Are you curious about how indigenous communities leverage tourism for their benefit? SIXT.VN dives into the fascinating world of economic anthropology to explore how the Trobriand Islanders and others strategically use tourism to improve their lives. Discover how cultural exchanges can lead to economic empowerment and sustainable development.
Exploring Economic Anthropology: How Communities Benefit from Tourism with SIXT.VN
Economic anthropology studies livelihoods, focusing on production, exchange, and consumption. It examines how different societies organize their economies and how people meet their needs. SIXT.VN understands the nuances of these interactions, especially in the context of tourism, offering tailored travel experiences that respect and support local cultures. Whether you’re exploring the Trobriand Islands or the bustling streets of Hanoi, understanding the economic impact of tourism is crucial. Let SIXT.VN guide you through responsible and enriching travel experiences.
1. What is Economic Anthropology and its Relevance to Tourism?
Economic anthropology studies how societies organize their economic lives, including production, exchange, and consumption. It’s relevant to tourism because it examines how communities interact with the tourism industry, the economic impacts of tourism on local cultures, and how indigenous populations can benefit from tourism.
Economic anthropology explores how people make a living across different cultures and societies. This field looks at the production, exchange, and consumption of goods and services. Its relevance to tourism lies in understanding how tourism affects local economies, cultural preservation, and the distribution of wealth within communities. According to the World Tourism Organization, sustainable tourism can contribute to economic growth, social inclusion, and the preservation of cultural and natural resources. By understanding these dynamics, SIXT.VN aims to promote tourism that benefits both visitors and the host communities.
2. What are the Three Modes of Production, and How Do They Relate to Tourism?
The three modes of production are domestic (kin-ordered), tributary, and capitalist. In tourism:
- Domestic Production: Families produce crafts or services for tourists.
- Tributary Production: Local communities provide goods or labor to tourism authorities.
- Capitalist Production: Private companies own and operate tourism businesses.
Understanding these modes helps analyze how tourism revenue is distributed and controlled.
Eric Wolf identified three modes of production: domestic, tributary, and capitalist. These modes help to explain how different societies organize their economic activities, including those related to tourism. According to a study by the United Nations Environment Programme, understanding these modes of production can help in developing sustainable tourism strategies that empower local communities.
-
Domestic (Kin-Ordered) Production: In this mode, work is organized based on family relations. For example, in some indigenous communities, families may create handicrafts or offer traditional meals to tourists. The income generated directly benefits the family, supporting their livelihoods.
-
Tributary Production: This mode involves a system where producers pay tribute in goods or labor to a ruling class. In tourism, this might manifest as local communities providing goods or services to a larger tourism authority in exchange for access to markets or resources.
-
Capitalist Production: This mode is characterized by private ownership of the means of production and wage labor. In the context of tourism, this involves large corporations owning hotels, tour companies, and other tourism-related businesses. Workers sell their labor for wages, and the profits accrue to the owners.
3. How Do the Trobriand Islanders Utilize Tourism?
The Trobriand Islanders participate in the Kula ring exchange, a ceremonial exchange of shell necklaces and armbands. Tourists are drawn to witness and learn about this unique cultural practice.
The Trobriand Islanders have found ways to integrate their traditional practices with the tourism industry. The Kula ring, a ceremonial exchange of shell necklaces and armbands, is a central aspect of their culture. According to Bronislaw Malinowski’s “Argonauts of the Western Pacific,” this exchange is not just economic but also social and cultural, fostering relationships and alliances between different islands. Tourism provides an opportunity for the Islanders to showcase this tradition, attracting visitors interested in experiencing and learning about their unique way of life. This cultural exchange can generate income through performances, demonstrations, and the sale of traditional crafts.
4. What is the Kula Ring, and How Does it Attract Tourists?
The Kula ring is a ceremonial exchange of shell necklaces (soulava) for shell arm bands (mwali) between trading partners on different islands. It attracts tourists interested in witnessing and understanding this unique cultural tradition.
The Kula ring is a fascinating example of balanced reciprocity. This system involves the ceremonial exchange of shell necklaces (soulava) for shell arm bands (mwali) between trading partners living on different islands. It is more than just an economic activity; it solidifies alliances among tribes and fosters social connections. Tourists are often drawn to witness and learn about this unique tradition, which creates opportunities for cultural exchange and economic benefits. As noted by Malinowski, the Kula ring serves important functions in Trobriand society beyond simple trade, reinforcing social relationships and cultural identity.
