Are you concerned about the environmental consequences of modern agriculture? At SIXT.VN, we understand the growing concerns surrounding the impact of pesticides and fertilizers on our planet. This article explores the detrimental effects of these agricultural practices and offers insights into sustainable alternatives, empowering you to make informed travel decisions that support eco-friendly initiatives in Vietnam and beyond. By understanding the challenges and embracing responsible tourism, you can contribute to preserving the natural beauty of destinations like Hanoi and its surrounding areas.
1. What Are the Primary Components of Modern Agriculture and Their Intended Purposes?
Modern agriculture relies heavily on pesticides and fertilizers to boost crop yields and protect against pests. Pesticides aim to control insects, weeds, and diseases, while fertilizers enrich the soil with essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These inputs help farmers produce more food, but their overuse can lead to severe environmental problems. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), global fertilizer use has increased dramatically over the past few decades, intensifying the pressure on ecosystems.
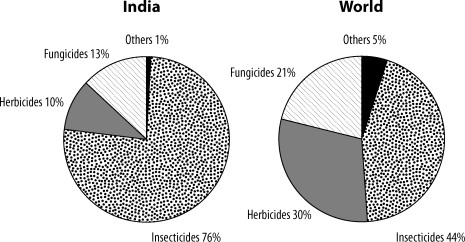 Pesticide Application in Agriculture
Pesticide Application in Agriculture
Alt Text: Pesticide application in agriculture showing consumption pattern of pesticides, highlighting the dominance of insecticides.
2. How Do Pesticides Impact the Environment?
Pesticides pose significant risks to the environment through several key pathways:
2.1. Water Contamination
Pesticides can contaminate surface and groundwater through runoff and leaching. This pollution harms aquatic life and can make water unsafe for human consumption. The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) has found pesticides in over 90% of water and fish samples from streams across the country.
2.2. Soil Contamination
Pesticides can persist in the soil, affecting beneficial microorganisms and soil fertility. This can disrupt the natural nutrient cycle and reduce the soil’s ability to support plant growth. Studies have shown that heavy pesticide use can lead to a decline in beneficial soil microorganisms.
2.3. Air Contamination
Pesticides can volatilize and drift from treated areas, contaminating the air and affecting non-target vegetation. This drift can spread pesticides over long distances, impacting ecosystems far from the application site. Research indicates that a significant percentage of applied pesticides can volatilize into the atmosphere.
2.4. Harm to Non-Target Organisms
Pesticides are often toxic to a wide range of organisms beyond the intended pests, including beneficial insects, birds, fish, and other wildlife. This can disrupt ecosystems and reduce biodiversity. The EPA has documented numerous cases of pesticide-related harm to non-target species.
3. What Specific Types of Pesticides Are Most Commonly Used and What Are Their Known Environmental Impacts?
Commonly used pesticides include insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides, each with distinct environmental impacts:
3.1. Insecticides
Insecticides like organophosphates and neonicotinoids are used to control insect pests but can harm beneficial insects such as bees and butterflies. Neonicotinoids, in particular, have been linked to declines in bee populations, which are crucial for pollination. According to the Xerces Society, neonicotinoids are a leading cause of pollinator decline.
3.2. Herbicides
Herbicides like glyphosate are used to control weeds but can also harm non-target plants and aquatic life. Glyphosate, the active ingredient in Roundup, has been shown to have toxic effects on fish and disrupt aquatic ecosystems. Studies have indicated that glyphosate can cause physiological stress in fish.
3.3. Fungicides
Fungicides are used to control fungal diseases but can also affect soil microorganisms and aquatic life. Some fungicides have been found to reduce algae growth, which is essential for aquatic food chains. Research has shown that certain fungicides can severely impact algae populations.
4. How Do Fertilizers Affect Water Quality, and What Are the Consequences?
Fertilizers, especially those containing nitrogen and phosphorus, can lead to water pollution through runoff:
4.1. Eutrophication
Excess nutrients from fertilizers can cause eutrophication, where bodies of water become overly enriched with nutrients, leading to excessive algae growth. This depletes oxygen levels, harming fish and other aquatic life. The EPA reports that eutrophication is a major water quality issue in many regions.
