Are you curious about how people predicted the weather before modern technology? Traditional weather forecasting methods offer fascinating insights into the natural world. Let SIXT.VN guide you through the age-old techniques used around the globe. Discover how keen observation and understanding of nature can provide valuable clues about the weather. Whether planning a trip to Vietnam or simply interested in local weather patterns, understanding traditional forecasting can enhance your appreciation for the environment.
1. Unveiling Time-Honored Weather Prediction Techniques
Traditional weather forecasting relies on observing natural phenomena. These methods, developed over centuries, use indicators like animal behavior, plant cycles, and atmospheric conditions to predict the weather. Across various cultures, these observations have become integral to daily life, aiding in agriculture, navigation, and community planning.
1.1. Delving into the Afar Pastoralists’ Traditional Weather Forecasting
The Afar pastoral communities in Ethiopia have a rich tradition of weather forecasting. Their methods involve customary institutions and detailed observations of the environment. This system is essential for their nomadic lifestyle and decision-making.
1.1.1. Customary Institutions of the Afar People
The Afar people use three primary institutions for weather forecasting:
- Adda: A traditional administration system led by respected elders (Asayamaras) who guide the community.
- Edo: A range scouting practice where young men gather information about weather and rangeland conditions.
- Dagu: An information network that shares knowledge relevant to pastoral life.
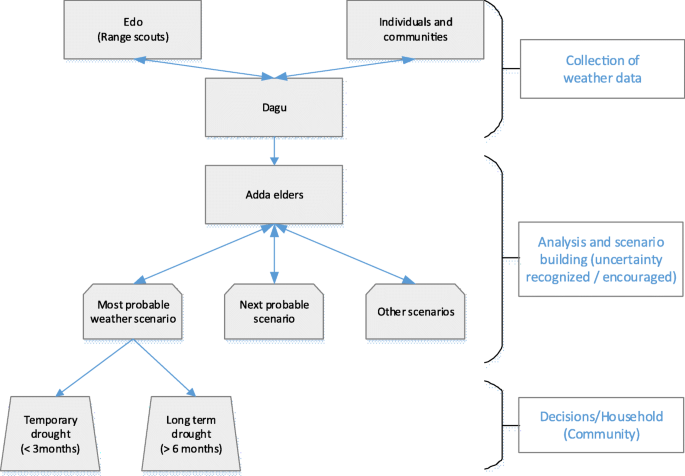 Afar elders Adda
Afar elders Adda
1.1.2. The Role of Observation in Afar Weather Prediction
The Edos make detailed observations about plants, soil, animals, and celestial bodies. They also gather information from people in different locations through the Dagu network. This information helps them predict future weather conditions.
1.1.3. Ensuring Credibility Through the Adda
The Adda administration interprets weather predictions and determines their practical implications. Elders collect information from various sources, including their observations, traditional seers, and formal weather forecasting services. This triangulation ensures the community receives reliable weather information.
1.2. Traditional Rain Calendar of the Afar People
The Afar people traditionally identify seven rainy periods:
- Konayto
- Datrob
- Debaba
- Deda’e
- Segum
- Karma
- Two periods of Gilal (cold) and Hagaya (hot).
Understanding this calendar is vital for their weather forecasting and decision-making.
2. How Do Bio-Physical Variables Play a Role in Weather Prediction?
Bio-physical variables, such as changes in plants, animals, and celestial bodies, are crucial indicators in traditional weather forecasting. These observations provide insights into upcoming weather conditions.
2.1. Tree Phenology and Weather Prediction
Changes in tree phenology, like blooming patterns, can indicate impending weather conditions.
- Acacia tortilits (Eepto) blooms in anticipation of rain.
- Dobera glabra (Gersa) turns deep green when rains are expected to fail.
- Adansonia digitata (Gabita) produces more leaves and fruits when drought is expected.
2.2. Animal Behavior as a Weather Indicator
Changes in animal behavior, such as plumage changes in birds and reproductive behavior in camels, can predict weather.
- A starling species (Wadartailoli) changes its plumage to deep glossy blue when good rain is expected.
- Increased libido and playful behavior in animals often indicate the coming of rains.
2.3. Insects and Their Role in Weather Prediction
Insects also exhibit behavior changes that can predict weather. The Afar people use the behavior of local black ants (Dakura) to forecast rain. If ants avoid ditches, it indicates a good rainy season.
