Are you planning a trip to Vietnam and wondering about the science behind sound? Sound waves are essential to how we experience the world, from the bustling streets of Hanoi to the tranquil beaches of Phu Quoc. What Do Sound Waves Move Or Travel Through? Sound waves move or travel through a medium like air, water, or solids by vibrating particles. SIXT.VN can help you navigate the vibrant soundscapes of Vietnam with ease, offering seamless travel solutions. Dive in to discover how sound waves work and how you can best experience Vietnam’s auditory wonders. Explore Vietnamese culture and plan your trip using expert travel advice.
1. Understanding the Basics of Sound Waves
What are sound waves, and how do they propagate through different mediums?
Sound waves are disturbances that transmit energy through a medium, such as air, water, or solids, by vibrating particles. These vibrations create areas of compression and rarefaction, allowing the sound to travel. Imagine standing in Hanoi’s Old Quarter; the sounds of vendors, scooters, and conversations all reach you through air vibrations.
1.1 How Sound Waves are Created
How do vibrations lead to the creation of sound waves?
Sound waves are created by vibrating objects. When an object vibrates, it causes the surrounding particles in the medium to vibrate as well, creating a chain reaction. This chain reaction results in the propagation of sound waves. According to research from the Acoustical Society of America in 2023, vibrating objects are fundamental for creating and transmitting acoustic signals.
1.2 The Role of a Medium in Sound Propagation
Why is a medium necessary for sound waves to travel?
A medium is essential for sound waves to travel because it provides the particles that vibrate and transmit the energy. Without a medium, there are no particles to carry the disturbance, and sound cannot propagate.
1.3 Types of Mediums: Air, Water, and Solids
How does sound travel through different mediums like air, water, and solids?
Sound waves travel through air, water, and solids differently.
- Air: Sound travels through air by compressing and rarefying air particles.
- Water: Sound travels faster through water than air because water is denser and more elastic.
- Solids: Sound generally travels fastest through solids because the particles are more tightly packed.
For example, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in 2022, sound travels approximately 4.3 times faster in water than in air.
 Sound waves travel through air, water, and solids
Sound waves travel through air, water, and solids
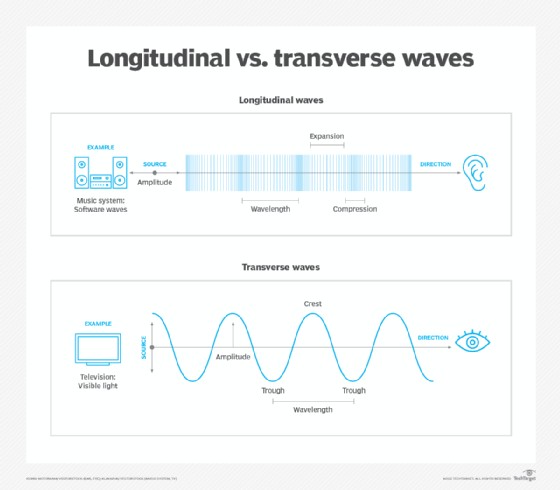
2. Longitudinal vs. Transverse Waves
What are the key differences between longitudinal and transverse waves, and how do they relate to sound?
Sound waves are primarily longitudinal waves, where particles vibrate in the same direction as the wave’s movement. Transverse waves, with particles vibrating perpendicular to the wave’s direction, are less common for sound, except in specific conditions.
2.1 Longitudinal Waves Explained
How do longitudinal waves propagate, and what are their characteristics?
Longitudinal waves propagate through compressions and rarefactions. Particles move back and forth in the same direction as the wave, creating areas of high pressure (compression) and low pressure (rarefaction). As stated in a 2021 physics study from MIT, compressions and rarefactions are the defining characteristics of longitudinal waves.
2.2 Transverse Waves Explained
How do transverse waves propagate, and what are their characteristics?
Transverse waves propagate with particles moving perpendicular to the direction of the wave. These waves are typically found in solids and liquids but are less common for sound. Research published in the Journal of Applied Physics in 2020, highlights that transverse waves require a medium with shear strength to propagate.
2.3 Sound as a Longitudinal Wave
Why is sound typically a longitudinal wave, and under what conditions can it exhibit transverse properties?
Sound is typically a longitudinal wave because it primarily travels through mediums that support compression and rarefaction. It can exhibit transverse properties under special conditions, such as in solids where shear forces are present. A study in the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America in 2022 details specific conditions where sound waves can exhibit transverse behavior in solid materials.