4.2. Nitrate Contamination
Nitrate from fertilizers can contaminate groundwater, posing health risks to humans, particularly infants. High nitrate levels in drinking water can cause methemoglobinemia, or blue baby syndrome. The World Health Organization (WHO) has set guidelines for acceptable nitrate levels in drinking water.
4.3. Dead Zones
Nutrient runoff can create dead zones in coastal areas, where oxygen levels are too low to support marine life. The Gulf of Mexico dead zone, caused by nutrient runoff from the Mississippi River, is one of the largest in the world. NOAA estimates that the Gulf of Mexico dead zone can cover thousands of square miles.
5. What Is the Role of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Fertilizer-Induced Water Pollution?
Nitrogen and phosphorus are essential nutrients for plant growth but become pollutants when overused:
5.1. Nitrogen
Nitrogen fertilizers can convert to nitrate, which is highly mobile in soil and easily leaches into groundwater. This can lead to nitrate contamination of drinking water and contribute to eutrophication in surface waters. Research has shown that nitrogen runoff is a major contributor to water pollution.
5.2. Phosphorus
Phosphorus tends to bind to soil particles but can still enter waterways through erosion and runoff. Even small amounts of phosphorus can trigger excessive algae growth in lakes and streams. Studies have indicated that phosphorus is often the limiting nutrient in freshwater eutrophication.
6. What Are the Environmental Consequences of Fertilizer Use on Soil Health and Biodiversity?
Excessive fertilizer use can degrade soil health and reduce biodiversity:
6.1. Soil Acidification
Certain fertilizers can acidify the soil, making it less hospitable for many plant species and beneficial microorganisms. Soil acidification can also release toxic metals into the soil, further harming plant growth. Research has shown that long-term fertilizer use can significantly lower soil pH.
6.2. Reduced Soil Biodiversity
Fertilizers can disrupt the natural balance of soil microorganisms, reducing the diversity of species and affecting soil functions. This can lead to a decline in soil health and reduced resilience to environmental stresses. Studies have found that fertilizer use can decrease the abundance of beneficial fungi and bacteria in the soil.
6.3. Imbalance of Nutrients
Overuse of certain fertilizers can create an imbalance of nutrients in the soil, leading to deficiencies of other essential elements. This can negatively impact plant health and reduce crop yields over time. Research has shown that nutrient imbalances can reduce plant resistance to pests and diseases.
7. How Do Agricultural Practices Affect Air Quality, and What Pollutants Are Released?
Agriculture contributes to air pollution through several pathways:
7.1. Ammonia Emissions
Fertilizer use and livestock operations release ammonia into the atmosphere, which can contribute to the formation of particulate matter and acid rain. Ammonia emissions can also react with other pollutants to form harmful aerosols. The EPA estimates that agriculture is a major source of ammonia emissions.
7.2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Agricultural activities, including fertilizer use and land management practices, contribute to greenhouse gas emissions such as nitrous oxide, methane, and carbon dioxide. These gases contribute to climate change and global warming. The FAO reports that agriculture is a significant contributor to global greenhouse gas emissions.
7.3. Dust and Particulate Matter
Agricultural practices such as tilling and harvesting can release dust and particulate matter into the air, affecting air quality and human health. Dust storms can also transport pollutants over long distances, impacting air quality in distant regions. Studies have shown that agricultural dust can contribute to respiratory problems.
8. What Is the Impact of Pesticides and Fertilizers on Human Health, Especially in Agricultural Communities?
Exposure to pesticides and fertilizers can have serious health impacts, especially for agricultural workers and communities:
8.1. Acute Poisoning
Pesticide exposure can cause acute poisoning, leading to symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, headaches, and in severe cases, death. Agricultural workers are at higher risk of acute poisoning due to direct contact with pesticides. The WHO estimates that there are millions of cases of pesticide poisoning each year.
8.2. Chronic Health Effects
Long-term exposure to pesticides and fertilizers has been linked to chronic health effects such as cancer, reproductive problems, neurological disorders, and respiratory illnesses. Studies have shown that agricultural communities with high pesticide use have higher rates of certain cancers.
