Are you planning a trip to Vietnam and wondering about the environmental conditions? The question, “Are There Visible Signs Of Pollution (river Pollution, Air Quality)?” is a valid concern for travelers. SIXT.VN can help you navigate your travel plans with helpful information and convenient services, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience while you explore Vietnam’s beauty. Air pollution and water contamination are environmental issues that prospective tourists should be aware of.
1. What is Particulate Matter (PM) and How Does it Affect Air Quality?
Particulate matter, or particle pollution, refers to the mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), some particles like dust and smoke are visible, while others are microscopic.
1.1 Understanding PM10 and PM2.5
Particle pollution includes:
- PM10: Inhalable particles with diameters generally 10 micrometers and smaller.
- PM2.5: Fine inhalable particles with diameters generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller.
To put this in perspective, a human hair is approximately 70 micrometers in diameter, making it significantly larger than even the largest fine particle.
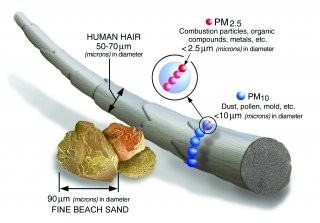 Comparison of particulate matter sizes
Comparison of particulate matter sizes
Size comparison for PM particles, showcasing the relative sizes of PM2.5 and PM10 compared to human hair and sand, illustrating the minute scale of these pollutants and their ability to penetrate deep into the lungs.
1.2 What are the Sources of Particulate Matter?
Particulate matter originates from various sources, each contributing differently to air pollution. Some particles are emitted directly from identifiable sources, while others form through complex atmospheric reactions.
- Direct Emissions: Construction sites, unpaved roads, agricultural fields, industrial smokestacks, and fires directly release particulate matter into the atmosphere.
- Indirect Formation: Most particles develop in the atmosphere due to chemical reactions involving pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. These precursor pollutants are typically emitted from power plants, industrial facilities, and automobiles.
- Natural Sources: Natural events such as volcanic eruptions and dust storms can also significantly increase particulate matter levels in the air. These events release large quantities of ash and dust, impacting air quality over wide areas.
- Residential Activities: Activities such as wood burning for heating and cooking can contribute to particulate matter pollution, especially in densely populated areas during colder months.
- Agricultural Practices: Agricultural activities, including tilling and the use of fertilizers, can release particulate matter and precursor gases that contribute to air pollution.
Understanding the diverse sources of particulate matter is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate air pollution and protect public health.
2. What are the Harmful Effects of Particulate Matter?
The microscopic size of particulate matter allows it to be inhaled deeply into the lungs, causing a range of health problems. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), PM2.5 poses the greatest risk to health because it can enter the bloodstream.
2.1 Health Impacts
Inhaling particulate matter can lead to various health issues, affecting both the respiratory and cardiovascular systems.
- Respiratory Issues: PM can exacerbate respiratory conditions like asthma and bronchitis, leading to increased coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. It can also trigger new cases of asthma, particularly in children.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Fine particles can enter the bloodstream and contribute to heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. Long-term exposure increases the risk of heart attacks and irregular heartbeats.
- Increased Mortality: Studies have shown a direct correlation between high levels of particulate matter and increased mortality rates, especially among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions.
- Other Health Effects: Particulate matter exposure has also been linked to other health issues, including reduced lung function, increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, and potential impacts on cognitive development in children.
- Specific Risks for Vulnerable Groups: Children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions are particularly vulnerable to the health effects of particulate matter. These groups may experience more severe symptoms and complications from exposure.
2.2 Environmental Impacts
Beyond health effects, particulate matter also has significant environmental impacts, primarily affecting visibility and ecosystem health.
- Reduced Visibility: Fine particles are a primary cause of reduced visibility, leading to haze and smog. This can obscure scenic views in national parks and wilderness areas, diminishing the aesthetic value of these natural landscapes.
- Ecosystem Damage: Deposition of particulate matter can alter soil and water chemistry, harming sensitive ecosystems. Acid deposition, caused by pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, can damage forests and aquatic habitats.
- Impact on Agriculture: Particulate matter can deposit on plant leaves, reducing photosynthesis and crop yields. This can have significant economic impacts on agricultural regions.
