Are you curious about the historical fortifications of Vietnam? The answer is a resounding yes! Vietnam boasts a rich history with numerous ancient citadels and fortifications. Let SIXT.VN guide you through these historical wonders, offering seamless travel solutions for an unforgettable exploration. Discover the remnants of Vietnam’s past, from grand citadels to strategic defensive structures, and uncover the stories they hold. Let SIXT.VN enhance your journey with convenient airport transfers, comfortable hotel bookings, and expertly curated tours. Vietnam awaits.
1. What are Some Famous Old Citadels and Fortifications in Vietnam?
Vietnam’s landscape is dotted with remarkable citadels and fortifications, each a testament to the country’s rich history and strategic importance. These structures showcase diverse architectural styles and reflect influences from various periods. Here are some of the most notable examples:
1.1. The Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty (Thanh Hóa)
Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty stands as a remarkable example of 14th-century military architecture. Constructed in 1397 by the Hồ Dynasty, this citadel is renowned for its massive stone walls and unique architectural design. According to UNESCO, the citadel represents a unique architectural style symbolizing the power of the Hồ Dynasty and reflecting the socio-political context of the late 14th century. Visiting this citadel offers a fascinating glimpse into Vietnam’s medieval past.
1.2. The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long (Hanoi)
The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long, also a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is a sprawling complex with layers of history dating back to the 7th century. This citadel served as the political center of Vietnam for centuries, witnessing the rise and fall of various dynasties. Its architectural remnants and archaeological findings provide valuable insights into the country’s imperial past.
1.3. The Citadel of Huế
The Citadel of Huế, part of the larger Complex of Huế Monuments (another UNESCO World Heritage Site), served as the imperial capital during the Nguyễn Dynasty. This expansive fortress features impressive walls, moats, and intricate palaces, reflecting the grandeur and opulence of the Nguyễn emperors. The citadel’s architecture blends Vietnamese, Chinese, and Western influences, creating a unique and visually stunning experience.
1.4. The Citadel of Saigon (Gia Định)
The Citadel of Saigon, also known as the Citadel of Gia Định, played a crucial role in Vietnam’s history, particularly during the Nguyễn Dynasty and the French colonial period. While much of the original structure has been lost to time and urban development, remnants and historical markers still exist, offering a glimpse into the city’s past as a strategic military and administrative center.
1.5. Cổ Loa Citadel (Hanoi)
Cổ Loa Citadel is an ancient archaeological site located near Hanoi, dating back to the Âu Lạc Kingdom in the 3rd century BC. This early spiral-shaped fortress is a testament to the ingenuity of ancient Vietnamese engineers and provides valuable insights into the country’s early history and military strategies. According to archaeological findings, Cổ Loa Citadel was a significant political and military center, reflecting the advanced state of the Âu Lạc civilization.
2. What Features Characterize These Old Vietnamese Fortifications?
Old Vietnamese fortifications showcase a diverse range of architectural and strategic features, reflecting the historical context and military needs of each era. Here are some key characteristics:
2.1. Strategic Location
Citadels were often strategically located on elevated ground or near vital waterways to control key transportation routes and provide natural defenses. For example, the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty was built in a strategic location to control trade routes between the north and south of Vietnam. The location provided a natural advantage against potential invaders.
2.2. Impressive Walls and Ramparts
Massive walls constructed from stone, brick, or earth were a common feature, designed to withstand sieges and protect the inner sanctum. These walls were often reinforced with ramparts and watchtowers to provide vantage points for defenders. The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long, for instance, features multiple layers of walls and ramparts, reflecting its importance as a political and military center.
2.3. Moats and Water Defenses
Many citadels incorporated moats or were built near rivers to create an additional layer of defense, making it difficult for attackers to approach the walls. The Citadel of Huế is surrounded by a network of canals and moats, which served as both a defensive barrier and a means of transportation within the complex.
2.4. Bastions and Gun Emplacements
Later fortifications, influenced by European military architecture, often included bastions—projecting structures that allowed defenders to fire upon attackers from multiple angles. Gun emplacements were strategically positioned to maximize firepower and protect vulnerable areas.
2.5. Gates and Gatehouses
Elaborately designed gates and gatehouses served as the main entrances to the citadel, often fortified with multiple layers of defense and intricate architectural details. These gates were not only functional but also served as symbols of power and authority. The Citadel of Huế, for example, features several impressive gates, each with its unique architectural design and historical significance.