8.3. Water Contamination and Health Risks
Contamination of drinking water with nitrates from fertilizers can pose health risks, particularly for infants. High nitrate levels in drinking water can cause methemoglobinemia, reducing the blood’s ability to carry oxygen. The CDC has issued guidelines for safe nitrate levels in drinking water.
9. What Are the Economic Impacts of Environmental Damage Caused by Pesticides and Fertilizers?
The environmental damage caused by pesticides and fertilizers can have significant economic consequences:
9.1. Water Treatment Costs
Contamination of water sources with pesticides and fertilizers increases the cost of water treatment to make it safe for drinking. Municipalities may need to invest in advanced treatment technologies to remove pollutants. The EPA estimates that water treatment costs are increasing due to agricultural pollution.
9.2. Loss of Fisheries and Aquaculture
Eutrophication and pollution can harm fisheries and aquaculture, leading to economic losses for fishermen and aquaculture farmers. Dead zones and contaminated fish can reduce the productivity of fisheries. NOAA reports that dead zones can cause significant economic losses for the fishing industry.
9.3. Reduced Agricultural Productivity
Soil degradation and loss of biodiversity can reduce agricultural productivity over time, leading to lower crop yields and economic losses for farmers. Soil health is essential for sustainable agricultural production. The FAO estimates that soil degradation costs billions of dollars each year.
9.4. Health Care Costs
Health problems associated with pesticide and fertilizer exposure can increase health care costs for individuals and communities. Treatment of pesticide poisoning, cancer, and other related illnesses can be expensive. Studies have shown that agricultural communities with high pesticide use have higher health care costs.
10. What Sustainable Agricultural Practices Can Minimize the Use of Pesticides and Fertilizers?
Several sustainable agricultural practices can reduce the reliance on pesticides and fertilizers:
10.1. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM involves using a combination of methods to control pests, including biological control, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide applications. IPM aims to minimize pesticide use while effectively managing pests. The EPA promotes IPM as a sustainable pest control strategy.
10.2. Crop Rotation
Rotating crops can help break pest and disease cycles, reduce weed pressure, and improve soil fertility. Crop rotation can also reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers by improving nutrient cycling. Research has shown that crop rotation can significantly reduce pesticide and fertilizer use.
10.3. Cover Cropping
Planting cover crops can protect the soil from erosion, improve soil structure, and increase soil fertility. Cover crops can also suppress weeds and reduce the need for herbicides. The USDA promotes cover cropping as a sustainable soil management practice.
10.4. Organic Farming
Organic farming relies on natural methods to control pests and diseases and improve soil fertility. Organic farmers avoid synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, using techniques such as composting, crop rotation, and biological control. The Organic Trade Association reports that organic farming is growing in popularity.
10.5. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture involves using technology to optimize inputs such as fertilizers and pesticides, applying them only where and when they are needed. Precision agriculture can reduce waste and minimize environmental impacts. Research has shown that precision agriculture can improve resource use efficiency.
11. What Policies and Regulations Are in Place to Control the Use of Pesticides and Fertilizers, and How Effective Are They?
Many countries have policies and regulations to control the use of pesticides and fertilizers:
11.1. Pesticide Registration and Regulation
Most countries require pesticides to be registered and regulated before they can be used. These regulations may include restrictions on the types of pesticides that can be used, application methods, and buffer zones to protect water bodies. The EPA regulates pesticides in the United States.
11.2. Fertilizer Management Plans
Some regions require farmers to develop fertilizer management plans to minimize nutrient runoff. These plans may include recommendations for fertilizer application rates, timing, and methods. The EU has implemented regulations to reduce nutrient pollution from agriculture.
11.3. Subsidies for Sustainable Practices
Governments may provide subsidies and incentives for farmers to adopt sustainable agricultural practices that reduce pesticide and fertilizer use. These incentives can help promote the adoption of IPM, crop rotation, and other sustainable methods. The USDA offers programs to support sustainable agriculture.
11.4. Monitoring and Enforcement
Effective monitoring and enforcement are essential to ensure that pesticide and fertilizer regulations are followed. Regular inspections and water quality monitoring can help identify violations and address pollution problems. The EPA conducts monitoring and enforcement activities to protect water quality.