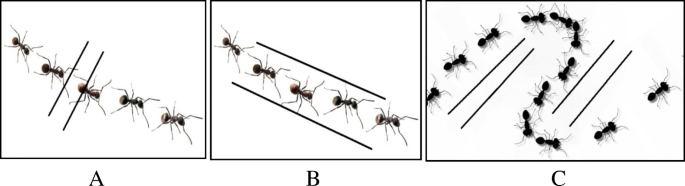 Ant-rout experiment
Ant-rout experiment
2.4. Celestial Bodies and Weather Forecasting
Observations of celestial bodies, including stars, the sun, and the moon, provide clues about upcoming weather. The Afar identify three types of stars:
- Dohra: A lone bright star symbolizing beauty.
- Kaihima: A group of stars mainly observable to camels.
- Malhino: A group of stars arranged in a specific pattern.
2.5. Winds as Weather Indicators
The Afar people characterize six types of winds based on timing, direction, and strength:
- Gilalta
- Burentu
- Woreru
- Kuya
- Silayto
- Kilb
Each wind provides specific information about rain conditions in different seasons.
3. The Significance of Traditional Weather Prediction Methods
Traditional weather forecasting methods offer valuable insights and have significant cultural and practical importance. They provide accessible and understandable weather information to local communities.
3.1. Cultural Importance
These methods are deeply rooted in cultural traditions and passed down through generations. They reflect a profound understanding of the natural environment and its cycles.
3.2. Practical Applications
Traditional forecasting aids in agriculture, livestock management, and community planning. It helps people make informed decisions based on anticipated weather conditions.
3.3. Integration with Modern Forecasting
Combining traditional knowledge with modern weather forecasting systems can enhance accuracy and usefulness. This integration allows for a more comprehensive understanding of weather patterns.
4. How Can Traditional and Modern Weather Forecasting Systems Work Together?
Combining traditional knowledge with modern weather forecasting systems offers numerous benefits. This integration allows for a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of weather patterns.
4.1. Enhancing Data Accessibility
Making modern weather forecasting information more accessible to local communities, especially the Afar Adda elders, is crucial. This allows them to compare modern data with their traditional indicators.
4.2. Collaborative Supervision and Feedback
National meteorological bureaus should closely supervise how local communities use their data and gather feedback. This helps in adjusting forecasts and improving accuracy.
4.3. Consensus Forecasting
Implementing a consensus forecasting approach, where traditional and modern systems collaborate, can lead to more reliable predictions. This approach has been successfully applied in Tanzania. According to research from the Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology, in 2017, consensus forecasting provides more reliable predictions.
4.4. Creating Indigenous Knowledge Databases
Converting traditional weather forecasting indicators into recordable and measurable data can create valuable databases. These databases can then be integrated into modern weather forecasting models.
4.5. Respecting Cultural Context
It’s crucial to remember that indigenous knowledge exists independently of its compatibility with modern analysis. Suggested strategies should not overshadow the cultural importance and values of indigenous data. Changes to traditional knowledge should only come from the indigenous people themselves.
5. Examples of Traditional Weather Forecasting Methods Around the World
Many cultures worldwide have developed unique traditional weather forecasting methods. These methods often rely on local environmental indicators and cultural practices.
5.1. European Traditions
In Europe, many traditional weather sayings are based on observing animal behavior and plant cycles. For example, if cows lie down in a field, it’s said to indicate approaching rain.
5.2. North American Traditions
Native American tribes have long used observations of wildlife and celestial events to predict weather. The appearance of certain birds or the position of stars can indicate changes in weather patterns.
5.3. Asian Traditions
In Asia, traditional weather forecasting often involves observing monsoon patterns and plant flowering. These observations help farmers plan their planting and harvesting seasons.
5.4. African Traditions
Various African cultures use animal behavior, wind patterns, and celestial observations to forecast weather. These methods are essential for agriculture and managing resources in arid regions.
6. The Science Behind Traditional Weather Forecasting
While traditional weather forecasting may seem based on folklore, many observations have a scientific basis. Understanding these connections can help appreciate the accuracy of these methods.
6.1. Animal Behavior and Weather Changes
Animals can detect subtle changes in atmospheric pressure, temperature, and humidity. These changes can trigger specific behaviors that act as early warning signs for weather events. According to research from the Indian Journal of Traditional Knowledge, in 2011, animals have instinctive capabilities of sensing and detecting subtle changes.
6.2. Plant Phenology and Climate Patterns
Plants respond to seasonal changes and can indicate shifts in climate patterns. Flowering times, leaf growth, and fruiting patterns are all influenced by temperature and rainfall. These patterns can provide insights into upcoming weather conditions. According to research from the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, in 2002, plants are naturally capable of predicting future weather.
