Are you curious about the bear species receiving top-notch care at specialized facilities? At SIXT.VN, we understand the importance of wildlife conservation and the dedication it takes to provide exceptional care for animals. This article explores the types of bears benefiting from expert attention, highlighting the vital role of veterinary medicine and conservation efforts. If you’re planning a trip to Vietnam and are interested in ethical wildlife tourism, let SIXT.VN assist you in creating a responsible and enriching travel experience with airport transfers, hotel booking, and exciting tours. We offer travel planning, and comprehensive travel guidance.
1. What Types of Bears Receive Care at Veterinary Facilities?
American black bears, like Judge Indy and Judge Belle, are often cared for at veterinary facilities, especially when they serve as mascots or require specialized medical attention. These facilities provide preventative exams, treatments for injuries or illnesses, and long-term care to ensure the bears’ well-being.
The care for bears in veterinary facilities includes a range of services, from routine check-ups to advanced medical treatments. According to research from the American Association of Zoo Veterinarians in 2022, preventative care programs significantly improve the lifespan and quality of life for captive bears. These programs typically involve regular physical exams, vaccinations, parasite control, and nutritional assessments. In cases where bears suffer from injuries or illnesses, veterinary facilities are equipped to provide advanced diagnostics such as CT scans and biopsies, as well as treatments like radiation therapy and surgery.
1.1 Preventative Care for Bears
Preventative care is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of bears in captivity. Regular check-ups can identify potential health issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and preventing more serious complications.
- Physical Exams: Veterinarians conduct thorough physical exams to assess the bear’s overall health, checking vital signs, examining the eyes, ears, and nose, and palpating the abdomen and lymph nodes.
- Vaccinations: Vaccinations protect bears from common diseases that could be detrimental to their health.
- Parasite Control: Regular deworming and parasite prevention are essential to keep bears free from internal and external parasites.
- Nutritional Assessments: Ensuring bears receive a balanced and appropriate diet is vital for their growth and development.
1.2 Advanced Medical Treatments for Bears
In addition to preventative care, veterinary facilities offer advanced medical treatments for bears suffering from injuries or illnesses.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Techniques like X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help veterinarians diagnose a wide range of conditions, from bone fractures to tumors.
- Surgery: Surgical procedures may be necessary to remove tumors, repair injuries, or correct congenital defects.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy can be used to treat certain types of cancer in bears, as demonstrated by the successful treatment of Judge Lady’s thymoma.
- Anesthesia and Pain Management: Veterinarians use anesthesia and pain management techniques to ensure bears are comfortable during medical procedures.
1.3 The Role of Veterinary Specialists
Veterinary specialists play a critical role in the care of bears at veterinary facilities. These specialists have extensive knowledge and experience in treating exotic animals and wildlife.
- Zoological Medicine Specialists: These specialists are trained to diagnose and treat diseases in a wide range of zoo animals, including bears.
- Wildlife Veterinarians: Wildlife veterinarians focus on the health and conservation of wild animals, including bears.
- Surgeons: Veterinary surgeons perform complex surgical procedures on bears.
- Radiologists: Veterinary radiologists interpret diagnostic images to help diagnose diseases and injuries.
- Anesthesiologists: Veterinary anesthesiologists ensure bears are safely anesthetized during medical procedures.
1.4 Ethical Considerations in Bear Care
Ethical considerations are paramount in the care of bears at veterinary facilities. Veterinarians and animal care staff must prioritize the well-being of the bears and ensure they are treated with respect and compassion.
- Animal Welfare: Ensuring bears have adequate space, enrichment, and social interaction is essential for their well-being.
- Minimizing Stress: Veterinary procedures should be performed in a way that minimizes stress for the bears.
- Pain Management: Pain management is crucial for bears undergoing medical procedures.
- Euthanasia: In cases where a bear’s quality of life is severely compromised, euthanasia may be the most humane option.
1.5 Success Stories in Bear Care
There have been many success stories in the care of bears at veterinary facilities. These stories highlight the dedication and expertise of veterinary professionals and the resilience of bears.
- Judge Lady’s Thymoma Treatment: The successful treatment of Judge Lady’s thymoma with stereotactic body radiation therapy is a testament to the advanced medical care available to bears.
- Rehabilitation of Injured Bears: Many injured bears have been successfully rehabilitated and released back into the wild thanks to the efforts of wildlife veterinarians.
- Conservation Programs: Veterinary facilities play a vital role in conservation programs aimed at protecting endangered bear species.