12. How Can Consumers Support Environmentally Friendly Agricultural Practices Through Their Purchasing Choices?
Consumers can play a significant role in promoting sustainable agriculture through their purchasing choices:
12.1. Buy Organic Products
Choosing organic products supports farmers who use sustainable practices and avoid synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Look for certified organic labels when shopping for food. The Organic Trade Association provides information on organic certification.
12.2. Support Local Farmers
Buying from local farmers and farmers markets can help support sustainable agriculture in your community. Local farmers are often more likely to use environmentally friendly practices. The Farmers Market Coalition provides information on local farmers markets.
12.3. Choose Products with Sustainable Certifications
Look for products with certifications such as Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance, and USDA Organic, which indicate that they were produced using sustainable practices. These certifications ensure that products meet certain environmental and social standards.
12.4. Reduce Food Waste
Reducing food waste can decrease the demand for agricultural production and minimize the environmental impacts of farming. Plan your meals, store food properly, and compost food scraps to reduce waste. The EPA promotes strategies to reduce food waste.
12.5. Advocate for Sustainable Policies
Support policies and regulations that promote sustainable agriculture and reduce pesticide and fertilizer use. Contact your elected officials and advocate for environmentally friendly agricultural practices. The National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition advocates for sustainable agricultural policies.
13. What Role Does Technology Play in Reducing the Environmental Impact of Agriculture?
Technology can play a crucial role in reducing the environmental impact of agriculture:
13.1. Precision Agriculture Technologies
GPS-guided equipment, remote sensing, and variable rate applicators can help farmers apply fertilizers and pesticides more precisely, reducing waste and minimizing environmental impacts. These technologies can optimize resource use efficiency. Research has shown that precision agriculture can improve crop yields and reduce environmental pollution.
13.2. Drone Technology
Drones can be used to monitor crop health, identify pest infestations, and apply pesticides in a targeted manner. Drones can also provide valuable data for precision agriculture management. The FAA regulates the use of drones in agriculture.
13.3. Data Analytics and Modeling
Data analytics and modeling can help farmers make informed decisions about crop management, fertilizer application, and pest control. These tools can predict crop yields, optimize resource use, and minimize environmental impacts. Research has shown that data-driven agriculture can improve sustainability.
13.4. Biotechnology
Biotechnology can be used to develop crops that are resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides. Genetically modified (GM) crops can also be more efficient at using nutrients, reducing the need for fertilizers. The USDA regulates the use of biotechnology in agriculture.
14. What Are the Most Promising Innovations in Sustainable Agriculture?
Several promising innovations are emerging in sustainable agriculture:
14.1. Biological Control Agents
Biological control involves using natural enemies of pests, such as predatory insects and beneficial microorganisms, to control pest populations. Biological control can reduce the need for synthetic pesticides and provide a more sustainable approach to pest management. The EPA promotes the use of biological control agents.
14.2. Biofertilizers
Biofertilizers contain beneficial microorganisms that can enhance nutrient availability in the soil and promote plant growth. Biofertilizers can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and improve soil health. Research has shown that biofertilizers can increase crop yields and reduce environmental impacts.
14.3. Vertical Farming
Vertical farming involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often indoors. Vertical farming can reduce the need for land, water, and pesticides. Vertical farms can also be located in urban areas, reducing transportation costs and improving food security. The Vertical Farm Project promotes vertical farming as a sustainable agricultural system.
14.4. Agroforestry
Agroforestry involves integrating trees and shrubs into agricultural systems. Agroforestry can improve soil health, provide habitat for wildlife, and reduce erosion. Agroforestry can also provide additional income for farmers through the sale of timber and other tree products. The USDA National Agroforestry Center promotes agroforestry practices.
15. How Can Tourists Support Sustainable Agriculture While Traveling, Particularly in Destinations Like Vietnam?
As a traveler, you can support sustainable agriculture in destinations like Vietnam through several actions:
15.1. Visit Local Farms and Markets
Explore local farms and markets to purchase fresh, locally grown produce. This supports local farmers who often employ more sustainable farming practices. In Vietnam, consider visiting farms in the Mekong Delta or the highlands of Sapa.
15.2. Choose Eco-Friendly Accommodations
Select hotels and resorts that prioritize sustainability, such as those with organic gardens or those that source food locally. This ensures that your tourism dollars support businesses committed to environmental stewardship.