- Climate Change: Certain components of particulate matter, such as black carbon, contribute to climate change by absorbing sunlight and warming the atmosphere. While other particles can have a cooling effect by reflecting sunlight, the overall impact of particulate matter on climate is complex and varies depending on its composition and location.
- Water Quality: Particulate matter deposition can contaminate water bodies, affecting aquatic life and water quality. This can lead to increased acidity, nutrient imbalances, and the accumulation of harmful substances in aquatic ecosystems.
Addressing particulate matter pollution is essential for protecting both human health and the environment, requiring comprehensive strategies to reduce emissions and mitigate its impacts.
3. What is Being Done to Reduce Particle Pollution?
Environmental Protection Agencies (EPAs) regulate inhalable particles to mitigate the harmful effects of particle pollution. According to the EPA, particles larger than 10 micrometers, such as sand and large dust, are not regulated.
3.1 Regulatory Measures
Government agencies implement various regulations and standards to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
- National Air Quality Standards: These standards set limits on the concentration of pollutants, including particulate matter, in the air. They are designed to protect public health and welfare.
- Emission Controls: Regulations require industries and vehicles to use technologies and practices that reduce emissions of particulate matter and its precursor pollutants. This includes measures such as installing scrubbers on smokestacks and mandating the use of cleaner fuels.
- Permitting Programs: Industries are required to obtain permits that set limits on their emissions and require them to monitor and report their pollution levels. This helps ensure compliance with air quality standards.
- Clean Air Act: This comprehensive law provides the framework for regulating air pollution in the United States, including provisions for setting air quality standards, controlling emissions, and enforcing regulations.
- International Agreements: Collaborative efforts among countries to address transboundary air pollution, such as agreements to reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, help mitigate regional air pollution problems.
3.2 Initiatives and Programs
Various initiatives and programs are in place to reduce particle pollution and promote cleaner air.
- Clean Diesel Programs: These programs provide funding for upgrading or replacing older, more polluting diesel engines with cleaner technologies. This includes retrofitting school buses, trucks, and construction equipment with emission control devices.
- Wood Stove Changeout Programs: These programs offer incentives for homeowners to replace older, inefficient wood stoves with cleaner-burning models. This helps reduce particulate matter emissions from residential wood burning.
- Green Infrastructure: Implementing green infrastructure, such as planting trees and creating green roofs, can help reduce air pollution by absorbing pollutants and cooling urban areas.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the sources and health effects of particle pollution can help promote behaviors that reduce emissions, such as using public transportation and conserving energy.
- Air Quality Monitoring Networks: These networks continuously monitor air quality levels and provide real-time data to the public, allowing people to take steps to protect their health when pollution levels are high.
These regulatory measures, initiatives, and programs are essential for reducing particle pollution and improving air quality, safeguarding public health and the environment.
4. How Can I Reduce My Exposure to PM?
You can use air quality alerts to protect yourself when PM reaches harmful levels. AirNow provides daily Air Quality Index (AQI) information to inform you about the cleanliness of outdoor air and associated health effects.
4.1 Monitoring Air Quality
Staying informed about air quality conditions is crucial for protecting your health.
- Air Quality Index (AQI): The AQI is a standardized measure used to communicate air quality levels to the public. It translates air quality data into numbers and colors that indicate the level of pollution and associated health risks.
- Real-Time Data: Many websites and mobile apps provide real-time air quality data, allowing you to check current pollution levels in your area. This information can help you make informed decisions about outdoor activities.
- Government Websites: Environmental agencies, such as the EPA, provide comprehensive information about air quality, including AQI forecasts, pollution monitoring data, and health advisories.
- Local News and Weather Reports: Local news and weather reports often include air quality updates, especially during periods of high pollution.
- Air Quality Alerts: Sign up for air quality alerts from your local environmental agency to receive notifications when pollution levels reach unhealthy levels.
4.2 Protective Measures
Taking proactive steps to reduce your exposure to particulate matter can help minimize its health impacts.
- Limit Outdoor Activities: On days when air quality is poor, reduce or avoid strenuous outdoor activities, especially during peak pollution hours.
- Stay Indoors: When air quality is unhealthy, stay indoors with windows and doors closed. Use air conditioning if available, and set it to recirculate air.
