: The energy requirements for creating and sustaining a warp bubble are immense, and the concept faces significant technical hurdles.
8.2. Hyperspace (Star Wars)
Concept: An alternate dimension that allows spacecraft to travel faster than light by bypassing normal space.
- Description: In Star Wars, hyperspace is a parallel universe that can be accessed through specific routes, allowing ships to travel vast distances in a relatively short time.
- Impact: Hyperspace is essential for interstellar travel in the Star Wars universe, connecting planets and facilitating galactic commerce and warfare.
Scientific Basis: The concept of hyperspace is purely fictional, although it draws inspiration from theoretical physics concepts like higher dimensions.
- Differences: Unlike warp drive, hyperspace does not involve warping space-time but rather traveling through a different realm altogether.
8.3. Wormholes (Various)
Concept: Theoretical tunnels that connect two distant points in space-time, allowing for near-instantaneous travel.
- Description: Wormholes are often depicted as shortcuts through the universe, bypassing the limitations of the speed of light. They have appeared in numerous science fiction works, including Contact, Interstellar, and Stargate.
- Impact: Wormholes provide a convenient plot device for enabling interstellar and intergalactic travel, connecting disparate worlds and civilizations.
Scientific Basis: Wormholes are predicted by Einstein’s theory of general relativity, but their existence has not been confirmed.
- Challenges: Creating and stabilizing a wormhole would require exotic matter with negative mass-energy density, which has never been observed.
8.4. Light Speed in “The Forever War”
Concept: This science fiction novel explores the consequences of near-light-speed travel on human relationships and society.
- Description: Soldiers traveling at relativistic speeds experience significant time dilation, causing them to age much slower than people on Earth.
- Impact: This creates a profound sense of alienation and disconnect as the soldiers return home to find that decades or even centuries have passed.
8.5. Faster-Than-Light Communication (Ender’s Game)
Concept: This science fiction book features instantaneous communication across interstellar distances.
- Description: The ansible is a device that allows characters to communicate with each other regardless of the distance separating them.
- Impact: FTL communication enables real-time strategic coordination in warfare.
8.6. Influence on Scientific Thought
Inspiration: Science fiction concepts related to the speed of light have inspired scientists and engineers to think creatively about the possibilities of space travel and communication.
- Research: While many of these concepts remain in the realm of fiction, they serve as a reminder of the potential for future technological breakthroughs.
- Innovation: By pushing the boundaries of imagination, science fiction encourages us to explore new frontiers and challenge conventional wisdom.
9. How Can You Experience Vietnam Efficiently with SIXT.VN?
Exploring Vietnam can be an enriching experience, and SIXT.VN ensures you do so with utmost efficiency and convenience. From airport transfers to curated tours, we’ve got you covered.
9.1. Streamlined Airport Transfers
Service: SIXT.VN provides seamless airport transfer services, ensuring a smooth transition from the airport to your hotel or destination.
- Convenience: Avoid the hassle of navigating public transportation or waiting in long taxi queues.
- Punctuality: Our professional drivers are punctual and reliable, ensuring you reach your destination on time.
Booking: Easily book your airport transfer online through our user-friendly platform.
- Customization: Choose from a range of vehicles to suit your needs, whether you’re traveling solo or with a group.
- Confirmation: Receive instant confirmation and detailed instructions, so you know exactly what to expect.
9.2. Comfortable Hotel Bookings
Options: SIXT.VN offers a wide selection of hotels to suit every budget and preference.
- Variety: From luxury resorts to boutique hotels, find the perfect accommodation for your stay in Vietnam.
- Locations: Choose from prime locations in major cities and popular tourist destinations.
Ease of Booking: Our online booking platform makes it easy to compare prices, read reviews, and book your hotel in just a few clicks.
- Secure Transactions: Rest assured that your transactions are secure and your personal information is protected.
- Support: Our customer support team is available 24/7 to assist you with any questions or concerns.
9.3. Curated Tours and Activities
Experiences: SIXT.VN offers a variety of curated tours and activities, designed to showcase the best of Vietnam.
- Cultural Tours: Immerse yourself in Vietnam’s rich history and culture with guided tours of ancient temples, historical sites, and local markets.
- Adventure Tours: Explore Vietnam’s stunning natural landscapes with hiking, biking, and kayaking tours.
Customization: Customize your tour to fit your interests and schedule.
- Flexibility: Choose from half-day, full-day, and multi-day tours.
- Expert Guides: Our knowledgeable guides will provide insights and stories that bring Vietnam to life.
9.4. Efficient Transportation Options
Car Rentals: Explore Vietnam at your own pace with our car rental services.
- Wide Selection: Choose from a range of vehicles, from compact cars to SUVs.
- Flexibility: Enjoy the freedom to travel wherever you want, whenever you want.
Private Car Service: Hire a private car with a driver for a comfortable and convenient way to get around.
- Relaxation: Sit back and relax while your driver navigates the busy streets of Vietnam.
- Efficiency: Maximize your time and see more sights with our private car service.
9.5. 24/7 Customer Support
Assistance: SIXT.VN provides 24/7 customer support to assist you with any travel-related issues.
- Availability: Whether you have a question about your booking or need assistance with directions, our team is always here to help.
- Multiple Channels: Contact us via phone, email, or live chat for prompt and efficient assistance.
9.6. Contact Information
For any inquiries or assistance, please contact us:
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
10. FAQs About the Speed of Light
Here are some frequently asked questions about the speed of light, providing clarity on this fascinating topic.
10.1. What is the exact speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is exactly 299,792,458 meters per second (approximately 186,282 miles per second).
10.2. Why is the speed of light important in physics?
The speed of light is a fundamental constant in physics because it is the maximum speed at which information or energy can travel. It is also a key component in Einstein’s theory of relativity.
10.3. Can anything travel faster than light?
According to current understanding, nothing that has mass can travel faster than light in a vacuum. However, there are some theoretical concepts, like warp drives and wormholes, that might allow for faster-than-light travel.
10.4. Does light travel at the same speed in all mediums?
No, light travels at its maximum speed in a vacuum. When it passes through other mediums, such as air, water, or glass, it slows down.
10.5. How was the speed of light first measured?
The first successful measurement of the speed of light was made by Ole Rømer in 1676, who observed variations in the timing of eclipses of Jupiter’s moon Io.
10.6. What is a light-year?
A light-year is the distance light travels in one year, approximately 9.46 trillion kilometers (5.88 trillion miles).
10.7. How does the speed of light affect our understanding of time?
The speed of light is central to Einstein’s theory of special relativity, which describes how time can pass differently for observers in relative motion, leading to phenomena like time dilation.
10.8. What are some practical applications of the speed of light?
Practical applications include fiber optic communication, satellite communication, medical imaging, laser technology, and GPS navigation.
10.9. How does GPS rely on the speed of light?
GPS satellites send signals to receivers on Earth, and the time it takes for these signals to arrive is used to calculate the receiver’s location. The accuracy of GPS depends on knowing the speed of light.
10.10. How does SIXT.VN use the concept of speed to improve travel experiences?
SIXT.VN uses the principles of efficient communication, navigation, and transportation to provide seamless and convenient travel services, ensuring travelers can explore Vietnam with ease and speed.
Ready to explore Vietnam with the efficiency of light speed? SIXT.VN offers seamless travel solutions, from airport transfers to curated tours. Contact us today to plan your unforgettable journey! Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. Website: SIXT.VN. Discover Vietnam with SIXT.VN – where your adventure awaits!