2.6. Interior Layout and Structures
Within the citadel walls, various structures served different purposes, including palaces, temples, administrative buildings, military barracks, and storage facilities. The layout of these structures reflected the social hierarchy and administrative functions of the ruling dynasty. The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long, for instance, contains numerous palaces, temples, and administrative buildings, reflecting its role as the political center of Vietnam for centuries.
3. What Can You Experience When Visiting These Sites Today?
Visiting these ancient citadels today offers a unique and enriching experience. Here’s what you can expect:
3.1. Historical Immersion
Step back in time as you wander through the ruins and restored sections of these citadels. Imagine life within these walls centuries ago, and learn about the historical events that shaped Vietnam’s past. The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long, with its layered history and archaeological findings, offers a captivating journey through Vietnam’s imperial past.
3.2. Architectural Appreciation
Marvel at the intricate architectural details and engineering feats of these ancient structures. From the massive stone walls of the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty to the elaborate palaces of the Citadel of Huế, each citadel showcases unique architectural styles and influences.
3.3. Cultural Insights
Explore the cultural significance of these citadels as you learn about the dynasties that ruled from within their walls. Discover the traditions, customs, and beliefs that shaped Vietnamese society. The Citadel of Huế, with its blend of Vietnamese, Chinese, and Western influences, provides valuable insights into the country’s cultural heritage.
3.4. Scenic Views
Many citadels offer panoramic views of the surrounding landscape, providing a unique perspective on the region’s natural beauty. The elevated location of many citadels allows visitors to appreciate the strategic importance of these fortifications and the beauty of the surrounding countryside.
3.5. Educational Opportunities
Guided tours and museums provide valuable information about the history, architecture, and cultural significance of these citadels. Knowledgeable guides can bring the past to life, offering insights and anecdotes that enhance your understanding and appreciation.
4. Where Can You Find the Best-Preserved Citadels?
Some citadels have fared better than others in terms of preservation. Here are some of the best-preserved citadels in Vietnam:
4.1. Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty
The Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty is remarkably well-preserved, thanks to its robust stone construction and UNESCO World Heritage status. Visitors can explore the imposing walls, gates, and other architectural features, gaining a sense of the citadel’s original grandeur. The UNESCO designation ensures ongoing preservation efforts, making it a prime example of Vietnam’s medieval military architecture.
4.2. Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long
While parts of the Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long have been lost to time, significant sections have been restored and are open to the public. Archaeological excavations continue to uncover new artifacts and insights, adding to the citadel’s appeal. The ongoing preservation efforts and archaeological discoveries make it a dynamic and fascinating historical site.
4.3. Citadel of Huế
The Citadel of Huế has undergone extensive restoration efforts, allowing visitors to explore its palaces, temples, and other structures in their former glory. The citadel’s UNESCO World Heritage status ensures ongoing preservation and conservation efforts. The restoration work has brought the citadel back to life, offering visitors a glimpse into the opulence and grandeur of the Nguyễn Dynasty.
5. How Were These Citadels Significant in Vietnamese History?
These citadels played pivotal roles in Vietnamese history, serving as centers of political power, military defense, and cultural identity.
5.1. Centers of Political Power
Citadels served as the seats of government for various dynasties, where emperors and officials made decisions that shaped the course of Vietnamese history. The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long, for instance, was the political center of Vietnam for centuries, witnessing the rise and fall of various dynasties.
5.2. Military Defense
Citadels were vital for protecting Vietnam from invaders, providing a safe haven for troops and resources. The strategic location and robust defenses of these citadels played a crucial role in repelling attacks and maintaining the country’s sovereignty. Cổ Loa Citadel, with its spiral-shaped walls and strategic location, played a key role in defending the Âu Lạc Kingdom from invaders.
5.3. Cultural Identity
Citadels served as symbols of Vietnamese cultural identity, reflecting the country’s unique architectural styles, traditions, and values. The architectural designs and cultural artifacts found within these citadels provide valuable insights into Vietnam’s rich heritage. The Citadel of Huế, with its blend of Vietnamese, Chinese, and Western influences, reflects the country’s cultural diversity and historical interactions.