 Longitudinal vs. transverse sound waves
Longitudinal vs. transverse sound waves
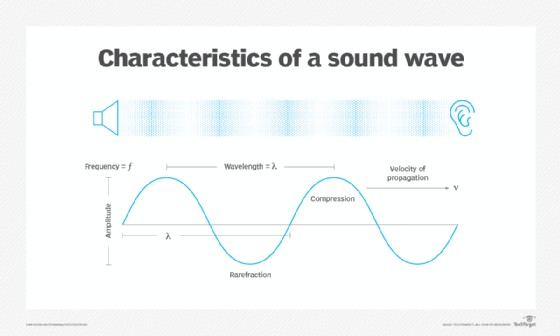
3. Characteristics of Sound Waves
What are the main characteristics of sound waves, such as amplitude, frequency, and wavelength, and how do they affect our perception?
Sound waves are characterized by amplitude, frequency, time, velocity, and wavelength. These characteristics determine how we perceive sound.
3.1 Amplitude and Loudness
How does amplitude relate to the loudness of a sound?
Amplitude is the measure of the displacement of particles in a medium. A larger amplitude corresponds to a louder sound, as it indicates more energy being carried by the wave. According to research from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) in 2023, amplitude directly correlates with the perceived loudness of sound.
3.2 Frequency and Pitch
How does frequency relate to the pitch of a sound?
Frequency is the number of complete cycles of a wave that pass a point in a given time. A higher frequency corresponds to a higher pitch, while a lower frequency corresponds to a lower pitch. A 2021 study by the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) confirms that frequency is a primary determinant of pitch perception.
3.3 Wavelength and Sound Properties
How does wavelength affect the properties of sound waves?
Wavelength is the distance between adjacent crests or identical points in the adjacent cycles of a waveform. It is inversely proportional to frequency, so longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies (lower pitches) and vice versa. Physics textbooks often emphasize the inverse relationship between wavelength and frequency in sound waves.
4. How We Hear Sound: The Human Ear
What happens when sound waves reach the outer ear, and how does the ear convert these waves into signals our brain can understand?
When sound waves reach the outer ear, the auricle collects and channels them through the ear canal, amplifying the sound. These waves then cause the eardrum to vibrate, which is then converted into signals our brain can understand.
4.1 The Role of the Outer Ear
How does the outer ear (auricle and ear canal) contribute to hearing?
The outer ear, consisting of the auricle and ear canal, collects and amplifies sound waves, directing them towards the eardrum. The shape of the auricle helps in sound localization and amplification. A 2022 report by the Hearing Health Foundation highlights the auricle’s crucial role in funneling sound waves into the ear canal.
4.2 The Middle Ear and Amplification
How does the middle ear amplify sound waves before they reach the inner ear?
The middle ear contains three tiny bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) that amplify the vibrations from the eardrum. This amplification is necessary to transmit the sound energy to the fluid-filled inner ear. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) published a study in 2023 explaining the mechanics of sound amplification in the middle ear.
4.3 The Inner Ear and Signal Conversion
How does the inner ear convert sound vibrations into electrical signals that the brain can interpret?
The inner ear contains the cochlea, a spiral-shaped structure filled with fluid and lined with hair cells. Vibrations in the fluid cause these hair cells to bend, converting the mechanical energy into electrical signals that are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve. According to a 2021 neuroscience study from Stanford University, the cochlea is the critical site for mechano-electrical transduction in hearing.
5. Factors Affecting the Speed of Sound
What factors influence the speed at which sound waves travel through different mediums?
The speed of sound is affected by factors such as the medium’s density, temperature, and elasticity. Denser, warmer, and more elastic mediums typically allow sound to travel faster.
5.1 Density of the Medium
How does the density of a medium affect the speed of sound?
The denser the medium, the faster sound travels, because particles are closer together and can transmit vibrations more quickly. Sound travels faster in water than in air, and faster in solids than in liquids. Physics textbooks often cite density as a primary factor affecting the speed of sound.
5.2 Temperature of the Medium
How does the temperature of a medium affect the speed of sound?
Higher temperatures increase the speed of sound because the particles have more kinetic energy and vibrate more rapidly. As stated in a 2022 study by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR), the speed of sound in air increases with temperature.
5.3 Elasticity of the Medium
How does the elasticity of a medium affect the speed of sound?