- Use Air Purifiers: Portable air purifiers with HEPA filters can help remove particulate matter from indoor air, improving air quality in your home or office.
- Wear a Mask: If you must spend time outdoors when air quality is poor, wear a NIOSH-certified N95 or P100 respirator mask to filter out fine particles.
- Avoid High-Traffic Areas: Limit your exposure to high-traffic areas, where pollution levels are often higher due to vehicle emissions.
- Protect Vulnerable Individuals: Take extra precautions to protect children, the elderly, and individuals with respiratory or cardiovascular conditions, as they are more susceptible to the health effects of particulate matter.
By monitoring air quality and taking appropriate protective measures, you can reduce your exposure to particulate matter and minimize its potential health impacts.
5. How Can SIXT.VN Enhance Your Travel Experience in Vietnam?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services designed to make your trip to Vietnam seamless and enjoyable, even with environmental concerns in mind.
5.1 Comprehensive Travel Solutions
SIXT.VN provides a variety of services to cater to all your travel needs.
- Tailored Travel Itineraries: We design personalized itineraries to match your interests and schedule, ensuring you experience the best of Vietnam while considering environmental factors.
- Airport Transfer Service: SIXT.VN offers reliable and comfortable airport transfer services, ensuring a smooth start and end to your trip. Our professional drivers will greet you at the airport and transport you to your accommodation safely and efficiently. This service eliminates the stress of navigating public transportation or finding a taxi upon arrival.
- Hotel Booking Service: Choose from a wide selection of hotels that suit your budget and preferences, with options that prioritize comfort and convenience. SIXT.VN provides access to a diverse range of accommodations, from budget-friendly options to luxury hotels, ensuring you find the perfect place to stay.
- Sightseeing Tour Booking: Discover famous landmarks in Hanoi and surrounding areas with our curated tour options, letting you explore the beauty of Vietnam. SIXT.VN offers a variety of tour options, including guided city tours, cultural excursions, and adventure activities. Our tours are designed to provide immersive and authentic experiences, showcasing the best of Vietnam’s culture and natural beauty.
- Flight Booking Assistance: SIXT.VN offers assistance with flight bookings, helping you find the best deals and convenient schedules for your travel. Our team can help you compare prices, select the most suitable flights, and manage your booking details, ensuring a hassle-free travel experience.
5.2 Advantages of Using SIXT.VN
Opting for SIXT.VN services enhances your travel experience in several ways.
- Convenience: Streamline your travel plans with our easy-to-use platform. SIXT.VN simplifies the travel planning process with its user-friendly platform, allowing you to easily book flights, accommodations, and tours in one place. Our intuitive interface and comprehensive search filters make it easy to find the perfect options for your trip.
- Speed: Book your travel services quickly and efficiently, saving valuable time. SIXT.VN provides fast and efficient booking services, allowing you to secure your travel arrangements in minutes. Our streamlined booking process and secure payment options ensure a seamless and hassle-free experience.
- Reliability: Trust in our dependable services to ensure a stress-free travel experience. SIXT.VN is committed to providing reliable and trustworthy services, ensuring your travel experience is smooth and stress-free. We partner with reputable airlines, hotels, and tour operators to deliver high-quality services and meet your expectations.
- Dedicated Support: Benefit from our dedicated support team, ready to assist you with any queries or concerns. SIXT.VN offers dedicated customer support to assist you with any queries or concerns you may have. Our friendly and knowledgeable team is available to provide assistance with bookings, itinerary planning, and any other travel-related inquiries.
5.3 Addressing Concerns About Pollution
SIXT.VN also helps travelers address concerns about pollution in Vietnam.
- Information and Guidance: We provide up-to-date information about air and water quality in different regions, helping you make informed decisions about your travel destinations. Our team can provide insights into areas with better environmental conditions and suggest activities that minimize exposure to pollution.
- Eco-Friendly Options: SIXT.VN promotes eco-friendly travel options, such as recommending accommodations and tours that prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility. We partner with businesses that are committed to reducing their environmental impact and promoting responsible tourism practices.
