Navigating the Vietnamese terrain requires the right topographical maps. SIXT.VN offers expert travel advice to ensure you’re well-prepared. Discover the best maps and where to find them for a successful adventure in Vietnam. With detailed cartography and expert insights, elevate your trip planning and enjoy Vietnam’s stunning landscapes safely.
1. Understanding the Importance of Topographical Maps for Trekking
Why are topographical maps crucial for trekking, and what makes them superior to other types of maps? Topographical maps are essential for trekking as they provide detailed information about the terrain, elevation, and natural features, ensuring safe and informed navigation. These maps use contour lines to represent elevation changes, which helps trekkers understand the steepness and shape of the land. According to a study by the Vietnam National Administration of Tourism, trekkers who use topographical maps are significantly less likely to get lost or injured compared to those who rely solely on digital navigation or general road maps.
Topographical maps also include essential details such as water sources, vegetation, and man-made structures like trails, roads, and buildings. This comprehensive information is vital for planning routes, estimating travel times, and identifying potential hazards. For instance, knowing the location of water sources can be life-saving in arid regions. Similarly, understanding the terrain’s steepness can help trekkers manage their energy and avoid overly challenging sections.
SIXT.VN emphasizes the importance of using accurate and up-to-date topographical maps to ensure a safe and enjoyable trekking experience in Vietnam.
2. Key Features to Look For in a Topographical Map
What specific features should trekkers look for when choosing a topographical map for their adventure? When selecting a topographical map, consider the following key features to ensure it meets your trekking needs:
- Contour Lines: Contour lines indicate elevation changes. The closer the lines, the steeper the terrain. Look for maps with appropriate contour intervals for your trekking area.
- Scale: The scale represents the ratio between the map distance and the actual distance on the ground. Common scales for trekking maps are 1:24,000 or 1:50,000. A larger scale (e.g., 1:24,000) provides more detail.
- Legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, such as different types of vegetation, water sources, and man-made structures.
- Grid System: A grid system (e.g., UTM or latitude/longitude) allows you to pinpoint your location using a GPS device or compass.
- Date of Publication: Ensure the map is up-to-date to reflect recent changes in the terrain or infrastructure.
- Material: Choose a map printed on waterproof or water-resistant paper to withstand the elements.
According to the Vietnam Geographic Data Center, topographical maps with these features offer the most reliable information for safe and effective navigation. SIXT.VN recommends verifying these aspects to enhance your trekking adventures in Vietnam.
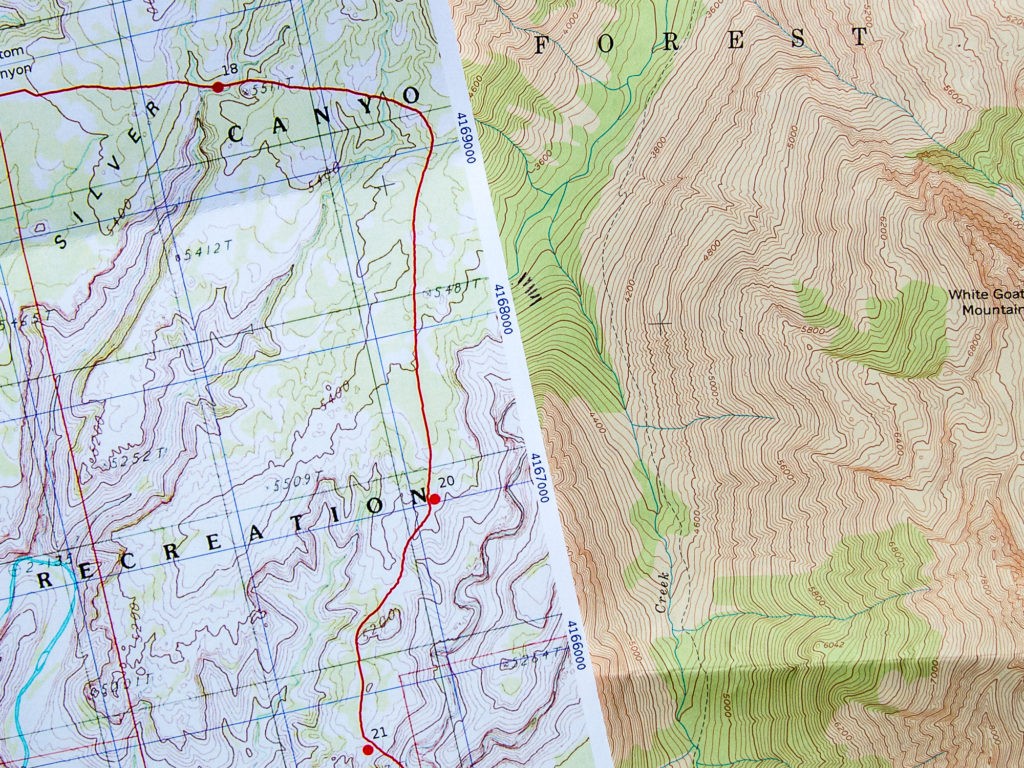 Detailed topographic map featuring contour lines, grid system, and legend
