DIstance An Object Travels In A Specific Time hinges on multiple factors, with air resistance and initial velocity playing crucial roles; SIXT.VN can help you navigate these complexities in planning your travel distances in Vietnam. Understanding the elements that affect movement allows travelers to estimate travel duration and prepare for different circumstances. With expertise in transportation and travel assistance, SIXT.VN ensures every journey is calculated for a seamless travel experience.
1. Understanding Distance and Its Determinants
The distance an object travels in a specific time depends on several key factors, including speed, time, acceleration, and external forces like air resistance; let’s explore each aspect in more detail for travelers in Vietnam.
1.1. Speed and Time
Speed is the rate at which an object covers distance, typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
The Formula:
Distance = Speed × Time
This formula shows that the greater the speed or the longer the time, the greater the distance covered.
1.2. Acceleration
Acceleration refers to the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It’s measured in meters per second squared (m/s²).
Impact on Distance:
- Constant Acceleration: If an object accelerates at a constant rate, the distance it travels can be calculated using kinematic equations.
- Variable Acceleration: When acceleration varies, the calculation becomes more complex, often requiring calculus to determine the distance accurately.
1.3. Initial Velocity
The initial velocity is the speed and direction of an object at the start of its motion. This is a crucial factor because it sets the stage for how the object will move under the influence of forces and acceleration.
1.4. External Forces: Air Resistance
Air resistance, also known as drag, is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air.
Impact on Distance:
- Significant Reduction: Air resistance can significantly reduce the distance an object travels, especially at high speeds.
- Dependency on Factors: The magnitude of air resistance depends on the object’s shape, size, speed, and the density of the air.
 A cyclist battling wind resistance on a rural road, showcasing the impact of air resistance on travel.
A cyclist battling wind resistance on a rural road, showcasing the impact of air resistance on travel.
1.5. Gravity
Gravity is the force that pulls objects toward each other. On Earth, it accelerates objects downwards at approximately 9.81 m/s².
Impact on Distance:
- Vertical Motion: Gravity primarily affects vertical motion, altering the trajectory and speed of objects moving upwards or downwards.
- Projectile Motion: Understanding gravity is crucial for calculating the range of projectiles, such as balls or bullets.
1.6. Other Resistive Forces
Besides air resistance, other forces can impede motion.
Types of Resistive Forces:
- Friction: Occurs when two surfaces slide against each other, converting kinetic energy into heat.
- Water Resistance: Similar to air resistance but more potent due to water’s higher density.
1.7. Mass
Mass is a measure of an object’s resistance to acceleration. According to Newton’s Second Law, force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma).
Impact on Distance:
- Inertia: More massive objects require more force to achieve the same acceleration, affecting the distance they travel in a given time.
- Momentum: Mass also influences momentum, which is essential for understanding collisions and changes in motion.
1.8. Angle of Projection
The angle at which an object is launched or projected can significantly affect its range, especially in projectile motion scenarios.
Optimal Angle:
- Maximum Range: Generally, an angle of 45 degrees provides the maximum range for a projectile in a vacuum, where air resistance is negligible.
- Adjustments in Reality: In real-world conditions, air resistance necessitates adjustments to this angle for optimal distance.
1.9. Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors such as wind speed, direction, and altitude can also impact the distance an object travels.
Examples:
- Wind: A tailwind can increase the distance, while a headwind can decrease it.
- Altitude: Higher altitudes mean less air density, reducing air resistance and potentially increasing distance.
2. In-Depth Look: Trajectory Calculation
Calculating the trajectory of an object involves understanding various physics principles, particularly kinematics and dynamics. Here’s a detailed look at how to compute trajectory, which can be useful for planning travel distances in Vietnam.
2.1. Basic Kinematic Equations
Kinematic equations are a set of formulas that describe the motion of an object with constant acceleration.