- Transportation Choices: We offer transportation options that minimize emissions, such as recommending electric vehicles or public transportation where available. SIXT.VN is committed to promoting sustainable transportation options and reducing the carbon footprint of your travel.
- Health and Safety Tips: We provide health and safety tips for traveling in polluted areas, such as advising on the use of air filters and face masks. Our team can provide guidance on how to protect your health and well-being during your trip.
By choosing SIXT.VN, you can enjoy a worry-free travel experience, knowing that your safety, comfort, and environmental concerns are well taken care of.
6. What are the Major Sources of River Pollution in Vietnam?
River pollution in Vietnam stems from a combination of industrial, agricultural, and domestic activities, each contributing unique pollutants. According to a study by the Vietnam Environment Administration (VEA), industrial discharge accounts for a significant portion of water contamination, especially near manufacturing zones.
6.1 Industrial Discharge
Industrial facilities often release untreated or inadequately treated wastewater directly into rivers. This wastewater can contain a variety of harmful substances.
- Chemical Pollutants: Heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and organic compounds from factories contaminate water sources, posing severe risks to aquatic life and human health. Industries such as textiles, chemicals, and mining are major contributors.
- High Organic Loads: Wastewater from food processing plants and breweries contains high levels of organic matter, which depletes oxygen in the water as it decomposes. This can lead to the death of fish and other aquatic organisms, disrupting the ecosystem.
- Thermal Pollution: Power plants and industrial processes often discharge heated water into rivers, raising the water temperature and reducing its ability to hold oxygen. This can harm temperature-sensitive species and alter the ecological balance of the river.
- Lack of Enforcement: Inadequate enforcement of environmental regulations allows many industrial facilities to operate without proper wastewater treatment systems, exacerbating the problem of industrial discharge.
- Illegal Dumping: Some companies resort to illegal dumping of hazardous waste into rivers to avoid treatment costs. This can have devastating consequences for water quality and public health, as these wastes often contain highly toxic substances.
6.2 Agricultural Runoff
Agricultural activities contribute significantly to river pollution through the runoff of fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste.
- Fertilizer Use: Excessive use of chemical fertilizers leads to nutrient runoff, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, which causes eutrophication in rivers. This process promotes excessive algae growth, depleting oxygen and harming aquatic life.
- Pesticide Contamination: Pesticides used in agriculture can leach into rivers, contaminating water sources and harming aquatic organisms. Some pesticides are persistent and can accumulate in the food chain, posing long-term risks.
- Animal Waste: Runoff from livestock farms carries animal waste into rivers, introducing pathogens and organic matter. This can contaminate drinking water sources and increase the risk of waterborne diseases.
- Soil Erosion: Deforestation and poor soil management practices contribute to soil erosion, which leads to sediment runoff into rivers. This can increase turbidity, reduce sunlight penetration, and smother aquatic habitats.
- Aquaculture Impacts: Intensive aquaculture practices can release large amounts of organic waste, antibiotics, and chemicals into rivers, causing pollution and disrupting the ecosystem.
6.3 Domestic Waste
Untreated or poorly treated domestic wastewater is a major source of river pollution in Vietnam, especially in urban areas with inadequate sewage systems.
- Sewage Discharge: Many households and businesses discharge untreated sewage directly into rivers, introducing pathogens, nutrients, and organic matter. This can contaminate drinking water sources and increase the risk of waterborne diseases.
- Lack of Wastewater Treatment: Insufficient investment in wastewater treatment infrastructure means that a large proportion of domestic wastewater is not adequately treated before being discharged into rivers.
- Solid Waste Disposal: Improper disposal of solid waste, including plastic and other debris, can lead to rivers becoming clogged and polluted. This not only harms aquatic life but also reduces the aesthetic value of the river.
- Informal Settlements: In many urban areas, informal settlements lack proper sanitation facilities, leading to untreated sewage and waste being discharged directly into rivers.
- Urban Runoff: Stormwater runoff from urban areas can carry pollutants such as oil, chemicals, and litter into rivers, further contributing to water pollution.
Addressing these major sources of river pollution requires a comprehensive approach that includes stricter environmental regulations, improved wastewater treatment infrastructure, sustainable agricultural practices, and public awareness campaigns.
