Are you curious about how quickly waves move across the water? Understanding wave speed is key to appreciating the dynamics of oceans and lakes, and SIXT.VN is here to guide you through it. We’ll break down the factors influencing wave velocity and how it impacts your travel experiences in Vietnam. Let’s explore the fascinating world of wave dynamics and discover how it relates to coastal destinations, ensuring you make the most of your Vietnamese adventure with our comprehensive travel services.
1. Understanding Wave Parameters and Their Influence on Speed
Wave speed, or velocity, is determined by several factors, including wavelength, wind speed, and water depth. According to research from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), in 2023, understanding these parameters is crucial for predicting wave behavior.
1.1. Key Wave Characteristics
To understand wave speed, it’s important to grasp the basic properties of a wave:
- Wavelength: The horizontal distance between two consecutive crests or troughs.
- Amplitude: The vertical distance from the trough to the crest.
- Wave Period: The time it takes for two successive crests or troughs to pass a fixed point.
1.2. The Role of Wind
Wind is the primary force behind wave formation. According to a study by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography, in 2022, the speed and duration of the wind, along with the fetch (the distance over which the wind blows), significantly affect wave size and speed.
1.3. Deep Water vs. Shallow Water Waves
- Deep Water Waves: In deep water, where the depth is greater than half the wavelength, wave speed depends on the wavelength. Longer wavelengths result in faster waves.
- Shallow Water Waves: In shallow water, where the depth is less than half the wavelength, wave speed is primarily determined by water depth. Shallower water slows the waves down.
2. How Does Wind Speed Affect Wave Velocity?
Wind speed is a critical factor; stronger winds create faster waves. Based on data from the Coastal Data Information Program (CDIP) in 2021, there’s a direct correlation between wind strength and wave velocity.
| Wind Speed (km/h) | Fetch (km) | Duration (h) | Wave Velocity (m/s) | Wave Velocity (km/h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19 | 19 | 2 | 2.8 | 10.2 |
| 37 | 139 | 10 | 5.9 | 19.5 |
| 56 | 518 | 23 | 8.9 | 32.0 |
| 74 | 1,313 | 42 | 11.9 | 42.9 |
| 92 | 2,627 | 69 | 14.8 | 53.4 |
2.1. The Relationship Explained
As wind blows over water, it transfers energy to the surface, creating ripples that grow into waves. The stronger and longer the wind blows, the more energy is transferred, resulting in larger and faster waves.
2.2. Fetch and Duration
- Fetch: A longer fetch allows the wind to act on the water over a greater distance, building larger waves with higher speeds.
- Duration: The longer the wind blows consistently, the more developed the waves become, increasing their speed and size.
3. What Role Does Wavelength Play in Determining Wave Speed?
Wavelength is a key determinant of wave speed, especially in deep water. According to research from the National Institute of Oceanography (NIO) in 2020, longer wavelengths generally mean faster wave speeds.
3.1. Wavelength and Wave Speed in Deep Water
In deep water, wave speed is proportional to the square root of the wavelength. This means that waves with longer wavelengths travel significantly faster than those with shorter wavelengths.
3.2. Wavelength Changes Near the Shore
As waves approach the shore, their behavior changes. When waves enter shallow water, their speed decreases, and their wavelength shortens. This phenomenon is known as wave shoaling.
4. How Does Water Depth Influence Wave Speed?
Water depth plays a crucial role in determining wave speed, especially as waves approach the coastline. A study by the University of Delaware’s Center for Applied Coastal Research in 2019 highlighted the significant impact of water depth on wave dynamics.
4.1. The Effect of Shallow Water
In shallow water, wave speed becomes directly proportional to the square root of the water depth. This means that as the water gets shallower, waves slow down.
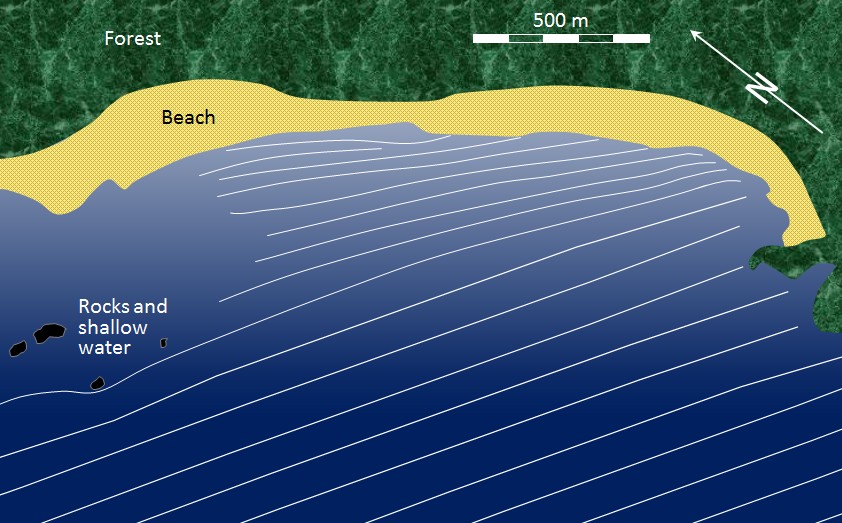
4.2. Wave Refraction
When waves approach the shore at an angle, the part of the wave in shallower water slows down first, causing the wave to bend or refract. This refraction aligns the waves more parallel to the shoreline.