Key Equations:
- Final Velocity: ( v = u + at )
- Displacement: ( s = ut + frac{1}{2}at^2 )
- Final Velocity Squared: ( v^2 = u^2 + 2as )
Where:
- ( v ) is the final velocity
- ( u ) is the initial velocity
- ( a ) is the acceleration
- ( t ) is the time
- ( s ) is the displacement (distance)
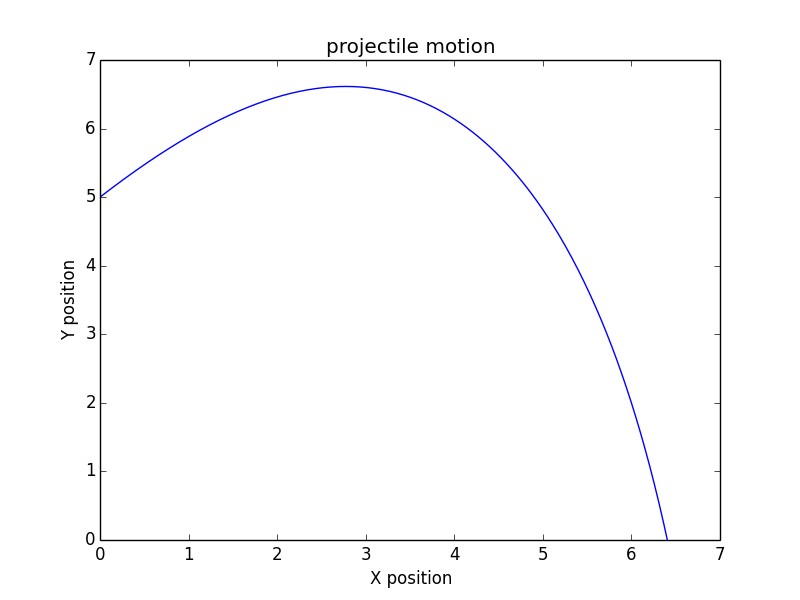
2.2. Projectile Motion
Projectile motion is a special case of kinematics where an object is launched into the air and is subject to gravity. The motion is typically analyzed in two dimensions: horizontal and vertical.
Horizontal Motion:
- Constant Velocity: Assuming no air resistance, the horizontal velocity remains constant.
- Equation: ( x = u_x cdot t ) (where ( x ) is the horizontal distance, and ( u_x ) is the initial horizontal velocity).
Vertical Motion:
- Constant Acceleration: The vertical motion is affected by gravity, causing a constant downward acceleration.
- Equations:
- ( y = u_y cdot t – frac{1}{2} g t^2 ) (where ( y ) is the vertical distance, ( u_y ) is the initial vertical velocity, and ( g ) is the acceleration due to gravity).
- ( v_y = u_y – gt )
2.3. Accounting for Air Resistance
Air resistance complicates trajectory calculations significantly. The force of air resistance is proportional to the square of the object’s velocity and acts in the opposite direction of motion.
Mathematical Representation:
The drag force ( F_d ) can be modeled as:
[ F_d = frac{1}{2} rho v^2 A C_d ]
Where:
- ( rho ) is the air density
- ( v ) is the velocity
- ( A ) is the cross-sectional area of the object
- ( C_d ) is the drag coefficient
Impact on Equations:
- Modified Acceleration: The net force on the object is now the sum of gravity and air resistance, leading to a modified acceleration.
- Numerical Methods: Due to the complexity, trajectory calculations with air resistance often require numerical methods.
2.4. Numerical Integration
Numerical integration involves breaking the motion into small time steps and iteratively calculating the object’s position and velocity at each step.
Steps:
- Initialize Values: Set initial position, velocity, and time.
- Calculate Forces: Determine the forces acting on the object (gravity, air resistance).
- Compute Acceleration: Use Newton’s Second Law (( F = ma )) to find the acceleration.
- Update Velocity: Update the velocity using ( v = u + at ).
- Update Position: Update the position using ( s = ut + frac{1}{2}at^2 ).
- Increment Time: Increase the time by a small increment ( Delta t ).
- Repeat Steps: Continue until the object reaches the ground or the simulation is complete.
2.5. Factors Affecting Trajectory
Several factors can affect the trajectory of an object, including:
Wind Conditions:
- Tailwind: Increases the range and time of flight.
- Headwind: Decreases the range and time of flight.
- Crosswind: Deflects the object horizontally.
Altitude:
- Air Density: Higher altitudes have lower air density, reducing air resistance.
- Gravity: The acceleration due to gravity varies slightly with altitude.
Object Properties:
- Shape: Aerodynamic shapes experience less air resistance.
- Mass: Higher mass results in greater inertia and less susceptibility to air resistance.