6.3. Atmospheric Conditions and Weather Prediction
Observing cloud formations, wind direction, and air moisture can provide clues about weather changes. These observations are often linked to scientific principles of meteorology.
7. How to Incorporate Traditional Weather Knowledge into Your Travels
Understanding traditional weather forecasting can enhance your travel experiences, especially when exploring natural environments. By learning to observe local indicators, you can gain a deeper connection to the places you visit.
7.1. Learning from Local Communities
Engage with local communities to learn about their traditional weather forecasting methods. This can provide unique insights into the environment and cultural practices.
7.2. Observing Natural Indicators
Pay attention to changes in plant life, animal behavior, and atmospheric conditions. These observations can help you anticipate weather changes during your travels.
7.3. Integrating Knowledge with Modern Forecasts
Combine traditional knowledge with modern weather forecasts to make informed decisions. This approach can provide a more comprehensive understanding of weather patterns.
8. What are the Limitations of Traditional Weather Forecasting?
While traditional weather forecasting methods offer valuable insights, they also have limitations that need to be considered.
8.1. Accuracy and Reliability
Traditional methods may not always be as accurate as modern forecasting techniques. They are often based on local observations and may not account for broader weather patterns.
8.2. Subjectivity
Observations can be subjective and influenced by personal interpretation. This can lead to variations in predictions and uncertainty.
8.3. Applicability
Traditional methods are often specific to certain regions and may not be applicable in other areas. Environmental conditions and cultural practices can influence the effectiveness of these methods.
9. The Future of Traditional Weather Forecasting
The future of traditional weather forecasting involves integrating these methods with modern science to create more accurate and comprehensive weather predictions.
9.1. Collaborative Research
Encouraging collaborative research between scientists and local communities can enhance our understanding of weather patterns. This research can help validate traditional knowledge and identify scientific connections.
9.2. Educational Programs
Developing educational programs that promote traditional weather forecasting can help preserve this knowledge and pass it on to future generations. These programs can also highlight the value of integrating traditional and modern methods.
9.3. Technological Integration
Using technology to record and analyze traditional weather observations can enhance accuracy and reliability. This integration can lead to the development of more effective forecasting models. According to research from the Meteorological Applications, in 2017, a database for traditional knowledge of weather and climate in the Pacific is helpful.
10. Frequently Asked Questions About Traditional Weather Forecasting
Have more questions about traditional weather forecasting? Here are some frequently asked questions to deepen your understanding.
10.1. What Is Traditional Weather Forecasting?
Traditional weather forecasting is a practice that uses observations of natural phenomena, such as animal behavior, plant cycles, and atmospheric conditions, to predict weather patterns.
10.2. How Accurate Are Traditional Weather Forecasts?
The accuracy of traditional weather forecasts can vary. While many observations have a scientific basis, they may not always be as precise as modern forecasting methods.
10.3. Can Traditional Weather Forecasting Be Integrated with Modern Science?
Yes, integrating traditional weather forecasting with modern science can enhance the accuracy and comprehensiveness of weather predictions.
10.4. What Are Some Examples of Traditional Weather Indicators?
Examples of traditional weather indicators include changes in animal behavior, flowering patterns in plants, and observations of cloud formations.
10.5. Why Is It Important to Preserve Traditional Weather Knowledge?
Preserving traditional weather knowledge is important because it reflects a deep understanding of the natural environment and provides valuable insights for sustainable living.
10.6. How Can I Learn More About Traditional Weather Forecasting?
You can learn more about traditional weather forecasting by engaging with local communities, observing natural indicators, and researching cultural practices.
10.7. What Role Do Animals Play in Traditional Weather Prediction?
Animals can detect subtle changes in atmospheric conditions, leading to behavioral changes that indicate impending weather events.
10.8. How Do Plants Indicate Weather Changes?
Plants respond to seasonal changes and can indicate shifts in climate patterns through their flowering times, leaf growth, and fruiting patterns.
10.9. Are Traditional Weather Methods Still Used Today?
Yes, traditional weather methods are still used in many communities around the world, often in conjunction with modern forecasting techniques.
10.10. Where Can I Find Resources on Traditional Weather Forecasting?
You can find resources on traditional weather forecasting through academic journals, cultural organizations, and local communities that practice these methods.
Planning a trip to Vietnam? Let SIXT.VN handle all your travel needs! We offer a range of services, including airport transfers, hotel bookings, and tours of Hanoi. Don’t let travel challenges hold you back. Contact us today and experience a smooth, enjoyable trip!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358
Website: SIXT.VN