6. What Were Some of the Battles or Conflicts Associated with These Fortifications?
Many of Vietnam’s citadels have been the sites of significant battles and conflicts, shaping the course of the country’s history.
6.1. Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long
The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long has witnessed numerous battles and conflicts throughout its history, including struggles for power among various dynasties and resistance against foreign invaders. The citadel’s strategic location and robust defenses made it a key target for military campaigns.
6.2. Citadel of Huế
The Citadel of Huế was the site of fierce fighting during the Vietnam War, particularly during the Tet Offensive in 1968. The battle caused significant damage to the citadel, but it has since been restored and remains a symbol of Vietnamese resilience. According to historical accounts, the Tet Offensive was a turning point in the Vietnam War, and the battle for the Citadel of Huế was one of its most intense and destructive engagements.
6.3. Cổ Loa Citadel
Cổ Loa Citadel played a crucial role in defending the Âu Lạc Kingdom against invasions from the north. The citadel’s strategic location and unique spiral-shaped walls provided a strong defense against enemy forces.
7. How Has Urban Development Impacted These Sites?
Urban development has had a mixed impact on Vietnam’s ancient citadels. While some citadels have been well-preserved and restored, others have suffered from neglect or encroachment.
7.1. Preservation and Restoration
Many citadels have benefited from preservation and restoration efforts, funded by the government, international organizations, and tourism revenue. These efforts have helped to protect and showcase the historical and cultural significance of these sites. The restoration of the Citadel of Huế, for instance, has been a major undertaking, involving extensive research, conservation, and reconstruction work.
7.2. Encroachment and Neglect
Some citadels have faced challenges from urban development, including encroachment by modern buildings, neglect of historical structures, and loss of archaeological sites. The rapid pace of urbanization in Vietnam has put pressure on historical sites, making it difficult to balance development with preservation.
7.3. Balancing Development and Preservation
Finding a balance between urban development and preservation is crucial for ensuring that Vietnam’s ancient citadels are protected for future generations. Sustainable tourism, community involvement, and responsible urban planning are essential for achieving this balance.
8. What Are Some Myths or Legends Associated with These Citadels?
Vietnamese citadels are often associated with myths and legends, adding to their mystique and cultural significance.
8.1. Cổ Loa Citadel
Legend has it that Cổ Loa Citadel was built with the help of a golden turtle, who advised King An Dương Vương on the best location and design for the fortress. The turtle also provided the king with a magical crossbow that could defeat any enemy. According to Vietnamese folklore, the golden turtle played a crucial role in the construction and defense of Cổ Loa Citadel, symbolizing the kingdom’s strength and resilience.
8.2. Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long
The Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long is said to be located on a dragon vein, a mystical energy source that brings good fortune and power to those who control it. This belief has contributed to the citadel’s importance as a political and spiritual center throughout Vietnamese history.
8.3. Citadel of Huế
Local legends claim that the Citadel of Huế is protected by supernatural forces, guarding it against harm and ensuring the prosperity of the Nguyễn Dynasty. These legends add to the citadel’s aura of mystery and cultural significance.
9. How Can SIXT.VN Enhance Your Visit to Vietnamese Citadels?
SIXT.VN offers a range of services to make your exploration of Vietnamese citadels seamless and unforgettable.
9.1. Airport Transfers
Start your journey with ease by booking a reliable airport transfer with SIXT.VN. Our professional drivers will greet you upon arrival and transport you comfortably to your hotel or directly to the citadel of your choice.
9.2. Hotel Bookings
Find the perfect accommodation near the citadels with SIXT.VN’s extensive selection of hotels. Whether you’re looking for a luxurious resort or a budget-friendly guesthouse, we have options to suit every traveler’s needs.
9.3. Guided Tours
Discover the history and culture of Vietnamese citadels with our expertly curated guided tours. Our knowledgeable guides will provide valuable insights and anecdotes, bringing the past to life.
9.4. Customized Itineraries
Let SIXT.VN create a personalized itinerary that includes visits to multiple citadels and other attractions. We’ll take care of all the details, so you can focus on enjoying your adventure.
9.5. Transportation Services
Explore the citadels and their surrounding areas with our convenient transportation services. Whether you prefer a private car, a comfortable van, or a guided tour bus, we have options to suit your travel style and budget.