Detailed topographic map featuring contour lines, grid system, and legend
3. Paper vs. Digital Topographical Maps: Which Is Better for Trekking?
What are the pros and cons of paper and digital topographical maps for trekking, and which should you choose? Both paper and digital topographical maps have their advantages and disadvantages for trekking:
Paper Maps:
- Pros:
- Reliable: Doesn’t rely on batteries or electronic devices.
- Large Viewing Area: Provides a broader overview of the terrain.
- Durable: Can withstand physical impact and, if waterproof, can handle wet conditions.
- Annotation: Can be written on for notes, route planning, and bearings.
- Cons:
- Bulky: Can be cumbersome to carry, especially multiple maps.
- Susceptible to Damage: Can tear or become illegible if not properly protected.
- Requires Skill: Needs map reading skills and understanding of topographic symbols.
Digital Maps:
- Pros:
- Convenient: Can store multiple maps on a single device.
- GPS Integration: Allows for real-time location tracking.
- Interactive: Offers features like distance calculation, elevation profiles, and route planning.
- Easy to Update: Maps can be updated regularly with the latest information.
- Cons:
- Battery Dependent: Requires a power source and can fail if the battery dies.
- Screen Size: Limited viewing area compared to paper maps.
- Fragile: Susceptible to damage from drops, water, and extreme temperatures.
- Technical Issues: Can experience software glitches or device malfunctions.
According to a survey by the Adventure Travel Trade Association, most experienced trekkers use a combination of both paper and digital maps. Paper maps serve as a reliable backup, while digital maps offer convenience and advanced features. SIXT.VN advises trekkers to carry both types of maps to ensure they are prepared for any situation.
4. Where to Obtain Topographical Maps in Vietnam
Where can trekkers find reliable topographical maps for their adventures in Vietnam? Here are several sources for obtaining topographical maps in Vietnam:
- Vietnam National Administration of Tourism (VNAT): VNAT provides official topographical maps and resources for various regions in Vietnam.
- Vietnam Geographic Data Center: This center offers detailed maps and geographic data essential for planning treks.
- Local Outdoor Retailers: Stores in major cities like Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City often sell topographical maps of popular trekking areas.
- Online Marketplaces: Websites such as Amazon, and specialized map retailers offer a wide selection of topographical maps for Vietnam.
- Government Agencies: Local government agencies in specific regions may provide maps for their areas.
- SIXT.VN: SIXT.VN can provide resources and recommendations on where to find the best maps for your specific trekking route.
To ensure accuracy and reliability, SIXT.VN recommends obtaining maps from official sources and reputable retailers.