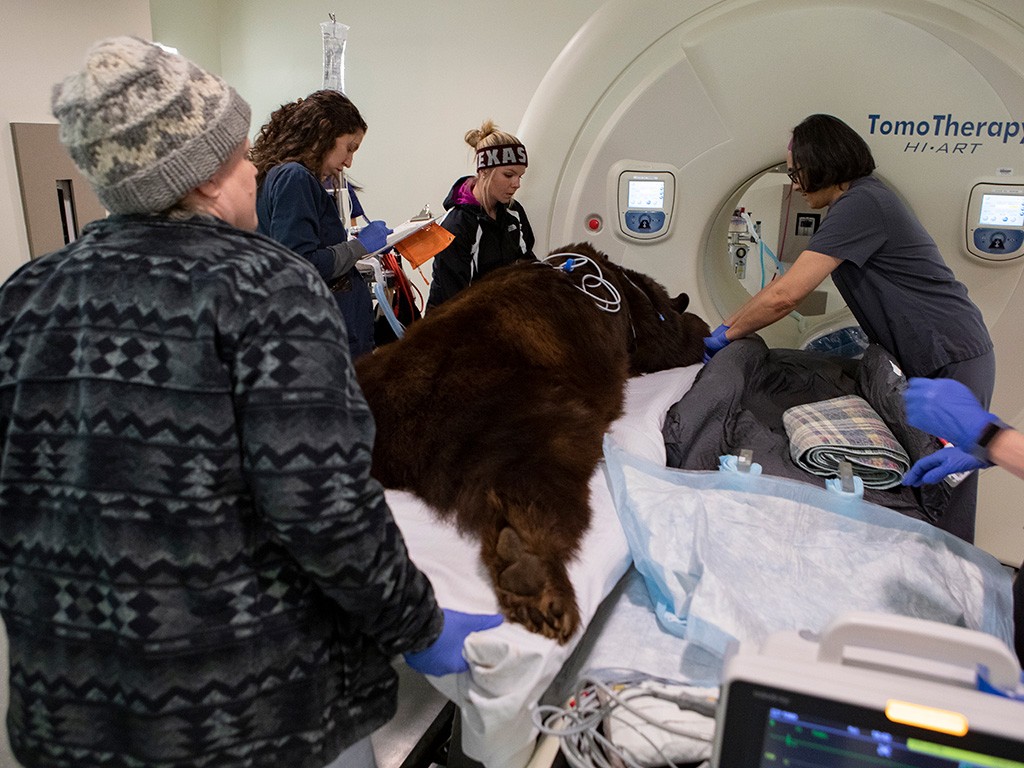 Adult black bear lying on its stomach on a hospital bed surrounded by veterinary hospital staff and equipment, showcasing advanced veterinary care for bears
Adult black bear lying on its stomach on a hospital bed surrounded by veterinary hospital staff and equipment, showcasing advanced veterinary care for bears
2. Where Do Mascots Like Judge Indy and Judge Belle Live?
Mascots like Judge Indy and Judge Belle live in specially designed habitats, such as the Bill and Eva Williams Bear Habitat, which is accredited by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA). These habitats provide a safe, enriching environment that meets the bears’ physical and behavioral needs.
The habitats for bear mascots are designed to mimic their natural environment as closely as possible while ensuring their safety and well-being. These habitats often include features such as:
- Spacious Enclosures: The enclosures are large enough to allow the bears to roam freely and engage in natural behaviors.
- Natural Substrates: The ground is covered with natural materials like dirt, grass, and wood chips to provide a comfortable and stimulating environment.
- Enrichment Features: Enrichment features such as climbing structures, water features, and toys are provided to keep the bears mentally and physically stimulated.
- Denning Areas: The habitats include denning areas where the bears can retreat for privacy and rest.
- Temperature Control: The habitats are designed to provide adequate shade and shelter to protect the bears from extreme weather conditions.
2.1 The Importance of AZA Accreditation
Accreditation by the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA) is a significant indicator of the quality of a bear habitat. AZA-accredited facilities meet rigorous standards for animal care, conservation, education, and research.
- Animal Care Standards: AZA-accredited facilities must adhere to strict standards for animal nutrition, veterinary care, enrichment, and habitat design.
- Conservation Efforts: AZA-accredited facilities are actively involved in conservation programs aimed at protecting endangered species and their habitats.
- Education Programs: AZA-accredited facilities provide educational programs to raise awareness about animals and conservation.
- Research Initiatives: AZA-accredited facilities conduct research to improve animal care and conservation practices.
2.2 The Role of Full-Time Staff and Volunteers
Full-time staff members and student volunteers play a crucial role in the care of bear mascots. These individuals are dedicated to providing the bears with the best possible care.
- Animal Care Staff: Animal care staff are responsible for feeding, cleaning, and providing enrichment for the bears.
- Veterinarians: Veterinarians provide medical care for the bears, including preventative exams, treatments for injuries and illnesses, and long-term care.
- Educators: Educators develop and deliver educational programs about the bears and conservation.
- Volunteers: Volunteers assist with a variety of tasks, such as cleaning enclosures, preparing food, and providing enrichment.
2.3 The Daily Life of Bear Mascots
The daily life of bear mascots is carefully managed to ensure their physical and behavioral needs are met.
- Feeding: The bears receive a balanced diet that is tailored to their individual needs.
- Enrichment: The bears are provided with a variety of enrichment activities to keep them mentally and physically stimulated.
- Training: The bears may participate in training programs to help them cooperate with veterinary procedures and other management activities.