 Sorting coffee beans
Sorting coffee beans
5. How Can Tourism Support Local Communities and Preserve Cultural Heritage?
Tourism can generate income for local communities through employment, sale of crafts, and provision of services. It can also incentivize the preservation of cultural heritage by making it a valuable asset.
Tourism can play a crucial role in supporting local communities and preserving cultural heritage. By creating economic opportunities through employment, craft sales, and service provision, tourism can directly benefit local residents. It also incentivizes the preservation of cultural heritage by turning it into a valuable asset. According to UNESCO, sustainable tourism development can empower local communities to protect their heritage and traditions while generating income. This balance between economic development and cultural preservation is essential for sustainable tourism.
6. What is Reciprocity, and How Does it Apply to Tourism?
Reciprocity involves the exchange of goods and services rooted in mutual obligation and identity. In tourism, it can mean tourists respecting local customs and contributing to the community, while locals provide authentic experiences.
Reciprocity is a fundamental concept in economic anthropology. It involves the exchange of goods and services based on mutual obligation and social relationships. In tourism, reciprocity can manifest in various ways, such as tourists respecting local customs and traditions in exchange for authentic cultural experiences. According to Marcel Mauss in “The Gift,” reciprocity creates links between people and fosters social cohesion. When tourists engage respectfully with local communities, they contribute to a positive exchange that benefits both parties.
7. What are the Different Types of Reciprocity, and How Do They Impact Tourist Interactions?
The types of reciprocity are generalized, balanced, and negative:
- Generalized Reciprocity: Giving without expecting immediate return.
- Balanced Reciprocity: Expecting something of equal value in return.
- Negative Reciprocity: Attempting to get something for nothing.
Understanding these types helps manage expectations and ensure fair exchanges in tourism.
The different types of reciprocity significantly impact tourist interactions. Understanding these dynamics can help manage expectations and ensure fair exchanges within the tourism industry.
-
Generalized Reciprocity: This involves giving without expecting an immediate return. For example, a tourist might donate to a local charity without expecting any direct benefit. This type of reciprocity fosters goodwill and strengthens community ties.
-
Balanced Reciprocity: This involves expecting something of equal value in return within a specific time period. For instance, a tourist might pay a fair price for a locally made craft, expecting a high-quality product in return. This type of reciprocity ensures a fair exchange and supports local artisans.
-
Negative Reciprocity: This involves attempting to get something for nothing. For example, a tourist might try to haggle excessively or avoid paying for services. This type of reciprocity can harm local businesses and create negative perceptions of tourists.
8. How Can Fair Trade Principles be Applied to Tourism?
Fair trade in tourism involves ensuring that local communities receive a fair share of tourism revenue, promoting ethical labor practices, and supporting sustainable environmental practices.
Fair trade principles can significantly enhance the sustainability and ethical dimensions of tourism. By ensuring that local communities receive a fair share of tourism revenue, promoting ethical labor practices, and supporting sustainable environmental practices, fair trade principles can transform tourism into a force for good. According to Fairtrade International, fair trade supports producers in developing countries by establishing a minimum price for their goods and services, providing access to markets, and promoting better working conditions. Applying these principles to tourism can create a more equitable and sustainable industry.
9. What is Redistribution, and How Does it Function in Tourism Economies?
Redistribution is the accumulation of goods or labor by an authority for later dispersal. In tourism, this can involve governments collecting taxes from tourism businesses and reinvesting in local infrastructure and services.
Redistribution is a critical mechanism for ensuring that the benefits of tourism are shared equitably. It involves the accumulation of goods or labor by a central authority, such as a government, for later dispersal. In tourism, this can involve governments collecting taxes from tourism businesses and reinvesting in local infrastructure, education, and healthcare. According to a report by the World Bank, effective redistribution policies can reduce poverty and inequality in tourism-dependent economies. This ensures that tourism contributes to the overall well-being of the community.
10. What Role Do Markets Play in Tourism, and How Can They Be Regulated?
Markets in tourism involve the exchange of goods and services between tourists and local businesses. They can be regulated through policies that ensure fair pricing, quality standards, and protection of local resources.