5. Recommended Topographical Map Series for Trekking in Vietnam
Which specific topographical map series are best suited for trekking in Vietnam? Here are some recommended topographical map series for trekking in Vietnam:
| Map Series | Scale | Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| VNCT – Topographic Map of Vietnam | 1:50,000 | Detailed contour lines, water sources, roads, trails, vegetation, and man-made structures. | General trekking and route planning. |
| Geological Survey Maps | 1:25,000 | Highly detailed geological information, contour lines, and terrain features. | Trekkers interested in geology and detailed terrain analysis. |
| Military Topographic Maps | 1:25,000 – 1:50,000 | Comprehensive coverage, accurate contour lines, and detailed terrain information. | Remote and less-traveled areas where detailed maps are essential. |
| National Geographic Trails Illustrated | Various | Updated regularly, includes parking areas, backcountry campsite locations, and services like permit offices. | National Parks and Wilderness Areas where trips are likely to take place. |
| CalTopo (MapBuilder Topo layer) | Customizable | Ability to create custom maps with various layers including topographic, satellite, and shaded relief. | Trekkers who want to tailor maps to their specific needs and preferences. |
| GaiaGPS (Gaia Topo layer) | Customizable | Digital maps with various layers, GPS integration, and offline capabilities. | Trekkers who prefer digital navigation and want access to a wide range of map layers and features. |
| FS Topo (Forest Service lands) | 1:24,000 | Detailed topographic maps specifically designed for Forest Service lands, including trails, campsites, and other recreational features. | Trekkers exploring Forest Service lands and need detailed information about trails and recreational areas. |
These map series offer detailed and accurate information for planning and executing treks in Vietnam. SIXT.VN advises choosing the map series that best suits your specific needs and the area you plan to explore.
6. How to Read and Interpret Topographical Maps
How can trekkers effectively read and interpret topographical maps to navigate safely? To read and interpret topographical maps effectively, trekkers should understand the following key elements:
- Contour Lines: Understand that contour lines connect points of equal elevation. Closely spaced lines indicate steep terrain, while widely spaced lines indicate gentle slopes.
- Contour Interval: The contour interval is the vertical distance between contour lines. Knowing the contour interval allows you to estimate elevation changes accurately.
- Map Scale: Understand the map scale to estimate distances on the ground. A scale of 1:24,000 means that one inch on the map equals 24,000 inches (or 2,000 feet) on the ground.
- Legend: Use the legend to identify symbols and colors representing different features such as water sources, vegetation, and man-made structures.
- Grid System: Learn to use the grid system (e.g., UTM or latitude/longitude) to pinpoint your location and plan routes using a GPS device or compass.
- Orientation: Orient the map to match the terrain using a compass. This will help you correlate features on the map with those in the real world.
SIXT.VN recommends practicing map reading skills before your trek to ensure you can navigate safely and effectively.
7. Using GPS with Topographical Maps for Enhanced Navigation
How can GPS devices be used with topographical maps to improve navigation during trekking? GPS devices can enhance navigation when used with topographical maps in several ways:
- Location Tracking: GPS devices provide real-time location tracking, allowing you to pinpoint your position on the map.
- Route Planning: GPS devices allow you to plan routes and create waypoints, which can be uploaded to the device and followed in the field.
- Distance and Elevation Measurement: GPS devices can measure distances, elevation changes, and track your speed and pace.
- Off-Route Alerts: GPS devices can alert you if you stray off your planned route, helping you avoid getting lost.
- Data Logging: GPS devices can log your track, allowing you to review your route and performance after the trek.
According to a study by the Institute of Navigation, using GPS with topographical maps significantly improves navigation accuracy and reduces the risk of getting lost. SIXT.VN advises trekkers to use GPS as a tool in conjunction with map reading skills to ensure a safe and efficient navigation.