- Social Interaction: The bears may have opportunities for social interaction with other bears or with their human caregivers.
- Rest and Relaxation: The bears have access to denning areas where they can retreat for privacy and rest.
2.4 Balancing Mascot Duties and Animal Welfare
Balancing mascot duties with animal welfare is a critical consideration in the care of bear mascots. It is essential to ensure that the bears’ well-being is not compromised by their role as mascots.
- Limited Public Appearances: The bears’ public appearances should be limited to minimize stress and disruption to their routine.
- Positive Reinforcement Training: Positive reinforcement training techniques should be used to encourage the bears to participate in mascot duties.
- Monitoring for Stress: The bears should be closely monitored for signs of stress during public appearances and other mascot duties.
- Prioritizing the Bears’ Needs: The bears’ needs should always be prioritized over mascot duties.
2.5 Community Engagement and Education
Bear habitats often serve as educational resources for the community, providing opportunities for people to learn about bears and conservation.
- Educational Programs: Educational programs can teach visitors about bear biology, behavior, and conservation.
- Interpretive Signage: Interpretive signage can provide information about the bears and their habitat.
- Volunteer Opportunities: Volunteer opportunities can allow community members to get involved in the care of the bears.
- Conservation Partnerships: Conservation partnerships can support bear conservation efforts around the world.
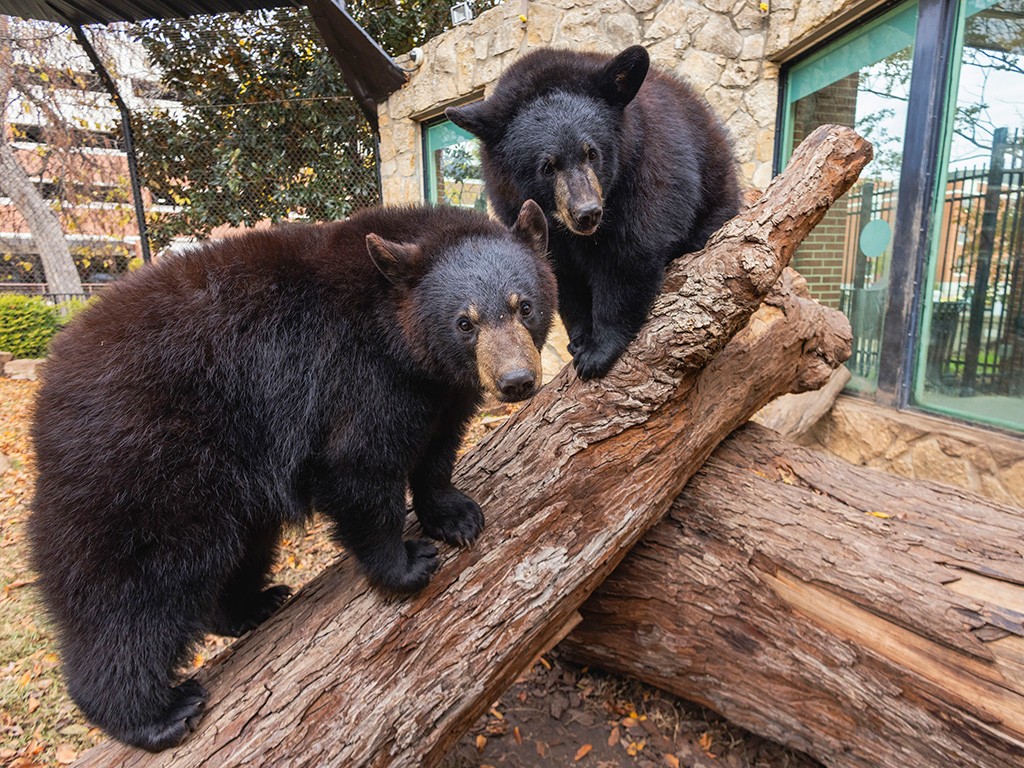 Two black bears standing on logs in an enclosure showcasing a natural and enriching habitat for bears
Two black bears standing on logs in an enclosure showcasing a natural and enriching habitat for bears
3. How Did Texas A&M and Baylor University Partner to Care for Bears?
Texas A&M and Baylor University formed a unique partnership in 2018 when Texas A&M’s College of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) began providing veterinary care for Baylor’s live bear mascots. This collaboration ensures the bears receive top-notch medical attention and offers valuable learning opportunities for veterinary students.
The partnership between Texas A&M and Baylor University is a testament to the importance of collaboration in animal care and conservation. This partnership has several key components:
- Veterinary Expertise: Texas A&M’s VMBS provides veterinary expertise to ensure the bears receive the best possible medical care.
- Specialized Facilities: Texas A&M’s Winnie Carter Wildlife Center offers specialized facilities for treating and caring for wild animals, including bears.
- Learning Opportunities: The partnership provides learning opportunities for Texas A&M veterinary students, allowing them to gain experience working with exotic animals.
- Conservation Focus: The partnership supports bear conservation efforts by raising awareness about the importance of protecting these animals and their habitats.