3. Practical Examples of Distance Calculation
Let’s explore several practical examples where understanding the factors affecting distance is crucial, especially for travel planning with SIXT.VN.
3.1. Example 1: Driving a Car
Consider a car driving on a highway in Vietnam. The distance the car travels depends on its speed, the time it travels, and factors like traffic and road conditions.
Variables:
- Speed: 80 km/h
- Time: 3 hours
Calculation:
- Distance: Distance = Speed × Time = 80 km/h × 3 h = 240 km
Additional Factors:
- Traffic: Heavy traffic can reduce the average speed, affecting the total distance covered.
- Road Conditions: Poor road conditions can also slow down the car.
3.2. Example 2: Airplane Flight
When an airplane flies from one city to another, the distance is affected by its speed, wind conditions, and the flight path.
Variables:
- Speed: 800 km/h
- Time: 2 hours
- Wind: Tailwind of 100 km/h
Calculation:
- Effective Speed: 800 km/h + 100 km/h = 900 km/h
- Distance: Distance = Effective Speed × Time = 900 km/h × 2 h = 1800 km
Additional Factors:
- Air Traffic: Can cause delays, affecting the total time and distance.
- Weather: Storms can alter the flight path, increasing the distance.
3.3. Example 3: Cycling
For a cyclist riding a bicycle, the distance covered is determined by their speed, the duration of the ride, and external factors like terrain and wind.
Variables:
- Speed: 20 km/h
- Time: 4 hours
- Terrain: Flat road
Calculation:
- Distance: Distance = Speed × Time = 20 km/h × 4 h = 80 km
Additional Factors:
- Hills: Can reduce the average speed, decreasing the total distance.
- Wind: Headwinds can significantly slow down the cyclist.
3.4. Example 4: A Ball Thrown in the Air
Consider a ball thrown upwards with an initial velocity. The distance (height) it reaches depends on the initial velocity and the acceleration due to gravity.
Variables:
- Initial Velocity: 15 m/s
- Acceleration due to Gravity: -9.81 m/s²
Calculation:
- *Using ( v^2 = u^2 + 2as ), where ( v = 0 ) at the highest point:
- ( 0 = (15 , text{m/s})^2 + 2 cdot (-9.81 , text{m/s}^2) cdot s )
- ( s = frac{(15 , text{m/s})^2}{2 cdot 9.81 , text{m/s}^2} approx 11.47 , text{m} )
Additional Factors:
- Air Resistance: Reduces the maximum height reached by the ball.
- Angle of Throw: The angle affects the horizontal distance and time of flight.
3.5. Example 5: Boat Trip on a River
When a boat travels on a river, the distance covered is influenced by the boat’s speed, the river’s current, and the travel time.
Variables:
- Boat Speed: 10 m/s
- River Current: 2 m/s (in the same direction)
- Time: 1 hour
Calculation:
- Effective Speed: 10 m/s + 2 m/s = 12 m/s
- Distance: Distance = Effective Speed × Time = 12 m/s × 3600 s = 43200 m = 43.2 km
Additional Factors:
- River Width: Affects the actual path and distance if the boat needs to cross the river.
- Obstacles: Rocks or other boats can alter the boat’s speed and path.
4. Optimizing Travel Distance with SIXT.VN
When planning your travels in Vietnam, understanding how various factors affect distance can help you make informed decisions. SIXT.VN offers several services to optimize your travel distance and ensure a smooth and efficient journey.
4.1. Route Planning
SIXT.VN provides detailed route planning services that consider various factors to optimize your travel distance.
Services:
- Optimal Route Selection: SIXT.VN uses advanced mapping technology to identify the shortest and most efficient routes.
- Traffic Monitoring: Real-time traffic updates help avoid congested areas, reducing travel time.
Benefits:
- Reduced Travel Time: By avoiding traffic and selecting optimal routes, you can significantly reduce travel time.
- Cost Savings: Efficient routes can save on fuel and other travel expenses.
4.2. Transportation Options
SIXT.VN offers a range of transportation options to suit your needs, each with its own implications for travel distance.
Options:
- Car Rentals: Choose from a variety of vehicles suitable for different terrains and travel needs.
- Airport Transfers: Convenient and reliable airport transfer services to minimize delays.
Benefits:
- Flexibility: Car rentals offer the flexibility to explore Vietnam at your own pace.