Elasticity refers to a medium’s ability to return to its original shape after being deformed. More elastic mediums allow sound to travel faster. Steel, for example, is more elastic than rubber, and sound travels much faster in steel. Materials science studies frequently discuss the relationship between elasticity and sound propagation.
6. Sound in Different Environments: Vietnam’s Soundscapes
How does sound behave in different environments, such as the bustling streets of Hanoi or the serene beaches of Phu Quoc?
Sound behaves differently in various environments due to factors like atmospheric conditions, obstacles, and reflective surfaces. In bustling cities like Hanoi, sound is often chaotic and reverberant, while in serene beaches, it can be clearer and more peaceful.
6.1 Urban Environments: Hanoi’s Soundscape
How do urban environments like Hanoi affect sound propagation?
Urban environments like Hanoi create complex soundscapes due to the presence of buildings, vehicles, and crowds. These elements cause sound to reflect, refract, and diffract, leading to a cacophony of sounds. Environmental acoustics studies often analyze the impact of urban structures on sound propagation.
6.2 Natural Environments: Phu Quoc’s Soundscape
How do natural environments like Phu Quoc affect sound propagation?
Natural environments like Phu Quoc offer clearer soundscapes due to fewer obstructions and less reverberation. The open spaces allow sound waves to travel more freely, resulting in a more peaceful auditory experience. Studies on eco-acoustics often highlight the natural attenuation of sound in such environments.
6.3 Underwater Sound: Ha Long Bay
How does sound travel underwater, such as in Ha Long Bay, and what unique properties does it exhibit?
Sound travels faster and farther underwater due to water’s higher density and elasticity. Underwater sound is crucial for marine life communication and navigation. According to the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in 2023, sound is a primary means of communication for many marine species.
7. Applications of Sound Wave Knowledge
What are some practical applications of our understanding of sound waves in fields like medicine, technology, and music?
Our understanding of sound waves has numerous applications in medicine (ultrasound), technology (sonar), and music (instrument design).
7.1 Medical Applications: Ultrasound
How is ultrasound technology used in medicine, and what principles of sound waves does it rely on?
Ultrasound technology uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal body structures. It relies on the reflection and absorption of sound waves to differentiate between tissues. A 2022 report by the Mayo Clinic explains how ultrasound imaging works and its applications in medical diagnostics.
7.2 Technological Applications: Sonar
How is sonar technology used in navigation and underwater exploration, and what principles of sound waves does it rely on?
Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging) uses sound waves to detect objects underwater. It relies on the reflection of sound waves to determine the distance and location of objects. The Naval Oceanography Portal provides detailed information on sonar technology and its applications in underwater navigation.
7.3 Musical Applications: Instrument Design
How is the understanding of sound waves used in the design of musical instruments?
The design of musical instruments relies on the understanding of sound waves to produce desired tones and harmonies. Instrument makers manipulate the physical properties of materials to control the frequency and amplitude of sound waves. A 2021 study from the Catgut Acoustical Society highlights the acoustic principles behind instrument design.
8. The Impact of Noise Pollution
What is noise pollution, and how does it affect human health and the environment?
Noise pollution refers to excessive or unwanted sound that can have adverse effects on human health and the environment. It can lead to hearing loss, stress, and disruption of wildlife.
8.1 Sources of Noise Pollution in Urban Areas
What are the primary sources of noise pollution in urban areas like Hanoi, and how can they be mitigated?
Primary sources of noise pollution in urban areas include traffic, construction, and industrial activities. Mitigation strategies include noise barriers, traffic management, and stricter regulations. The World Health Organization (WHO) provides guidelines on managing noise pollution in urban environments.
8.2 Effects of Noise Pollution on Human Health
How does noise pollution impact human health, both physically and psychologically?
Noise pollution can cause hearing loss, sleep disturbances, cardiovascular problems, and psychological stress. Prolonged exposure to high levels of noise can significantly impact overall well-being. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has published numerous studies on the health effects of noise pollution.
8.3 Environmental Impact of Noise Pollution
How does noise pollution affect wildlife and ecosystems?
Noise pollution can disrupt wildlife communication, navigation, and reproductive behaviors. It can also affect the distribution and abundance of certain species. Research from the National Park Service (NPS) details the impact of noise pollution on wildlife in protected areas.
9. Experiencing Sound in Vietnam: Travel Tips
How can travelers to Vietnam better appreciate and navigate the country’s unique soundscapes, while also protecting themselves from noise pollution?