3.1 The Genesis of the Partnership
The partnership began when Dr. Sharman Hoppes, a professor emerita at Texas A&M’s VMBS, was invited to take over the veterinary care of Baylor’s bear mascots, Lady and Joy, in 2018.
- Shared Values: Both universities share a commitment to animal welfare and conservation.
- Complementary Expertise: Texas A&M’s VMBS has extensive expertise in veterinary medicine, while Baylor University has a long tradition of caring for live bear mascots.
- Geographic Proximity: The close proximity of the two universities makes it easier for veterinarians and staff to travel between campuses to provide care for the bears.
3.2 Key Individuals Involved
Several key individuals have played a crucial role in the success of the partnership.
- Dr. Sharman Hoppes: Dr. Hoppes, a professor emerita at Texas A&M’s VMBS, has been instrumental in providing veterinary care for Baylor’s bear mascots.
- Dr. Alice Blue-McLendon: Dr. Blue-McLendon, a clinical associate professor and wildlife center director at Texas A&M’s VMBS, has also been involved in the care of the bears.
- Dakota Farquhar-Caddell: Dakota Farquhar-Caddell, associate director of student activities and the Robert L. Reid Director of the Baylor Chamber of Commerce, has been a key liaison between the two universities.
3.3 Benefits for Baylor University
Baylor University benefits from the partnership by having access to the expertise and resources of Texas A&M’s VMBS.
- Access to Specialists: Baylor has access to veterinary specialists with expertise in exotic animal medicine.
- Advanced Medical Care: Baylor’s bear mascots receive advanced medical care, including diagnostic imaging, surgery, and radiation therapy.
- Learning Opportunities for Students: Baylor students have opportunities to learn about animal care and conservation by interacting with the bears and the veterinary team.
3.4 Benefits for Texas A&M University
Texas A&M University benefits from the partnership by providing learning opportunities for veterinary students and advancing research in exotic animal medicine.
- Hands-On Experience: Veterinary students gain hands-on experience working with exotic animals in a captive setting.
- Research Opportunities: The partnership provides opportunities for research in areas such as bear health, behavior, and nutrition.
- Community Outreach: The partnership raises awareness about the importance of animal welfare and conservation.
3.5 The Future of the Partnership
The partnership between Texas A&M and Baylor University is expected to continue for many years to come, providing ongoing benefits for both universities and for the bears in their care.
- Continued Veterinary Care: Texas A&M’s VMBS will continue to provide veterinary care for Baylor’s bear mascots.
- Expanded Research Opportunities: The partnership may expand to include additional research projects related to bear health and conservation.
- Increased Community Engagement: The partnership may increase community engagement through educational programs and outreach events.
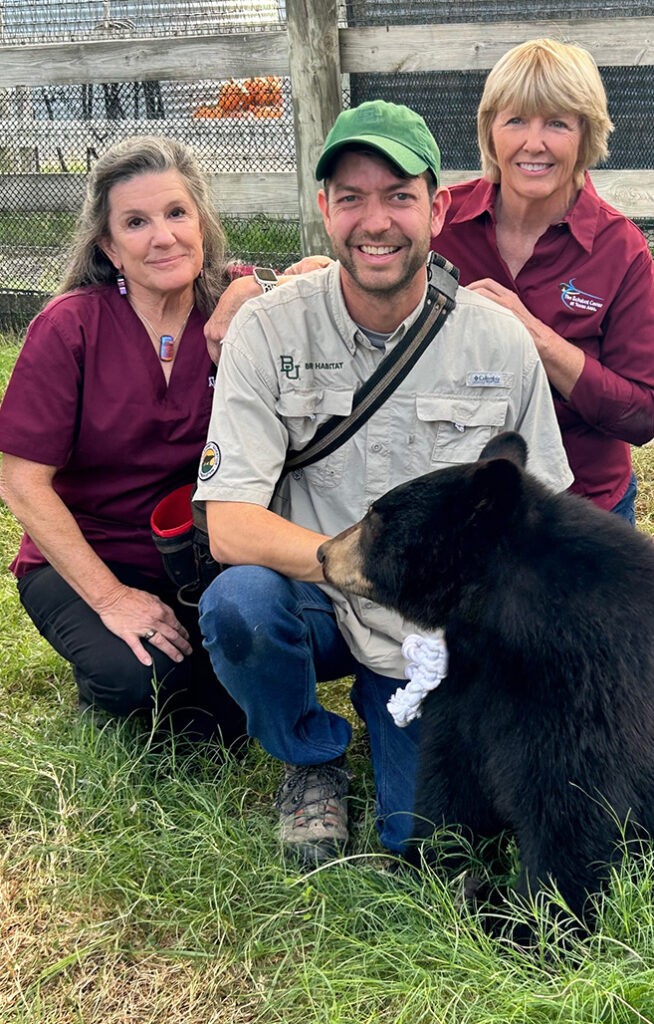 A man in a green baseball cap and two women in maroon shirts kneel beside a young black bear illustrating the partnership between Texas A&M and Baylor University
A man in a green baseball cap and two women in maroon shirts kneel beside a young black bear illustrating the partnership between Texas A&M and Baylor University
4. What Kind of Medical Breakthroughs Resulted from Caring for Baylor’s Bears?
Caring for Baylor’s bears led to significant medical breakthroughs, most notably the use of stereotactic body radiation therapy to treat Judge Lady’s thymoma. This innovative treatment, never before used on a bear, greatly reduced the tumor’s size and allowed Lady to resume her normal life.