- Convenience: Airport transfers ensure a seamless transition to your destination.
4.3. Accommodation Planning
Selecting the right accommodation can also impact your travel distance.
Services:
- Strategic Locations: SIXT.VN helps you find hotels and accommodations in central locations or near key attractions.
- Transportation Access: Recommends accommodations with easy access to public transportation.
Benefits:
- Reduced Commute: Staying in strategic locations minimizes the distance to popular attractions.
- Convenient Access: Easy access to transportation makes it easier to explore the city.
4.4. Real-Time Information
Staying informed with real-time data can help you adjust your plans and optimize travel distance.
Information:
- Weather Updates: Weather forecasts to prepare for potential disruptions.
- Traffic Alerts: Instant alerts about traffic incidents and alternative routes.
Benefits:
- Informed Decisions: Make timely decisions based on current conditions.
- Adaptive Planning: Adjust your travel plans to avoid delays and optimize distance.
4.5. Tailored Travel Packages
SIXT.VN offers customized travel packages designed to meet your specific needs and preferences, ensuring an optimized travel experience.
Features:
- Custom Itineraries: Personalized itineraries based on your interests and schedule.
- Comprehensive Services: Includes transportation, accommodation, and activity planning.
Benefits:
- Optimized Experience: Packages are designed to maximize your enjoyment while minimizing travel distance.
- Stress-Free Travel: All details are taken care of, allowing you to focus on enjoying your trip.
5. Overcoming Travel Challenges in Vietnam
Traveling in Vietnam can present unique challenges that affect travel distance and time. SIXT.VN is equipped to help you navigate these issues effectively.
5.1. Language Barriers
Communicating with locals can be challenging due to language differences, potentially leading to misunderstandings and delays.
SIXT.VN Solutions:
- Multilingual Support: SIXT.VN offers customer support in multiple languages.
- Translation Services: Access to translation services to facilitate communication.
Benefits:
- Improved Communication: Clear communication reduces the risk of errors and delays.
- Enhanced Experience: Smooth interactions with locals enhance your overall travel experience.
5.2. Traffic Congestion
Major cities in Vietnam, like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, often experience heavy traffic congestion, impacting travel time and distance.
SIXT.VN Solutions:
- Route Optimization: Advanced route planning to avoid congested areas.
- Real-Time Updates: Traffic alerts to help you adjust your route accordingly.
Benefits:
- Reduced Delays: Avoid traffic jams and arrive at your destination on time.
- Efficient Travel: Optimize your route to minimize travel distance.
5.3. Infrastructure Limitations
While Vietnam’s infrastructure has improved significantly, some areas still have limitations, such as poor road conditions or limited public transportation options.
SIXT.VN Solutions:
- Suitable Vehicle Selection: Car rentals with vehicles suited for different terrains.
- Private Transportation: Options for private transportation to overcome public transport limitations.
Benefits:
- Access to Remote Areas: Reach destinations with limited infrastructure.
- Comfortable Travel: Enjoy a smooth and comfortable journey despite infrastructure challenges.
5.4. Cultural Differences
Navigating cultural differences can sometimes lead to misunderstandings and affect travel plans.
SIXT.VN Solutions:
- Cultural Guides: Access to cultural guides to help you understand local customs and etiquette.
- Local Insights: Tips and advice on navigating cultural nuances.
Benefits:
- Respectful Interactions: Engage with locals in a respectful and appropriate manner.
- Enriched Experience: Gain a deeper appreciation of Vietnamese culture.
5.5. Safety Concerns
Like any travel destination, safety is a concern in Vietnam. Being aware of potential risks and taking necessary precautions is essential.
SIXT.VN Solutions:
- Safe Transportation: Reliable and safe transportation options.
- Emergency Support: Access to emergency support and assistance.
Benefits:
- Peace of Mind: Travel with confidence knowing that your safety is a priority.
- Quick Assistance: Access to help in case of emergencies.
6. Maximizing Your Vietnam Trip with SIXT.VN
To make the most of your trip to Vietnam, understanding the factors that influence travel distance and utilizing SIXT.VN’s services are key.
6.1. Plan Ahead
Planning your itinerary in advance can help you optimize travel distance and time.
Tips:
- Prioritize Destinations: Identify the must-see attractions and plan your route accordingly.