10. What Travel Tips Should You Keep in Mind When Visiting?
To make the most of your visit to Vietnamese citadels, keep these travel tips in mind:
10.1. Best Time to Visit
The best time to visit Vietnam is during the dry season, which typically runs from November to April. The weather is pleasant, and you’ll avoid the heavy rains that can make exploring the citadels more challenging.
10.2. What to Wear
Wear comfortable shoes, as you’ll be doing a lot of walking. Dress respectfully when visiting temples and religious sites within the citadels. Lightweight, breathable clothing is recommended, especially during the hotter months.
10.3. What to Bring
Bring sunscreen, a hat, and sunglasses to protect yourself from the sun. Carry water to stay hydrated, especially during long walks. A camera is essential for capturing the beauty and historical significance of the citadels.
10.4. Local Customs
Be mindful of local customs and traditions. Dress modestly when visiting religious sites, and ask for permission before taking photos of people. Learning a few basic Vietnamese phrases can also enhance your interactions with locals.
10.5. Safety Precautions
Stay aware of your surroundings and take precautions against petty theft. Keep your valuables secure and avoid walking alone in poorly lit areas at night. Follow the advice of local authorities and tour guides to ensure your safety.
FAQ About Old Citadels and Fortifications Remaining in Vietnam
1. Are there any remaining parts of the Citadel of Saigon?
Yes, while much of the original Citadel of Saigon has been lost, some remnants and historical markers still exist.
2. How much does it cost to visit the Citadel of Huế?
The entrance fee to the Citadel of Huế is approximately 150,000 VND (about $6.50 USD).
3. Can I hire a tour guide at the Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long?
Yes, you can hire a tour guide at the Imperial Citadel of Thăng Long for a more in-depth exploration.
4. What is the best way to get to Cổ Loa Citadel from Hanoi?
The best way to get to Cổ Loa Citadel from Hanoi is by taxi, bus, or private car, which takes about 30-45 minutes. SIXT.VN can arrange for private transportation.
5. Are there any hotels near the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty?
Yes, there are several hotels and guesthouses in the nearby city of Thanh Hóa. SIXT.VN can assist with hotel bookings.
6. What kind of architectural influences can be seen in Vietnamese citadels?
Vietnamese citadels often blend Vietnamese, Chinese, and Western architectural styles.
7. How long does it take to tour the Citadel of Huế?
It takes at least half a day to fully explore the Citadel of Huế.
8. Is the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty accessible year-round?
Yes, the Citadel of the Hồ Dynasty is generally accessible year-round, but it’s best to visit during the dry season (November to April).
9. What were the citadels primarily built for?
Citadels were primarily built for military defense and as centers of political power.
10. Can I book a full tour package to explore multiple citadels with SIXT.VN?
Yes, SIXT.VN offers full tour packages to explore multiple citadels, including transportation, accommodations, and guided tours.
Ready to explore the ancient citadels of Vietnam? Let SIXT.VN be your trusted travel partner. Visit SIXT.VN today to book your airport transfer, hotel, and guided tour, and embark on an unforgettable journey through Vietnam’s rich history and culture. Contact our Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358 or visit our Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Discover Vietnam’s historical fortifications with SIXT.VN.