Markets play a central role in the tourism industry, facilitating the exchange of goods and services between tourists and local businesses. However, unregulated markets can lead to exploitation, environmental degradation, and cultural commodification. According to the United Nations World Tourism Organization, effective regulation is essential for ensuring fair pricing, quality standards, and protection of local resources. Policies such as licensing, environmental regulations, and community involvement can help to create a more sustainable and equitable tourism market.
 Roadside Salaula trader, Zambia
Roadside Salaula trader, Zambia
11. How Can Local Currency Systems Like Ithaca Hours Benefit Tourism?
Local currency systems encourage local spending, support local businesses, and create deeper connections between tourists and the community. They can also help to keep tourism revenue within the local economy.
Local currency systems, such as Ithaca Hours, can offer numerous benefits for tourism. These systems encourage local spending, support local businesses, and create deeper connections between tourists and the community. By using a local currency, tourists are more likely to patronize locally owned establishments, which helps to keep tourism revenue within the local economy. According to research by the New Economics Foundation, local currency systems can boost local economic activity and promote community resilience. They also offer a unique way for tourists to engage with the local culture and economy.
12. What is Consumption in the Context of Tourism, and How Does it Impact Local Cultures?
Consumption in tourism involves the buying and using of local resources, goods, and services by tourists. It can impact local cultures positively through economic support or negatively through commodification and cultural erosion.
Consumption in tourism is a multifaceted phenomenon that involves the buying and using of local resources, goods, and services by tourists. While it can bring economic benefits, it also carries the risk of commodification and cultural erosion. According to a study by the World Wildlife Fund, unsustainable consumption patterns in tourism can deplete natural resources, damage ecosystems, and undermine local cultures. It is essential to promote responsible consumption practices that support local economies while minimizing negative impacts on cultural heritage and the environment.
13. How Do Commodities Become Personally and Socially Meaningful in Tourism?
Commodities become meaningful through their association with local culture, history, and personal experiences. Tourists often seek out unique souvenirs that represent their travel experiences and connect them to the places they have visited.
Commodities in tourism gain personal and social significance through their association with local culture, history, and the unique experiences of travel. Tourists often seek out souvenirs that represent their journey and connect them emotionally to the places they have visited. According to Arjun Appadurai in “The Social Life of Things,” commodities have a “social life” that extends beyond their economic value. Souvenirs, local crafts, and traditional goods become imbued with memories and cultural meaning, serving as tangible reminders of the tourist’s experience.
14. What is Political Economy, and How Does it Explain Inequality in Tourism?
Political economy examines how state structures, political processes, and social structures influence economic relations. It explains inequality in tourism by analyzing how power dynamics affect the distribution of tourism benefits.
Political economy provides a critical lens for understanding inequality in tourism. This approach examines how state structures, political processes, and social structures influence economic relations. By analyzing how power dynamics affect the distribution of tourism benefits, political economy helps to explain why some communities benefit more than others. According to research by the International Labour Organization, unequal power relations can lead to exploitation of workers, environmental degradation, and the marginalization of local communities. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing policies that promote more equitable and sustainable tourism.
15. How Can Structural Violence Affect Tourism Development in Certain Regions?
Structural violence, where social structures harm people by preventing them from meeting basic needs, can undermine tourism development by creating instability, poverty, and lack of infrastructure.
Structural violence can significantly hinder tourism development by creating instability, poverty, and a lack of essential infrastructure. This form of violence, where social structures or institutions prevent people from meeting their basic needs, can undermine the potential benefits of tourism. According to a report by the United Nations Development Programme, regions affected by structural violence often struggle to attract investment, develop sustainable tourism practices, and ensure the safety and well-being of tourists and local communities. Addressing these underlying issues is crucial for fostering inclusive and sustainable tourism development.
16. What are Some Examples of Successful Community-Based Tourism Initiatives?
Examples include:
- The Annapurna Community Homestay in Nepal: Local families provide accommodation and meals, directly benefiting from tourism revenue.
- The Uros Floating Islands in Peru: Indigenous communities manage tourism on their man-made islands, preserving their culture.
- The Trobriand Islands in Papua New Guinea: Showcasing their unique Kula Ring tradition
Successful community-based tourism initiatives empower local communities, preserve cultural heritage, and promote sustainable development.
