Are you curious about wave mechanics and how they behave in different environments while planning your Vietnam adventure? Mechanical waves and their ability to travel through space are fascinating topics. Let’s explore whether mechanical waves can journey through the vast emptiness of space. Discover the answers with SIXT.VN, your trusted travel companion in Vietnam, offering seamless travel experiences from airport transfers to hotel bookings.
1. What Are Mechanical Waves and How Do They Propagate?
Mechanical waves require a medium to travel.
Mechanical waves, such as sound waves or water waves, are disturbances that propagate through a medium, which can be a solid, liquid, gas, or plasma. These waves transmit energy by causing particles in the medium to vibrate. According to research from the University of Cambridge, mechanical waves transfer energy through molecular collisions within the medium.
1.1. Understanding the Medium’s Role
A medium is crucial for the propagation of mechanical waves. The wave’s energy is transferred from one particle to another in the medium. Without a medium, there are no particles to vibrate, and the wave cannot travel. The speed of a mechanical wave depends on the properties of the medium, such as density and elasticity.
1.2. Examples of Mechanical Waves
Here are some common examples of mechanical waves:
- Sound Waves: Travel through air, water, or solids.
- Water Waves: Propagate on the surface of water.
- Seismic Waves: Move through the Earth’s crust.
- Waves on a String: Travel along a stretched string or rope.
These waves all require a physical medium to carry their energy.
2. What is Space and Why Can’t Mechanical Waves Travel Through It?
Space is a vacuum, and mechanical waves need a medium to propagate, which is why they can’t travel through space.
Space, for the most part, is a vacuum, meaning it contains very little matter. In the absence of a medium, mechanical waves cannot propagate. This is because the mechanism by which these waves transfer energy involves the vibration of particles in a medium. Without these particles, there is nothing to sustain the wave motion.
2.1. The Vacuum of Space
The vacuum of space is characterized by extremely low density. While it’s not a perfect vacuum, the amount of matter present is insufficient to support the propagation of mechanical waves. According to NASA, the density of interstellar space is about 1 atom per cubic centimeter, which is far too sparse for mechanical waves to travel effectively.
2.2. Contrasting with Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves, do not require a medium to travel. They can propagate through the vacuum of space because they are disturbances in electric and magnetic fields, not physical vibrations of matter. This fundamental difference allows us to see stars and receive radio signals from distant galaxies.
3. How Do Electromagnetic Waves Differ from Mechanical Waves?
Electromagnetic waves don’t need a medium, unlike mechanical waves, and travel through the vacuum of space via oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
Electromagnetic waves and mechanical waves differ significantly in their propagation mechanisms. Mechanical waves require a medium, while electromagnetic waves do not. Electromagnetic waves consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that sustain each other, allowing them to travel through the vacuum of space.
3.1. Key Differences
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between electromagnetic and mechanical waves:
| Feature | Mechanical Waves | Electromagnetic Waves |
|---|---|---|
| Medium Required | Yes | No |
| Propagation Method | Vibration of particles in a medium | Oscillating electric and magnetic fields |
| Examples | Sound waves, water waves, seismic waves | Light waves, radio waves, X-rays |
| Speed | Dependent on the medium | Constant in a vacuum (speed of light) |
| Energy Transfer | Kinetic energy transfer through particle collisions | Energy transfer through electromagnetic field changes |
3.2. Implications for Space Travel
The ability of electromagnetic waves to travel through space is crucial for communication and observation in astronomy. Without electromagnetic waves, we would not be able to receive signals from satellites, explore distant galaxies, or study the universe.
4. What Happens to Sound in Space?
Sound cannot travel in space because it needs a medium to propagate.
In space, sound cannot travel because there is no medium to carry the vibrations. Sound waves are mechanical waves that require a substance, such as air or water, to propagate. In the vacuum of space, there are not enough particles to transmit sound vibrations.
4.1. The Role of a Medium for Sound
Sound waves propagate through a medium by causing particles to vibrate. These vibrations transfer energy from one particle to the next, allowing the sound wave to travel. The speed of sound depends on the properties of the medium, such as density and temperature.
4.2. Experiencing Silence in Space
Astronauts in space cannot hear each other directly unless they are in contact through a solid medium, such as their spacecraft. Communication in space relies on radio waves, which are electromagnetic waves that can travel through the vacuum.