The medical breakthroughs resulting from the care of Baylor’s bears have had a significant impact on the field of veterinary medicine.
- Advancements in Radiation Therapy: The successful use of stereotactic body radiation therapy to treat Judge Lady’s thymoma has demonstrated the potential of this technique for treating cancer in other animals.
- Improved Anesthesia Protocols: Veterinarians have developed improved anesthesia protocols for bears, making it safer to perform medical procedures on these animals.
- Enhanced Diagnostic Techniques: The care of Baylor’s bears has led to the development of enhanced diagnostic techniques for detecting and monitoring diseases in bears.
- Increased Knowledge of Bear Health: The partnership between Texas A&M and Baylor University has increased knowledge of bear health, behavior, and nutrition.
4.1 The Story of Judge Lady’s Thymoma Treatment
Judge Lady’s thymoma treatment was a groundbreaking achievement in veterinary medicine.
- Diagnosis: During a geriatric exam, veterinarians discovered a mass near Lady’s heart on an X-ray.
- Confirmation: A CT scan and biopsy confirmed the mass was a benign thymoma.
- Treatment: The veterinary team decided to treat the tumor with stereotactic body radiation therapy using the TomoTherapy system.
- Outcome: After three doses of radiation treatment, Lady’s mass was greatly reduced in size, and she was able to resume her normal life.
4.2 Significance of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Stereotactic body radiation therapy is a highly precise form of radiation therapy that delivers large doses of radiation to the tumor while sparing surrounding tissues.
- Non-Invasive: Stereotactic body radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment option that does not require surgery.
- Precise Targeting: The treatment targets the tumor with high precision, minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
- Reduced Side Effects: Stereotactic body radiation therapy is associated with fewer side effects than traditional radiation therapy.
- Improved Outcomes: The treatment has been shown to improve outcomes for patients with certain types of cancer.
4.3 Application to Other Animals
The successful use of stereotactic body radiation therapy to treat Judge Lady’s thymoma has opened up new possibilities for treating cancer in other animals.
- Dogs and Cats: The treatment has been used to treat a variety of cancers in dogs and cats, including lymphoma, sarcoma, and carcinoma.
- Horses: Stereotactic body radiation therapy has been used to treat certain types of cancer in horses, such as squamous cell carcinoma.
- Zoo Animals: The treatment may be a viable option for treating cancer in other zoo animals, such as elephants and rhinoceroses.
4.4 Dissemination of Knowledge
The knowledge gained from Judge Lady’s thymoma treatment has been disseminated to other veterinary professionals through publications, presentations, and training programs.
- Publications: Veterinarians have published articles in scientific journals describing the treatment and its outcomes.
- Presentations: Veterinarians have presented their findings at veterinary conferences and meetings.
- Training Programs: Veterinarians have developed training programs to teach other veterinary professionals how to perform stereotactic body radiation therapy.
4.5 Impact on Bear Care Standards
Judge Lady’s thymoma treatment has raised the standard of black bear care globally.
- Increased Awareness: The treatment has increased awareness about the importance of providing advanced medical care for bears.
- Improved Treatment Options: The treatment has expanded the range of treatment options available for bears with cancer.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: The treatment has improved the quality of life for bears with cancer.
5. What Does Preventative Care for Bears Include?
Preventative care for bears includes regular physical exams, vaccinations, parasite control, and nutritional assessments. These measures help maintain their health and detect potential issues early.
Preventative care is essential for maintaining the health and well-being of bears in captivity.
- Early Detection of Health Problems: Regular physical exams can help detect health problems early on when they are easier to treat.
- Prevention of Diseases: Vaccinations can prevent bears from contracting common diseases.
- Control of Parasites: Parasite control measures can prevent bears from becoming infested with internal and external parasites.
- Optimal Nutrition: Nutritional assessments can ensure that bears are receiving a balanced and appropriate diet.
5.1 Regular Physical Exams
Regular physical exams are a cornerstone of preventative care for bears.
- Frequency: Bears should receive a physical exam at least once a year, and more frequently if they have a history of health problems.
- Components: A physical exam typically includes checking vital signs, examining the eyes, ears, and nose, palpating the abdomen and lymph nodes, and listening to the heart and lungs.
- Early Detection: Physical exams can help detect early signs of health problems, such as weight loss, skin lesions, or changes in behavior.
5.2 Vaccinations
Vaccinations are an important tool for preventing infectious diseases in bears.
- Common Vaccines: Common vaccines for bears include those for rabies, distemper, adenovirus, parvovirus, and parainfluenza.