15.3. Participate in Farm-to-Table Dining
Opt for restaurants that emphasize farm-to-table dining, where meals are prepared with locally sourced, seasonal ingredients. This reduces the carbon footprint associated with food transportation and supports local agriculture.
15.4. Support Agritourism Initiatives
Engage in agritourism activities like farm stays or agricultural tours. This provides direct financial support to farmers and promotes sustainable agricultural practices. Many regions in Vietnam offer agritourism experiences.
15.5. Educate Yourself and Others
Learn about the agricultural practices in the regions you visit and share this knowledge with fellow travelers. Increased awareness can drive demand for sustainable agricultural products and practices.
16. What Are the Potential Long-Term Consequences if Current Agricultural Practices Continue Unabated?
If current agricultural practices continue without changes, the long-term consequences could be severe:
16.1. Widespread Water Pollution
Continued overuse of fertilizers and pesticides could lead to widespread water pollution, affecting drinking water supplies and harming aquatic ecosystems. This could result in higher water treatment costs and reduced access to clean water.
16.2. Soil Degradation and Loss of Productivity
Soil degradation could lead to reduced agricultural productivity, threatening food security and economic stability. Loss of topsoil and soil fertility could make it more difficult to grow crops and sustain agricultural production.
16.3. Loss of Biodiversity
Continued habitat destruction and pesticide use could lead to further loss of biodiversity, affecting ecosystem services and reducing the resilience of agricultural systems. Loss of pollinators and beneficial insects could reduce crop yields.
16.4. Increased Health Risks
Exposure to pesticides and fertilizers could lead to increased health risks, particularly for agricultural workers and communities. Chronic health effects such as cancer, reproductive problems, and neurological disorders could become more common.
16.5. Climate Change Impacts
Agricultural practices could continue to contribute to climate change through greenhouse gas emissions, exacerbating the impacts of global warming. This could lead to more frequent and severe weather events, affecting agricultural production and food security.
17. How Can Governments and International Organizations Promote Sustainable Agriculture on a Global Scale?
Governments and international organizations can play a key role in promoting sustainable agriculture:
17.1. Policy Support
Implement policies that encourage sustainable agricultural practices, such as subsidies for organic farming, regulations on pesticide use, and incentives for soil conservation. Policy support can help level the playing field for sustainable farmers.
17.2. Research and Development
Invest in research and development to improve sustainable agricultural technologies and practices. Research can help identify more effective and environmentally friendly methods for pest control and nutrient management.
17.3. Education and Training
Provide education and training to farmers on sustainable agricultural practices. Training can help farmers adopt new technologies and practices that reduce environmental impacts.
17.4. Market Development
Support the development of markets for sustainable agricultural products. Market development can help create demand for organic and sustainably produced foods.
17.5. International Cooperation
Promote international cooperation to address global challenges related to agriculture and the environment. International cooperation can help share best practices and coordinate efforts to promote sustainable agriculture.
18. What Are Some Examples of Successful Sustainable Agriculture Initiatives Around the World?
Several successful sustainable agriculture initiatives exist around the world:
18.1. Organic Farming in Europe
Europe has seen a significant increase in organic farming, driven by consumer demand and government support. Organic farming has helped reduce pesticide use and improve soil health.
18.2. Conservation Agriculture in South America
Conservation agriculture practices, such as no-till farming and cover cropping, have been widely adopted in South America, reducing soil erosion and improving water quality.
18.3. Integrated Pest Management in Asia
Integrated pest management programs have been successful in reducing pesticide use in rice production in several Asian countries, including Vietnam. IPM has helped protect beneficial insects and reduce health risks.
18.4. Agroforestry in Africa
Agroforestry practices have been used to improve soil fertility and provide additional income for farmers in many African countries. Agroforestry has also helped sequester carbon and mitigate climate change.
19. How Does Sustainable Agriculture Contribute to Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation?
Sustainable agriculture can play a significant role in climate change mitigation and adaptation:
19.1. Carbon Sequestration
Sustainable agricultural practices, such as cover cropping and agroforestry, can increase carbon sequestration in the soil, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Soil carbon sequestration can help mitigate climate change.