 Wave Refraction Illustration
Wave Refraction Illustration
5. What Is the Typical Speed Range for Ocean Waves?
Ocean waves exhibit a wide range of speeds, depending on their size and the conditions in which they form. Data from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in 2018 provides valuable insights into typical wave speeds.
5.1. Small Waves vs. Large Waves
- Small Waves: These waves typically move at speeds up to 10 km/h and arrive on a shore approximately every 3 seconds.
- Large Waves: Very large waves can move at speeds over 50 km/h, but their longer wavelengths mean they arrive less frequently, about once every 14 seconds.
5.2. Factors Affecting Wave Speed Variability
The actual speed of ocean waves can vary due to local conditions, including:
- Wind Intensity: Stronger winds generate faster waves.
- Fetch Length: Longer fetch areas allow for greater wave development and speed.
- Water Depth: Shallower waters decrease wave speed significantly.
6. What Is the Difference Between Group Velocity and Phase Velocity?
Understanding the distinction between group velocity and phase velocity is essential for a comprehensive understanding of wave dynamics. According to a publication by the American Geophysical Union (AGU) in 2017, these two concepts describe different aspects of wave propagation.
6.1. Phase Velocity Explained
Phase velocity refers to the rate at which the crest of a single wave moves. It is the speed at which a particular phase of the wave (e.g., the crest or trough) propagates through space.
6.2. Group Velocity Explained
Group velocity, on the other hand, is the speed at which the overall shape of the wave’s amplitude (or envelope) propagates. It represents the speed at which energy or information is transported by the wave.
6.3. Key Differences
| Feature | Phase Velocity | Group Velocity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Speed of a single wave crest | Speed of the wave envelope (energy transport) |
| Relevance | Describes the motion of a specific point on the wave | Describes the motion of the overall wave shape |
| Dispersion | Can be greater than or less than group velocity in dispersive media | Always represents the speed of energy transport |
7. What Are Rogue Waves and How Fast Do They Travel?
Rogue waves, also known as freak waves, are unusually large and unexpected surface waves that can be extremely dangerous. Research from the University of Oxford’s Department of Engineering Science in 2016 shed light on the nature and speed of these phenomena.
7.1. Characteristics of Rogue Waves
- Unpredictability: They appear suddenly and without warning.
- Size: They are significantly larger than the surrounding waves.
- Steepness: They often have unusually steep crests.
7.2. Speed of Rogue Waves
Rogue waves can travel at speeds similar to other large waves, but their sudden appearance and extreme height make them particularly hazardous. Their speed depends on factors such as wind speed, wavelength, and water depth, similar to regular waves.
7.3. Factors Contributing to Rogue Wave Formation
- Constructive Interference: The merging of multiple waves to create a single, larger wave.
- Focusing of Energy: Certain weather conditions can focus wave energy into a specific area.
- Current Interactions: Interactions with strong ocean currents can amplify wave height.
8. How Do Tsunamis Differ in Speed Compared to Regular Waves?
Tsunamis are a type of wave caused by sudden displacement of large volumes of water, typically due to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or underwater landslides. The speed of tsunamis is vastly different from that of regular wind-driven waves. According to data from the International Tsunami Information Center (ITIC) in 2015, tsunamis have unique characteristics and behaviors.
8.1. Speed of Tsunamis
In the open ocean, tsunamis can travel at speeds of up to 800 kilometers per hour (500 miles per hour), similar to the speed of a jet plane. This high speed is due to their extremely long wavelengths, which can be hundreds of kilometers.
8.2. Behavior as They Approach Shore
As tsunamis approach shallower coastal waters, their speed decreases significantly, but their height increases dramatically. This is because the energy of the tsunami is compressed into a smaller volume of water.
8.3. Key Differences Between Tsunamis and Regular Waves
| Feature | Tsunami | Regular Wave |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Underwater disturbances (earthquakes, landslides) | Wind |
| Wavelength | Very long (hundreds of kilometers) | Short (tens to hundreds of meters) |
| Speed | Very high in open ocean (up to 800 km/h) | Much slower (up to 50 km/h) |
| Height | Small in open ocean, increases dramatically near shore | Relatively constant |
9. Can Weather Forecasts Predict Wave Speed?
Yes, weather forecasts can predict wave speed by analyzing various meteorological and oceanographic data. According to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) in 2014, accurate wave speed prediction relies on sophisticated models and data inputs.
9.1. Data Inputs for Wave Forecasting
- Wind Speed and Direction: These are primary drivers of wave formation and speed.