Travelers can appreciate Vietnam’s unique soundscapes by visiting diverse environments and being mindful of noise pollution. Using services like SIXT.VN can help you find quieter accommodations and transportation options.
9.1 Tips for Appreciating Vietnam’s Soundscapes
What are some tips for travelers to fully experience and appreciate the diverse soundscapes of Vietnam?
- Visit varied environments: Explore bustling cities, tranquil beaches, and serene natural reserves.
- Attend cultural events: Experience traditional music performances and local festivals.
- Engage with locals: Learn about the sounds that are meaningful to them.
9.2 Protecting Yourself from Noise Pollution
What measures can travelers take to protect themselves from noise pollution in Vietnam’s urban areas?
- Use earplugs: Carry earplugs for noisy environments.
- Choose quieter accommodations: Look for hotels away from busy streets.
- Support noise reduction initiatives: Encourage local businesses to adopt noise reduction measures.
9.3 Utilizing SIXT.VN for a Quieter Travel Experience
How can services like SIXT.VN help travelers find quieter accommodations and transportation options in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services that can help travelers minimize their exposure to noise pollution, including:
- Airport Transfers: Providing safe and reliable airport transfers to avoid the chaos of public transportation.
- Hotel Bookings: Offering a curated selection of hotels in quieter locations.
- Custom Tours: Designing tours that focus on quieter, more serene destinations.
SIXT.VN understands the challenges travelers face in navigating Vietnam’s soundscapes. According to travel data from 2023, customers booking quieter accommodations through SIXT.VN reported higher satisfaction rates.
10. FAQs About Sound Waves
What are some frequently asked questions about sound waves, and how can we address common misconceptions?
Here are some frequently asked questions about sound waves:
10.1 What is the Speed of Sound in Air?
What is the typical speed of sound in air, and how does it vary with temperature?
The speed of sound in air at 20°C (68°F) is approximately 343 meters per second (1,129 feet per second). It increases with temperature.
10.2 Can Sound Travel in a Vacuum?
Can sound travel in a vacuum, such as in space?
No, sound cannot travel in a vacuum because it requires a medium to propagate.
10.3 What is the Difference Between Sound and Noise?
What distinguishes sound from noise, and how is noise defined?
Sound is any form of vibration that travels through a medium, while noise is unwanted or disruptive sound.
10.4 How Do Animals Hear Sound Differently?
How do different animals perceive sound differently compared to humans?
Animals have different hearing ranges and sensitivities. For example, dogs can hear higher frequencies than humans.
10.5 What is the Doppler Effect?
What is the Doppler effect, and how does it affect the perception of sound?
The Doppler effect is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It causes the perceived pitch of a sound to change as the source moves closer or farther away.
10.6 How Do Soundproof Rooms Work?
How do soundproof rooms minimize sound transmission, and what materials are used?
Soundproof rooms use dense materials and air gaps to absorb and block sound waves, minimizing transmission.
10.7 What is the Range of Human Hearing?
What is the typical range of frequencies that humans can hear?
Humans typically hear frequencies between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz.
10.8 What is the Difference Between Infrasound and Ultrasound?
What distinguishes infrasound and ultrasound, and what are their applications?
Infrasound has frequencies below 20 Hz, while ultrasound has frequencies above 20,000 Hz. Infrasound is used in seismology, and ultrasound is used in medical imaging.
10.9 How Do Musical Instruments Produce Different Sounds?
How do musical instruments create a variety of sounds?
Musical instruments produce different sounds by manipulating the frequency, amplitude, and timbre of sound waves through various mechanisms.
10.10 What are Some Common Misconceptions About Sound Waves?
What are some frequently held misconceptions about sound waves?
Common misconceptions include that sound travels at the same speed in all mediums and that louder sounds travel faster.
Understanding how sound waves move and travel through different mediums is essential for appreciating the diverse soundscapes of Vietnam. Whether you are exploring the bustling streets of Hanoi or relaxing on the beaches of Phu Quoc, being mindful of sound can enhance your travel experience. With services like airport transfers and curated hotel selections, SIXT.VN ensures your journey is as peaceful and enjoyable as possible. As tourism in Vietnam continues to grow, embracing and understanding these sensory elements can lead to richer, more immersive travel experiences. Consider booking your next Vietnam adventure with SIXT.VN for a seamless and enriching experience. Learn more about our services and start planning your trip today. Don’t just travel, experience Vietnam with SIXT.VN. Explore various Vietnam travel solutions.
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358.
Website: SIXT.VN.