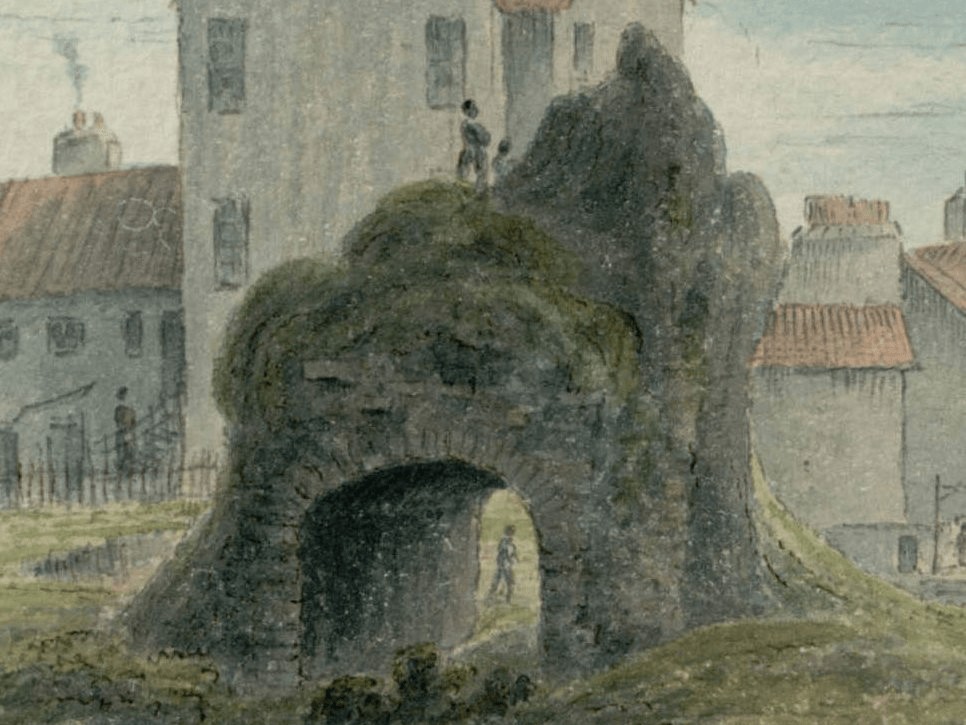 The Citadel gateway, close-up
The Citadel gateway, close-up
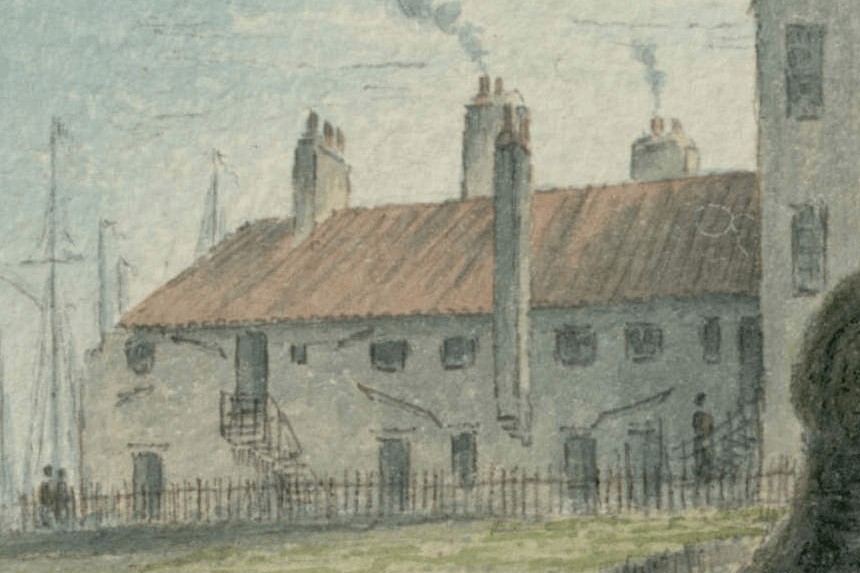
 Pantile roofs and whitewash
Pantile roofs and whitewash
 Pantile roofs and non-right angles
Pantile roofs and non-right angles