5. Are There Any Exceptions? Can Mechanical Waves Exist in Space in Some Forms?
While space is largely a vacuum, some regions contain sparse matter, but these conditions rarely support mechanical wave propagation.
While the vacuum of space generally prevents the propagation of mechanical waves, there are a few exceptions where sparse matter exists. However, these conditions are typically not conducive to sustaining mechanical waves over long distances.
5.1. Interstellar Medium
The interstellar medium (ISM) contains sparse gas and dust. While the density is low, it is not a perfect vacuum. However, the conditions in the ISM are not generally suitable for mechanical waves to propagate effectively due to the low density and other factors.
5.2. Plasma Waves
In certain regions of space, plasma waves can exist. Plasma is a state of matter in which gas is ionized and carries electrical charges. Plasma waves are complex phenomena that involve the interaction of charged particles and electromagnetic fields. While they share some characteristics with mechanical waves, they are fundamentally different and behave according to the principles of plasma physics.
6. How Are Radio Waves Used for Communication in Space?
Radio waves facilitate space communication because they are electromagnetic and travel through the vacuum of space without needing a medium.
Radio waves are used for communication in space because they are a type of electromagnetic wave that can travel through the vacuum without needing a medium. These waves are part of the electromagnetic spectrum and are characterized by their long wavelengths and low frequencies.
6.1. Why Radio Waves?
Radio waves are ideal for space communication for several reasons:
- Propagation in Vacuum: They can travel through the vacuum of space.
- Long Distance: They can travel long distances with minimal attenuation.
- Penetration: They can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Information Encoding: They can be modulated to carry information.
6.2. Communication Process
The process of using radio waves for communication involves:
- Encoding: Converting information (voice, data, images) into an electrical signal.
- Modulation: Superimposing the electrical signal onto a radio wave.
- Transmission: Broadcasting the radio wave from an antenna.
- Reception: Receiving the radio wave with an antenna.
- Demodulation: Extracting the electrical signal from the radio wave.
- Decoding: Converting the electrical signal back into the original information.
This process allows for reliable communication between Earth and spacecraft.
7. What Is the Speed of Electromagnetic Waves in Space?
Electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light in space, approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
In the vacuum of space, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (about 186,282 miles per second). This speed is a fundamental constant in physics, often denoted as c.
7.1. Factors Affecting Speed
The speed of electromagnetic waves can vary when they travel through a medium, such as air or water. The speed is affected by the properties of the medium, such as its refractive index. However, in the vacuum of space, there is no medium to slow down or alter the speed of electromagnetic waves.
7.2. Implications for Distance Measurement
The constant speed of light is used to measure distances in space. One light-year is the distance that light travels in one year, which is approximately 9.461 × 10^15 meters (about 5.879 trillion miles). This unit of measurement is essential for understanding the vast distances between stars and galaxies.
8. How Does the Absence of a Medium Affect Other Types of Waves?
The absence of a medium prevents mechanical waves like sound and water waves from traveling, but it does not affect electromagnetic waves.
The absence of a medium primarily affects mechanical waves, such as sound waves and water waves, by preventing their propagation. Electromagnetic waves, however, are unaffected and can travel freely.
8.1. Sound Waves
Sound waves cannot travel in the vacuum of space because they require a medium to transmit vibrations. Without a medium, there are no particles to vibrate, and sound cannot be heard.
8.2. Water Waves
Water waves, which are surface waves on a liquid, also require a medium. They cannot exist in the vacuum of space.
8.3. Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic waves, including light, radio waves, and X-rays, can travel through the vacuum of space because they do not rely on a medium. They consist of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that sustain each other.
9. What Are Some Applications of Understanding Wave Propagation?
Understanding wave propagation is crucial in fields like telecommunications, medical imaging, and space exploration, leading to technological advancements.
Understanding wave propagation has numerous applications in various fields, leading to technological advancements and improved quality of life.
9.1. Telecommunications
In telecommunications, understanding how electromagnetic waves propagate is essential for designing efficient communication systems. This includes:
- Radio and Television Broadcasting: Optimizing the transmission and reception of radio and television signals.