There are numerous examples of successful community-based tourism initiatives around the world. These initiatives empower local communities, preserve cultural heritage, and promote sustainable development.
-
The Annapurna Community Homestay in Nepal: This initiative involves local families providing accommodation and meals to tourists, allowing them to directly benefit from tourism revenue.
-
The Uros Floating Islands in Peru: The indigenous communities manage tourism on their unique man-made islands, showcasing their culture while controlling the economic benefits.
-
The Trobriand Islands in Papua New Guinea: The Islanders showcase their unique Kula Ring tradition, attracting tourists interested in experiencing their cultural heritage.
These examples demonstrate how tourism can be a powerful tool for community empowerment when managed effectively.
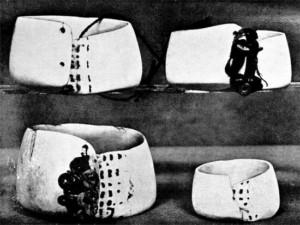 Mwali from the Kula Exchange
Mwali from the Kula Exchange
17. How Can Tourists Contribute to Sustainable Tourism Practices?
Tourists can contribute by:
- Respecting local customs and traditions.
- Buying local products and services.
- Minimizing environmental impact.
- Supporting community-based tourism initiatives.
- Educating themselves about the local culture and economy.
By making informed and responsible choices, tourists can help ensure that their travels benefit local communities and protect the environment.
Tourists play a vital role in promoting sustainable tourism practices. By making informed and responsible choices, they can help ensure that their travels benefit local communities and protect the environment.
-
Respecting Local Customs and Traditions: Understanding and adhering to local customs shows respect and helps to preserve cultural heritage.
-
Buying Local Products and Services: Supporting local businesses ensures that tourism revenue stays within the community.
-
Minimizing Environmental Impact: Reducing waste, conserving water, and respecting wildlife helps to protect natural resources.
-
Supporting Community-Based Tourism Initiatives: Choosing accommodations and tours that are managed by local communities ensures that they directly benefit from tourism.
-
Educating Themselves: Learning about the local culture and economy helps tourists to make more informed and responsible decisions.
18. What Measures Can Be Taken to Prevent Cultural Commodification in Tourism?
Preventing cultural commodification involves:
- Empowering local communities to control how their culture is presented.
- Promoting authentic cultural experiences over staged performances.
- Educating tourists about the meaning and significance of local traditions.
- Ensuring that cultural heritage is respected and preserved.
Empowering local communities and promoting authentic cultural experiences are key to preventing cultural commodification in tourism.
Cultural commodification, the process of turning cultural elements into marketable products, can have detrimental effects on local traditions and communities. Preventing this involves a multifaceted approach that prioritizes community empowerment and cultural preservation.
-
Empowering Local Communities: Giving local communities control over how their culture is presented ensures that traditions are respected and authentically portrayed.
-
Promoting Authentic Experiences: Encouraging tourists to engage in real cultural experiences, rather than staged performances, helps to preserve the integrity of local traditions.
-
Educating Tourists: Informing tourists about the meaning and significance of local traditions fosters a deeper appreciation and respect for the culture.
-
Ensuring Cultural Heritage is Respected: Implementing policies that protect cultural sites and traditions helps to preserve them for future generations.
19. What Are the Challenges and Opportunities of Ecotourism for Local Communities?
Challenges include:
- Ensuring that ecotourism benefits local communities.
- Minimizing environmental impact.
- Preventing greenwashing.
- Managing tourist expectations.
Opportunities include:
- Generating income for local communities.
- Promoting environmental conservation.
- Raising awareness about local ecosystems.
- Providing sustainable employment opportunities.
Balancing the challenges and opportunities of ecotourism is crucial for its success and sustainability.
Ecotourism presents both challenges and opportunities for local communities. Balancing these factors is crucial for ensuring its success and sustainability.
Challenges:
-
Ensuring Benefits for Local Communities: Ensuring that ecotourism projects genuinely benefit local communities, rather than just a few individuals or outside investors, is a key challenge.
-
Minimizing Environmental Impact: Managing the environmental impact of tourism activities, such as hiking, wildlife viewing, and accommodation, is essential for preserving the natural environment.