7. What Measures Are Being Taken to Combat River Pollution in Vietnam?
The Vietnamese government and various organizations are implementing several measures to address river pollution, aiming to improve water quality and protect aquatic ecosystems. These efforts involve regulatory actions, infrastructure development, community engagement, and international cooperation.
7.1 Government Regulations and Policies
The Vietnamese government has enacted various laws and regulations to control pollution and protect water resources.
- Environmental Protection Law: This law provides the legal framework for environmental management, including regulations on water pollution control, wastewater discharge standards, and environmental impact assessments.
- Water Resources Law: This law governs the management and utilization of water resources, including provisions for water quality monitoring, water allocation, and protection of water sources.
- National Action Plan on Water Pollution Control: This plan outlines specific targets and measures for reducing water pollution, including investments in wastewater treatment infrastructure, promotion of cleaner production technologies, and enforcement of environmental regulations.
- Stricter Emission Standards: The government has been tightening emission standards for industries and wastewater treatment plants, requiring them to reduce the amount of pollutants discharged into rivers.
- Increased Monitoring and Enforcement: Efforts are being made to strengthen environmental monitoring and enforcement, including increased inspections of industrial facilities and stricter penalties for violations of environmental regulations.
7.2 Infrastructure Development
Investing in wastewater treatment and solid waste management infrastructure is crucial for reducing river pollution.
- Wastewater Treatment Plants: The government is investing in the construction and upgrading of wastewater treatment plants in urban and industrial areas to reduce the amount of untreated sewage and industrial wastewater discharged into rivers.
- Sewerage Systems: Expanding sewerage systems in cities and towns helps collect and transport wastewater to treatment plants, preventing it from being discharged directly into rivers.
- Solid Waste Management Facilities: Developing modern solid waste management facilities, including landfills and recycling plants, helps reduce the amount of waste that ends up in rivers.
- Upgrading Drainage Systems: Improving urban drainage systems helps prevent stormwater runoff from carrying pollutants into rivers.
- Decentralized Treatment Systems: Promoting decentralized wastewater treatment systems, such as constructed wetlands and biofilters, can provide cost-effective solutions for treating wastewater in rural and peri-urban areas.
7.3 Community Engagement and Education
Engaging local communities and raising awareness about the importance of protecting water resources is essential for the success of pollution control efforts.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Conducting public awareness campaigns to educate people about the sources and impacts of water pollution and promote responsible behaviors, such as reducing waste and conserving water.
- Community Monitoring Programs: Involving local communities in monitoring water quality and reporting pollution incidents helps increase accountability and encourages community participation in environmental protection.
- Environmental Education in Schools: Integrating environmental education into school curricula helps raise awareness among young people and promotes a culture of environmental stewardship.
- Incentives for Cleaner Production: Providing incentives for industries to adopt cleaner production technologies and reduce their environmental footprint encourages sustainable business practices.
- Promoting Eco-Tourism: Developing eco-tourism initiatives that highlight the natural beauty of rivers and wetlands can help raise awareness about the importance of protecting these ecosystems.
7.4 International Cooperation
Collaborating with international organizations and other countries helps Vietnam access expertise, technology, and financial resources for combating river pollution.
- Partnerships with International Organizations: Working with organizations such as the World Bank, the Asian Development Bank, and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) to implement water pollution control projects and promote sustainable water management practices.
- Technology Transfer: Facilitating the transfer of advanced wastewater treatment technologies from developed countries to Vietnam helps improve the efficiency and effectiveness of pollution control efforts.
- Joint Research Programs: Conducting joint research programs with international research institutions to study the causes and impacts of water pollution and develop innovative solutions.
- Regional Cooperation: Participating in regional initiatives, such as the Mekong River Commission, to address transboundary water pollution issues and promote sustainable water management in the Mekong River Basin.
- Financial Assistance: Seeking financial assistance from international donors and development banks to support investments in water pollution control infrastructure and capacity building.
These comprehensive measures demonstrate Vietnam’s commitment to combating river pollution and protecting its valuable water resources for future generations.
8. What are Some Specific Examples of River Pollution Issues in Vietnam?
Several rivers in Vietnam face significant pollution challenges due to industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and domestic waste. These issues affect water quality, aquatic life, and human health in surrounding communities.