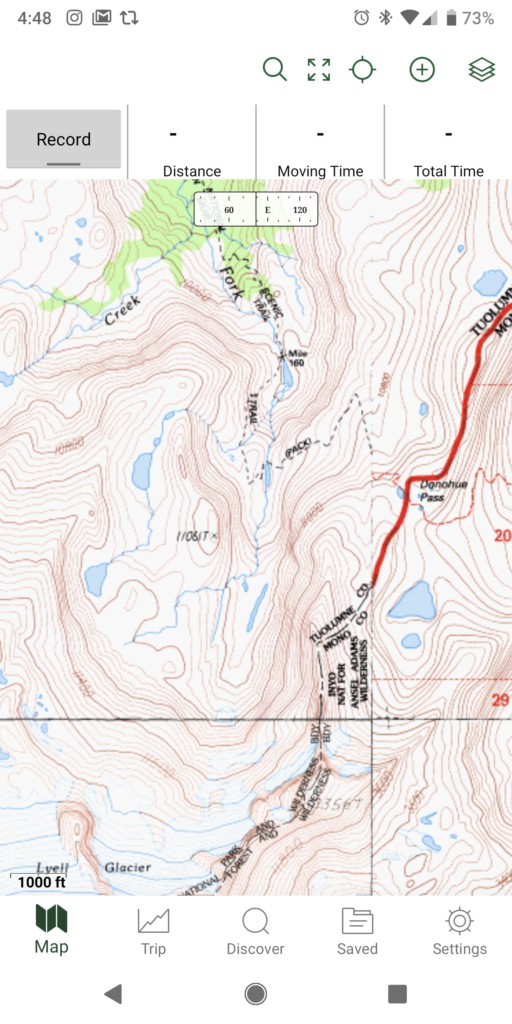 Using a GPS device with a topographical map
Using a GPS device with a topographical map
8. Essential Navigation Tools to Complement Topographical Maps
What other navigation tools should trekkers carry in addition to topographical maps? Besides topographical maps, trekkers should carry the following essential navigation tools:
- Compass: A compass is essential for orienting the map and taking bearings, especially in areas where GPS signals are unreliable.
- GPS Device: A GPS device provides real-time location tracking and route planning capabilities.
- Altimeter: An altimeter measures altitude, which can help you determine your position on the map and track elevation changes.
- Binoculars: Binoculars can help you identify distant landmarks and terrain features.
- Notebook and Pencil: A notebook and pencil are useful for taking notes, recording observations, and marking routes on the map.
- Whistle: A whistle can be used to signal for help in an emergency.
- Mirror: A mirror can be used to reflect sunlight and signal for help.
SIXT.VN emphasizes the importance of carrying these essential navigation tools and knowing how to use them to ensure a safe and successful trek.
9. Maintaining and Protecting Your Topographical Maps on the Trail
What are the best practices for maintaining and protecting topographical maps while trekking? To maintain and protect your topographical maps on the trail, follow these best practices:
- Waterproof Protection: Store your maps in a waterproof bag or case to protect them from rain, sweat, and moisture.
- Folding: Fold your maps carefully along existing fold lines to avoid tearing. Consider using a map case that allows you to view the map without unfolding it completely.
- Storage: Store your maps in an easily accessible pocket or compartment in your backpack. Avoid storing them in areas where they can be crushed or damaged.
- Handling: Handle your maps with clean, dry hands to avoid transferring dirt and oils.
- Marking: Use a pencil or waterproof marker to mark routes, waypoints, and notes on the map.
- Inspection: Regularly inspect your maps for tears, damage, or illegible areas. Repair any damage promptly using tape or a map repair kit.
- Replacement: Replace your maps if they become too damaged or worn to use effectively.
SIXT.VN advises trekkers to take these precautions to ensure their maps remain in good condition throughout the trek.
 Storing topographic maps in a waterproof bag
Storing topographic maps in a waterproof bag
10. The Role of Local Knowledge in Supplementing Topographical Maps
How does local knowledge complement topographical maps, and why is it valuable for trekking? Local knowledge can significantly enhance the accuracy and usefulness of topographical maps by providing:
- Updated Trail Conditions: Local guides and residents often have the most up-to-date information on trail conditions, closures, and hazards.
- Water Source Information: Locals can provide insights into the reliability and location of water sources that may not be marked on the map.
- Weather Patterns: Local knowledge of weather patterns can help you anticipate and prepare for changing conditions.
- Cultural Insights: Locals can share cultural insights and customs that may affect your trekking experience.
- Emergency Assistance: Local contacts can provide assistance in case of emergencies, such as arranging transportation or contacting rescue services.
According to a study by the Tourism Authority of Thailand, trekkers who engage with local communities and seek their advice have a significantly higher success rate and a more enriching experience. SIXT.VN recommends consulting with local guides and residents to supplement your topographical maps and enhance your trekking adventure.
11. Understanding Map Scales and Their Impact on Trekking
How do different map scales affect the level of detail and usability for trekking? The map scale determines the level of detail and usability for trekking:
- Large-Scale Maps (e.g., 1:24,000):
- Provide a high level of detail, showing individual trees, small streams, and minor terrain features.