-
Preventing Greenwashing: Avoiding “greenwashing,” where companies falsely promote their activities as environmentally friendly, requires transparency and accountability.
-
Managing Tourist Expectations: Managing tourist expectations to ensure they align with the realities of ecotourism and the local environment is important for visitor satisfaction.
Opportunities:
-
Generating Income: Ecotourism can generate income for local communities through employment, sale of local products, and provision of services.
-
Promoting Conservation: Ecotourism can incentivize the conservation of natural resources and biodiversity by making them economically valuable.
-
Raising Awareness: Ecotourism can raise awareness among tourists and local communities about the importance of protecting local ecosystems.
-
Providing Sustainable Employment: Ecotourism can provide sustainable employment opportunities that are less exploitative and more environmentally friendly than other industries.
20. How Can Technology be Used to Promote and Support Sustainable Tourism?
Technology can be used to:
- Promote sustainable tourism initiatives through online platforms.
- Provide tourists with information about local cultures and environmental conservation.
- Facilitate direct bookings with local businesses.
- Monitor and manage environmental impacts.
- Enhance the overall tourist experience.
Leveraging technology can enhance the sustainability and inclusivity of the tourism sector.
Technology offers numerous opportunities to promote and support sustainable tourism. By leveraging digital platforms, information dissemination, and direct booking systems, the tourism sector can become more sustainable and inclusive.
-
Promote Sustainable Initiatives: Online platforms can be used to promote sustainable tourism initiatives, highlighting eco-friendly accommodations, tours, and activities.
-
Provide Information: Technology can provide tourists with easy access to information about local cultures, environmental conservation efforts, and responsible travel practices.
-
Facilitate Direct Bookings: Direct booking systems can connect tourists directly with local businesses, ensuring that more revenue stays within the community.
-
Monitor Environmental Impacts: Technology can be used to monitor and manage the environmental impacts of tourism, such as carbon emissions, water usage, and waste generation.
-
Enhance Tourist Experience: Mobile apps, virtual tours, and interactive maps can enhance the overall tourist experience while promoting responsible travel.
Plan Your Trip with SIXT.VN
Ready to explore Vietnam responsibly? SIXT.VN offers expert travel advice, convenient airport transfers, hotel bookings, and exciting Hanoi tours. We ensure your trip is seamless, sustainable, and supports local communities.
- Expert Travel Advice: Get personalized recommendations for your perfect itinerary.
- Airport Transfers: Enjoy hassle-free transportation upon arrival.
- Hotel Bookings: Choose from a range of accommodations to suit your budget and preferences.
- Hanoi Tours: Discover the best of Hanoi with our expertly guided tours.
Contact us today:
- Address: 260 Cau Giay, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Hotline/WhatsApp: +84 986 244 358
- Website: SIXT.VN
FAQs: Tourism and Community Benefits
Q1: How can I ensure my tourism activities benefit local communities?
Choose community-based accommodations and tours, buy local products, and respect local customs.
Q2: What is the role of economic anthropology in tourism?
It helps understand the economic impacts of tourism on local cultures and how to ensure fair distribution of benefits.
Q3: What are the benefits of fair trade tourism?
It ensures fair wages, ethical labor practices, and sustainable environmental practices.
Q4: How can local currency systems enhance tourism benefits?
They encourage spending at local businesses, keeping revenue within the community.
Q5: What are the challenges of ecotourism?
Ensuring benefits for local communities, minimizing environmental impact, and preventing greenwashing.
Q6: How can technology support sustainable tourism?
By promoting sustainable initiatives, providing information, and facilitating direct bookings.
Q7: What is structural violence, and how does it affect tourism?
It’s when social structures harm people, leading to instability and hindering tourism development.
Q8: How can cultural commodification be prevented in tourism?
By empowering local communities to control how their culture is presented and promoting authentic experiences.
Q9: What is the Kula ring, and how does it relate to tourism?
A ceremonial exchange in the Trobriand Islands that attracts tourists interested in cultural traditions.
Q10: How can redistribution function in tourism economies?
Governments can collect taxes from tourism businesses and reinvest in local infrastructure and services.
Let SIXT.VN help you explore the beauty and culture of Vietnam while ensuring your travels contribute positively to local communities. Book your adventure today and experience the best of sustainable tourism!