- Vaccination Schedule: The vaccination schedule for bears may vary depending on the species of bear and the risk of exposure to specific diseases.
- Protection: Vaccinations can protect bears from contracting serious and potentially fatal diseases.
5.3 Parasite Control
Parasite control is essential for preventing bears from becoming infested with internal and external parasites.
- Internal Parasites: Internal parasites, such as roundworms and tapeworms, can cause a variety of health problems in bears, including weight loss, diarrhea, and anemia.
- External Parasites: External parasites, such as fleas and ticks, can cause skin irritation, itching, and the transmission of diseases.
- Control Measures: Parasite control measures include regular deworming, flea and tick prevention, and proper hygiene practices.
5.4 Nutritional Assessments
Nutritional assessments are important for ensuring that bears are receiving a balanced and appropriate diet.
- Dietary Needs: The dietary needs of bears vary depending on their age, species, and activity level.
- Assessment Methods: Nutritional assessments may include evaluating the bear’s body condition, analyzing their diet, and monitoring their weight and growth.
- Dietary Adjustments: Based on the results of the nutritional assessment, dietary adjustments may be necessary to ensure that the bear is receiving optimal nutrition.
5.5 Enrichment Activities
Enrichment activities are an important part of preventative care for bears, as they help to promote physical and mental well-being.
- Types of Enrichment: Enrichment activities may include providing the bears with climbing structures, water features, toys, and opportunities for social interaction.
- Benefits of Enrichment: Enrichment activities can help to reduce stress, prevent boredom, and promote natural behaviors.
- Customization: Enrichment activities should be customized to meet the individual needs and preferences of each bear.
6. What Do Bears Eat Under the Care of Veterinary Teams?
Under the care of veterinary teams, bears eat a carefully balanced diet consisting of high-quality protein, fresh fruits and vegetables, and specialized supplements to ensure their nutritional needs are fully met. The diet is often adjusted based on the bear’s age, health condition, and activity level.
The diet of bears under the care of veterinary teams is carefully formulated to meet their specific nutritional needs.
- Balanced Diet: The diet should be balanced in terms of protein, carbohydrates, and fats.
- High-Quality Ingredients: The diet should consist of high-quality ingredients that are easily digestible.
- Variety: The diet should include a variety of foods to ensure that the bears are receiving all the nutrients they need.
- Adjustments: The diet may need to be adjusted based on the bear’s age, health condition, and activity level.
6.1 Key Components of a Bear’s Diet
The key components of a bear’s diet include:
- Protein: Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates provide energy for the bears.
- Fats: Fats provide energy and help the bears absorb certain vitamins.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins and minerals are essential for overall health.
- Fiber: Fiber helps to promote healthy digestion.
6.2 Examples of Foods Included in a Bear’s Diet
Examples of foods that may be included in a bear’s diet include:
- Meat: Meat is a good source of protein.
- Fish: Fish is a good source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Fruits: Fruits are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Vegetables: Vegetables are a good source of vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
- Grains: Grains are a good source of carbohydrates.
- Nuts and Seeds: Nuts and seeds are a good source of protein, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
- Commercial Bear Food: Commercial bear food is a specially formulated diet that provides all the nutrients that bears need.
6.3 Supplements
Supplements may be added to a bear’s diet to ensure that they are receiving all the nutrients they need.
- Vitamin Supplements: Vitamin supplements may be added to the diet to ensure that the bears are receiving adequate amounts of vitamins.
- Mineral Supplements: Mineral supplements may be added to the diet to ensure that the bears are receiving adequate amounts of minerals.
- Joint Supplements: Joint supplements may be added to the diet to help support joint health.
6.4 Monitoring a Bear’s Diet
Veterinary teams carefully monitor a bear’s diet to ensure that they are receiving adequate nutrition.
- Weight Monitoring: The bears’ weight is monitored regularly to ensure that they are maintaining a healthy weight.
- Appetite Monitoring: The bears’ appetite is monitored to ensure that they are eating enough food.
- Fecal Monitoring: The bears’ feces is monitored to check for signs of digestive problems.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be performed to assess the bears’ nutritional status.
6.5 Adjusting a Bear’s Diet
A bear’s diet may need to be adjusted based on their age, health condition, and activity level.
- Age: Young bears may need a diet that is higher in protein to support growth.
- Health Condition: Bears with certain health conditions may need a special diet.
- Activity Level: Bears that are very active may need a diet that is higher in calories.
7. How Do Veterinary Students Benefit from Working with Bears?
Veterinary students benefit immensely from working with bears by gaining hands-on experience with exotic animals, learning specialized handling techniques, and expanding their knowledge of zoological medicine. This experience is invaluable for students interested in pursuing careers in wildlife or zoo veterinary medicine.
Veterinary students gain valuable experience by working with bears.
- Hands-On Experience: Veterinary students gain hands-on experience working with exotic animals in a captive setting.
- Specialized Techniques: Veterinary students learn specialized techniques for handling and treating bears.