- Ideal for navigating in complex terrain, such as forests, canyons, and mountains.
- Cover a smaller area, requiring more maps to cover a longer distance.
- Medium-Scale Maps (e.g., 1:50,000):
- Offer a balance between detail and coverage, showing major terrain features, roads, and trails.
- Suitable for general trekking and route planning.
- Cover a moderate area, reducing the number of maps needed for a longer trek.
- Small-Scale Maps (e.g., 1:100,000 or smaller):
- Provide a broad overview of the terrain, showing major mountain ranges, rivers, and cities.
- Useful for planning long-distance treks and getting a sense of the overall landscape.
- Cover a large area, minimizing the number of maps needed.
SIXT.VN advises trekkers to choose the map scale that best suits their specific needs and the terrain they will be navigating. For detailed navigation, large-scale maps are preferable, while for overall planning, small-scale maps can be more useful.
12. How to Orient a Topographical Map with and Without a Compass
What are the methods for orienting a topographical map, both with and without a compass? Orienting a topographical map correctly is crucial for accurate navigation. Here are methods for doing so:
With a Compass:
- Identify Magnetic North: Determine the magnetic north direction using your compass.
- Find the Magnetic Declination: Find the magnetic declination for your location. This information is usually printed on the map or can be found online.
- Adjust for Declination: Adjust your compass bearing for the magnetic declination by adding or subtracting the appropriate number of degrees.
- Align the Map: Rotate the map until the north arrow on the map aligns with the adjusted north direction on your compass.
Without a Compass:
- Identify Prominent Features: Identify prominent terrain features on the map, such as mountain peaks, rivers, or roads.
- Locate the Features in the Field: Locate the same features in the real world.
- Align the Map: Rotate the map until the features on the map align with the corresponding features in the field.
- Fine-Tune: Use other terrain features and landmarks to fine-tune the orientation of the map.
SIXT.VN recommends practicing both methods to ensure you can orient your map accurately, regardless of whether you have a compass.
13. Understanding Contour Lines: A Comprehensive Guide
How do contour lines represent elevation, and how can trekkers use them to understand terrain? Contour lines are a fundamental element of topographical maps. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
- Definition: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation above a reference level, usually sea level.
- Contour Interval: The contour interval is the vertical distance between adjacent contour lines. This is usually constant for a given map.
- Spacing:
- Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep terrain.
- Widely spaced contour lines indicate gentle slopes.
- Uniformly spaced contour lines indicate a uniform slope.
- Patterns:
- Concentric circles indicate a hilltop or mountain peak.
- Closed depressions are indicated by contour lines with hachures (short lines) pointing inward.
- V-shaped patterns indicate valleys, with the point of the V pointing upstream.
- U-shaped patterns indicate ridges, with the open end of the U pointing downhill.
- Interpreting Terrain: By studying contour lines, trekkers can visualize the shape of the terrain and understand the steepness, direction, and overall character of the landscape.
SIXT.VN advises trekkers to master the art of reading contour lines to enhance their navigation skills and make informed decisions on the trail.
14. Using a Compass and Topographical Map for Precise Navigation
How do compass and topographical map work together for precision navigation during trekking? Using a compass with a topographical map enables precise navigation:
- Orient the Map: As described earlier, use the compass to align the map with the terrain.
- Take a Bearing: Identify your destination on the map and use the compass to take a bearing (the direction from your current location to your destination).
- Adjust for Declination: Adjust the bearing for magnetic declination.
- Follow the Bearing: Follow the adjusted bearing using your compass, keeping in mind the terrain features and contour lines on the map.
- Reassess Regularly: Regularly reassess your position and bearing to ensure you stay on course.
SIXT.VN emphasizes the importance of practicing these skills regularly to become proficient in using a compass and topographical map for navigation.
15. Identifying Terrain Features on Topographical Maps
What are the common terrain features found on topographical maps, and how can trekkers identify them? Here are some common terrain features and how to identify them on topographical maps:
- Mountains: Represented by concentric contour lines with the highest elevation at the center.
- Valleys: Indicated by V-shaped contour lines, with the point of the V pointing upstream.