- Fetch Length: The distance over which the wind blows affects wave development.
- Water Depth: Critical for determining wave speed in coastal areas.
- Ocean Currents: Can influence wave propagation and speed.
9.2. Forecasting Models
Numerical weather prediction models are used to simulate atmospheric conditions and predict wind patterns, which in turn are used to forecast wave conditions. These models take into account various factors to estimate wave speed, height, and direction.
9.3. Tools and Resources for Checking Wave Speed Forecasts
- National Weather Services: Provide detailed wave forecasts for coastal regions.
- Marine Forecast Websites: Offer real-time wave data and predictions.
- Mobile Apps: Provide convenient access to wave forecasts for surfers and sailors.
10. How Can Understanding Wave Speed Enhance Your Travel Experience in Vietnam with SIXT.VN?
Understanding wave speed can greatly enhance your travel experiences in Vietnam, especially when planning coastal activities. SIXT.VN offers a range of services to help you make the most of your trip, from airport transfers to hotel bookings and guided tours.
10.1. Planning Coastal Activities
Knowing wave conditions is crucial for activities like swimming, surfing, and boating. By understanding wave speed and behavior, you can choose the best times and locations for these activities.
10.2. Utilizing SIXT.VN Services for a Seamless Experience
- Airport Transfers: Arrive in Vietnam stress-free with our reliable airport transfer services. We ensure a smooth transition from the airport to your accommodation.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358. - Hotel Bookings: Find the perfect beachfront hotel with SIXT.VN. We offer a wide selection of accommodations to suit every budget and preference.
- Guided Tours: Explore Vietnam’s stunning coastline with our expertly guided tours. We provide knowledgeable guides who can help you discover the best spots for water activities and relaxation.
- Flight Bookings: Easily book your flights to Vietnam with SIXT.VN. We offer competitive prices and convenient booking options.
 Waves breaking on the shore
Waves breaking on the shore
10.3. Safety Tips for Coastal Activities
- Check Wave Forecasts: Always check the local wave forecasts before engaging in water activities.
- Swim in Designated Areas: Swim only in areas that are marked as safe for swimming.
- Be Aware of Rip Currents: Understand the signs of rip currents and how to escape them.
10.4. How SIXT.VN Addresses Common Travel Challenges
- Planning Difficulties: SIXT.VN offers personalized travel itineraries tailored to your interests and preferences.
- Language Barriers: Our multilingual support team is available to assist you with any questions or concerns.
- Reliability and Quality: We partner with trusted service providers to ensure a high-quality and reliable travel experience.
- Transportation: Our convenient transportation options make it easy to explore Hanoi and beyond.
FAQ About Wave Speed
1. What is the formula for calculating wave speed?
Wave speed (v) can be calculated using the formula: v = λ / T, where λ is the wavelength and T is the wave period.
2. How do tides affect wave speed?
Tides themselves are very long-wavelength waves. The tidal flow can influence the speed of smaller wind-generated waves, either increasing or decreasing their speed depending on the direction of the tidal current.
3. Are there waves on other planets?
Yes, waves exist on other planets, but they aren’t always water waves. For example, Saturn’s rings have density waves, and some planets have atmospheric waves.
4. How do scientists measure wave speed?
Scientists use various tools, including buoys, satellites, and radar systems, to measure wave speed and other wave characteristics.
5. Can waves travel faster than the speed of light?
No, only the phase velocity of a wave can sometimes exceed the speed of light, but this does not mean that energy or information is traveling faster than light. The group velocity, which represents the speed of energy transfer, always remains below the speed of light.
6. How does temperature affect wave speed?
Temperature can indirectly affect wave speed by influencing wind patterns and water density, which can then affect wave formation and propagation.
7. What is a swell, and how fast does it travel?
A swell is a series of mechanical waves that propagate along the interface between water and air and so are often referred to as surface gravity waves. Swells can travel thousands of kilometers from their source and can travel at speeds of 30 to 50 kilometers per hour.
8. How do waves erode coastlines?
Waves erode coastlines through hydraulic action (the force of the water), abrasion (the grinding of rocks and sediment), and solution (the dissolving of rocks).
9. What is wave shoaling?
Wave shoaling is the process by which waves entering shallower water increase in height and decrease in speed and wavelength.
10. How do rip currents form, and are they related to wave speed?
Rip currents form when water that has been pushed ashore by waves flows back out to sea in a narrow channel. While wave speed isn’t the direct cause, the volume of water pushed ashore by waves contributes to the strength of rip currents.
Ready to explore the beautiful coastlines of Vietnam? Let SIXT.VN take care of all your travel needs. From convenient airport transfers to comfortable hotel bookings and exciting guided tours, we ensure a seamless and unforgettable experience. Contact us today to plan your dream vacation in Vietnam.
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
Don’t let planning difficulties or language barriers hold you back. With SIXT.VN, your Vietnamese adventure is just a click away. Book now and experience the best of Vietnam with ease and confidence.