- Exposure to Zoological Medicine: Veterinary students are exposed to the field of zoological medicine, which focuses on the health and care of zoo animals and wildlife.
- Networking Opportunities: Veterinary students have the opportunity to network with experienced veterinarians and animal care professionals.
7.1 Unique Learning Opportunities
Working with bears provides veterinary students with unique learning opportunities that are not typically available in traditional veterinary education.
- Exotic Animal Handling: Veterinary students learn how to safely handle and restrain bears, which requires specialized techniques and equipment.
- Anesthesia and Surgery: Veterinary students have the opportunity to assist with anesthesia and surgery on bears, which provides valuable experience in these areas.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Veterinary students learn how to interpret diagnostic images, such as X-rays and CT scans, of bears.
- Preventative Care: Veterinary students participate in preventative care programs for bears, such as vaccinations and parasite control.
7.2 Enhancing Skills and Knowledge
Working with bears helps veterinary students enhance their skills and knowledge in a variety of areas.
- Clinical Skills: Veterinary students improve their clinical skills, such as physical examination, diagnostic testing, and treatment planning.
- Communication Skills: Veterinary students develop their communication skills by interacting with veterinarians, animal care staff, and the public.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Veterinary students learn how to solve complex medical problems in bears.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Veterinary students develop their critical thinking skills by evaluating scientific literature and making informed decisions about patient care.
7.3 Career Advancement
Working with bears can help veterinary students advance their careers in zoological medicine.
- Residency Programs: Veterinary students who have experience working with bears are more competitive for residency programs in zoological medicine.
- Job Opportunities: Veterinary students who have experience working with bears are more likely to be hired for jobs in zoos, wildlife parks, and other animal care facilities.
- Research Opportunities: Veterinary students who have experience working with bears may have opportunities to participate in research projects related to bear health and conservation.
7.4 Inspiration and Motivation
Working with bears can inspire and motivate veterinary students to pursue careers in zoological medicine.
- Passion for Wildlife: Veterinary students who have a passion for wildlife are often inspired by the opportunity to work with bears.
- Commitment to Conservation: Veterinary students who are committed to conservation are often motivated by the opportunity to help protect bears and their habitats.
- Sense of Purpose: Veterinary students often feel a sense of purpose by working with bears and contributing to their well-being.
7.5 Ethical Considerations
Veterinary students who work with bears are exposed to ethical considerations related to the care and management of captive wildlife.
- Animal Welfare: Veterinary students learn about the importance of animal welfare and how to provide bears with a high quality of life in captivity.
- Conservation Ethics: Veterinary students learn about the ethical considerations related to conservation and how to balance the needs of individual animals with the needs of the population.
- Public Education: Veterinary students learn about the importance of public education and how to communicate effectively about bear conservation.
8. What Special Techniques Are Used to Provide Veterinary Care Safely to Bears?
Veterinary care for bears requires specialized techniques to ensure the safety of both the animals and the veterinary staff. These techniques include positive reinforcement, target training, and remote drug delivery systems, allowing for examinations and treatments with minimal stress to the bears.
Veterinary care for bears requires special techniques to ensure the safety of both the animals and the veterinary staff.
- Positive Reinforcement: Positive reinforcement is a training technique that involves rewarding bears for desired behaviors.
- Target Training: Target training is a technique that involves training bears to touch a target with their nose or paw.
- Remote Drug Delivery Systems: Remote drug delivery systems, such as dart guns, can be used to administer medications to bears from a distance.
8.1 Positive Reinforcement Training
Positive reinforcement training is an effective way to train bears to cooperate with veterinary procedures.
- Building Trust: Positive reinforcement helps to build trust between the bears and the veterinary staff.
- Reducing Stress: Positive reinforcement helps to reduce stress for the bears during veterinary procedures.
- Encouraging Cooperation: Positive reinforcement encourages the bears to cooperate with veterinary procedures.
8.2 Target Training
Target training can be used to train bears to present different parts of their body for examination or treatment.
- Presenting a Paw: Bears can be trained to present a paw for blood draws or nail trims.
- Opening the Mouth: Bears can be trained to open their mouth for dental exams.
- Positioning for Injections: Bears can be trained to position themselves for injections.
8.3 Remote Drug Delivery Systems
Remote drug delivery systems can be used to administer medications to bears from a distance, avoiding the need for close contact.
- Dart Guns: Dart guns can be used to deliver tranquilizers or other medications to bears.
- Blowpipes: Blowpipes can be used to deliver small doses of medication to bears.
- Safety Considerations: It is important to use remote drug delivery systems safely and effectively to avoid injuring the bears.
8.4 Protective Barriers
Protective barriers, such as fences and cages, can be used to separate bears from veterinary staff during procedures.
- Ensuring Safety: Protective barriers help to ensure the safety of both the bears and the veterinary staff.
- Facilitating Procedures: Protective barriers can facilitate veterinary procedures by allowing the staff to work without being in close proximity to the bears.
- Maintaining Comfort: Protective barriers should be designed to minimize stress for the bears.