19.2. Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Sustainable agriculture can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing fertilizer use, improving nutrient management, and reducing tillage. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions can help slow down climate change.
19.3. Increased Resilience
Sustainable agricultural practices can increase the resilience of agricultural systems to climate change impacts, such as droughts, floods, and extreme weather events. Diversified farming systems and healthy soils can help buffer against climate change impacts.
19.4. Water Conservation
Sustainable agriculture can conserve water resources through practices such as drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and soil moisture management. Water conservation can help ensure water availability for agriculture in a changing climate.
20. How Can I Plan an Eco-Conscious Trip to Vietnam with SIXT.VN?
Planning an eco-conscious trip to Vietnam is easy with SIXT.VN. We offer a range of services designed to help you explore Vietnam responsibly:
20.1. Sustainable Travel Packages
Choose our sustainable travel packages that focus on eco-friendly accommodations, farm-to-table dining, and support for local communities.
20.2. Eco-Friendly Transportation Options
We provide options for transportation with lower environmental impacts, such as hybrid vehicles or bicycle rentals, so you can explore Vietnam without increasing your carbon footprint.
20.3. Support Local Communities
Our tours are designed to support local businesses and communities, ensuring that your tourism dollars contribute to the well-being of the places you visit. We work with local guides and operators committed to sustainable practices.
20.4. Responsible Tour Options
We offer tours that focus on environmental conservation and cultural preservation, allowing you to learn about Vietnam’s natural beauty and cultural heritage in a responsible way.
20.5. Expert Travel Advice
Our knowledgeable travel consultants can provide advice on how to minimize your environmental impact while traveling in Vietnam. We can help you choose eco-friendly activities and accommodations.
By choosing SIXT.VN for your travel needs, you can explore Vietnam while minimizing your environmental impact and supporting sustainable practices.
The impact of agriculture, specifically the use of pesticides and fertilizers, on the environment is a complex and critical issue. By understanding the consequences and adopting sustainable practices, we can work towards a healthier planet. Whether you’re planning a trip to Vietnam or simply making everyday purchasing decisions, your choices can make a difference. Remember, responsible tourism and sustainable consumption are vital for preserving the beauty and health of our world.
Ready to plan your eco-conscious adventure in Vietnam? Contact SIXT.VN today to discover our sustainable travel options and start your journey towards responsible exploration. Visit our website at SIXT.VN or call our hotline/WhatsApp at +84 986 244 358. Our address is 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam. Let’s make a positive impact together!
FAQ: Impact of Agriculture (Pesticides, Fertilizers) on the Environment
What are the main environmental impacts of pesticides?
Pesticides can contaminate water, soil, and air, harm non-target organisms, and disrupt ecosystems. They can also pose health risks to humans and wildlife.
How do fertilizers contribute to water pollution?
Fertilizers, particularly those containing nitrogen and phosphorus, can cause eutrophication, nitrate contamination, and dead zones in water bodies.
What is eutrophication, and why is it harmful?
Eutrophication is the excessive enrichment of water bodies with nutrients, leading to algae blooms that deplete oxygen levels and harm aquatic life.
What are some sustainable agricultural practices to reduce pesticide and fertilizer use?
Sustainable practices include integrated pest management (IPM), crop rotation, cover cropping, organic farming, and precision agriculture.
How can consumers support sustainable agriculture?
Consumers can support sustainable agriculture by buying organic products, supporting local farmers, choosing products with sustainable certifications, and reducing food waste.
What role does technology play in reducing the environmental impact of agriculture?
Technology can improve resource use efficiency through precision agriculture, drone monitoring, data analytics, and biotechnology.
What are some promising innovations in sustainable agriculture?
Promising innovations include biological control agents, biofertilizers, vertical farming, and agroforestry.
How can tourists support sustainable agriculture while traveling?
Tourists can visit local farms and markets, choose eco-friendly accommodations, participate in farm-to-table dining, and support agritourism initiatives.
What are the potential long-term consequences if current agricultural practices continue?
Potential consequences include widespread water pollution, soil degradation, loss of biodiversity, increased health risks, and climate change impacts.
How can governments promote sustainable agriculture on a global scale?
Governments can implement policy support, invest in research and development, provide education and training, support market development, and promote international cooperation.