- Mobile Communications: Ensuring reliable mobile phone and data services.
- Satellite Communications: Facilitating communication between Earth and satellites.
9.2. Medical Imaging
In medical imaging, different types of waves are used to create images of the inside of the body. This includes:
- X-rays: Used for visualizing bones and detecting abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Used for imaging soft tissues and monitoring pregnancies.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Used for detailed imaging of organs and tissues.
9.3. Space Exploration
In space exploration, understanding wave propagation is critical for:
- Communication with Spacecraft: Ensuring reliable communication with spacecraft and rovers.
- Remote Sensing: Studying distant planets and galaxies using electromagnetic waves.
- Navigation: Using radio waves for navigation and positioning.
9.4. Other Applications
Other applications include:
- Geophysics: Studying the Earth’s interior using seismic waves.
- Oceanography: Studying ocean currents and waves using acoustic waves.
- Material Science: Characterizing materials using various types of waves.
10. FAQ About Mechanical Waves and Space
Here are some frequently asked questions about mechanical waves and their ability to travel through space.
Here are some frequently asked questions to clarify your understanding of mechanical waves and their behavior in space.
10.1. Can sound travel on the Moon?
No, sound cannot travel on the Moon because the Moon has virtually no atmosphere, meaning there is no medium to carry sound waves.
10.2. Why do astronauts use radios to communicate in space?
Astronauts use radios to communicate in space because radio waves are electromagnetic waves that can travel through the vacuum of space without a medium.
10.3. What is the difference between a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave?
A transverse wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of the wave. A longitudinal wave is a wave in which the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of the wave.
10.4. Can mechanical waves travel through a solid?
Yes, mechanical waves can travel through solids. Seismic waves, for example, travel through the Earth’s crust, which is solid.
10.5. Do all mechanical waves travel at the same speed?
No, the speed of a mechanical wave depends on the properties of the medium through which it is traveling. The speed of sound, for example, is different in air, water, and solids.
10.6. What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
The frequency and wavelength of a wave are inversely proportional. This means that as the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases, and vice versa. The relationship is described by the equation v = fλ, where v is the wave speed, f is the frequency, and λ is the wavelength.
10.7. How are electromagnetic waves used in everyday life?
Electromagnetic waves are used in many everyday applications, including:
- Mobile Phones: For wireless communication.
- Microwave Ovens: For heating food.
- Remote Controls: For controlling electronic devices.
- Medical Imaging: For diagnosing medical conditions.
10.8. What is the electromagnetic spectrum?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
10.9. Can mechanical waves be used for communication?
Yes, mechanical waves can be used for communication. For example, sonar uses sound waves to detect objects underwater, and seismic waves can be used to study the Earth’s interior.
10.10. What is the importance of understanding wave behavior?
Understanding wave behavior is important for designing and optimizing various technologies, including communication systems, medical imaging devices, and scientific instruments.
Mechanical waves cannot travel through space due to the absence of a medium, but this limitation highlights the unique properties of electromagnetic waves, which are essential for space communication and exploration. As you plan your trip to Vietnam, remember that just as understanding wave propagation is crucial for technology, understanding your travel needs is crucial for a smooth and enjoyable experience.
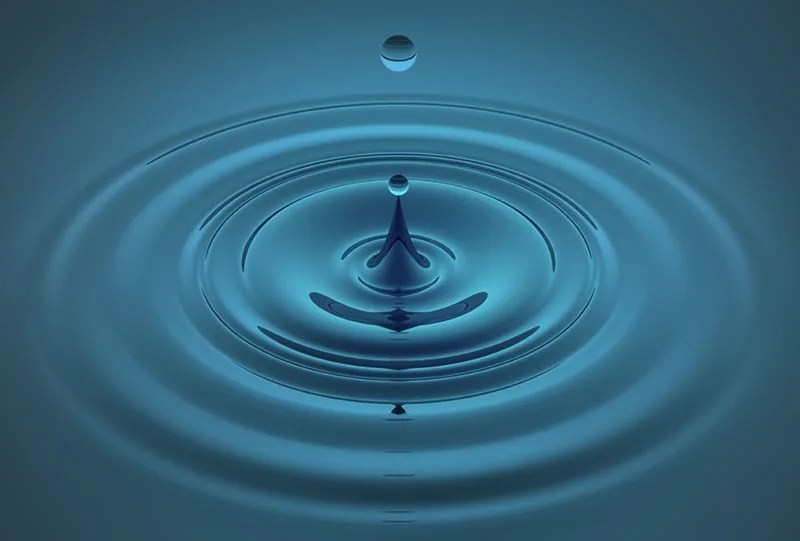 Ripples in a pool illustrating mechanical waves needing a medium.