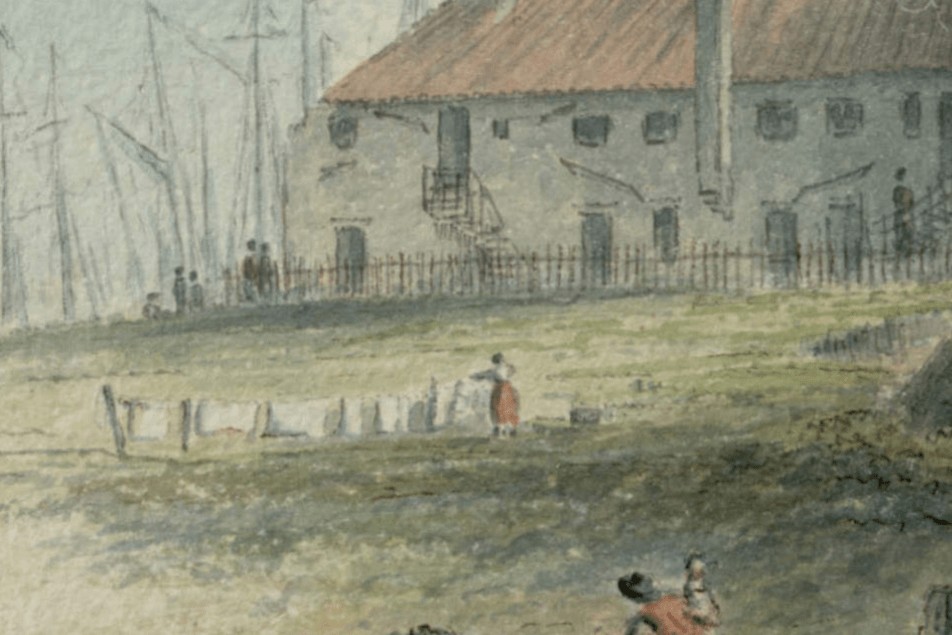 Washing day
Washing day
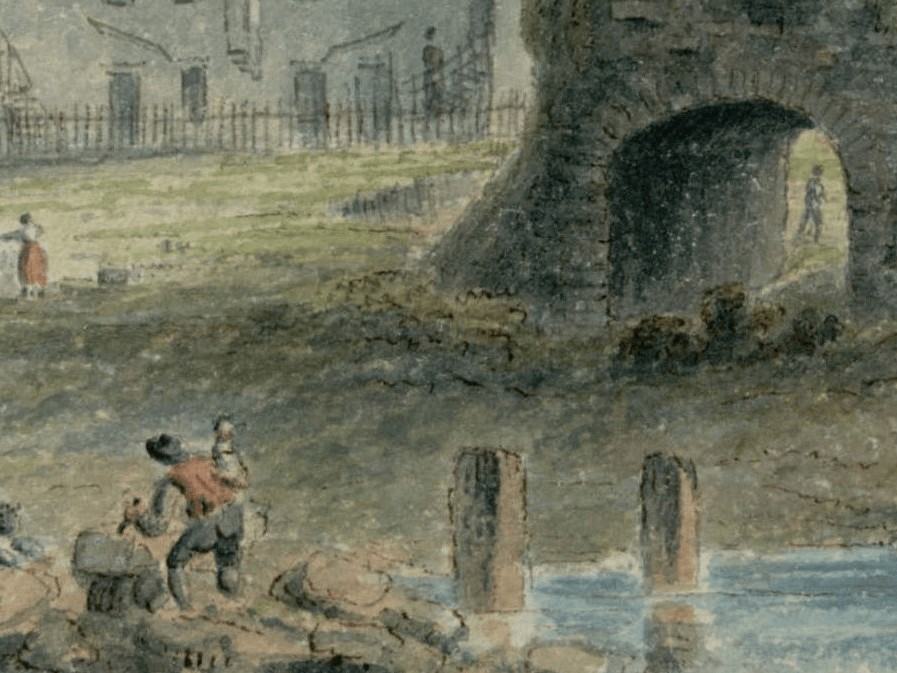 Wooden posts in the water infront of the gateway
Wooden posts in the water infront of the gateway
 Curving external stairs to the first floor
Curving external stairs to the first floor