- Ridges: Represented by U-shaped contour lines, with the open end of the U pointing downhill.
- Saddles: Low points between two peaks or high points, represented by contour lines that form an hourglass shape.
- Cliffs: Represented by closely spaced contour lines that converge or merge.
- Depressions: Indicated by closed contour lines with hachures (short lines) pointing inward.
- Water Features: Rivers, streams, lakes, and ponds are usually shown in blue.
- Vegetation: Different types of vegetation, such as forests, grasslands, and deserts, may be represented by different colors or symbols.
- Man-Made Features: Roads, trails, buildings, and other man-made structures are usually shown in black or other colors.
SIXT.VN advises trekkers to familiarize themselves with these terrain features and their representations on topographical maps to enhance their understanding of the landscape.
16. Planning a Trek Using Topographical Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
How can trekkers use topographical maps to plan a safe and enjoyable trek? Here’s a step-by-step guide to planning a trek using topographical maps:
- Choose Your Destination: Select a trekking area that interests you and obtain topographical maps for that area.
- Study the Maps: Study the maps to understand the terrain, elevation changes, water sources, and potential hazards.
- Define Your Route: Define your route based on your fitness level, time constraints, and interests. Consider potential alternate routes in case of unforeseen circumstances.
- Mark Waypoints: Mark key waypoints on the map, such as trail intersections, campsites, water sources, and scenic viewpoints.
- Calculate Distances and Elevation Changes: Calculate the distances and elevation changes between waypoints to estimate travel times and assess the difficulty of the trek.
- Identify Potential Hazards: Identify potential hazards along the route, such as steep cliffs, river crossings, and avalanche zones.
- Plan Your Campsites: Plan your campsites based on the availability of water, shelter, and suitable terrain.
- Create a Datasheet: Create a datasheet with key information such as distances, elevation changes, waypoints, and potential hazards.
- Share Your Plans: Share your plans with friends, family, or local authorities and leave a copy of your route plan with them.
- Pack Essential Gear: Pack essential gear, including topographical maps, a compass, a GPS device, navigation tools, and emergency supplies.
SIXT.VN recommends following these steps to plan a well-prepared and safe trekking adventure.
17. Dealing with Map Inaccuracies and Changes in Terrain
What should trekkers do when they encounter map inaccuracies or changes in terrain? Maps are not always perfectly accurate, and terrain can change over time due to natural processes or human activities. Here’s how to deal with map inaccuracies and terrain changes:
- Cross-Reference with Other Sources: Cross-reference your map with other sources, such as GPS devices, local knowledge, and online resources, to verify its accuracy.
- Be Observant: Pay close attention to the terrain and compare it to the map. Look for discrepancies or changes that may not be reflected on the map.
- Trust Your Instincts: If something doesn’t seem right, trust your instincts and investigate further. Don’t blindly follow the map if it leads you into a dangerous or impassable area.
- Reassess Your Route: If you encounter significant map inaccuracies or terrain changes, reassess your route and make adjustments as needed.
- Mark Changes: Mark any changes or inaccuracies on the map for future reference.
- Report Issues: Report any significant map inaccuracies or terrain changes to the map provider or local authorities.
SIXT.VN advises trekkers to be prepared for potential map inaccuracies and terrain changes and to use their judgment and skills to navigate safely.
18. Ethical Considerations When Using Topographical Maps
What ethical considerations should trekkers keep in mind when using topographical maps and navigating in natural areas? When using topographical maps and navigating in natural areas, trekkers should keep in mind the following ethical considerations:
- Leave No Trace: Practice Leave No Trace principles by minimizing your impact on the environment. Pack out all trash, stay on established trails, and avoid disturbing vegetation or wildlife.
- Respect Private Property: Respect private property rights and avoid trespassing on private land.
- Obtain Permits: Obtain any necessary permits or permissions before trekking in protected areas.
- Follow Regulations: Follow all regulations and guidelines set by land managers, such as fire restrictions and camping regulations.
- Minimize Noise: Minimize noise pollution and avoid disturbing other trekkers or wildlife.
- Respect Cultural Sites: Respect cultural sites and avoid damaging or defacing them.