- Book in Advance: Secure transportation and accommodation to avoid last-minute hassles.
SIXT.VN Support:
- Custom Itineraries: Personalized itineraries tailored to your preferences.
- Advance Booking: Easy booking of transportation and accommodation.
6.2. Stay Flexible
While planning is essential, being flexible can help you adapt to unforeseen circumstances.
Tips:
- Allow Extra Time: Build buffer time into your schedule to account for delays.
- Be Open to Changes: Be prepared to adjust your plans based on real-time information.
SIXT.VN Support:
- Real-Time Updates: Instant alerts about traffic, weather, and other disruptions.
- Flexible Options: Options for modifying your bookings as needed.
6.3. Utilize Local Knowledge
Leveraging local knowledge can provide valuable insights and help you navigate Vietnam more effectively.
Tips:
- Talk to Locals: Seek advice from locals about the best routes and attractions.
- Explore Off the Beaten Path: Discover hidden gems away from the tourist crowds.
SIXT.VN Support:
- Local Guides: Access to knowledgeable local guides.
- Insider Tips: Recommendations for authentic experiences.
6.4. Choose the Right Transportation
Selecting the appropriate transportation mode can significantly impact your travel distance and time.
Options:
| Transportation Mode | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Car Rental | Flexibility, access to remote areas | Traffic, parking |
| Airport Transfer | Convenience, reliability | Cost |
| Public Transport | Cost-effective | Crowded, limited routes |
| Private Car | Comfort, personalized service | Higher cost |
SIXT.VN Support:
- Wide Range of Options: A variety of transportation choices to suit your needs.
- Expert Advice: Guidance on selecting the best transportation mode.
6.5. Embrace the Experience
Traveling in Vietnam is an adventure. Embrace the challenges and enjoy the unique experiences it has to offer.
Tips:
- Be Open-Minded: Embrace new cultures and perspectives.
- Stay Positive: Maintain a positive attitude even when things don’t go as planned.
SIXT.VN Support:
- Comprehensive Assistance: Support throughout your journey.
- Memorable Experiences: Opportunities to create lasting memories.
By understanding the factors that affect travel distance and utilizing SIXT.VN’s comprehensive services, you can optimize your trip to Vietnam for a seamless and unforgettable experience.
7. Advanced Factors Affecting Distance
Beyond the basics, several advanced factors can further influence the distance an object travels. Understanding these can be crucial in specialized scenarios.
7.1. Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis effect is a phenomenon where a mass moving in a rotating system experiences a force (the Coriolis force) perpendicular to the direction of motion and the axis of rotation.
Impact on Distance:
- Long-Range Trajectories: Affects long-range trajectories, such as ballistic missiles and weather patterns.
- Deflection: Causes moving objects to deflect to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
Real-World Example:
- Artillery: Military artillery calculations must account for the Coriolis effect to ensure accurate targeting over long distances.
7.2. Magnus Effect
The Magnus effect is the force exerted on a spinning object moving through a fluid. It results from pressure differences created by the spinning motion.
Impact on Distance:
- Curved Trajectories: Causes objects to curve in their path, either increasing or decreasing their range.
- Spin-Dependent Forces: The direction and magnitude of the curve depend on the object’s spin rate and direction.
Real-World Example:
- Sports: Commonly seen in sports like soccer, baseball, and tennis, where players use spin to control the ball’s trajectory.
7.3. Buoyancy
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object.
Impact on Distance:
- Reduced Effective Weight: Reduces the effective weight of an object, affecting its motion through the fluid.
- Floating vs. Sinking: Determines whether an object floats or sinks, influencing its vertical distance traveled.
Real-World Example:
- Submarines: Submarines use buoyancy control to adjust their depth and movement underwater.
7.4. Relativistic Effects
At very high speeds, approaching the speed of light, relativistic effects become significant. These effects are described by Einstein’s theory of relativity.
Impact on Distance:
- Time Dilation: Time dilation causes time to pass slower for a moving object relative to a stationary observer.
- Length Contraction: Length contraction causes the length of a moving object to appear shorter in the direction of motion.
Real-World Example:
- Particle Physics: Essential in particle physics experiments where particles are accelerated to near-light speeds.
7.5. Quantum Tunneling
Quantum tunneling is a phenomenon where a particle can pass through a potential barrier even if it does not have enough energy to overcome the barrier classically.