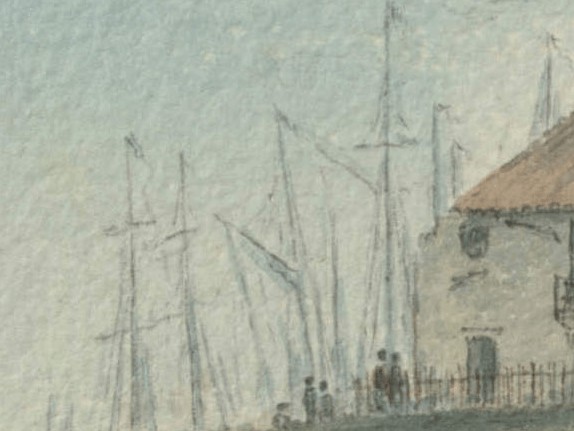 Masts and rigging of the Port of Leith
Masts and rigging of the Port of Leith
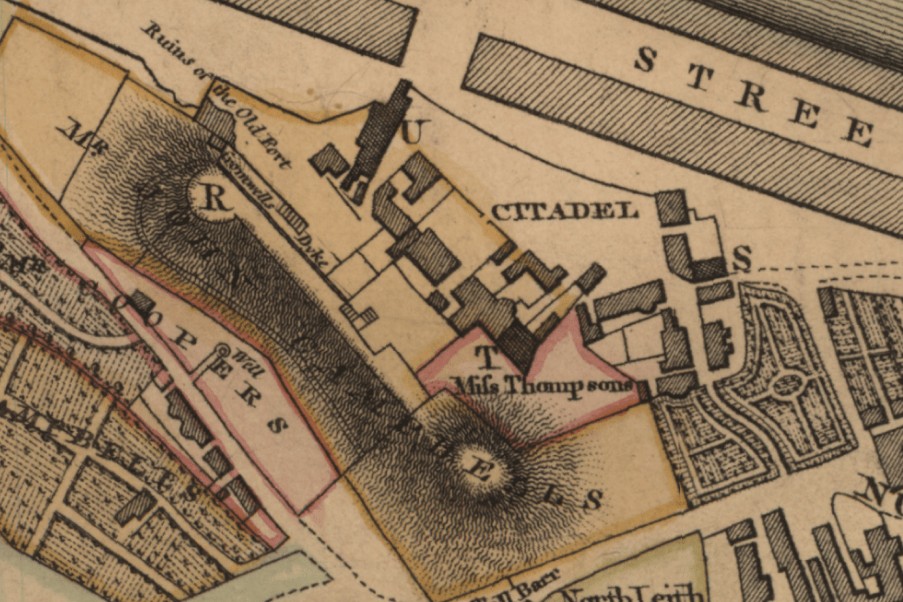 Ainslie
Ainslie
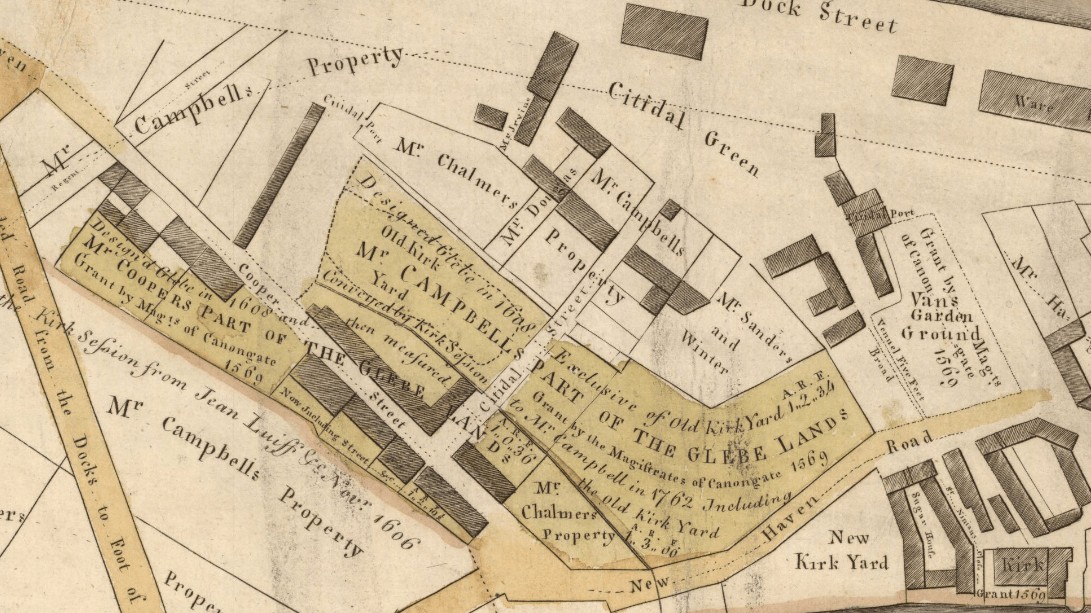 Bell
Bell
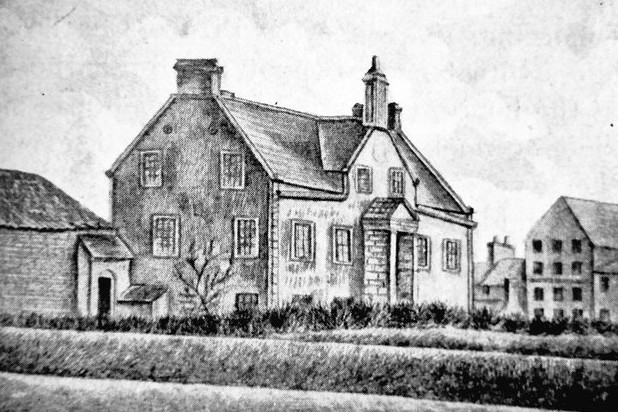 “Cromwell House” from the Story of Leith.