8.5 Anesthesia
Anesthesia is often necessary to perform more invasive veterinary procedures on bears.
- Careful Monitoring: Bears should be carefully monitored during anesthesia to ensure their safety.
- Appropriate Anesthetic Agents: Appropriate anesthetic agents should be used to minimize the risk of side effects.
- Pain Management: Pain management should be provided to bears after anesthesia to ensure their comfort.
9. What Conservation Efforts Support Bear Populations?
Numerous conservation efforts support bear populations worldwide, including habitat preservation, anti-poaching patrols, research and monitoring programs, and community education initiatives. These efforts aim to protect bears and their habitats, ensuring their long-term survival.
Conservation efforts are essential for protecting bear populations around the world.
- Habitat Preservation: Habitat preservation is crucial for ensuring that bears have adequate space to live and thrive.
- Anti-Poaching Patrols: Anti-poaching patrols help to protect bears from illegal hunting.
- Research and Monitoring Programs: Research and monitoring programs provide valuable information about bear populations, which can be used to inform conservation efforts.
- Community Education Initiatives: Community education initiatives help to raise awareness about the importance of bear conservation.
9.1 Habitat Preservation
Habitat preservation is one of the most important conservation efforts for bears.
- Protecting Existing Habitats: Protecting existing habitats from deforestation, development, and other threats is essential for ensuring that bears have adequate space to live and thrive.
- Restoring Degraded Habitats: Restoring degraded habitats can help to increase the amount of suitable habitat available for bears.
- Creating Wildlife Corridors: Creating wildlife corridors can help to connect fragmented habitats, allowing bears to move freely between different areas.
9.2 Anti-Poaching Patrols
Anti-poaching patrols help to protect bears from illegal hunting.
- Enforcing Laws: Anti-poaching patrols enforce laws that protect bears from illegal hunting.
- Deterring Poachers: Anti-poaching patrols deter poachers from hunting bears.
- Removing Snares and Traps: Anti-poaching patrols remove snares and traps that can injure or kill bears.
9.3 Research and Monitoring Programs
Research and monitoring programs provide valuable information about bear populations.
- Population Size and Distribution: Research and monitoring programs help to determine the size and distribution of bear populations.
- Habitat Use: Research and monitoring programs help to understand how bears use their habitat.
- Diet and Nutrition: Research and monitoring programs help to understand what bears eat and how they obtain their nutrition.
- Health and Disease: Research and monitoring programs help to monitor the health of bear populations and detect any signs of disease.
9.4 Community Education Initiatives
Community education initiatives help to raise awareness about the importance of bear conservation.
- School Programs: School programs can teach children about bears and the importance of protecting them.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Public awareness campaigns can educate the general public about bears and the threats they face.
- Community Involvement: Community involvement in conservation efforts can help to ensure their success.
9.5 International Cooperation
International cooperation is essential for protecting bear populations that cross international borders.
- Treaties and Agreements: Treaties and agreements between countries can help to protect bears and their habitats.
- Joint Research Projects: Joint research projects can help to improve our understanding of bear populations.
- Information Sharing: Information sharing between countries can help to coordinate conservation efforts.
10. How Does the Public Benefit from Caring for Bears in Educational Settings?
Caring for bears in educational settings offers significant public benefits, including increased awareness and appreciation for wildlife, educational opportunities for students and the community, and support for conservation efforts through research and funding. These settings also provide a unique opportunity for people to connect with nature and learn about the importance of protecting our planet’s biodiversity.
The public benefits in many ways from caring for bears in educational settings.
- Increased Awareness: Caring for bears in educational settings helps to increase public awareness about bears and the threats they face.
- Educational Opportunities: Educational settings provide educational opportunities for students and the general public to learn about bears.
- Conservation Support: Caring for bears in educational settings supports conservation efforts through research and funding.
10.1 Raising Awareness about Bears
Caring for bears in educational settings helps to raise public awareness about these amazing animals.
- Dispelling Myths: Educational programs can dispel myths and misconceptions about bears.
- Promoting Understanding: Educational programs can promote understanding of bear behavior, ecology, and conservation.
- Inspiring Action: Increased awareness can inspire people to take action to protect bears and their habitats.
10.2 Providing Educational Opportunities
Educational settings provide a variety of educational opportunities for students and the general public to learn about bears.
- School Programs: School programs can teach children about bears and the importance of protecting them.
- Zoo and Aquarium Exhibits: Zoo and aquarium exhibits can provide visitors with the opportunity to see bears up close and learn about their natural history.
- Online Resources: Online resources, such as websites and videos, can provide information about bears to a wider audience.
10.3 Supporting Conservation Efforts
Caring for bears in educational settings can support conservation efforts in a variety of ways.
- Research: Research conducted at educational settings can help to improve our understanding of bear health, behavior, and ecology.
- Funding: Educational settings can raise money for bear conservation through donations, grants, and fundraising events.
- Advocacy: Educational settings can advocate for policies that protect bears and their habitats.
10.4 Promoting Ethical Practices
C