Impact on Distance:
- Short Distances: Relevant at extremely small distances, such as within atoms.
- Probability-Based Motion: The particle’s motion becomes probabilistic, with a non-zero chance of appearing on the other side of the barrier.
Real-World Example:
- Nuclear Fusion: Plays a crucial role in nuclear fusion reactions in stars.
7.6. Atmospheric Refraction
Atmospheric refraction is the bending of light as it passes through the Earth’s atmosphere due to variations in air density.
Impact on Distance:
- Distorted Perception: Distorts the perceived position of distant objects.
- Extended Horizon: Allows us to see objects that would otherwise be below the horizon.
Real-World Example:
- Astronomy: Astronomers must account for atmospheric refraction when observing celestial objects.
7.7. Geodesics
In the context of general relativity, objects follow geodesics, which are the curves that represent the shortest distance between two points in curved spacetime.
Impact on Distance:
- Curved Spacetime: Mass and energy curve spacetime, affecting the paths of objects moving through it.
- Orbital Motion: Explains the orbital motion of planets around stars.
Real-World Example:
- GPS Satellites: GPS satellites rely on general relativity to provide accurate positioning data.
8. FAQs About Factors Influencing Travel Distance
8.1. What is the primary factor affecting the distance an object travels?
The primary factor is the object’s speed combined with the time it travels; according to the formula, Distance = Speed × Time, an increase in either speed or time will result in a greater distance covered.
8.2. How does air resistance affect the distance traveled by a projectile?
Air resistance significantly reduces the distance a projectile travels by exerting a force opposite to the motion; this force, also known as drag, depends on the object’s shape, size, and speed, as well as the air density, leading to a decrease in both horizontal and vertical distances.
8.3. Can acceleration increase the distance traveled, and how?
Yes, acceleration can increase the distance traveled; when an object accelerates, its velocity increases over time, which directly contributes to covering more distance within a given timeframe, especially if the acceleration is constant and sustained.
8.4. How does gravity influence the distance an object travels vertically?
Gravity exerts a constant downward force, causing objects to accelerate towards the Earth at approximately 9.81 m/s²; this acceleration affects the vertical distance an object can travel, especially in projectile motion, where gravity reduces the upward distance and increases the downward speed.
8.5. What role does the initial velocity play in determining the distance covered?
The initial velocity sets the stage for the object’s motion; a higher initial velocity allows the object to cover more distance right from the start, influencing both the speed and range of its trajectory, particularly before external forces like air resistance or gravity start to have a significant impact.
8.6. How do wind conditions affect the distance an airplane flies?
Wind conditions can significantly affect an airplane’s distance; a tailwind increases the plane’s effective speed, allowing it to cover more distance in a given time, while a headwind reduces the effective speed, resulting in less distance covered, and crosswinds can deflect the plane from its intended path.
8.7. Does the mass of an object influence the distance it travels?
Yes, mass influences the distance an object travels; according to Newton’s Second Law (F = ma), a more massive object requires more force to achieve the same acceleration, affecting how quickly it can change its velocity and, consequently, the distance it covers.
8.8. How does the angle of projection impact the range of a projectile?
The angle of projection significantly impacts the range of a projectile; in ideal conditions (without air resistance), an angle of 45 degrees provides the maximum range, but in real-world conditions, air resistance necessitates adjustments to this angle for optimal distance.
8.9. Can environmental conditions, like altitude, affect travel distance?
Yes, environmental conditions like altitude affect travel distance; at higher altitudes, air density is lower, reducing air resistance and allowing objects to travel farther, which is crucial for long-distance flights and projectile motion calculations.
8.10. How can SIXT.VN help optimize travel distance in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN optimizes travel distance in Vietnam through advanced route planning, real-time traffic updates, strategic accommodation locations, tailored travel packages, and a variety of transportation options, ensuring travelers can navigate efficiently and reach their destinations with minimal hassle.
Vietnam is waiting to be discovered. Let SIXT.VN be your guide in navigating the intricacies of travel distances, ensuring a journey filled with exploration and ease. Contact us today to plan your perfect Vietnamese adventure! You can reach us at Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam, Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358, or visit our Website: SIXT.VN. Let’s make your travel dreams a reality.