“Cromwell House” from the Story of Leith.
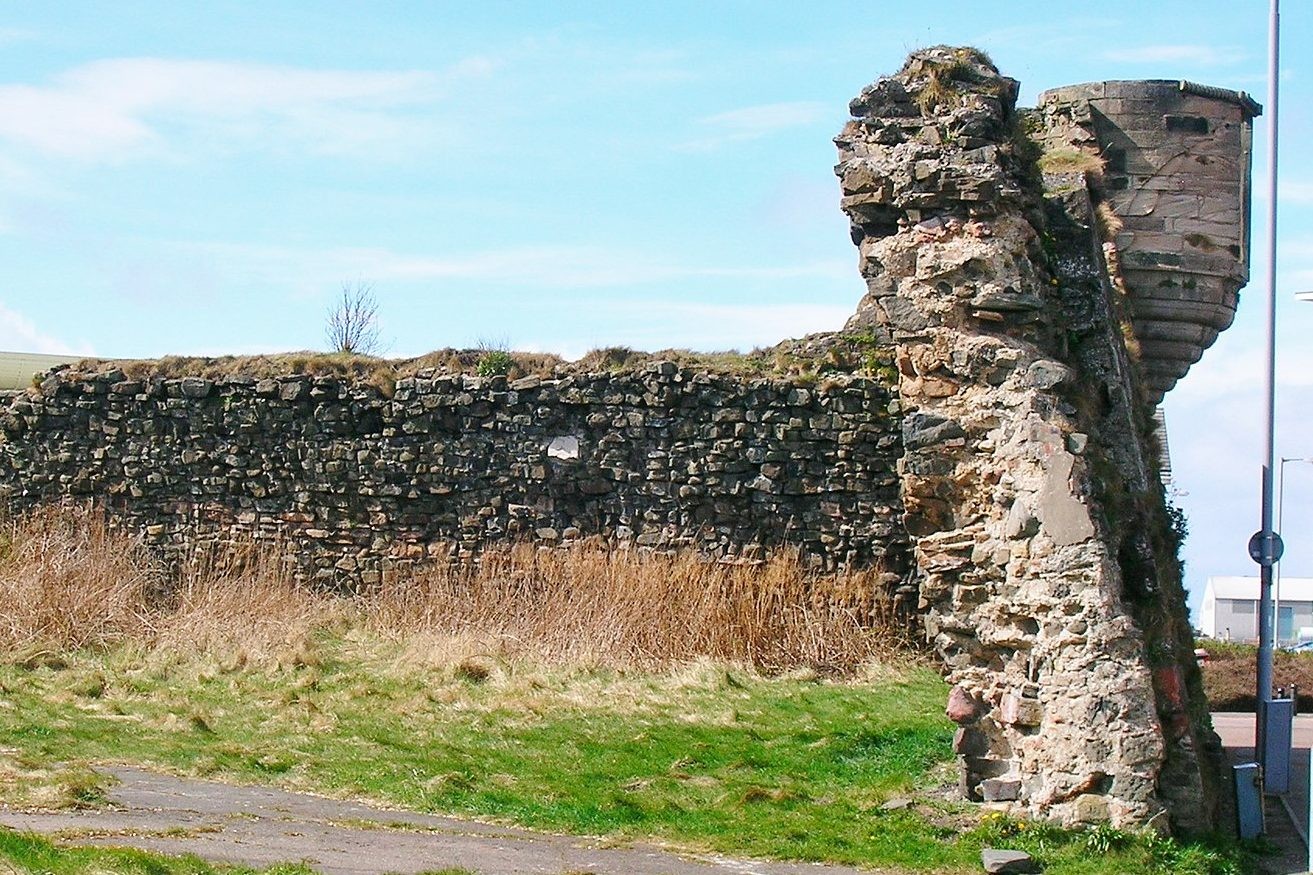 A bastion of Ayr Citadel. The projecting turret is a
A bastion of Ayr Citadel. The projecting turret is a
 Transition animation of the Citadel. NLS maps reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland
Transition animation of the Citadel. NLS maps reproduced with the permission of the National Library of Scotland