8.1 The Nhue-Day River Basin
The Nhue-Day River Basin, which flows through Hanoi and several surrounding provinces, is heavily polluted due to industrial and domestic wastewater discharge.
- Sources of Pollution: Industrial parks, handicraft villages, and residential areas along the river discharge untreated or poorly treated wastewater, containing high levels of organic matter, chemicals, and pathogens.
- Impacts on Water Quality: The river water is often black, emits foul odors, and has very low levels of dissolved oxygen, making it unsuitable for aquatic life and human use.
- Health Risks: Residents who rely on the river for irrigation and domestic purposes are exposed to health risks from contaminated water, including waterborne diseases and exposure to toxic chemicals.
- Government Efforts: The government has invested in wastewater treatment plants and implemented regulations to reduce pollution in the Nhue-Day River Basin, but challenges remain due to the scale and complexity of the problem.
- Community Initiatives: Local communities have organized clean-up campaigns and monitoring programs to raise awareness about the river’s pollution and advocate for stronger pollution control measures.
8.2 The Saigon River
The Saigon River, which flows through Ho Chi Minh City, faces significant pollution challenges from industrial, domestic, and agricultural sources.
- Sources of Pollution: Industrial zones, informal settlements, and agricultural areas along the river discharge untreated wastewater, containing heavy metals, pesticides, and organic pollutants.
- Impacts on Water Quality: The river water is often turbid, contains high levels of bacteria and other pathogens, and is subject to saltwater intrusion due to reduced freshwater flow.
- Ecosystem Damage: Pollution has led to the loss of biodiversity, degradation of aquatic habitats, and reduced fish populations in the Saigon River.
- Water Supply Challenges: The city relies on the Saigon River for its water supply, but pollution has made it more difficult and costly to treat the water to meet drinking water standards.
- Community Involvement: Local residents and environmental organizations have been working to raise awareness about the river’s pollution and promote sustainable water management practices.
8.3 The Mekong Delta
The Mekong Delta, Vietnam’s “rice bowl,” faces increasing pollution challenges from agricultural runoff, aquaculture waste, and industrial discharge.
- Sources of Pollution: Intensive agriculture, aquaculture, and seafood processing industries discharge wastewater containing pesticides, fertilizers, antibiotics, and organic pollutants into the delta’s waterways.
- Impacts on Water Quality: The delta’s water resources are increasingly polluted, with high levels of nutrients, pathogens, and toxic chemicals, affecting aquatic life and human health.
- Ecosystem Degradation: Pollution has led to the degradation of mangrove forests, loss of biodiversity, and reduced fish stocks in the Mekong Delta.
- Livelihood Impacts: Farmers and fishermen who depend on the delta’s water resources for their livelihoods are facing economic hardship due to pollution and resource depletion.
- Sustainable Practices: Efforts are being made to promote sustainable agricultural and aquaculture practices to reduce pollution and protect the delta’s ecosystems.
These examples highlight the diverse and complex challenges of river pollution in Vietnam and underscore the need for comprehensive and integrated solutions to protect water resources and ensure sustainable development.
9. What Can Tourists Do to Minimize Their Environmental Impact in Vietnam?
As tourists, there are many ways to minimize your environmental impact while visiting Vietnam, helping to preserve its natural beauty and resources for future generations.
9.1 Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle
Apply the principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle to minimize waste and conserve resources.
- Bring Reusable Items: Bring your own reusable water bottle, shopping bag, and coffee cup to avoid using disposable plastic items.
- Say No to Plastic: Refuse single-use plastics such as straws, plastic bags, and disposable cutlery.
- Recycle Properly: Dispose of recyclable materials in designated recycling bins whenever possible.
- Reduce Packaging: Choose products with minimal packaging and avoid buying individually wrapped items.
- Compost Food Waste: If possible, compost food waste to reduce the amount of organic matter sent to landfills.
9.2 Conserve Water and Energy
Use water and energy responsibly to minimize your environmental footprint.
- Take Shorter Showers: Reduce water consumption by taking shorter showers and turning off the tap while brushing your teeth.
- Use Water Wisely: Report leaky faucets and toilets to your hotel and use water sparingly.