Ripples in a pool illustrating mechanical waves needing a medium.
Planning Your Vietnam Adventure with SIXT.VN
Are you ready to explore the beauty of Vietnam? Whether you’re fascinated by science or simply seeking an unforgettable travel experience, SIXT.VN is here to assist. We understand the challenges travelers face, from language barriers to logistical concerns. That’s why we offer a range of services designed to make your trip seamless and enjoyable.
1. Tailored Travel Itineraries
SIXT.VN provides personalized travel itineraries that match your interests and schedule. Whether you’re interested in historical sites, natural wonders, or cultural experiences, we can create a custom plan just for you.
2. Convenient Airport Transfers
Start your trip stress-free with our reliable airport transfer service. Our professional drivers will greet you at the airport and ensure you reach your destination comfortably and safely.
3. Hotel Booking Assistance
Find the perfect accommodation with our hotel booking service. We offer a wide range of options to suit every budget and preference, from luxurious hotels to cozy guesthouses.
4. Guided Tours
Explore Hanoi and its surroundings with our expertly guided tours. Our knowledgeable guides will take you to the most iconic landmarks and hidden gems, providing fascinating insights into the local culture and history.
5. Flight Booking Services
Book your flights with ease through our flight booking service. We offer competitive prices and flexible options to fit your travel plans.
6. 24/7 Customer Support
Our dedicated customer support team is available 24/7 to assist with any questions or concerns you may have. We are committed to ensuring your trip is smooth and hassle-free.
7. Why Choose SIXT.VN?
- Convenience: We handle all the details, so you can relax and enjoy your trip.
- Reliability: Our services are dependable and trustworthy.
- Expertise: We have extensive knowledge of Vietnam and its travel destinations.
- Personalization: We tailor our services to meet your unique needs and preferences.
- Support: Our team is always available to assist you.
Don’t let the challenges of travel hold you back. Contact SIXT.VN today to start planning your dream vacation in Vietnam. Let us take care of the details so you can focus on creating lasting memories.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN
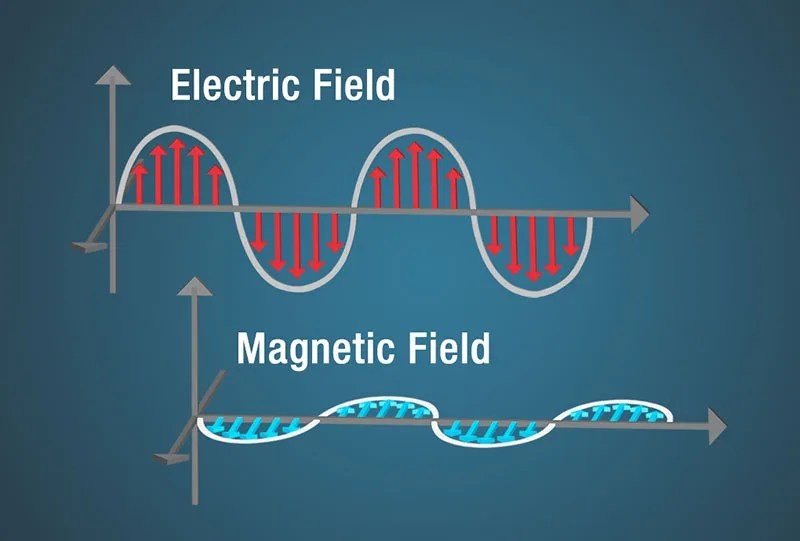 Diagram of electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave, showing the wave's structure.
Diagram of electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave, showing the wave's structure.
Ready to experience the best of Vietnam? Visit SIXT.VN now to explore our services and book your unforgettable adventure. We are here to make your travel dreams a reality.