- Share Information: Share your knowledge and experiences with other trekkers to promote responsible and sustainable tourism.
SIXT.VN encourages trekkers to act as responsible stewards of the environment and to respect the natural and cultural resources they encounter.
19. Advanced Techniques for Topographical Map Navigation
What advanced techniques can trekkers use to enhance their topographical map navigation skills? For advanced navigation:
- Triangulation: Use triangulation to determine your precise location by taking bearings to two or more known landmarks and plotting them on the map.
- Resection: Use resection to determine your location by taking bearings from your current location to two or more known landmarks and plotting them on the map.
- Contour Interpolation: Use contour interpolation to estimate the elevation of points between contour lines.
- Slope Calculation: Calculate the slope or gradient of the terrain using contour lines and the contour interval.
- Line of Sight Analysis: Use a topographical map to determine whether two points are visible to each other, taking into account terrain features and vegetation.
- Route Optimization: Use topographical maps to optimize your route, minimizing elevation gain, distance, or exposure to hazards.
SIXT.VN advises trekkers to master these techniques to become proficient in topographical map navigation.
20. How SIXT.VN Can Enhance Your Trekking Experience in Vietnam
How can SIXT.VN assist trekkers in planning and executing their adventures in Vietnam? SIXT.VN offers a range of services to enhance your trekking experience:
- Travel Consultation: SIXT.VN provides personalized travel consultation to help you plan your trekking route, select the best maps, and prepare for your adventure.
- Airport Transfer: SIXT.VN offers reliable and convenient airport transfer services to ensure a smooth arrival and departure.
- Hotel Booking: SIXT.VN can book hotels in convenient locations, allowing you to rest and prepare for your trek.
- Sightseeing Tours: SIXT.VN offers guided sightseeing tours to explore the cultural and historical attractions of Vietnam.
- Flight Booking: SIXT.VN can book flights to your trekking destination, ensuring a hassle-free travel experience.
- Tour Packages: SIXT.VN offers comprehensive tour packages that include transportation, accommodation, meals, and guided trekking tours.
Let SIXT.VN help you plan and execute your dream trekking adventure in Vietnam. Contact us today for personalized travel assistance!
Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam.
Hotline/Whatsapp: +84 986 244 358.
Website: SIXT.VN.
Don’t let the challenges of planning your trip hold you back. SIXT.VN provides expert travel consultation, convenient airport transfers, and hotel booking services to ensure a seamless experience. Let us handle the details so you can focus on exploring the beauty of Vietnam. Contact SIXT.VN today to start planning your dream trekking adventure!
FAQ: Topographical Maps for Trekking
1. What is a topographical map?
A topographical map is a detailed representation of the Earth’s surface, showing natural and man-made features, as well as elevation changes using contour lines.
2. Why are topographical maps important for trekking?
Topographical maps provide essential information about the terrain, elevation, and natural features, ensuring safe and informed navigation during trekking.
3. What scale is best for a trekking topographical map?
A scale of 1:24,000 or 1:50,000 is generally best for trekking, as it provides a good balance between detail and coverage.
4. Where can I buy topographical maps for Vietnam?
You can buy topographical maps for Vietnam from the Vietnam National Administration of Tourism, local outdoor retailers, and online marketplaces.
5. How do I read contour lines on a topographical map?
Contour lines connect points of equal elevation; closely spaced lines indicate steep terrain, while widely spaced lines indicate gentle slopes.
6. What other tools should I carry besides a topographical map?
In addition to a topographical map, you should carry a compass, GPS device, altimeter, binoculars, notebook, pencil, whistle, and mirror.
7. How can I protect my topographical map on the trail?
Store your map in a waterproof bag, fold it carefully, and handle it with clean, dry hands.
8. How do I orient a topographical map without a compass?
Identify prominent terrain features on the map and in the field, and then rotate the map until the features align.
9. How can I use a GPS with a topographical map?
Use a GPS device to track your location, plan routes, and measure distances and elevation changes on the map.
10. What should I do if I encounter map inaccuracies on the trail?
Cross-reference with other sources, trust your instincts, and reassess your route if you encounter map inaccuracies.