- Turn Off Lights and Electronics: Turn off lights, air conditioning, and electronic devices when you leave your hotel room.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances: Opt for hotels and accommodations that use energy-efficient appliances and lighting.
- Support Green Hotels: Stay at hotels that have implemented sustainable practices, such as using renewable energy, conserving water, and reducing waste.
9.3 Choose Sustainable Transportation
Opt for eco-friendly transportation options to reduce your carbon emissions.
- Walk or Bike: Explore cities and towns on foot or by bicycle to reduce your carbon footprint and enjoy the scenery.
- Use Public Transportation: Take advantage of public transportation options such as buses, trains, and trams to get around.
- Carpool: Share rides with other travelers to reduce the number of vehicles on the road.
- Choose Fuel-Efficient Vehicles: If renting a car, opt for a fuel-efficient model or an electric vehicle.
- Offset Your Carbon Footprint: Consider purchasing carbon offsets to compensate for the emissions from your flights and other travel activities.
9.4 Respect Local Ecosystems
Avoid activities that harm natural ecosystems and wildlife.
- Stay on Marked Trails: Stick to marked trails when hiking or exploring natural areas to avoid damaging vegetation and disturbing wildlife.
- Avoid Touching or Feeding Wildlife: Refrain from touching or feeding wild animals, as this can disrupt their natural behaviors and harm their health.
- Do Not Litter: Dispose of trash properly and avoid leaving any waste behind in natural areas.
- Respect Marine Life: When snorkeling or diving, avoid touching or disturbing coral reefs and other marine life.
- Support Conservation Efforts: Donate to local conservation organizations or participate in volunteer activities to support environmental protection efforts.
9.5 Support Local Communities
Choose locally owned businesses and products to support the local economy and promote sustainable development.
- Shop at Local Markets: Buy souvenirs and other items from local markets and shops to support local artisans and businesses.
- Eat at Local Restaurants: Dine at local restaurants and try traditional Vietnamese dishes made with locally sourced ingredients.
- Stay at Locally Owned Accommodations: Choose guesthouses and hotels that are owned and operated by local families.
- Hire Local Guides: Hire local guides to learn about the culture, history, and natural environment of the area you are visiting.
- Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of local customs and traditions and dress modestly when visiting temples and other religious sites.
By following these tips, you can minimize your environmental impact and contribute to the sustainable development of Vietnam.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Pollution and Travel in Vietnam
Here are some frequently asked questions about pollution and travel in Vietnam to help you plan your trip.
Q1: Is air pollution a major concern in Vietnamese cities?
Yes, air pollution can be a concern, especially in major cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City.
Q2: What causes air pollution in Vietnam?
Major sources include vehicle emissions, industrial activities, construction, and burning of agricultural residue.
Q3: How can I check the air quality in Vietnam?
You can use websites and apps like AirNow or local environmental monitoring sites to check real-time air quality.
Q4: Are there specific times of the year when air quality is worse?
Air quality tends to be worse during the dry season (November to April) due to less rain to clear pollutants.
Q5: What precautions can I take to protect myself from air pollution?
Consider wearing a mask, limiting outdoor activities during peak pollution times, and using air purifiers indoors.
Q6: Is river pollution a problem in Vietnam?
Yes, many rivers in Vietnam are polluted due to industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and domestic waste.
Q7: How does river pollution affect tourism?
Pollution can affect the aesthetic appeal of destinations and pose health risks for tourists engaging in water-based activities.
Q8: What is the government doing to address pollution?
The government is implementing stricter regulations, investing in wastewater treatment, and promoting sustainable practices.
Q9: Can tourists help reduce pollution in Vietnam?
Yes, by reducing waste, conserving resources, supporting local businesses, and respecting local ecosystems.
Q10: How can SIXT.VN assist me with my travel plans considering pollution concerns?
SIXT.VN provides information, eco-friendly travel options, and support to ensure a safe and enjoyable trip while minimizing your environmental impact.
Contact SIXT.VN Today
Ready to explore Vietnam with peace of mind? Contact SIXT.VN for personalized travel advice and convenient services.
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
By choosing SIXT.VN, you can enjoy a seamless and sustainable travel experience, knowing that your comfort and environmental impact are our top priorities.



